Using Machine Learning with Impulse Oscillometry Data to Develop a Predictive Model for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Asthma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
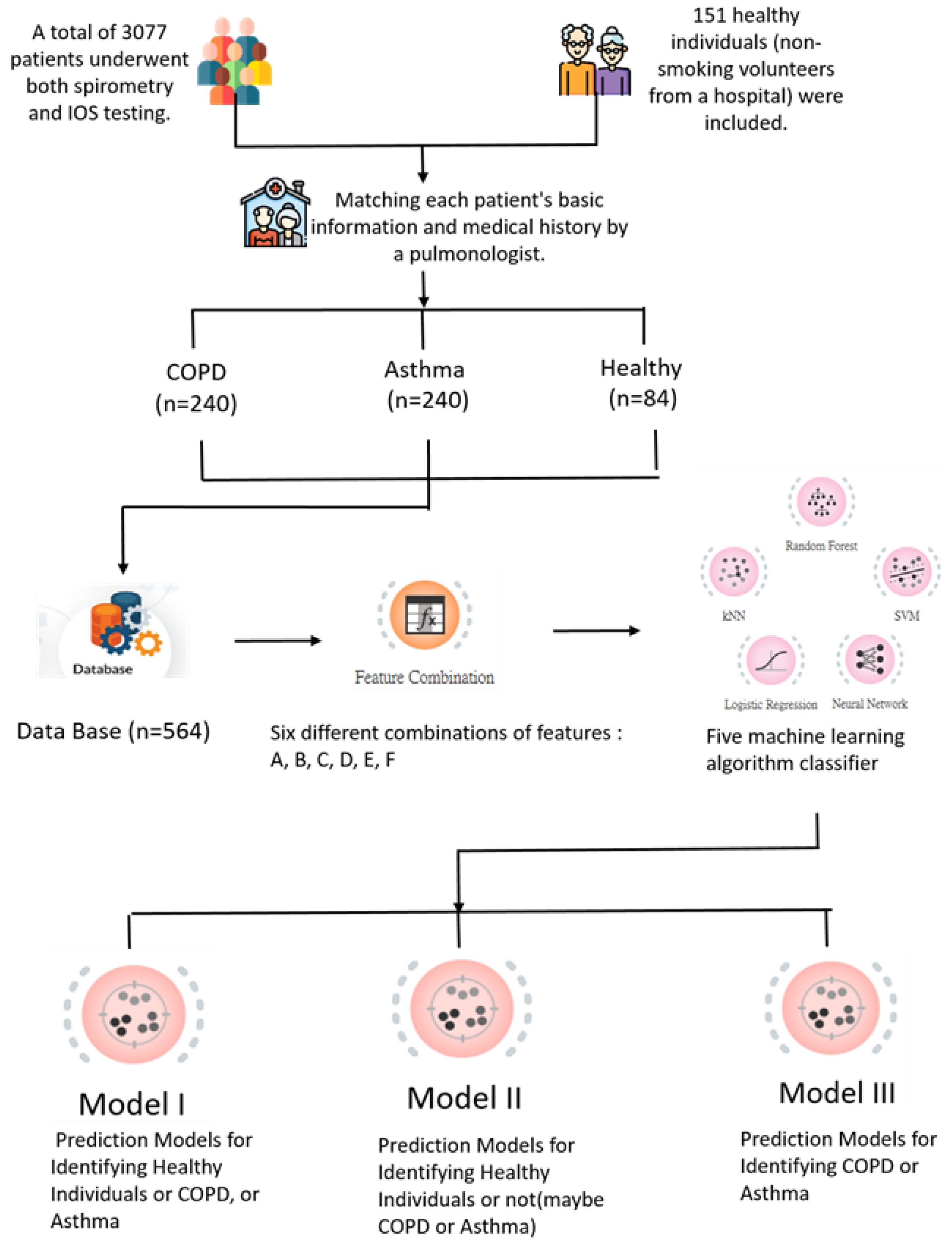
2.1. Participants
- Patients with other respiratory conditions or comorbidities that could significantly affect lung function, such as lung cancer, interstitial lung diseases, or severe respiratory infections.
