Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Mast Cell Activation Syndrome and Response to Mast-Cell-Directed Treatment: A Case Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
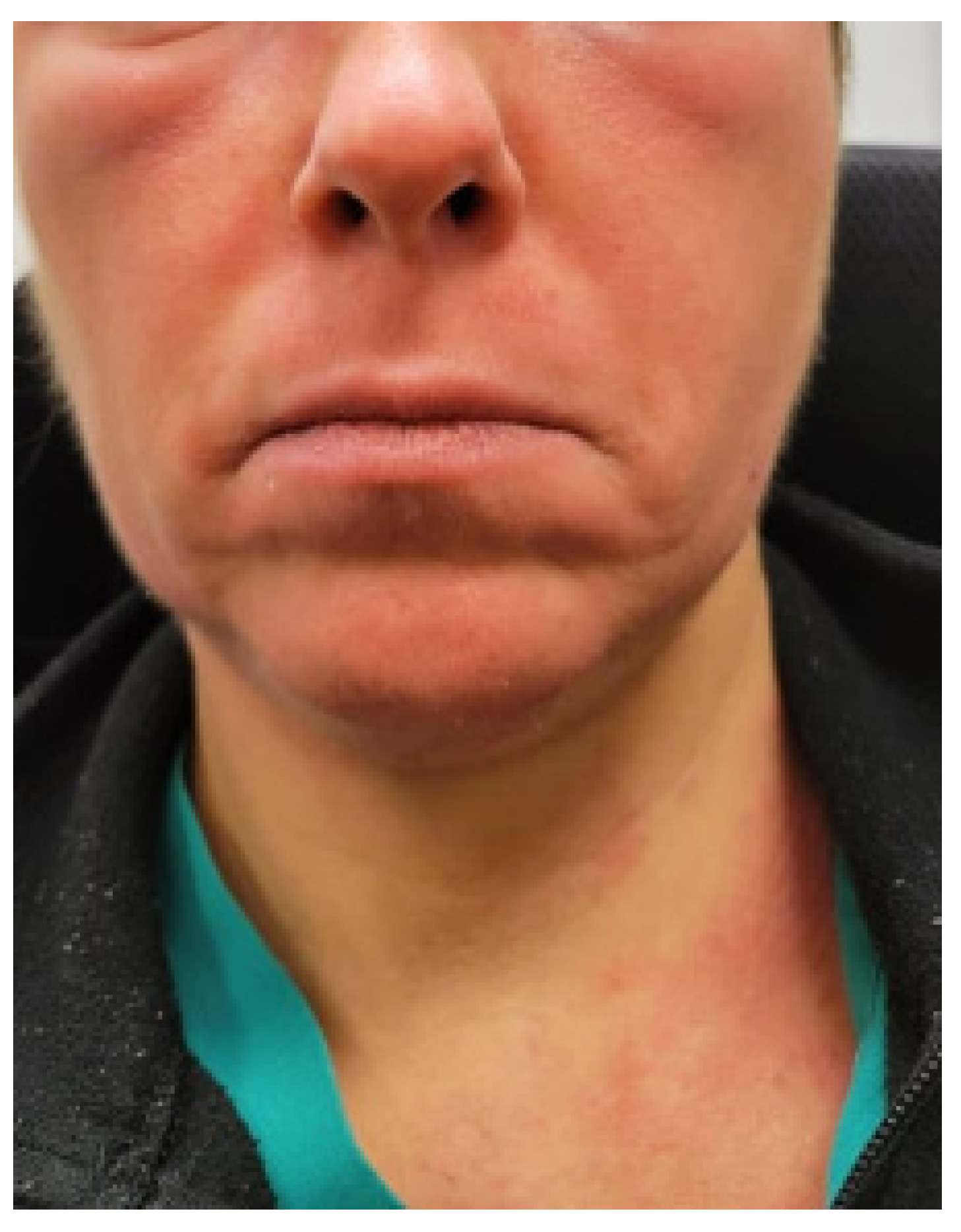
3.1. Illustrative Case: Patient 1
3.2. Illustrative Case: Patient 4—Personal Account
4. Discussion
5. Mast Cells
6. Histamine and Histamine Receptors
7. Mast-Cell-Directed Treatment
8. Autonomic Dysfunction and MCAS
9. Limitations
10. Clinical Relevance in Personalized Care
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Afrin, L.B.; Butterfield, J.H.; Raithel, M.; Molderings, G.J. Often seen, rarely recognized: Mast cell activation disease—A guide to diagnosis and therapeutic options. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afrin, L.B.; Self, S.; Menk, J.; Lazarchick, J. Characterization of Mast Cell Activation Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 353, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, M.J. Nonclonal Mast Cell Activation Syndrome: A Growing Body of Evidence. Immunol. Allergy Clin. N. Am. 2018, 38, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, L.B.; Pöhlau, D.; Raithel, M.; Haenisch, B.; Dumoulin, F.L.; Homann, J.; Mauer, U.M.; Harzer, S.; Molderings, G.J. Mast cell activation disease: An underappreciated cause of neurologic and psychiatric symptoms and diseases. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 50, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molderings, G.J.; Haenisch, B.; Bogdanow, M.; Fimmers, R.; Nöthen, M.M. Familial Occurrence of Systemic Mast Cell Activation Disease. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, L.B.; Ackerley, M.B.; Bluestein, L.S.; Brewer, J.H.; Brook, J.B.; Buchanan, A.D.; Cuni, J.R.; Davey, W.P.; Dempsey, T.T.; Dorff, S.R.; et al. Diagnosis of mast cell activation syndrome: A global “consensus-2”. Diagnosis 2020, 8, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molderings, G.J.; Kolck, U.W.; Scheurlen, C.; Brüss, M.; Homann, J.; Von Kügelgen, I. Multiple novel alterations in Kit tyrosine kinase in patients with gastrointestinally pronounced systemic mast cell activation disorder. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelestak, J.; Singhal, N.; Frankle, L.; Tomor, R.; Sternbach, S.; McDonough, J.; Freeman, E.; Clements, R. Increased blood-brain barrier hyperpermeability coincides with mast cell activation early under cuprizone administration. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, L.B.; Pace, L.A.; Rezaie, A.; Afrin, L.B.; Molderings, G.J. Mast Cell Activation Syndrome: A Primer for the Gastroenterologist. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 66, 965–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molderings, G.J. The genetic basis of mast cell activation disease—Looking through a glass darkly. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2015, 93, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiBaise, J.K.; Harris, L.A.; Goodman, B. Postural Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) and the GI Tract: A Primer for the Gastroenterologist. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 113, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinkle, B.; Castori, M.; Berglund, B.; Cohen, H.; Grahame, R.; Kazkaz, H.; Levy, H. Hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (a.k.a. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Type III and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome hypermobility type): Clinical description and natural history. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part C Semin. Med. Genet. 