Comparative Study of Methods for Cycle Length Estimation in Fractionated Electrograms of Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. LAW Detection Methods
2.1.1. Adaptive Amplitude Threshold Method
2.1.2. Atrial Cycle Length Iteration Method
2.1.3. Hyperbolic Tangent Method
2.2. Performance Evaluation
2.2.1. Detection Performance
2.2.2. Mean CL Error Estimation
2.2.3. Individual CL Error Estimation
2.2.4. Influence of Electrograms Duration
3. Results
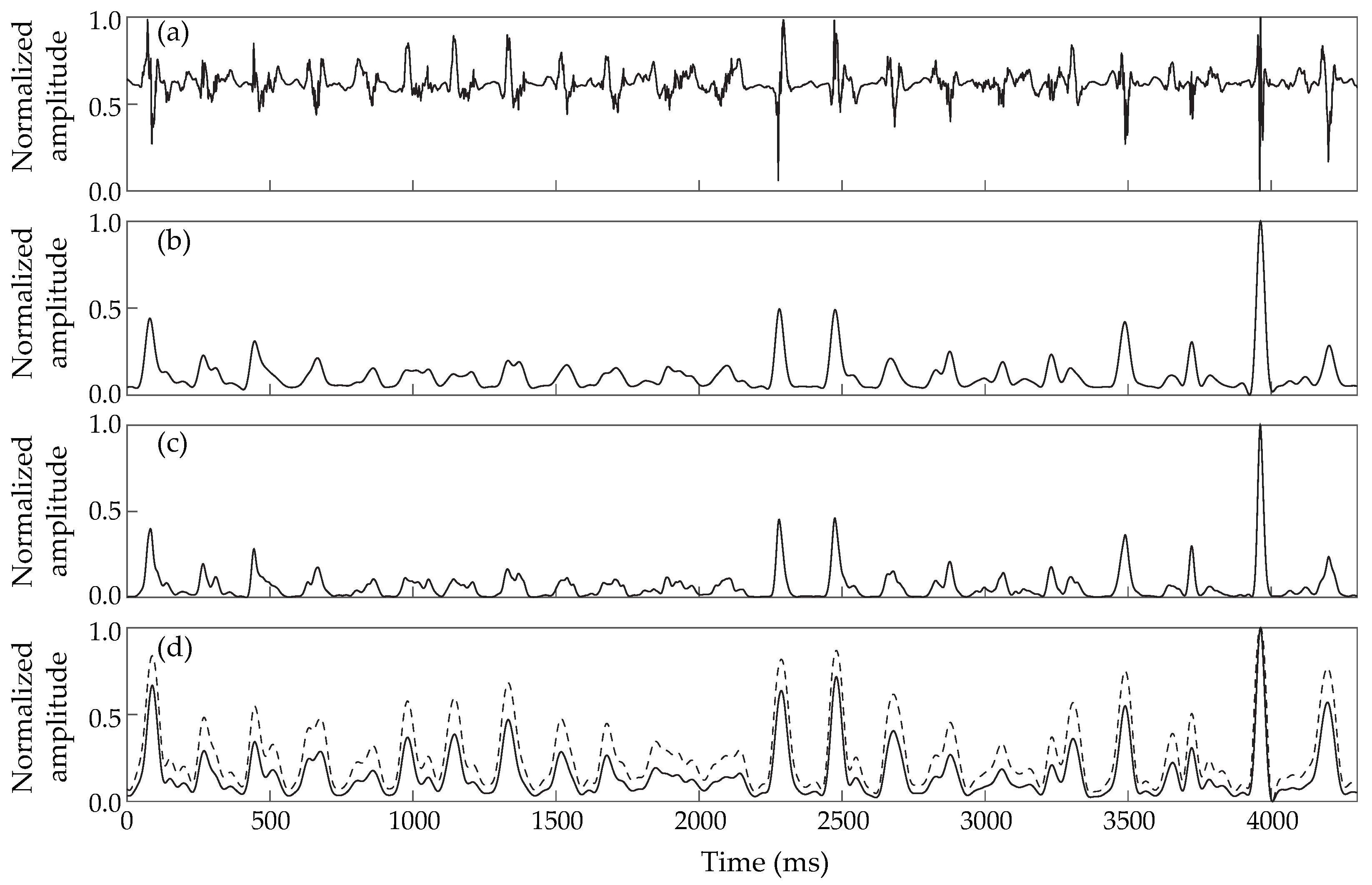
3.1. Detection Results
3.2. Cycle Length Estimation
3.3. EGM Length Influence
4. Discussion
4.1. Evaluation on Different Levels of Fractionation
4.2. Cycle Length as an Evaluation Parameter
4.3. Effect of Signal Length
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveriset, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuin, M.; Roncon, L.; Passaro, A.; Bosi, C.; Cervellati, C.; Zuliani, G. Risk of dementia in patients with atrial fibrillation: Short versus long follow-up. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2021, 36, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, R.; Evans, M.; Middeldorp, M.; Mahajan, R.; Mehta, A.; Meredith, M.; Twomey, D.; Wong, C.; Hendriks, J.; Abhayaratna, W.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness and Clinical Effectiveness of the Risk Factor Management Clinic in Atrial Fibrillation: The CENT Study. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2017, 3, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oral, H.; Knight, B.P.; Tada, H. Pulmonary vein isolation for paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation. Circulation 2002, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrall, G.; Lane, D.; Carroll, D.; Lip, G. Quality of Life in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 448.e1–448.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, P.; Zografos, T.; Christoforatou, E.; Kouvelas, K.; Tsoumeleas, A.; Vassilopoulos, C. The Electrophysiology of Atrial Fibrillation: From Basic Mechanisms to Catheter Ablation. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2021, 2021, 4109269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Jaïs, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Le Mouroux, A.; Le Métayer, P.; Clémenty, J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, D.; Schotten, U.; Mahajan, R.; Antic, N.; Hatem, S.; Pathak, R.; Hendriks, J.; Kalman, J.; Sanders, P. Novel mechanisms in the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation: Practical applications. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allessie, M. Electrical, contractile and structural remodeling during atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 54, 230–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Marrouche, N.F. Recurrence Post-Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: Think Outside the Pulmonary Veins. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2018, 11, e006379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, K.; Ulfarsson, M.; Tada, H.; Chugh, A.; Good, E.; Kuhne, M.; Crawford, T.; Sarrazin, J.F.; Chalfoun, N.; Wells, D.; et al. Complex Electrograms Within the Coronary Sinus: Time- and Frequency-Domain Characteristics, Effects of Antral Pulmonary Vein Isolation, and Relationship to Clinical Outcome in Patients with Paroxysmal and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2008, 19, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nademanee, K.; McKenzie, J.; Kosar, E.; Schwab, M.; Sunsaneewitayakul, B.; Vasavakul, T.; Khunnawat, C.; Ngarmukos, T. A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Mapping of the electrophysiologic substrate. