Personalized Medicine Workflow in Post-Traumatic Orbital Reconstruction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Post-Traumatic Orbital Reconstruction Workflow
2.1. Diagnostics
2.2. Advanced Diagnostics
2.3. Virtual Surgical Planning
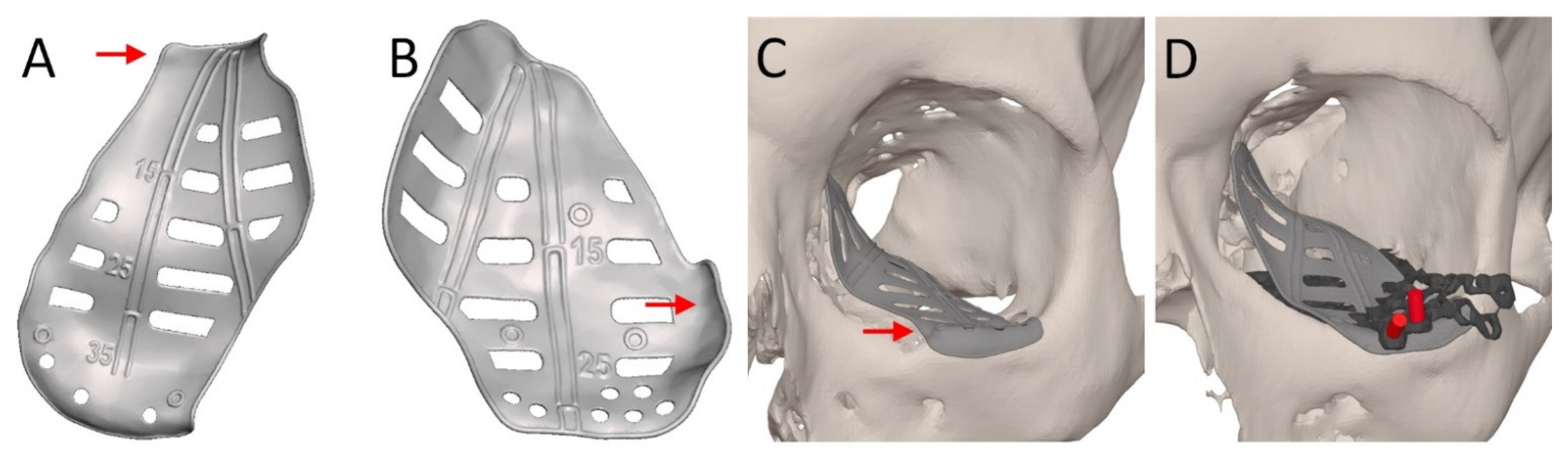
2.4. Patient-Specific Implant Design
2.5. Intraoperative Feedback
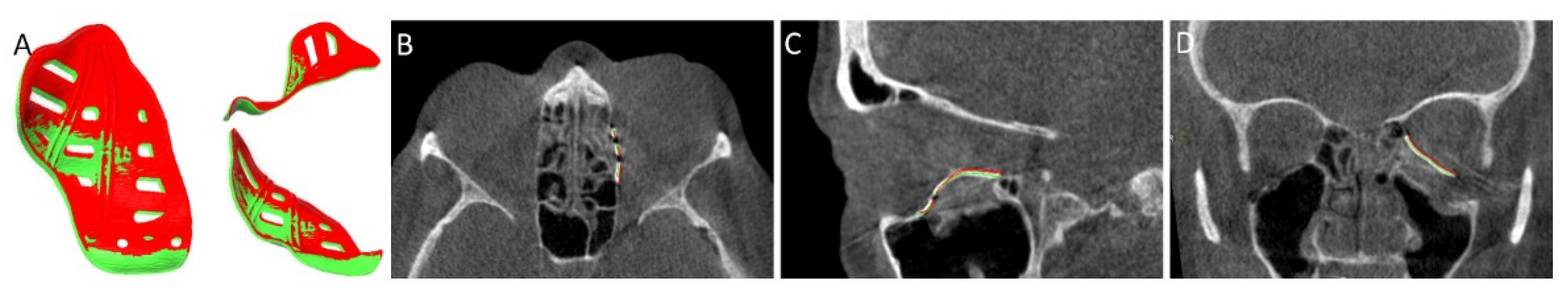
2.6. Evaluation
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornelius, C.P.; Probst, F.; Metzger, M.C.; Gooris, P.J.J. Anatomy of the Orbits: Skeletal Features and Some Notes on the Periorbital Lining. Atlas Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, E., 3rd; el-Attar, A.; Moos, K.F. An analysis of 2,067 cases of zygomatico-orbital fracture. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1985, 43, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Cornelius, C.P.; Groten, M.; Pröbster, L.; Pfannenberg, C.; Schwenzer, N. Orbital reconstruction with individually copy-milled ceramic implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998, 101, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koornneef, L. Orbital septa: Anatomy and function. Ophthalmology 1979, 86, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S. Primary Orbital Fracture Repair. Atlas Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 29, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raflo, G.T. Blow-in and blow-out fractures of the orbit: Clinical correlations and proposed mechanisms. Ophthalmic Surg. 1984, 15, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Grob, S.; Yonkers, M.; Tao, J. Orbital Fracture Repair. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2017, 31, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foletti, J.M.; Martinez, V.; Haen, P.; Godio-Raboutet, Y.; Guyot, L.; Thollon, L. Finite element analysis of the human orbit. Behavior of titanium mesh for orbital floor reconstruction in case of trauma recurrence. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 120, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, L.; Dillon, J.; Jansen, J.; Becking, A.G. Ongoing Debate in Clinical Decision Making in Orbital Fractures: Indications, Timing, and Biomaterials. Atlas Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 29, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wevers, M.; Strabbing, E.M.; Engin, O.; Gardeniers, M.; Koudstaal, M.J. CT parameters in pure orbital wall fractures and their relevance in the choice of treatment and patient outcome: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 51, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, A.; Sisson, A.; Olson, K.; Sivam, S. Predictors of Delayed Enophthalmos After Orbital Fractures: A Systematic Review. Facial Plast. Surg. Aesthet. Med. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnstine, M.A. Clinical recommendations for repair of isolated orbital floor fractures: An evidence-based analysis. Ophthalmology 2002, 109, 1207–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.; Dubois, L.; Maal, T.J.J.; Mourits, M.P.; Jellema, H.M.; Neomagus, P.; de Lange, J.; Hartman, L.J.C.; Gooris, P.J.J.; Becking, A.G. A nonsurgical approach with repeated orthoptic evaluation is justified for most blow-out fractures. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2020, 48, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, L.; Steenen, S.A.; Gooris, P.J.; Mourits, M.P.; Becking, A.G. Controversies in orbital reconstruction–I. Defect-driven orbital reconstruction: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, L.; Steenen, S.A.; Gooris, P.J.; Bos, R.R.; Becking, A.G. Controversies in orbital reconstruction-III. Biomaterials for orbital reconstruction: A review with clinical recommendations. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, M.C.; Schön, R.; Tetzlaf, R.; Weyer, N.; Rafii, A.; Gellrich, N.C.; Schmelzeisen, R. Topographical CT-data analysis of the human orbital floor. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 36, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelius, C.P.; Mayer, P.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Metzger, M.C. The orbits--anatomical features in view of innovative surgical methods. Facial Plast. Surg. 2014, 30, 487–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooris, P.J.J.; Muller, B.S.; Dubois, L.; Bergsma, J.E.; Mensink, G.; van den Ham, M.F.E.; Becking, A.G.; Seubring, K. Finding the Ledge: Sagittal Analysis of Bony Landmarks of the Orbit. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 75, 2613–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlittler, F.; Schmidli, A.; Wagner, F.; Michel, C.; Mottini, M.; Lieger, O. What Is the Incidence of Implant Malpositioning and Revision Surgery After Orbital Repair? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.Y.; Langer, P.D. Pediatric orbital blowout fractures. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 28, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, R.; Wilde, F.; Schramm, A.; Gellrich, N.C. Intraoperative Feedback and Quality Control in Orbital Reconstruction: The Past, the Present, and the Future. Atlas Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 29, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreurs, R.; Klop, C.; Gooris, P.J.J.; Maal, T.J.J.; Becking, A.G.; Dubois, L. Critical appraisal of patient-specific implants for secondary post-traumatic orbital reconstruction. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 51, 790–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkenke, E.; Maier, T.; Benz, M.; Wiltfang, J.; Holbach, L.M.; Kramer, M.; Häusler, G.; Neukam, F.W. Hertel exophthalmometry versus computed tomography and optical 3D imaging for the determination of the globe position in zygomatic fractures. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 33, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davanger, M. Principles and sources of error in exophthalmometry. A new exophthalmometer. Acta Ophthalmol. 1970, 48, 625–633. [Google Scholar]