2017, 175, 48–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häder, T.; Molderings, G.J.; Klawonn, F.; Conrad, R.; Mücke, M.; Sellin, J. Cluster-Analytic Identification of Clinically Meaningful Subtypes in MCAS: The Relevance of Heat and Cold. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2023, 68, 3400–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molderings, G.J.; Haenisch, B.; Brettner, S.; Homann, J.; Menzen, M.; Dumoulin, F.L.; Panse, J.; Butterfield, J.; Afrin, L.B. Pharmacological treatment options for mast cell activation disease. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2016, 389, 671–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, Q.; Wang, Z.; Di Nardo, A.; Boulanger, N. Interaction of primary mast cells with Borrelia burgdorferi (sensu stricto): Role in transmission and dissemination in C57BL/6 mice. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, L.B.; Rezaie, A.; Brook, J.B.; Kaleem, Z.; Afrin, L.B.; Molderings, G.J. Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth is Common in Mast Cell Activation Syndrome. J. Med. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritas, S.K.; Conti, P. Impact of mold on mast cell-cytokine immune response. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2018, 32, 763–768. [Google Scholar]
- Dearman, R.J.; Betts, C.J.; Humphreys, N.; Flanagan, B.F.; Gilmour, N.J.; Basketter, D.A.; Kimber, I. Chemical Allergy: Considerations for the Practical Application of Cytokine Profiling. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 71, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schedle, A.; Samorapoompichit, P.; Füreder, W.; Rausch-Fan, X.H.; Franz, A.; Sperr, W.R.; Slavicek, R.; Simak, S.; Klepetko, W.; Ellinger, E.; et al. Metal ion-induced toxic histamine release from human basophils and mast cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1998, 39, 560–567. [Google Scholar]
- Mischoulon, D.; Hylek, L.; Yeung, A.S.; Clain, A.J.; Baer, L.; Cusin, C.; Ionescu, D.F.; Alpert, J.E.; Soskin, D.P.; Fava, M. Randomized, proof-of-concept trial of low dose naltrexone for patients with breakthrough symptoms of major depressive disorder on antidepressants. J. Affect. Disord. 2017, 208, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, L.B.; Brook, J.B.; Myers, T.L.; Goodman, B. Successful treatment of postural orthostatic tachycardia and mast cell activation syndromes using naltrexone, immunoglobulin and antibiotic treatment. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, L.B.; Brook, J.B.; Molderings, G.J. Efficacy and toxicity of hydroxyurea in mast cell activation syndrome patients refractory to standard medical therapy: Retrospective case series. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2022, 395, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstock, L.B.; Brook, J.B.; Brook, J.B.; Blasingame, K.E.; Kaleem, Z.; Afrin, L.B.; Molderings, G.J. Tinnitus in Mast Cell Activation Syndrome: A Prospective Survey of 114 Patients. J. Otolaryngol. Neurotol. Res. 2021, 4, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock, L.B.; Walters, A.S.; Brook, J.B.; Kaleem, Z.; Afrin, L.B.; Molderings, G.J. Restless legs syndrome is associated with mast cell activation syndrome. Sleep Med. 2020, 16, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, L.; Vang, D.; Nguyen, J.; Gupta, M.; Luk, K.; Ericson, M.E.; Simone, D.A.; Gupta, K. Mast cell activation contributes to sickle cell pathobiology and pain in mice. Blood 2013, 122, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriksen, E.; van Bergeijk, D.; Oosting, R.S.; Redegeld, F.A. Mast cells in neuroinflammation and brain disorders. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 79, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X. Mast Cells and Neuroinflammation. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2014, 20, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.; Ganti, T.; Vaou, E.; Hohler, A. The relationship between mast cell activation syndrome, postural tachycardia syndrome, and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2021, 42, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelb, S.; Stock, A.D.; Anzi, S.; Putterman, C.; Ben-Zvi, A. Mechanisms of neuropsychiatric lupus: The relative roles of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier versus blood-brain barrier. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 91, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, D.S.; Sultan, S.; Georgin-Lavialle, S.; Pillet, N.; Montestruc, F.; Gineste, P.; Barete, S.; Damaj, G.; Moussy, A.; Lortholary, O.; et al. Depression in Patients with Mastocytosis: Prevalence, Features and Effects of Masitinib Therapy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgin-Lavialle, S.; Gaillard, R.; Moura, D.; Hermine, O. Mastocytosis in adulthood and neuropsychiatric disorders. Transl. Res. 2016, 174, 77–85.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempuraj, D.; Selvakumar, G.P.; Thangavel, R.; Ahmed, M.E.; Zaheer, S.; Raikwar, S.P.; Iyer, S.S.; Bhagavan, S.M.; Beladakere-Ramaswamy, S.; Zaheer, A. Mast Cell Activation in Brain Injury, Stress, and Post-traumatic Stress Disorder and Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoloro-SantaBarbara, J.; Carroll, J.; Lobel, M. Coping, social support, and anxiety in people with mast cell disorders. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 127, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SantaBarbara, J.N.; Lobel, M. Depression, psychosocial correlates, and psychosocial resources in individuals with mast cell activation syndrome. J. Health Psychol. 2021, 27, 2013–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jendoubi, F.; Severino-Freire, M.; Negretto, M.; Arbus, C.; Paul, C.; Livideanu, C.B. Neuropsychiatric, cognitive and sexual impairment in mastocytosis patients. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidri, M.; Royer, B.; Averlant, G.; Bismuth, G.; Guillosson, J.-J.; Arock, M. Inhibition of mouse mast cell proliferation and proinflammatory mediator release by benzodiazepines. Immunopharmacology 1999, 43, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikarashi, Y.; Yuzurihara, M. Experimental anxiety induced by histaminergics in mast cell-deficient and congenitally normal mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 72, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boddaert, N.; Salvador, A.; Chandesris, M.O.; Lemaître, H.; Grévent, D.; Gauthier, C.; Hermine, O. Neuroimaging evidence of brain abnormalities in mastocytosis. Transl. Psychiatry 2017, 7, e1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenisch, B.; Molderings, G. White matter abnormalities are also repeatedly present in patients with systemic mast cell activation syndrome. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuutinen, S.; Panula, P. Histamine in neurotransmission and brain diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 709, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravhe, I.S.; Krishnan, A.; Manoj, N. Evolutionary history of histamine receptors: Early vertebrate origin and expansion of the H3-H4 subtypes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 154, 106989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangam, E.B.; Jemima, E.A.; Singh, H.; Baig, M.S.; Khan, M.; Mathias, C.B.; Church, M.K.; Saluja, R. The Role of Histamine and Histamine Receptors in Mast Cell-Mediated Allergy and Inflammation: The Hunt for New Therapeutic Targets. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiligada, E.; Kyriakidis, K.; Chazot, P.L.; Passani, M.B. Histamine Pharmacology and New CNS Drug Targets. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2011, 17, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, P.; Hernandez-Trujillo, V.; Lieberman, J.; Frew, A.J. Clinical Immunology, 3rd ed.; Rich, R.R., Fleisher, T.A., Shearer, W.T., Schroeder, H.W., Frew, A.J., Weyand, C.M., Eds.; Mosby: St. Louis, MI, USA, 2008; Chapter 89; pp. 1317–1329. ISBN 9780323044042. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, L.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z. The Histaminergic System in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindskog, M. Histamine Receptors in the Cross-Talk between Periphery and Brain. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2017, 20, 400–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Branco, A.C.C.C.; Yoshikawa, F.S.Y.; Pietrobon, A.J.; Sato, M.N. Role of Histamine in Modulating the Immune Response and Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 9524075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, J.R.; Afrin, L.B. Recognition and Management of Medication Excipient Reactivity in Patients with Mast Cell Activation Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 357, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenisch, B.; Huber, M.; Wilhelm, T.; Steffens, M.; Molderings, G.J. Investigation into mechanisms mediating the inhibitory effect of 1,4-benzodiazepines on mast cells by gene expression profiling. Life Sci. 2013, 92, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukudo, S.; Kano, M.; Sato, Y.; Muratsubaki, T.; Kanazawa, M.; Tashiro, M.; Yanai, K. Histamine Neuroimaging in Stress-Related Disorders. In The Functional Roles of Histamine Receptors; Current Topics in Behavioral Neurosciences; 2022; Volume 59, pp. 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Panula, P. Histamine receptors, agonists, and antagonists in health and disease. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2021, 180, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Qian, Q.; Wang, Y.; Dong, H.; Li, N.; Qian, Y.; Jin, W. Histamine upregulates the expression of histamine receptors and increases the neuroprotective effect of astrocytes. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lortholary, O.; Chandesris, M.O.; Livideanu, C.B.; Paul, C.; Guillet, G.; Jassem, E.; Niedoszytko, M.; Barete, S.; Verstovsek, S.; Grattan, C.; et al. Masitinib for treatment of severely symptomatic indolent systemic mastocytosis: A randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet 2017, 389, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, R.; Cannom, D.S.; Olshansky, B.; Xi, S.C.; Krishnappa, D.; Adkisson, W.O.; Norby, F.L.; Fedorowski, A.; Benditt, D.G. Mast Cell Activation Disorder and Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome: A Clinical Association. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e021002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, P.; Giannetti, M.P.; Weller, E.; Hamilton, M.J.; Castells, M. Mast cell disorders are associated with decreased cerebral blood flow and small fiber neuropathy. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021, 128, 299–306.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blitshteyn, S. Dysautonomia, Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders and Mast Cell Activation Syndrome as Migraine Comorbidities. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2023. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Constitutional | Fatigue, subjective hyperthermia and/or hypothermia, sweats, change in appetite, weight gain/loss, chemical/physical sensitivities, poor healing |
