Scoring Systems to Evaluate the Mortality Risk of Patients with Emphysematous Cystitis: A Retrospective Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Definition
2.2. Scoring Systems
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Laboratory Data and Scoring Systems
3.3. Microbiology
3.4. Clinical Management and Outcomes
3.5. Univariate and Multivariate Analysis of Risk Factors
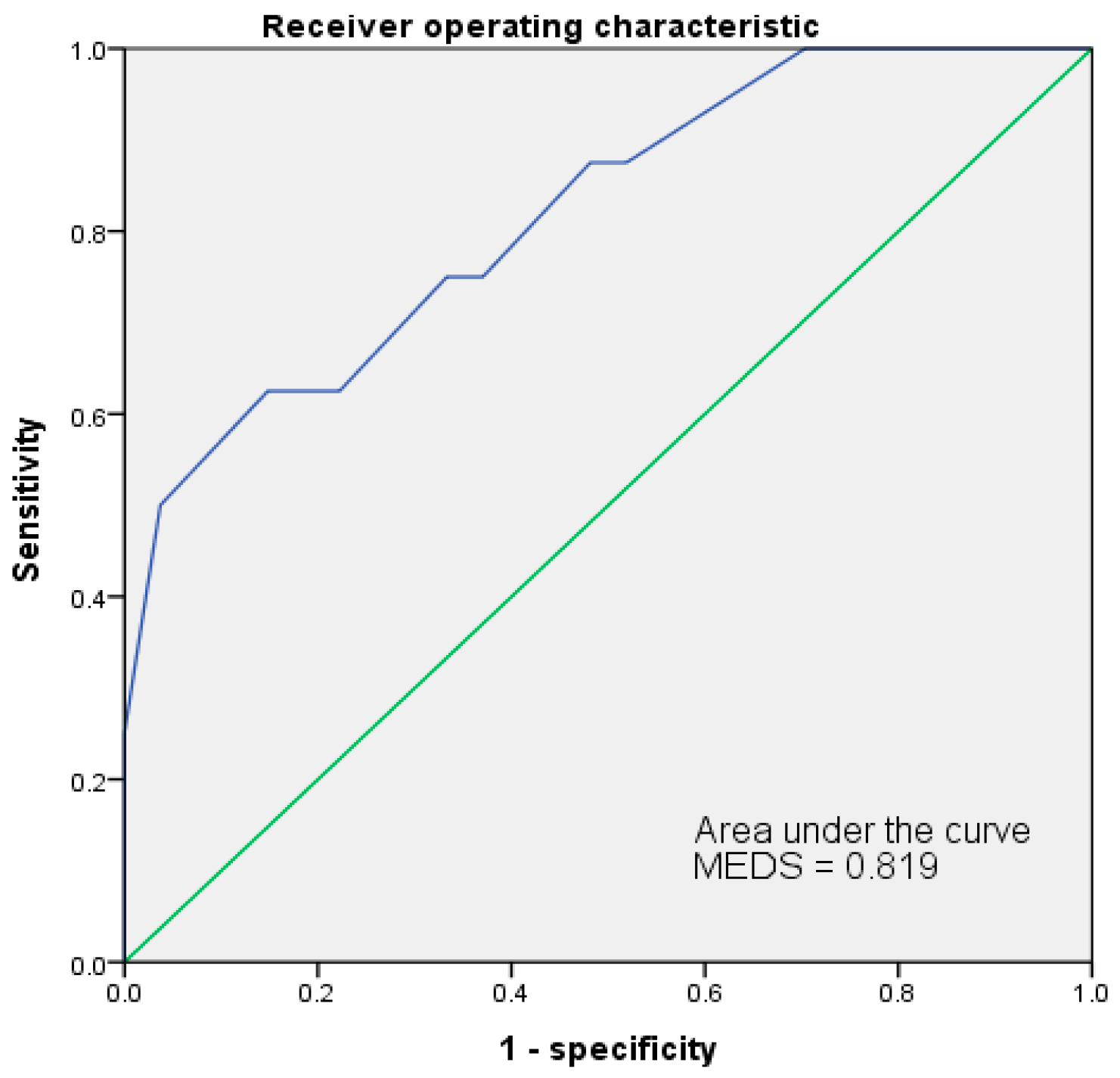
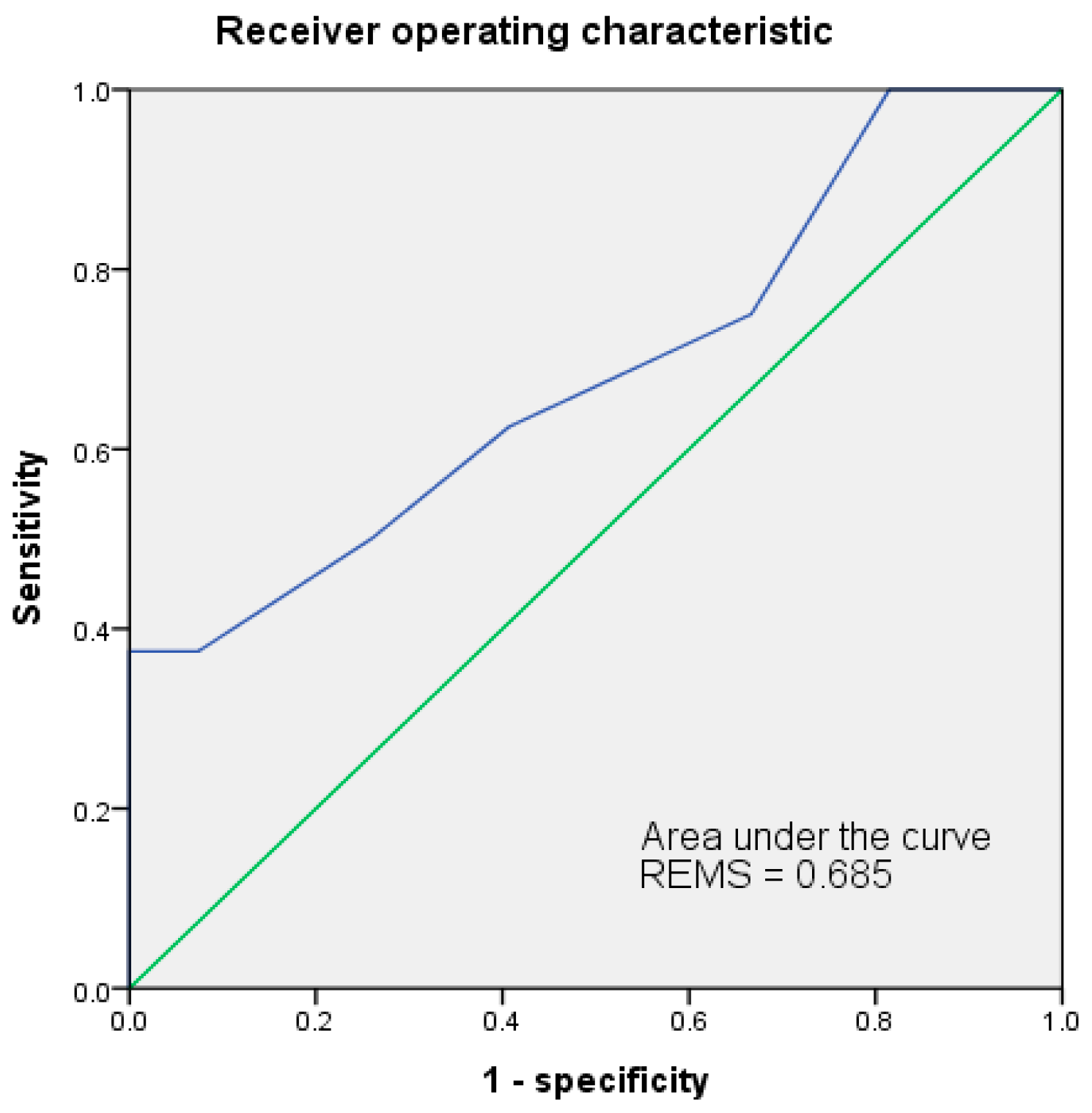
3.6. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC)
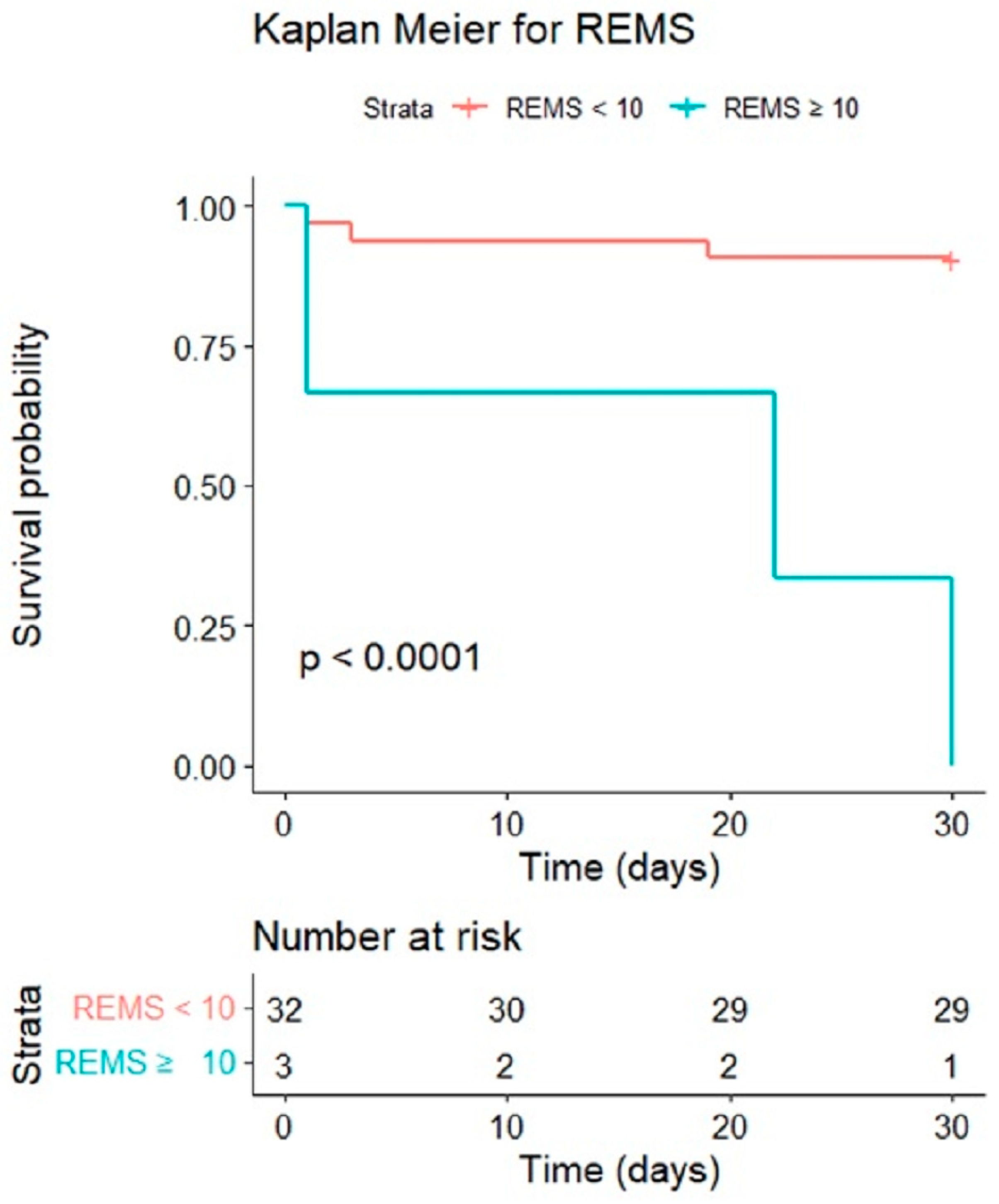
3.7. Cumulative Survival Rates by Kaplan–Meier and Discrimination Plots
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finemans, S.; Ferber, W.L.; Roginsky, D.N. Primary pneumaturia, with a report of two cases. Radiology 1952, 59, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.A.; Lane, B.R.; Thomas, A.Z.; Remer, E.M.; Campbell, S.C.; Shoskes, D.A. Emphysematous cystitis: A review of 135 cases. BJU Int. 2007, 100, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranjan, S.K.; Navriya, S.C.; Kumar, S.; Mittal, A.; Bhirud, D.P. Emphysematous cystitis: A case report and literature review of 113 cases. Urol. Ann. 2021, 13, 312–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Choi, S.K.; Lee, S.H.; Yoo, K.H. Clinical Outcomes and Risk Factor Analysis of Patients Presenting with Emphysematous Cystitis: A 15-Year Retrospective Multicenter Study. Medicina 2021, 57, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, R.; Jha, R.; Muthukrishnan, J.; Gude, D.; Nath, V.; Shekhar, S.; Narayan, G.; Sinha, S.; Mandal, S.N.; Rao, B.S.; et al. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: A single center study. Indian J. Nephrol. 2013, 23, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, N.I.; Howell, M.D.; Talmor, D.; Donnino, M.; Ngo, L.; Bates, D.W. Mortality in Emergency Department Sepsis (MEDS) score predicts 1-year mortality. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanasit, P.; Khwannimit, B. Comparison the accuracy of early warning scores with qSOFA and SIRS for predicting sepsis in the emergency department. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 46, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivayoham, N.; Hussain, A.N.; Shabbo, L.; Christie, D. An observational cohort study of the performance of the REDS score compared to the SIRS criteria, NEWS2, CURB65, SOFA, MEDS and PIRO scores to risk-stratify emergency department suspected sepsis. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 1863–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dam, P.M.E.L.; Zelis, N.; van Kuijk, S.M.J.; Linkens, A.E.M.J.H.; Brüggemann, R.A.G.; Spaetgens, B.; van der Horst, I.C.C.; Stassen, P.M. Performance of prediction models for short-term outcome in COVID-19 patients in the emergency department: A retrospective study. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inacio, M.C.; Jorissen, R.N.; Khadka, J.; Whitehead, C.; Maddison, J.; Bourke, A.; Pham, C.T.; Karnon, J.; Wesselingh, S.L.; Lynch, E.; et al. Predictors of short-term hospitalization and emergency department presentations in aged care. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 69, 3142–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, W.Y.; Han, K.S.; Kim, S.J.; Kang, H. Development and validation of a scoring system for mortality prediction and application of standardized W statistics to assess the performance of emergency departments. BMC Emerg. Med. 2021, 21, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, K.; Zheng, X.; Cui, W.; Hong, Y.; Zhang, Z. Performance of the MEDS score in predicting mortality among emergency department patients with a suspected infection: A meta-analysis. Emerg. Med. J. 2020, 37, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbaih, A.H.; Elsayed, Z.M.; Ahmed, R.M.; Abd-Elwahed, S.A. Sepsis patient evaluation emergency department (SPEED) score & mortality in emergency department sepsis (MEDS) score in predicting 28-day mortality of emergency sepsis patients. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2019, 22, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schicho, A.; Stroszczynski, C.; Wiggermann, P. Emphysematous Cystitis: Mortality, Risk Factors, and Pathogens of a Rare Disease. Clin. Pract. 2017, 7, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemi, O.A.; Flaherty, J.P. Emphysematous Cystitis. Cureus 2020, 12, e11723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, M.; Shimizu, T. Emphysematous cystitis: A review of the literature. Intern. Med. 2014, 53, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupper, M.; Kravtsov, A.; Potasman, I. Emphysematous cystitis: Illustrative case report and review of the literature. Medicine 2007, 86, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, B.; George, A.; Owen, R. A nontraditional presentation and treatment for emphysematous cystitis. Urol. Case Rep. 2023, 46, 102321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.J.; Parmar, K.; Mukherjee, A.; Sonawane, P.; Badrakumar, C. Emphysematous cystitis: An incidental finding with varying outcomes. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2023, 105, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, E.E.; Guo, L.; Schwendeman, A.; Li, X.A. HDL in sepsis-risk factor and therapeutic approach. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 23, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerapornratana, S.; Manrique-Caballero, C.L.; Gómez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 1083–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarbock, A.; Gomez, H.; Kellum, J.A. Sepsis-induced acute kidney injury revisited: Pathophysiology, prevention and future therapies. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2014, 20, 588–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelesidis, T.; Osman, S.; Tsiodras, S. Emphysematous cystitis in the absence of known risk factors: An unusual clinical entity. South. Med. J. 2009, 102, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overhaus, M.; Tögel, S.; Pezzone, M.A.; Bauer, A.J. Mechanisms of polymicrobial sepsis-induced ileus. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 287, G685–G694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, T.; Ohara, S.; Moriyama, H. Emphysematous cystitis occurred in the case treated with steroid for autoimmune hepatitis. Case Rep. Urol. 2013, 2013, 821780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokokawa, D.; Uehara, T.; Ikusaka, M. Emphysematous cystitis in a patient using immunosuppressant agents. J. Gen. Fam. Med. 2020, 22, 92–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakaldimis, G.; Bousiou, Z.; Dimou-Besikli, S.; Karakasis, N.; Papalakis, A.; Giannakopoulos, S.; Sakellari, I.; Kalaitzis, C. Pneumomediastinum as a rare complication in an immunosuppressed patient with emphysematous cystitis. Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 10, e05429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhusayni, S.A.; Alshammari, T.H.; Althomali, A.A.; Alqahtani, M.M.; Alanazi, W.A.; Alghamdi, M.A.; AlDawsari, F.M.; Homoud, E.M.; Alharbi, A.A.; Althobaiti, K.E.; et al. Emphysematous Cystitis: A Radiological Diagnosis of Potentially Life-Threatening Infection. Cureus 2021, 13, e20201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellathy, T.P.; Pinsky, M.R.; Hravnak, M. Intensive Care Unit Scoring Systems. Crit. Care Nurse 2021, 41, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Chou, S.E.; Liu, H.T.; Hsieh, T.M.; Su, W.T.; Chien, P.C.; Hsieh, C.H. Performance of Prognostic Scoring Systems in Trauma Patients in the Intensive Care Unit of a Trauma Center. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Tian, Z.R.; Li, F.; Guan, Y.M.; Ma, Z.F.; Lu, Z.H.; Wang, A.P. Risk prediction using the National Early Warning Score and the Worthing Physiological Scoring System in patients who were transported to the Intensive Care Unit from the Emergency Department: A cohort study. Intensive Crit. Care Nurs. 2021, 64, 103015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oduncu, A.F.; Kıyan, G.S.; Yalçınlı, S. Comparison of qSOFA, SIRS, and NEWS scoring systems for diagnosis, mortality, and morbidity of sepsis in emergency department. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2021, 48, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.T.; Wang, H.P.; Lien, W.C. Life-threatening urinary tract infection. QJM 2009, 102, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.C.; Yang, C.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Chi, C.H.; Lee, C.C. Validation of MEDS score in predicting short-term mortality of adults with community-onset bacteremia. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2020, 38, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourn, S.S.; Crowe, R.P.; Fernandez, A.R.; Matt, S.E.; Brown, A.L.; Hawthorn, A.B.; Myers, J.B. Initial prehospital Rapid Emergency Medicine Score (REMS) to predict outcomes for COVID-19 patients. J. Am. Coll. Emerg. Physicians Open 2021, 2, e12483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong-Minh, K.; Welten, I.; Endeman, H.; Hagenaars, T.; Ramakers, C.; Gommers, D.; van Gorp, E.; van der Does, Y. Predicting mortality in adult patients with sepsis in the emergency department by using combinations of biomarkers and clinical scoring systems: A systematic review. BMC Emerg. Med. 2021, 21, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmatinejad, Z.; Tohidinezhad, F.; Rahmatinejad, F.; Eslami, S.; Pourmand, A.; Abu-Hanna, A.; Reihani, H. Internal validation and comparison of the prognostic performance of models based on six emergency scoring systems to predict in-hospital mortality in the emergency department. BMC Emerg. Med. 2021, 21, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.H.; Hsieh, M.S.; Hu, S.Y.; Huang, S.C.; Tsai, C.A.; Hsu, C.Y.; Lin, T.C.; Lee, Y.C.; Liao, S.H. Performance of Scoring Systems in Predicting Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Bacteremia of Listeria monocytogenes: A 9-Year Hospital-Based Study. Biology 2021, 10, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, T.; Terent, A.; Lind, L. Rapid Emergency Medicine Score: A new prognostic tool for in-hospital mortality in non-surgical emergency department patients. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 255, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, N.I.; Wolfe, R.E.; Moore, R.B.; Smith, E.; Burdick, E.; Bates, D.W. Mortality in Emergency Department Sepsis (MEDS) score: A prospectively derived and validated clinical prediction rule. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 31, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| General Data | All (n = 35) | Survival (n = 27) | Expired (n = 8) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male f | 11 (31.4%) | 10 (37.0%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0.387 |
| Age | 69.4 ± 11.4 | 66.7 ± 11.4 | 77.3 ± 6.6 | 0.027 * |
| Vital signs | ||||
| SBP | 135.6 ± 30.5 | 135.9 ± 32.0 | 134.8 ± 27.2 | 0.665 |
| DBP | 83.2 ± 26.2 | 82.6 ± 24.6 | 85.1 ± 32.9 | 0.736 |
| MAP | 100.7 ± 25.6 | 100.4 ± 25.1 | 101.7 ± 29.2 | 0.630 |
| HR | 98.54 ± 20.51 | 96.30 ± 19.61 | 106.13 ± 22.99 | 0.224 |
| RR | 18.8 ± 2.2 | 18.6 ± 2.1 | 19.5 ± 2.8 | 0.240 |
| BT | 37.15 ± 1.06 | 37.32 ± 0.95 | 36.58 ± 1.29 | 0.109 |
| GCS | 14.5 ± 1.6 | 14.4 ± 1.8 | 14.8 ± 0.7 | 1.000 |
| SpO2 | 97.5 ± 3.6 | 97.7 ± 2.3 | 96.6 ± 6.4 | 0.682 |
| Symptoms | ||||
| Fever f | 12 (34.3%) | 11 (40.8%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0.216 |
| Flank pain f | 8 (22.9%) | 8 (29.6%) | 0 (0%) | 0.154 |
| Abdominal pain f | 8 (22.9%) | 7 (25.9%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0.648 |
| Consciousness change f | 4 (11.4%) | 4 (14.8%) | 0 (0%) | 0.553 |
| GI symptoms f | 7 (20.0%) | 3 (11.1%) | 4 (50.0%) | 0.033 * |
| LUTS f | 4 (11.4%) | 1 (3.7%) | 3 (37.5%) | 0.030 * |
| Nonspecific f | 8 (22.9%) | 7 (25.9%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0.648 |
| Comorbidities | ||||
| Cardiovascular disease f | 19 (54.9%) | 17 (63.0%) | 2 (25.0%) | 0.105 |
| DM f | 20 (57.1%) | 17 (63.0%) | 3 (37.5%) | 0.246 |
| Hyperlipidemia f | 14 (20.0%) | 14 (51.9%) | 0 (0%) | 0.012 * |
| Gout f | 3 (8.6%) | 2 (7.4%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0.553 |
| CVA f | 4 (11.4%) | 3 (11.1%) | 1 (12.5%) | 1.000 |
| COPD f | 3 (8.6%) | 3 (11.1%) | 0 (0%) | 1.000 |
| GI disease f | 17 (48.6%) | 11 (40.7%) | 6 (75.0%) | 0.121 |
| Chronic renal failure f | 16 (45.7%) | 12 (44.4%) | 4 (50.0%) | 1.000 |
| Transplant f | 1 (2.9%) | 1 (3.7%) | 0 (0%) | 0.479 |