- Patients with incomplete or missing data from either spirometry or IOS testing.
- Patients who were unable to perform the lung function tests adequately due to cognitive or physical limitations.
- Healthy volunteers with a history of smoking or any known respiratory condition.
2.2. Methods
2.3. Feature Combinations
3. Results
3.1. Model Performance
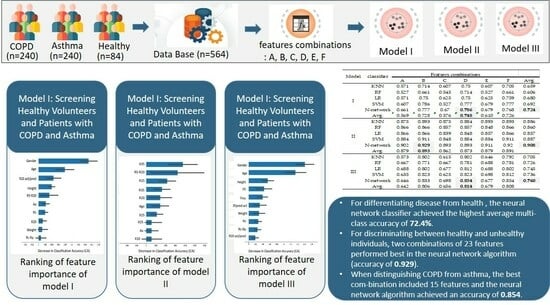
3.1.1. Model I: Screening Healthy Volunteers and Patients with COPD and Asthma
3.1.2. Model II: Detecting Respiratory Abnormalities
3.1.3. Model III: Diagnostic Differentiation between Asthma and COPD
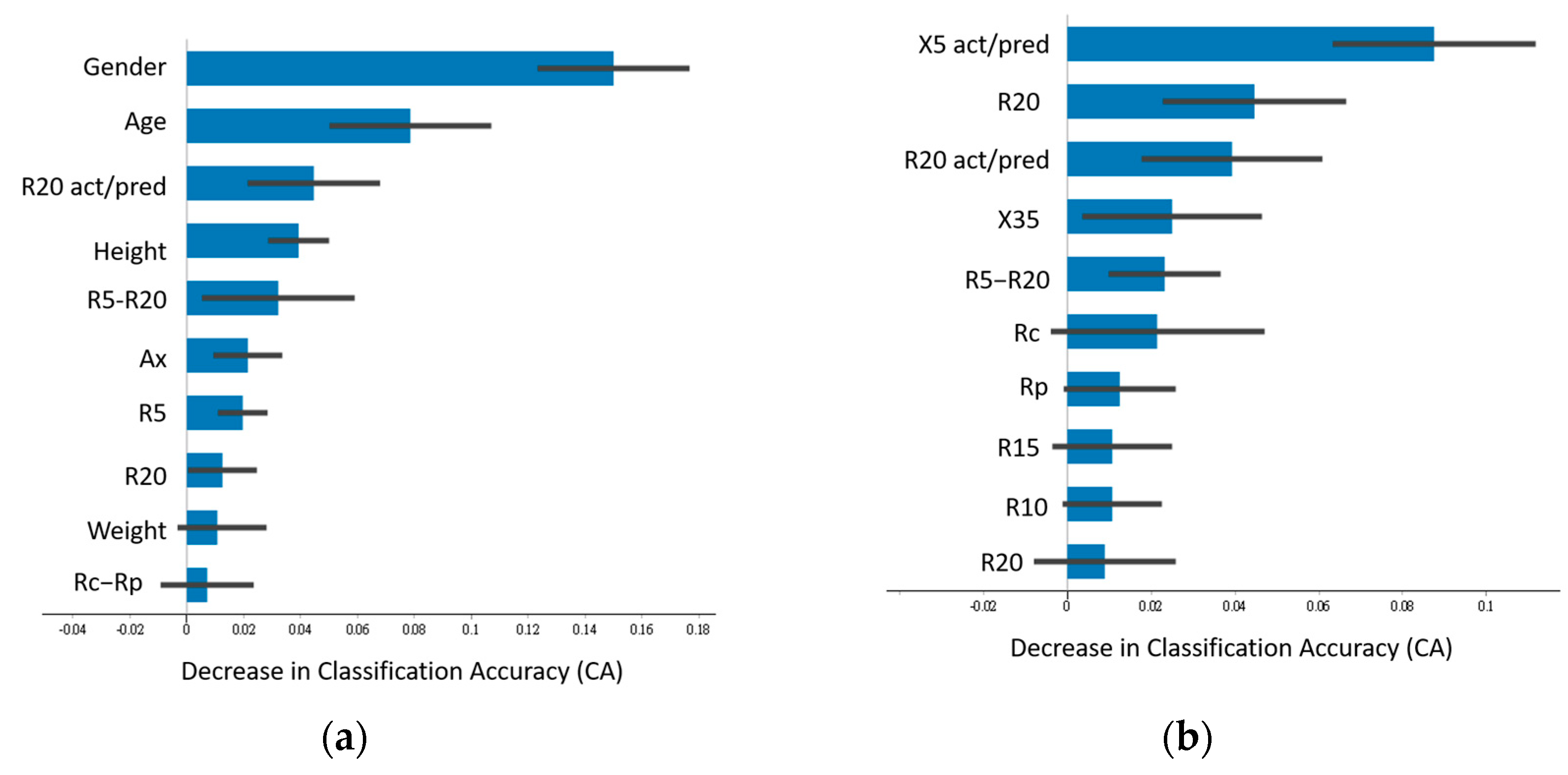
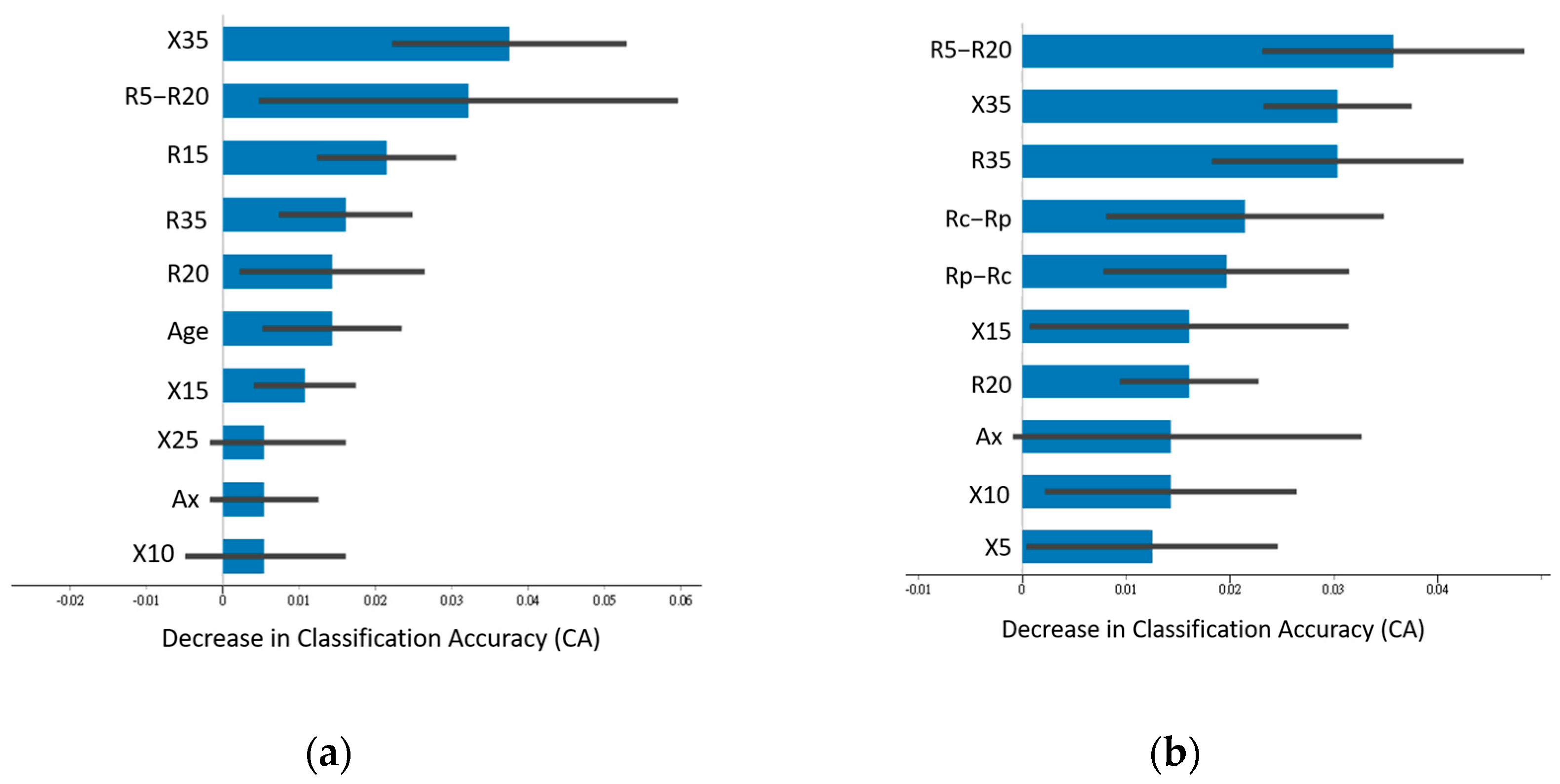
3.2. Feature Importance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, P.; Lin, C.T.; Li, Y.; Tammemagi, M.C.; Brock, M.V.; Garner, M.; Ettinger, D.S.; Atkar-Khattra, S.; Xu, Y.; Bhujwalla, Z.M.; et al. Deep Machine Learning Predicts Cancer Risk in Follow-Up Lung Screening with Low-Dose CT: A Training and Validation Study of a Deep Learning Method. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3384912 (accessed on 7 October 2020).
- Walsh, S.L.F.; Calandriello, L.; Silva, M.; Sverzellati, N. Deep learning for classifying fibrotic lung disease on high-resolution computed tomography: A case-cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, E.J.; Park, S.; Jin, K.-N.; Kim, J.I.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Goo, J.M.; Aum, J.; Yim, J.J.; Cohen, J.G.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning-Based Automated Detection Algorithm for Major Thoracic Diseases on Chest Radiographs. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e191095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, E.J.; Yates, L.C.; Harvey, H. Machine learning “red dot”: Open-source, cloud, deep convolutional neural networks in chest radiograph binary normality classification. Clin. Radiol. 