| Dermatologic | Urticaria, itch, flushing, hemangiomas with itch/pain, various rashes, telangiectasias, striae, skin tags, folliculitis, ulcers, eczema, angioedema, alopecia, onychodystrophy |
| Ophthalmologic | Irritated, “dry” eyes, difficulty focusing, blepharospasm |
| Otologic | Tinnitus, hearing loss, coryza, rhinitis, nasal congestion, epistaxis |
| Oropharyngeal | Pain, burning, leukoplakia, ulcers, angioedema, dysgeusia, dental and/or periodontal inflammation/decay |
| Lymphatic | Lymphadenopathy, rare splenomegaly |
| Pulmonary | Dry cough, dyspnea (difficulty taking a deep breath), wheezing, obstructive sleep apnea |
| Cardiovascular | Presyncope, hypertension, blood pressure lability, palpitations, edema, chest pain, allergic angina (Kounis syndrome) |
| Gastrointestinal | Dyspepsia, gastroesophageal reflux, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea and/or constipation, gastroparesis, angioedema, dysphagia (usually proximal), bloating (post-prandial or spontaneous), malabsorption |
| Genitourinary | Menorrhagia, pelvic pain, endometriosis, vulvodynia, vaginitis, dysmenorrhea, miscarriages, infertility, dysuria |
| Musculoskeletal | Myalgias, migratory bone/joint pain, osteopenia/osteoporosis |
| Neurologic | Headache, migraine, sensory neuropathies, dysautonomia, episodic weakness, seizure disorders, non-epileptic seizures, cognitive dysfunction, insomnia, hypersomnolence, restless leg syndrome |
| Psychiatric | Depression, anger/irritability, mood lability, anxiety, panic, obsession–compulsion, attention deficit/hyperactivity |
| Hematologic | Easy bruising, polycythemia, anemia |
| Immunologic | Hypersensitivity reactions, increased risk for malignancy and autoimmunity, impaired healing, increased susceptibility to infection |
| Consensus 1: |
|
| Consensus 2: |
Presence of 2 systems with typical mast cell activation symptoms and ≥1 of the following:
|
| N | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Age (years), sex | 47, female | 50, female | 37, female | 71, female |
| Prior psychiatric diagnoses | GAD, OCD, phobia | GAD, panic disorder | Bipolar disorder (suicide attempt age 15), GAD, ADHD, Tourette’s, narcolepsy | MDD (suicide attempt age 16) |
| Clinical course in childhood and adolescence | Anaphylaxis to nuts and antibiotics | None | Brain fog, diarrhea, urticaria, self-abusive behavior, asthma | Headaches, recurrent viral infections, hives, edema with insect bites, allergies, nausea, abdominal pain, depression, menorrhagia |
| Clinical course in adulthood | Postpartum phobias, rashes, facial swelling, pruritus, syncope, tachycardia, migraine | Syncope/presyncope during pregnancy, pacemaker for bradycardia, tachycardia, blurred vision, anxiety, joint pain | Depression (daily suicidal ideation), mania, hallucinations, anxiety, fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, myalgia, hives, bone pain, episodic hypertension, bedridden 4 days/week | Depression (daily suicidal ideation), pelvic pain leading to hysterectomy age 21, tinnitus, chest and body pain, interstitial cystitis |
| Prior psychiatric therapy | Multiple SSRIs without efficacy | Prescribed SSRI: elected not to take it | 1 SSRI, 2 SSRNIs, 2 anti-psychotics, 3 benzos, lamotrigine, atomoxetine, dextroamphetamine, guanfacine | 3 classes of anti-depressants—multiple agents, lithium, and ECT |