| GU disease f | 10 (28.6%) | 9 (33.3%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0.390 |
| Immune disorder f | 8 (22.9%) | 7 (25.9%) | 1 (12.5%) | 0.648 |
| Tumor f | 10 (28.6%) | 5 (18.5%) | 5 (62.5%) | 0.027 * |
| Laboratory Data | All (n = 35) | Survival (n = 27) | Expired (n = 8) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood cell counts | ||||
| WBC (×103 counts/mm3) | 17.10 ± 10.42 | 18.26 ± 10.30 | 13.15 ± 10.47 | 0.283 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.43 ± 2.23 | 10.56 ± 2.35 | 9.98 ± 1.86 | 0.368 |
| Platelet (×103 counts/mm3) | 253.06 ± 163.66 | 265.19 ± 148.23 | 212.13 ± 214.49 | 0.204 |
| Band (%) | 3.0 ± 11.6 | 0.8 ± 1.9 | 10.4 ± 23.6 | 0.101 |
| Neutrophil (Segment) (%) | 107.22 ± 41.30 | 103.89 ± 40.87 | 122.23 ± 43.62 | 0.130 |
| Biochemistry | ||||
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.85 ± 0.70 | 2.88 ± 0.72 | 2.73 ± 0.62 | 0.568 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.01 ± 1.72 | 1.07 ± 1.97 | 0.82 ± 0.50 | 0.657 |
| ALT (U/L) | 29.2 ± 30.4 | 28.8 ± 30.3 | 30.6 ± 32.6 | 0.885 |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 36.7 ± 27.6 | 29.0 ± 19.4 | 62.4 ± 36.4 | 0.005 ** |
| Cr (mg/dL) | 1.81 ± 1.24 | 1.54 ± 1.01 | 2.70 ± 1.61 | 0.034 * |
| CRP (mg/dL) | 17.80 ± 12.12 | 17.65 ± 12.28 | 18.35 ± 12.41 | 0.967 |
| Lactate (mg/dL) | 26.26 ± 30.78 | 18.53 ± 20.53 | 48.49 ± 44.43 | 0.081 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 208.9 ± 121.41 | 214.0 ± 130.7 | 191.5 ± 87.9 | 0.839 |
| PT (s) | 11.61 ± 2.20 | 11.76 ± 2.39 | 11.16 ± 1.57 | 0.634 |
| APTT (s) | 32.11 ± 8.06 | 31.83 ± 6.80 | 32.90 ± 11.50 | 0.947 |
| Arterial blood gas | ||||
| pH | 7.40 ± 0.07 | 7.41 ± 0.06 | 7.34 ± 0.09 | 0.094 |
| PaCO2 (mmHg) | 36.58 ± 8.11 | 37.36 ± 8.33 | 33.81 ± 7.13 | 0.276 |
| PaO2 (mmHg) | 69.77 ± 41.22 | 70.00 ± 39.57 | 68.96 ± 50.17 | 0.503 |
| HCO3− (mmol) | 21.92 ± 4.87 | 22.95 ± 4.46 | 18.21 ± 4.72 | 0.033 * |
| Scoring Systems | All (n = 35) | Survival (n = 27) | Expired (n = 8) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEDS | 6.8 ± 5.5 | 5.4 ± 4.7 | 11.8 ± 5.3 | 0.005 ** |
| MEWS | 2.7 ± 1.8 | 2.7 ± 1.8 | 2.8 ± 1.7 | 0.900 |
| NEWS | 3.4 ± 2.8 | 2.9 ± 2.5 | 4.9 ± 3.5 | 0.146 |
| RAPS | 1.9 ± 2.0 | 1.7 ± 1.9 | 2.3 ± 2.3 | 0.585 |
| REMS | 6.5 ± 2.4 | 6.0 ± 2.0 | 8.1 ± 2.9 | 0.116 |
| qSOFA | 0.3 ± 0.6 | 0.3 ± 0.65 | 0.3 ± 0.7 | 0.550 |
| Characteristics | Hazard Ratios | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 1.134 | 1.005–1.278 | 0.041 * |