2018, 73, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.T.; Ivanov, A.; Mayrhofer, T.; Hosny, A.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Hoffmann, U. Deep learning to assess long-term mortality from chest radiographs. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e197416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardila, D.; Kiraly, A.P.; Bharadwaj, S.; Choi, B.; Reicher, J.J.; Peng, L.; Tse, D.; Etemadi, M.; Ye, W.; Corrado, G.; et al. End-to-end lung cancer screening with three-dimensional deep learning on low-dose chest computed tomography. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, F.; Barnes, N.; Allen, M.; Angus, R.; Corris, P.; Knox, A.; Miles, J.; Morice, A.; O’Driscoll, B.; Richardson, M. Assessing Asthma Control. In A Guide for Clinicians and Patients; NIH Publication No. 19-5051; Asthma UK: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miravitlles, M.; Kraan, J.; Wedzicha, J.A.; van der Molen, T.; Beier, J.; Soriano, J.B.; Strandberg, E.; Brun, M.; Cegla, U.; Gerken, F. New horizons in the diagnosis and pharmacotherapy of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, J.; Yang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, C. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in China (the China Pulmonary Health [CPH] study): A national cross-sectional study. Lancet 2018, 391, 1706–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miravitlles, M.; Soler-Cataluña, J.J.; Calle, M.; Soriano, J.B. Treatment of COPD by clinical phenotypes: Putting old evidence into clinical practice. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 41, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jans, M.P.; Schellevis, F.G.; van Hensbergen, W.; Dukkers van Emden, T.; van Eijk, J.T. Management of asthma and COPD patients: Feasibility of the application of guidelines in general practice. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 1998, 10, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, V.V.; Allison, D.R.; Andrews, S.; Mejia, J.; Mills, P.K.; Peterson, M.W. Misdiagnosis among frequent exacerbations of clinically diagnosed asthma and COPD in absence of confirmation of airflow obstruction. Lung 2015, 193, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaron, S.D.; Boulet, L.-P.; Reddel, H.K.; Gershon, A. Under-diagnosis and over-diagnosis of asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 1012–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diab, N.; Gershon, A.S.; Sin, D.D.; Tan, W.C.; Bourbeau, J.; Boulet, L.-P.; Aaron, S.D. Underdiagnosis and overdiagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, J.A.; Walters, E.H.; Nelson, M.; Robinson, A.; Scott, J.; Turner, P.; Wood-Baker, R. Factors associated with misdiagnosis of COPD in primary care. Prim. Care Respir. J. 2011, 20, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starren, E.S.; Roberts, N.J.; Tahir, M.; O’Byrne, L.; Haffenden, R.; Patel, I.S.; Partridge, M.R. A centralised respiratory diagnostic service for primary care: A 4-year audit. Prim. Care Respir. J. 2012, 21, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sator, L.; Horner, A.; Studnicka, M.; Lamprecht, B.; Kaiser, B.; McBurnie, M.A.; Buist, A.S.; Gnatiuc, L.; Mannino, D.M.; Janson, C.; et al. Overdiagnosis of COPD in subjects with unobstructed spirometry: A BOLD analysis. Chest 2019, 156, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalovic, M.; Das, N.; Burgel, P.R.; Daenen, M.; Derom, E.; Haenebalcke, C.; Janssen, R.; Kerstjens, H.A.M.; Liistro, G.; Louis, R.; et al. Artificial intelligence outperforms pulmonologists in the interpretation of pulmonary function tests. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A.; Cao, H.; FitzGerald, J.M.; Iannotti, N.; Yang, E.; Kocks, J.W.H.; Kostikas, K.; Price, D.; Reddel, H.K.; Tsiligianni, I.; et al. Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning in Respiratory Medicine and Potential Role in Asthma and COPD Diagnosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Sachdev, A.; Gupta, D.; Gupta, S. Oscillometry—The future of estimating pulmonary functions. Karnataka Paediatr. J. 2020, 35, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, S.; Popler, J.; Lesnick, B.; Eid, N. Impulse oscillometry: Interpretation and practical applications. Chest 2014, 146, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarow, H.D.; Myles, I.A.; Uzzaman, A.; Metcalfe, D.D. Impulse oscillometry in the evaluation of diseases of the airways in children. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011, 106, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, S.; Fujimoto, K.; Komatsu, Y.; Yasuo, M.; Hanaoka, M.; Kubo, K. Evaluation of respiratory impedance in asthma and COPD by an impulse oscillation system. Intern. Med. 2010, 49, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, L.; Liu, X. Clinical application value of impulse oscillometry in geriatric patients with COPD. Int. J. Chronic Obstr. Pulm. Dis. 2017, 12, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.Y.; Yan, T.S.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.Q.; Fu, L.X.; Lan, L.; Liang, B.M.; Wang, M.Y.; Luo, F.M. Impulse oscillometry for detection of small airway dysfunction in subjects with chronic respiratory symptoms and preserved pulmonary function. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD). Global Strategy for the Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: 2023 Report; GOLD: Fontana, WI, USA, 2023; Available online: https://goldcopd.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/GOLD-2023-ver-1.3-17Feb2023_WMV.pdf (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA). Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, 2023 Update; GINA: Fontana, WI, USA, 2023; Available online: https://ginasthma.org/gina-reports/ (accessed on 2 April 2024).