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 2044–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Groot, N.; Shah, D.; Boyle, P.M.; Anter, E.; Clifford, G.D.; Deisenhofer, I.; Deneke, T.; van Dessel, P.; Doessel, O.; Dilaveris, P.; et al. Critical appraisal of technologies to assess electrical activity during atrial fibrillation: A position paper from the European Heart Rhythm Association and European Society of Cardiology Working Group on eCardiology in collaboration with the Heart Rhythm Society, Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society, Latin American Heart Rhythm Society and Computing in Cardiology. EP Eur. 2021, 24, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Jiang, C.; Betts, T.; Chen, J.; Deisenhofer, I.; Mantovan, R.; Macle, L.; Morillo, C.; Haverkamp, W.; Weerasooriya, R.; et al. Approaches to catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1812–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar-Busch, S.; Reents, T.; Knecht, S.; Rostock, T.; Arentz, T.; Duytschaever, M.; Neumann, T.; Cauchemez, B.; Albenque, J.P.; Hessling, G.; et al. Correlation between atrial fibrillation driver locations and complex fractionated atrial electrograms in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2018, 41, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maille, B.; Das, M.; Hussein, A.; Shaw, M.; Chaturvedi, V.; Williams, E.; Morgan, M.; Ronayne, C.; Snowdon, R.L.; Gupta, D. Reverse electrical and structural remodeling of the left atrium occurs early after pulmonary vein isolation for persistent atrial fibrillation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2020, 58, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, D.; Linz, D.; Schotten, U.; Mahajan, R.; Sanders, P.; Kalman, J. Pathophysiology of Paroxysmal and Persistent Atrial Fibrillation: Rotors, Foci and Fibrosis. Heart Lung Circ. 2017, 26, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botteron, G.; Smith, J. A Technique for Measurement of the Extent of Spatial Organization of Atrial Activation During Atrial Fibrillation in the Intact Human Heart. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1995, 42, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faes, L.; Nollo, G.; Antolini, R.; Gaita, F.; Ravelli, F. A method for quantifying atrial fibrillation organization based on wave-morphology similarity. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 49, 1504–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houben, R.; Allessie, M. Processing of intracardiac electrograms in atrial fibrillation: Diagnosis of electropathological substrate of AF. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2006, 25, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Lo, M.T.; Lin, C.; Chang, S.L.; Lo, L.W.; Hu, Y.F.; Chao, T.F.; Li, C.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Hsieh, W.H.; et al. Nonlinear analysis of fibrillatory electrogram similarity to optimize the detection of complex fractionated electrograms during persistent atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2013, 24, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.; Sehgal, V.; Ng, J.; Gordon, D.; Goldberger, J. Iterative method to detect atrial activations and measure cycle length from electrograms during atrial fibrillation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalvi, R.; Suszko, A.; Chauhan, V.S. Graph search based detection of periodic activations in complex periodic signals: Application in atrial fibrillation electrograms. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 28th Canadian Conference on Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE), Halifax, NS, Canada, 3–6 May 2015; pp. 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, D.; Vraka, A.; Quesada, A.; Hornero, F.; Alcaraz, R.; Rieta, J.J. An Efficient Hybrid Methodology for Local Activation Waves Detection under Complex Fractionated Atrial Electrograms of Atrial Fibrillation. Sensors 2022, 22, 5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costabal, F.S.; Zaman, J.A.B.; Kuhl, E.; Narayan, S.M. Interpreting Activation Mapping of Atrial Fibrillation: A Hybrid Computational/Physiological Study. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 46, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, B.; Hendriks, R.C.; van der Veen, A.J.; de Groot, N.M.S. Improved local activation time annotation of fractionated atrial electrograms for atrial mapping. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 117, 103590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kölling, B.; Abdi, B.; de Groot, N.M.; Hendriks, R.C. Local Activation Time Estimation in Atrial Electrograms Using Cross-Correlation over Higher-Order Neighbors. In Proceedings of the 2020 28th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Dublin, Ireland, 23–27 August 2021; pp. 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.L., Jr.; Karp, R.; Kouchoukos, N.; MacLean, W.; James, T.; Waldo, A. Characterization of Atrial Fibrillation in Man: Studies Following Open Heart Surgery. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1978, 1, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Iniesta, M.; Ródenas, J.; Alcaraz, R.; Rieta, J.J. Waveform Integrity in Atrial Fibrillation: The Forgotten Issue of Cardiac Electrophysiology. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 1890–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Method | Type I | Type II | Type III | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | [%] | |
| AAT | 91.82 | 95.60 | 95.66 | 95.90 | 97.35 | 98.33 | 78.89 | 85.38 | 91.11 |
| ACLI | 98.58 | 99.91 | 98.68 | 98.78 | 99.73 | 99.05 | 85.13 | 87.51 | 96.89 |
| HT | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 92.77 | 95.30 | 97.24 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osorio, D.; Vraka, A.; Moreno-Arribas, J.; Bertomeu-González, V.; Alcaraz, R.; Rieta, J.J. Comparative Study of Methods for Cycle Length Estimation in Fractionated Electrograms of Atrial Fibrillation. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101712
Osorio D, Vraka A, Moreno-Arribas J, Bertomeu-González V, Alcaraz R, Rieta JJ. Comparative Study of Methods for Cycle Length Estimation in Fractionated Electrograms of Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(10):1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101712
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsorio, Diego, Aikaterini Vraka, José Moreno-Arribas, Vicente Bertomeu-González, Raúl Alcaraz, and José J. Rieta. 2022. "Comparative Study of Methods for Cycle Length Estimation in Fractionated Electrograms of Atrial Fibrillation" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 10: 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101712
APA StyleOsorio, D., Vraka, A., Moreno-Arribas, J., Bertomeu-González, V., Alcaraz, R., & Rieta, J. J. (2022). Comparative Study of Methods for Cycle Length Estimation in Fractionated Electrograms of Atrial Fibrillation. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(10), 1712. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12101712