| Male | 0.020 | 0.000–10.997 | 0.224 |
| Clinical conditions | |||
| Shock | 3.841 | 0.708–20.857 | 0.119 |
| Respiratory failure | 0.440 | 0.051–3.769 | 0.454 |
| ICU admission | 0.029 | 0.000–48.310 | 0.349 |
| Vital signs | |||
| SBP (mmHg) | 1.008 | 0.983–1.034 | 0.538 |
| MAP (mmHg) | 1.008 | 0.981–1.036 | 0.565 |
| HR (bpm) | 1.025 | 0.979–1.073 | 0.296 |
| RR (bpm) | 1.190 | 0.899–1.575 | 0.225 |
| BT (°C) | 0.378 | 0.138–1.040 | 0.060 |
| GCS | 1.075 | 0.550–2.103 | 0.832 |
| SpO2 (%) | 0.932 | 0.805–1.080 | 0.349 |
| Comorbidities | |||
| Cardiovascular disease | 0.348 | 0.067–1.797 | 0.208 |
| DM | 0.308 | 0.060–1.589 | 0.159 |
| CKD | 1.667 | 0.372–7.483 | 0.504 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.019 | 0.000–5.989 | 0.177 |
| Immune disorder | 0.027 | 0.000–31.769 | 0.317 |
| Tumor | 3.083 | 0.678–14.023 | 0.145 |
| Laboratory data | |||
| White blood cell (counts/µL) | 1.000 | 1.000–1.000 | 0.894 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 1.111 | 0.782–1.578 | 0.557 |
| Platelet (×103 counts/µL) | 1.000 | 1.000–1.000 | 0.510 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 4.761 | 0.640–35.430 | 0.128 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 0.782 | 0.278–2.198 | 0.641 |
| ALT (U/L) | 1.003 | 0.981–1.026 | 0.772 |
| BUN | 1.036 | 1.013–1.060 | 0.002 ** |
| Cr | 1.877 | 1.120–3.145 | 0.017 * |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dL) | 0.964 | 0.892–1.042 | 0.354 |
| Lactate (mg/dL) | 1.019 | 1.002–1.037 | 0.030 * |
| PT (s) | 0.843 | 0.549–1.295 | 0.435 |
| APTT (s) | 0.990 | 0.897–1.093 | 0.843 |
| pH | 0.000 | 0.000–0.124 | 0.020 * |
| HCO3− (mmol/L) | 0.990 | 0.897–1.046 | 0.843 |
| Scoring systems | |||
| MEDS | 1.101 | 0.940–1.290 | 0.233 |
| MEWS | 1.059 | 0.704–1.594 | 0.783 |
| NEWS | 1.203 | 0.954–1.519 | 0.119 |
| RAPS | 1.262 | 0.885–1.801 | 0.199 |
| REMS | 1.457 | 1.089–1.950 | 0.011 * |
| qSOFA | 0.900 | 0.221–3.660 | 0.883 |
| Symptoms | |||
| Fever | 0.313 | 0.037–2.613 | 0.283 |
| Flank pain | 0.036 | 0.000–312.580 | 0.472 |
| Abdominal pain | 0.711 | 0.082–6.128 | 0.756 |
| Consciousness change | 0.036 | 0.000–205.275 | 0.452 |
| GI symptoms | 6.261 | 1.386–28.286 | 0.017 * |
| LUTS | 5.195 | 1.126–23.969 | 0.035 * |
| Nonspecific | 0.033 | 0.000–63.335 | 0.376 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value |
| REMS | 1.457 | 1.089–1.950 | 0.011 * | 1.374 | 1.040–1.814 | 0.025 * |
| Lactate | 1.019 | 1.002–1.037 | 0.030 * | 1.021 | 1.004–1.039 | 0.015 * |