- Demsar, J.; Curk, T.; Erjavec, A.; Gorup, C.; Hocevar, T.; Milutinovic, M.; Mozina, M.; Polajnar, M.; Toplak, M.; Staric, A.; et al. Orange: Data Mining Toolbox in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2013, 14, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar]
- Porojan-Suppini, N.; Fira-Mladinescu, O.; Marc, M.; Tudorache, E.; Oancea, C. Lung Function Assessment by Impulse Oscillometry in Adults. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2020, 16, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirai, T.; Kurosawa, H. Clinical Application of the Forced Oscillation Technique. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, W.; Yan, L.; Fan, S.; Lian, Y.; Zhu, X.; Gao, J.; Zhao, J.; et al. Comparison and development of machine learning tools for the prediction of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in the Chinese population. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Ling, Z.; Ren, Y.; Xiong, D.; Guo, L. Machine learning in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chin. Med. J. 2023, 136, 536–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, J.L.; Lopes, A.J.; Jansen, J.M.; Faria, A.C.; Melo, P.L. Machine learning algorithms and forced oscillation measurements applied to the automatic identification of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2012, 105, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Combination | IOS Data (N = 19) | Selected IOS Data (N = 7) | Physiological Data (N = 4) | Conversion of IOS Data (N = 4) | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | v | 19 | |||
| B | v | v | 23 | ||
| C | v | v | 11 | ||
| D | v | v | v | 15 | |
| E | v | v | 23 | ||
| F | v | v | v | 27 |
| Feature Combination A | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.815 (0.747, 0.883) | 0.661 | 0.661 | 0.661 | 0.661 |
| KNN | 0.778 (0.706, 0.805) | 0.571 | 0.571 | 0.574 | 0.571 |
| RF | 0.751 (0.675, 0.827) | 0.527 | 0.504 | 0.528 | 0.527 |
| LR | 0.771 (0.698, 0.844) | 0.571 | 0.566 | 0.567 | 0.571 |
| SVM | 0.758 (0.683, 0.833) | 0.607 | 0.602 | 0.605 | 0.607 |
| Feature Combination B | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.924 (0.889, 0.959) | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 | 0.777 |
| KNN | 0.828 (0.762, 0.894) | 0.714 | 0.709 | 0.716 | 0.714 |
| RF | 0.861 (0.803, 0.919) | 0.661 | 0.643 | 0.649 | 0.661 |
| LR | 0.912 (0.872, 0.952) | 0.750 | 0.726 | 0.743 | 0.750 |
| SVM | 0.917 (0.880, 0.954) | 0.786 | 0.778 | 0.795 | 0.786 |
| Feature Combination C | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.822 (0.756, 0.888) | 0.670 | 0.670 | 0.673 | 0.670 |
| KNN | 0.736 (0.663, 0.810) | 0.607 | 0.599 | 0.620 | 0.607 |
| RF | 0.735 (0.662, 0.809) | 0.545 | 0.539 | 0.647 | 0.545 |
| LR | 0.783 (0.714, 0.852) | 0.625 | 0.617 | 0.615 | 0.625 |
| SVM | 0.738 (0.665, 0.811) | 0.527 | 0.507 | 0.535 | 0.527 |
| Feature Combination D | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.911 (0.872, 0.950) | 0.786 | 0.783 | 0.792 | 0.786 |
| KNN | 0.863 (0.805, 0.921) | 0.750 | 0.747 | 0.749 | 0.750 |