| New diagnoses | MCAS, hEDS, NCS, IST | MCAS, NCS, labile hypertension | MCAS, POTS, RLS, labile hypertension | MCAS, POTS |
| Mast cell treatment | Hydroxyzine, cetirizine daily. Prednisone PRN flares | Cetirizine and famotidine daily. | Step 1 therapy, LDN. Maintained on aripiprazole, dextro-amphetamine, and lamotrigine | Antihistamines 1 and 2, hydroxyurea |
| Outcomes of mast cell treatment on neuropsychiatric conditions | Complete response: works full time | Complete response: works full time. Tachycardia, syncope, flushing, and anxiety resolved | Partial response: works part time | Complete response: independent in ADLs and iADLs. Depression resolved |
| N | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| Age (years), sex | 18, male | 18, female | 19, female | 33, female |
| Prior neuropsychiatric diagnoses | Panic disorder, GAD, MDD | Panic disorder, GAD, MDD | Panic disorder, MDD | Panic disorder, GAD, MDD |
| Clinical course in childhood and adolescence | Brain fog, fatigue, rhinitis, diarrhea, abdominal pain with gluten | Constipation, diarrhea, dysphagia, heartburn, nausea, eczema, headache, menorrhagia, syncope | Nausea, diarrhea, menorrhagia, flushing, fatigue, brain fog, tinnitus | Headache, multiple viral infections |
| Clinical course in adulthood | Myalgias | Constipation, diarrhea, dysphagia, heartburn, nausea, eczema, headache, menorrhagia, syncope | Weight loss, nausea, diarrhea, menorrhagia, flushing, fatigue, brain fog, tinnitus | Nausea, pain, fatigue, weakness, tinnitus, palpitations, flushing, presyncope, migraine, brain fog, hives, itch, bone pain |
| Prior psychiatric therapy | Escitalopram | Escitalopram, buspirone | Desvenlafaxine, fluvoxamine, fluoxetine | None |
| New diagnoses | MCAS | MCAS, RLS, hEDS | MCAS, POTS, hEDS | MCAS, POTS, hEDS |
| Mast cell treatment | Step 1, LDN | H1/2 blockers, LDN, buspirone PRN anxiety | Step 1, LDN | GFD, Step 1, LDN |
| Outcome on mast cell treatment for neuropsychiatric conditions | Complete response: Able to return to college after withdrawal | Complete response: Able to attend college after home schooling | Marked improvement: Able to return to college. Regained 15 pounds | Complete response: Able to work full time |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weinstock, L.B.; Nelson, R.M.; Blitshteyn, S. Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Mast Cell Activation Syndrome and Response to Mast-Cell-Directed Treatment: A Case Series. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111562
Weinstock LB, Nelson RM, Blitshteyn S. Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Mast Cell Activation Syndrome and Response to Mast-Cell-Directed Treatment: A Case Series. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(11):1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111562
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeinstock, Leonard B., Renee M. Nelson, and Svetlana Blitshteyn. 2023. "Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Mast Cell Activation Syndrome and Response to Mast-Cell-Directed Treatment: A Case Series" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 11: 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111562
APA StyleWeinstock, L. B., Nelson, R. M., & Blitshteyn, S. (2023). Neuropsychiatric Manifestations of Mast Cell Activation Syndrome and Response to Mast-Cell-Directed Treatment: A Case Series. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(11), 1562. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13111562