| pH | <0.0001 | 0.000–0.124 | 0.020 * | <0.0001 | 0.000–0.661 | 0.042 * |
| Scores | AUC | COP | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | Accuracy | SE | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEDS | 0.819 | 12 | 62.5% | 85.2% | 55.6% | 88.5% | 80.0% | 0.087 | 0.007 ** |
| REMS | 0.685 | 10 | 37.5% | 100.0% | 100.0% | 84.4% | 85.7% | 0.117 | 0.016 * |
| Points | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | +5 | +6 |
| Age (years) | <45 | 45–54 | 55–64 | 65–74 | >74 | ||
| Mean arterial pressure | 70–109 | 110–129 50–69 | 130–159 | >159 ≤49 | |||
| Heart rate | 70–109 | 110–139 55–69 | 140–179 40–54 | >179 ≤39 | |||
| Respiratory rate | 12–24 | 25–34 10–11 | 6–9 | 35–49 | >49 ≤5 | ||
| O2 saturation | >89 | 86–89 | 75–85 | <75 | |||
| Glasgow Coma Scale | 14 or 15 | 11–13 | 8–10 | 5–7 | 3 or 4 | ||
| Variables | Points |
|---|---|
| 1. Terminal illness with possible death in 1 month | 6 |
| 2. Hypoxia or tachypnea | 3 |
| 3. Shock from sepsis | 3 |
| 4. Platelet count below 150,000 | 3 |
| 5. Granulocytic bands > 5% of white blood cells | 3 |
| 6. Patient older than 65 years old | 3 |
| 7. Lower respiratory infection | 2 |
| 8. Patient is from a nursing home | 2 |
| 9. Mental status is altered | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-H.; Hsieh, M.-S.; Hu, S.-Y.; Huang, S.-C.; Tsai, C.-A.; Tsai, Y.-C. Scoring Systems to Evaluate the Mortality Risk of Patients with Emphysematous Cystitis: A Retrospective Observational Study. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020318
Chen Y-H, Hsieh M-S, Hu S-Y, Huang S-C, Tsai C-A, Tsai Y-C. Scoring Systems to Evaluate the Mortality Risk of Patients with Emphysematous Cystitis: A Retrospective Observational Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(2):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020318
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yi-Hsuan, Ming-Shun Hsieh, Sung-Yuan Hu, Shih-Che Huang, Che-An Tsai, and Yi-Chun Tsai. 2023. "Scoring Systems to Evaluate the Mortality Risk of Patients with Emphysematous Cystitis: A Retrospective Observational Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 2: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020318
APA StyleChen, Y.-H., Hsieh, M.-S., Hu, S.-Y., Huang, S.-C., Tsai, C.-A., & Tsai, Y.-C. (2023). Scoring Systems to Evaluate the Mortality Risk of Patients with Emphysematous Cystitis: A Retrospective Observational Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(2), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13020318