| RF | 0.867 (0.811, 0.923) | 0.714 | 0.685 | 0.719 | 0.714 |
| LR | 0.901 (0.859, 0.943) | 0.750 | 0.727 | 0.732 | 0.750 |
| SVM | 0.898 (0.855, 0.941) | 0.777 | 0.769 | 0.774 | 0.777 |
| Feature Combination E | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.818 (0.750, 0.886) | 0.679 | 0.678 | 0.683 | 0.679 |
| KNN | 0.761 (0.686, 0.836) | 0.607 | 0.606 | 0.620 | 0.607 |
| RF | 0.760 (0.685, 0.835) | 0.527 | 0.509 | 0.521 | 0.527 |
| LR | 0.791 (0.723, 0.859) | 0.625 | 0.621 | 0.621 | 0.625 |
| SVM | 0.803 (0.733, 0.873) | 0.679 | 0.676 | 0.684 | 0.679 |
| Feature Combination F | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.909 (0.869, 0.949) | 0.768 | 0.766 | 0.765 | 0.768 |
| KNN | 0.842 (0.780, 0.904) | 0.705 | 0.702 | 0.706 | 0.705 |
| RF | 0.858 (0.800, 0.916) | 0.661 | 0.643 | 0.654 | 0.661 |
| LR | 0.914 (0.875, 0.953) | 0.759 | 0.740 | 0.755 | 0.759 |
| SVM | 0.909 (0.869, 0.949) | 0.777 | 0.770 | 0.787 | 0.777 |
| Feature Combination A | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.953 (0.934, 0.972) | 0.902 | 0.595 | 0.894 | 0.902 |
| KNN | 0.865 (0.809, 0.921) | 0.875 | 0.872 | 0.869 | 0.875 |
| RF | 0.867 (0.811, 0.923) | 0.866 | 0.838 | 0.845 | 0.866 |
| LR | 0.871 (0.816, 0.926) | 0.866 | 0.829 | 0.852 | 0.866 |
| SVM | 0.931 (0.900, 0.962) | 0.884 | 0.871 | 0.871 | 0.884 |
| Feature Combination B | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.942 (0.912, 0.972) | 0.929 | 0.927 | 0.926 | 0.929 |
| KNN | 0.819 (0.752, 0.886) | 0.893 | 0.883 | 0.883 | 0.893 |
| RF | 0.850 (0.789, 0.911) | 0.866 | 0.829 | 0.852 | 0.866 |
| LR | 0.894 (0.852, 0.936) | 0.866 | 0.829 | 0.852 | 0.866 |
| SVM | 0.928 (0.897, 0.959) | 0.911 | 0.899 | 0.909 | 0.911 |
| Feature Combination C | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.916 (0.879, 0.953) | 0.893 | 0.883 | 0.883 | 0.893 |
| KNN | 0.795 (0.726, 0.864) | 0.875 | 0.868 | 0.865 | 0.875 |
| RF | 0.824 (0.757, 0.891) | 0.857 | 0.831 | 0.830 | 0.857 |
| LR | 0.843 (0.781, 0.905) | 0.839 | 0.789 | 0.774 | 0.839 |
| SVM | 0.869 (0.813, 0.925) | 0.848 | 0.816 | 0.812 | 0.848 |
| Feature Combination D | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.906 (0.866, 0.946) | 0.893 | 0.883 | 0.883 | 0.893 |
| KNN | 0.874 (0.819, 0.930) | 0.884 | 0.882 | 0.881 | 0.884 |
| RF | 0.828 (0.761, 0.895) | 0.857 | 0.812 | 0.833 | 0.857 |
| LR | 0.876 (0.821, 0.931) | 0.848 | 0.794 | 0.801 | 0.848 |
| SVM | 0.880 (0.826, 0.934) | 0.884 | 0.871 | 0.871 | 0.884 |
| Feature Combination E | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.957 (0.938, 0.976) | 0.911 | 0.908 | 0.907 | 0.911 |
| KNN | 0.861 (0.805, 0.917) | 0.893 | 0.887 | 0.885 | 0.893 |
| RF | 0.859 (0.802, 0.916) | 0.848 | 0.816 | 0.812 | 0.848 |
| LR | 0.890 (0.847, 0.933) | 0.857 | 0.812 | 0.833 | 0.857 |
| SVM | 0.928 (0.897, 0.959) | 0.884 | 0.871 | 0.871 | 0.884 |
| Feature Combination F | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.946 (0.917, 0.975) | 0.920 | 0.916 | 0.916 | 0.920 |
| KNN | 0.821 (0.754, 0.888) | 0.893 | 0.887 | 0.885 | 0.893 |
| RF | 0.863 (0.806, 0.920) | 0.866 | 0.829 | 0.852 | 0.866 |