- Traber, G.; Kordic, H.; Knecht, P.; Chaloupka, K. Hypoglobus—Illusive or real? Etiologies of vertical globe displacement in a tertiary referral centre. Klinische Monatsblatter Augenheilkunde 2013, 230, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gart, M.S.; Gosain, A.K. Evidence-Based Medicine: Orbital Floor Fractures. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 134, 1345–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willaert, R.; Shaheen, E.; Deferm, J.; Vermeersch, H.; Jacobs, R.; Mombaerts, I. Three-dimensional characterisation of the globe position in the orbit. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 258, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braaksma-Besselink, Y.; Jellema, H.M. Orthoptic Evaluation and Treatment in Orbital Fractures. Atlas Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 29, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matic, D.B.; Tse, R.; Banerjee, A.; Moore, C.C. Rounding of the inferior rectus muscle as a predictor of enophthalmos in orbital floor fractures. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2007, 18, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Moore, C.C.; Tse, R.; Matic, D. Rounding of the inferior rectus muscle as an indication of orbital floor fracture with periorbital disruption. J. Otolaryngol. 2007, 36, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Lee, K.A.; Sun, H. Swelling of the inferior rectus muscle and enophthalmos in orbital floor fracture. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2013, 24, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, M.; Hähnel, S.; Sartor, K. The value of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of orbital floor fractures. Eur. Radiol. 2002, 12, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, J.; Dubois, L.; Schreurs, R.; Gooris, P.J.J.; Maal, T.J.J.; Beenen, L.F.; Becking, A.G. Should Virtual Mirroring Be Used in the Preoperative Planning of an Orbital Reconstruction? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regensburg, N.I.; Kok, P.H.; Zonneveld, F.W.; Baldeschi, L.; Saeed, P.; Wiersinga, W.M.; Mourits, M.P. A new and validated CT-based method for the calculation of orbital soft tissue volumes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, J.; Schreurs, R.; Dubois, L.; Maal, T.J.J.; Gooris, P.J.J.; Becking, A.G. The advantages of advanced computer-assisted diagnostics and three-dimensional preoperative planning on implant position in orbital reconstruction. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, E.Z.; Koh, Y.P.; Hing, E.C.; Low, J.R.; Shen, J.Y.; Wong, H.C.; Sundar, G.; Lim, T.C. Computer-assisted navigational surgery improves outcomes in orbital reconstructive surgery. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2012, 23, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Chui, C.H.K.; Wagner, M.; Zimmerer, R.; Rana, M.; Gellrich, N.-C. Increasing the Accuracy of Orbital Reconstruction With Selective Laser-Melted Patient-Specific Implants Combined With Intraoperative Navigation. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärkkäinen, M.; Wilkman, T.; Mesimäki, K.; Snäll, J. Primary reconstruction of orbital fractures using patient-specific titanium milled implants: The Helsinki protocol. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 56, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gander, T.; Essig, H.; Metzler, P.; Lindhorst, D.; Dubois, L.; Rücker, M.; Schumann, P. Patient specific implants (PSI) in reconstruction of orbital floor and wall fractures. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellrich, N.C.; Dittmann, J.; Spalthoff, S.; Jehn, P.; Tavassol, F.; Zimmerer, R. Current Strategies in Post-traumatic Orbital Reconstruction. J. Maxillofac. Oral Surg. 2019, 18, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer, M.; Essig, H.; Steigmiller, K.; Wagner, M.E.; Gander, T. Surgical Outcomes of Orbital Fracture Reconstruction Using Patient-Specific Implants. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajibandeh, J.; Be, A.; Lee, C. Custom Interlocking Implants for Primary and Secondary Reconstruction of Large Orbital Floor Defects: Case Series and Description of Workflow. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 79, 2539.e1–2539.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeller, A.N.; Neuhaus, M.T.; Gessler, N.; Skade, S.; Korn, P.; Jehn, P.; Gellrich, N.C.; Zimmerer, R.M. Self-centering second-generation patient-specific functionalized implants for deep orbital reconstruction. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 122, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kormi, E.; Männistö, V.; Lusila, N.; Naukkarinen, H.; Suojanen, J. Accuracy of Patient-Specific Meshes as a Reconstruction of Orbital Floor Blow-Out Fractures. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2021, 32, e116–e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelet, J.T.; Cordier, G.; Porcheray, M.; Bourlet, J.; Gleizal, A.; Foletti, J.M. Orbital Reconstruction by Patient-Specific Implant Printed in Porous Titanium: A Retrospective Case Series of 12 Patients. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 2161–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mommaerts, M.Y.; Büttner, M.; Vercruysse, H., Jr.; Wauters, L.; Beerens, M. Orbital Wall Reconstruction with Two-Piece Puzzle 3D Printed Implants: Technical Note. Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2016, 9, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.; Schlittler, F.L. Going beyond the limitations of the non-patient-specific implant in titanium reconstruction of the orbit. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 59, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, J.; Mesimäki, K.; Snäll, J. Patient-specific two-piece screwless implant for the reconstruction of a large orbital fracture. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 58, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, A.; Sinko, K.; Dorner, G. Late Reconstruction of the Orbit With Patient-Specific Implants Using Computer-Aided Planning and Navigation. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, S101–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedemonte Trewhela, C.; Díaz Reiher, M.; Muñoz Zavala, T.; González Mora, L.E.; Vargas Farren, I. Correction of Delayed Traumatic Enophthalmos Using Customized Orbital Implants. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spalthoff, S.; Dittmann, J.; Zimmerer, R.; Jehn, P.; Tavassol, F.; Gellrich, N.C. Intraorbital volume augmentation with patient-specific titanium spacers. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 121, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, L.; Essig, H.; Schreurs, R.; Jansen, J.; Maal, T.J.; Gooris, P.J.; Becking, A.G. Predictability in orbital reconstruction. A human cadaver study, part III: Implant-oriented navigation for optimized reconstruction. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2015, 43, 2050–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittichokechai, P.; Sirichatchai, K.; Puncreobutr, C.; Lohwongwatana, B.; Saonanon, P. A Novel Patient-specific Titanium Mesh Implant Design for Reconstruction of Complex Orbital Fracture. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreurs, R.; Dubois, L.; Becking, A.G.; Maal, T.J.J. The orbit first! A novel surgical treatment protocol for secondary orbitozygomatic reconstruction. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabelis, J.F.; Youssef, S.; Hoefnagels, F.W.A.; Becking, A.G.; Schreurs, R.; Dubois, L. Technical Note on Three- and Four-Wall Orbital Reconstructions with Patient-Specific Implants. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2021, 33, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venosta, D.; Sun, Y.; Matthews, F.; Kruse, A.L.; Lanzer, M.; Gander, T.; Grätz, K.W.; Lübbers, H.T. Evaluation of two dental registration-splint techniques for surgical navigation in cranio-maxillofacial surgery. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, B.W.; Scawn, R.L.; Korn, B.S.; Kikkawa, D.O. Secondary Orbital Reconstruction in Patients with Prior Orbital Fracture Repair. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 32, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebbers, H.T.; Messmer, P.; Obwegeser, J.A.; Zwahlen, R.A.; Kikinis, R.; Graetz, K.W.; Matthews, F. Comparison of different registration methods for surgical navigation in cranio-maxillofacial surgery. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2008, 36, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, R.; Baan, F.; Klop, C.; Dubois, L.; Beenen, L.F.M.; Habets, P.; Becking, A.G.; Maal, T.J.J. Virtual splint registration for electromagnetic and optical navigation in orbital and craniofacial surgery. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, R.; Dubois, L.; Becking, A.G.; Maal, T.J. Quantitative Assessment of Orbital Implant Position—A Proof of Concept. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz-Sawińska, E.; Lachowicz, E. Conservative management of posttraumatic diplopia. Klinika Oczna/Acta Ophthalmologica Polonica 2015, 117, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zimmerer, R.M.; Gellrich, N.C.; von Bülow, S.; Strong, E.B.; Ellis, E., 3rd; Wagner, M.E.H.; Sanchez Aniceto, G.; Schramm, A.; Grant, M.P.; Thiam Chye, L.; et al. Is there more to the clinical outcome in posttraumatic reconstruction of the inferior and medial orbital walls than accuracy of implant placement and implant surface contouring? A prospective multicenter study to identify predictors of clinical outcome. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, E.; Lockyer, J.; Erasmus, J.; Lim, C. Improved Outcomes of Orbital Reconstruction With Intraoperative Imaging and Rapid Prototyping. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2019, 77, 1211–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotecha, S.; Ferro, A.; Harrison, P.; Fan, K. Orbital reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating the role of patient-specific implants. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreurs, R.; Becking, A.G.; Jansen, J.; Dubois, L. Advanced Concepts of Orbital Reconstruction: A Unique Attempt to Scientifically Evaluate Individual Techniques in Reconstruction of Large Orbital Defects. Atlas Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am 2021, 29, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedemonte, C.; Sáez, F.; Vargas, I.; González, L.E.; Canales, M.; Salazar, K. Can customized implants correct enophthalmos and delayed diplopia in post-traumatic orbital deformities? A volumetric analysis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1086–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlittler, F.; Vig, N.; Burkhard, J.P.; Lieger, O.; Michel, C.; Holmes, S. What are the limitations of the non-patient-specific implant in titanium reconstruction of the orbit? Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 58, e80–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consorti, G.; Betti, E.; Catarzi, L. Customized and Navigated Primary Orbital Fracture Reconstruction: Computerized Operation Neuronavigated Surgery Orbital Recent Trauma (CONSORT) Protocol. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2022, 33, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.J.; Chung, N.N.; Liu, C.Y.; MacIntosh, P.W.; Korn, B.S.; Kikkawa, D.O. Precision in Oculofacial Surgery: Made-To-Specification Cast-Molded Implants in Orbital Reconstruction. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 36, 268–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, R.; Malińska, M.; Kozakiewicz, M. Classical versus custom orbital wall reconstruction: Selected factors regarding surgery and hospitalization. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2017, 45, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodson, A.M.C.; Parmar, S.; Ganesh, S.; Zakai, D.; Shafi, A.; Wicks, C.; O’Connor, R.; Yeung, E.; Khalid, F.; Tahim, A.; et al. Printed titanium implants in UK craniomaxillofacial surgery. Part I: Access to digital planning and perceived scope for use in common procedures. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 59, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarsitano, A.; Badiali, G.; Pizzigallo, A.; Marchetti, C. Orbital Reconstruction: Patient-Specific Orbital Floor Reconstruction Using a Mirroring Technique and a Customized Titanium Mesh. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2016, 27, 1822–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiters, S.; Mombaerts, I. Applications of three-dimensional printing in orbital diseases and disorders. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 30, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkhausen, R.; Mitsimponas, K.; Adler, W.; Brand, M.; von Wilmowsky, C. Clinical outcome of patients with orbital fractures treated with patient specific CAD/CAM ceramic implants—A retrospective study. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2021, 49, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timoshchuk, M.A.; Murnan, E.J.; Chapple, A.G.; Christensen, B.J. Do Patient-Specific Implants Decrease Complications and Increase Orbital Volume Reconstruction Accuracy in Primary Orbital Fracture Reconstruction? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerer, R.M.; Ellis, E., 3rd; Aniceto, G.S.; Schramm, A.; Wagner, M.E.; Grant, M.P.; Cornelius, C.P.; Strong, E.B.; Rana, M.; Chye, L.T.; et al. A prospective multicenter study to compare the precision of posttraumatic internal orbital reconstruction with standard preformed and individualized orbital implants. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1485–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönegg, D.; Wagner, M.; Schumann, P.; Essig, H.; Seifert, B.; Rücker, M.; Gander, T. Correlation between increased orbital volume and enophthalmos and diplopia in patients with fractures of the orbital floor or the medial orbital wall. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 1544–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essig, H.; Wagner, M.E.H.; Blumer, M. Secondary Corrections of the Orbit: Solitary Fractures. Atlas Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 29, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, D.I.; Hall, A.J.; Gwini, S.; Ben Artsi, E. Patient-specific Implants for Orbital Fractures: A Systematic Review. Ophthalmic Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kwon, J.; Ahn, C.J.; Esmaeli, B.; Kim, G.B.; Kim, N.; Sa, H.S. Generation of customized orbital implant templates using 3-dimensional printing for orbital wall reconstruction. Eye 2018, 32, 1864–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodson, A.M.C.; Parmar, S.; Ganesh, S.; Zakai, D.; Shafi, A.; Wicks, C.; O’Connor, R.; Yeung, E.; Khalid, F.; Tahim, A.; et al. Printed titanium implants in UK craniomaxillofacial surgery. Part II: Perceived performance (outcomes, logistics, and costs). Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 59, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, P.; Jehn, P.; Nejati-Rad, N.; Winterboer, J.; Gellrich, N.C.; Spalthoff, S. Pitfalls of Surgeon-Engineer Communication and the Effect of In-House Engineer Training During Digital Planning of Patient-Specific Implants for Orbital Reconstruction. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 80, 676–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chepurnyi, Y.; Chernogorskyi, D.; Kopchak, A.; Petrenko, O. Clinical efficacy of peek patient-specific implants in orbital reconstruction. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 10, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoor, P.; Suomalainen, A.; Lindqvist, C.; Mesimäki, K.; Danielsson, D.; Westermark, A.; Kontio, R.K. Rapid prototyped patient specific implants for reconstruction of orbital wall defects. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Clerc, N.; Baudouin, R.; Carlevan, M.; Khoueir, N.; Verillaud, B.; Herman, P. 3D titanium implant for orbital reconstruction after maxillectomy. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2020, 73, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.H.; Khavanin, N.; Grant, M.; Kumar, A.R. Correction of Complex Neurofibromatosis Orbital and Globe Malposition Using the Orbital Box Segmentation Osteotomy With Patient-Specific Internal Orbit Reconstruction. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


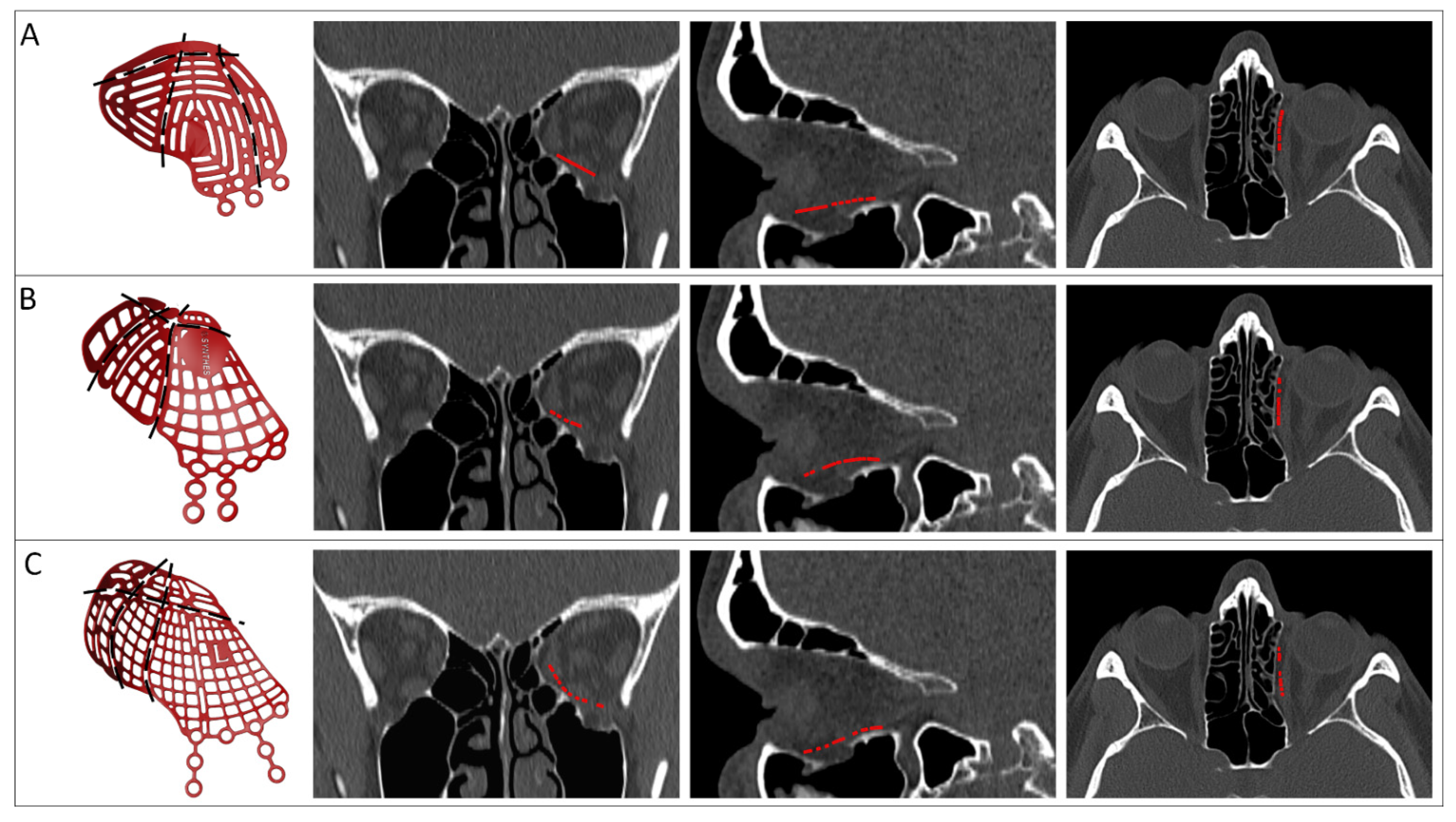
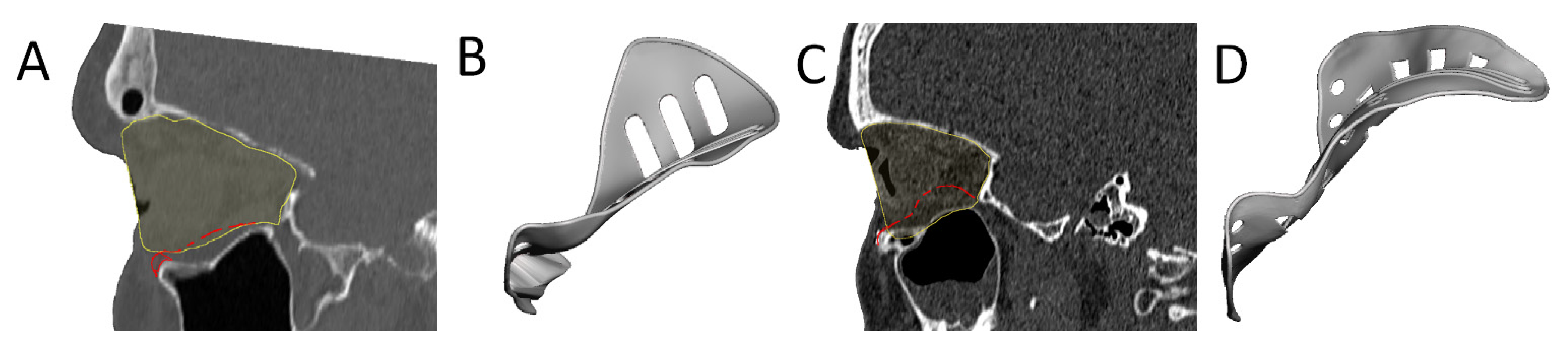
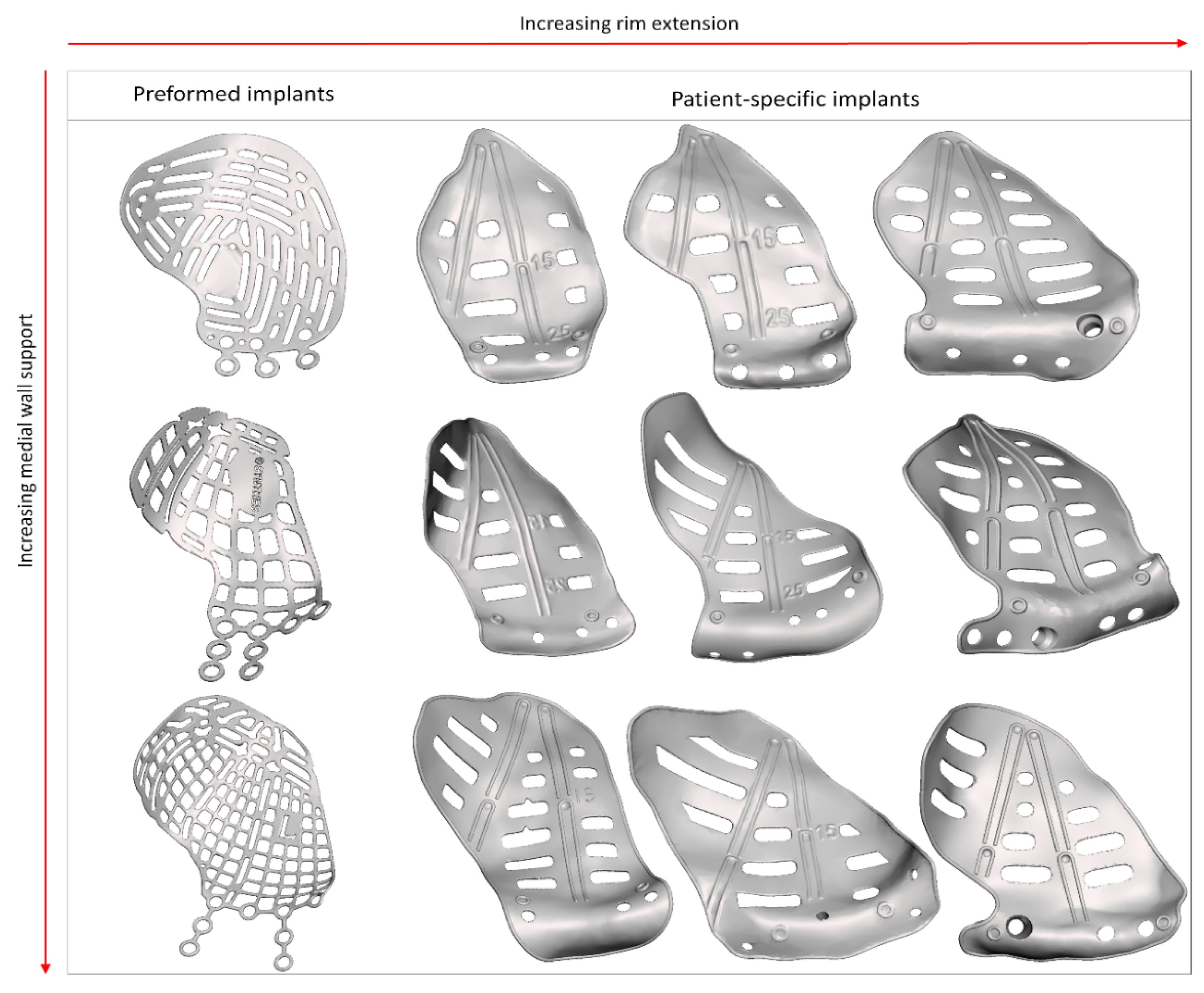
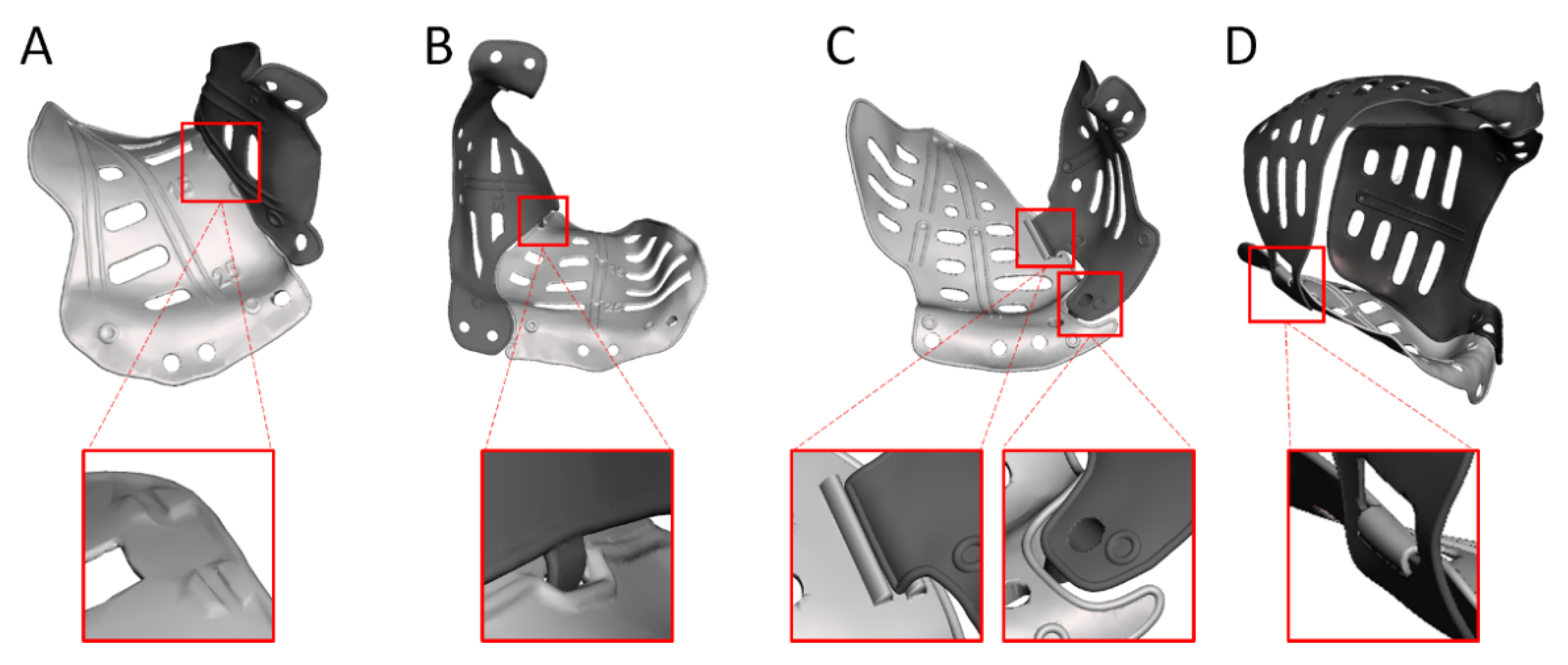
| Design Consideration | Effect on | Options | References | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness | Positioning, stability | 0.3 mm | [22,37,38] | |
| Atraumatic cord | Positioning, stability | Present | [37,39,40] | |
| Absent | [38,41,42] | |||
| Grid | Clinical symptoms | Horizontal | [22,37,40,43] | |
| Squares | [38,39,41,44] | |||
| Porous | [42,45,46] | |||
| Support | Stability, accuracy | Three points | [22] | Infraorbital rim, medial wall, posterior ledge |
| [38] | Anteromedial, anterolateral, posterior | |||
| Ledge | [37,40,43] | Inverted shovel design | ||
| Lateral posterior wall | [43] | Stabilizer for self-centering implant | ||
| Extension | Accuracy | Orbital rim | [22,42,44,46,47,48] | |
| Lateral posterior wall | [43] | |||
| Specific bone features | [45] | |||
| Anterior elevation | Clinical symptoms | [22] | Rim elevation to correct hypoglobus | |
| Overcorrection | Clinical symptoms | Location | [22] | Posterior to bulbus |
| [49] | Orbital floor elevated in sagittal relation | |||
| Amount | [22] | Based on clinical findings, advanced diagnostics | ||
| [38] | Slight overcorrection | |||
| [50] | Same amount in cubic cm as mm enophthalmos | |||
| Intraoperatively | [51] | Spacers | ||
| Navigation | Accuracy | Markers | [22,37,38,39,52] | Eminence lacrimal foramen [38] |
| Vectors | [37,40,43] | |||
| Fixation | Stability | Absent | [38,44,48] | |
| Present | [22,37,39,40,42,46,47,53] | Eccentric screw alters implant position [47] Fix implant if form stable [40] | ||
| Fixation re-use | Accuracy | Re–used screw hole | [54] | Only in secondary reconstruction |
| Multi-piece | Positioning, stability, | Lazy-S | [42,47,49] | |
| accuracy | Interlocking | [46,48,55,56] |
| Feedback Method | Static/Dynamic |
|---|---|
| Virtual surgical planning | Static |
| Compelling fit patient-specific implant | Static |
| Fixation re-use | Static |
| Navigation | Dynamic |
| Markers and vectors | Dynamic |
| Intraoperative imaging | Static |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabelis, J.F.; Schreurs, R.; Essig, H.; Becking, A.G.; Dubois, L. Personalized Medicine Workflow in Post-Traumatic Orbital Reconstruction. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091366
Sabelis JF, Schreurs R, Essig H, Becking AG, Dubois L. Personalized Medicine Workflow in Post-Traumatic Orbital Reconstruction. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2022; 12(9):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091366
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabelis, Juliana F., Ruud Schreurs, Harald Essig, Alfred G. Becking, and Leander Dubois. 2022. "Personalized Medicine Workflow in Post-Traumatic Orbital Reconstruction" Journal of Personalized Medicine 12, no. 9: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091366
APA StyleSabelis, J. F., Schreurs, R., Essig, H., Becking, A. G., & Dubois, L. (2022). Personalized Medicine Workflow in Post-Traumatic Orbital Reconstruction. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(9), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm12091366