| LR | 0.901 (0.859, 0.943) | 0.866 | 0.829 | 0.852 | 0.866 |
| SVM | 0.931 (0.900, 0.962) | 0.911 | 0.899 | 0.909 | 0.911 |
| Feature Combination A | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.751 (0.674, 0.828) | 0.646 | 0.644 | 0.657 | 0.646 |
| KNN | 0.635 (0.552, 0.718) | 0.573 | 0.569 | 0.586 | 0.573 |
| RF | 0.755 (0.679, 0.831) | 0.667 | 0.665 | 0.678 | 0.667 |
| LR | 0.762 (0.686, 0.838) | 0.688 | 0.686 | 0.700 | 0.688 |
| SVM | 0.619 (0.535, 0.703) | 0.635 | 0.636 | 0.637 | 0.635 |
| Feature Combination B | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.902 (0.863, 0.941) | 0.833 | 0.833 | 0.844 | 0.833 |
| KNN | 0.851 (0.790, 0.912) | 0.802 | 0.801 | 0.821 | 0.802 |
| RF | 0.883 (0.830, 0.936) | 0.771 | 0.767 | 0.808 | 0.771 |
| LR | 0.902 (0.863, 0.941) | 0.802 | 0.800 | 0.829 | 0.802 |
| SVM | 0.897 (0.854, 0.940) | 0.823 | 0.822 | 0.843 | 0.823 |
| Feature Combination C | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.763 (0.688, 0.838) | 0.698 | 0.693 | 0.725 | 0.698 |
| KNN | 0.685 (0.606, 0.764) | 0.615 | 0.611 | 0.630 | 0.615 |
| RF | 0.723 (0.645, 0.801) | 0.667 | 0.667 | 0.668 | 0.667 |
| LR | 0.750 (0.674, 0.826) | 0.677 | 0.670 | 0.709 | 0.677 |
| SVM | 0.672 (0.591, 0.753) | 0.625 | 0.624 | 0.624 | 0.625 |
| Feature Combination D | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.899 (0.858, 0.940) | 0.854 | 0.854 | 0.861 | 0.854 |
| KNN | 0.865 (0.809, 0.921) | 0.802 | 0.802 | 0.807 | 0.802 |
| RF | 0.869 (0.813, 0.925) | 0.781 | 0.779 | 0.807 | 0.781 |
| LR | 0.900 (0.860, 0.940) | 0.812 | 0.811 | 0.836 | 0.812 |
| SVM | 0.901 (0.861, 0.941) | 0.823 | 0.822 | 0.837 | 0.823 |
| Feature Combination E | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.753 (0.677, 0.829) | 0.677 | 0.672 | 0.702 | 0.677 |
| KNN | 0.695 (0.616, 0.774) | 0.646 | 0.640 | 0.671 | 0.646 |
| RF | 0.762 (0.686, 0.838) | 0.688 | 0.685 | 0.705 | 0.688 |
| LR | 0.778 (0.704, 0.852) | 0.688 | 0.680 | 0.725 | 0.688 |
| SVM | 0.703 (0.623, 0.783) | 0.698 | 0.693 | 0.725 | 0.698 |
| Feature Combination F | |||||
| Classifier | AUC (95%C.I) | CA | F1 | Precision | Recall |
| MLP | 0.890 (0.846, 0.934) | 0.854 | 0.854 | 0.866 | 0.854 |
| KNN | 0.866 (0.810, 0.922) | 0.792 | 0.791 | 0.807 | 0.792 |
| RF | 0.881 (0.828, 0.934) | 0.781 | 0.778 | 0.815 | 0.781 |
| LR | 0.902 (0.863, 0.941) | 0.802 | 0.800 | 0.829 | 0.802 |
| SVM | 0.899 (0.858, 0.940) | 0.812 | 0.812 | 0.829 | 0.812 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-H.; Chou, K.-T.; Perng, D.-W.; Hsiao, Y.-H.; Huang, C.-W. Using Machine Learning with Impulse Oscillometry Data to Develop a Predictive Model for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Asthma. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040398
Huang C-H, Chou K-T, Perng D-W, Hsiao Y-H, Huang C-W. Using Machine Learning with Impulse Oscillometry Data to Develop a Predictive Model for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Asthma. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(4):398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040398
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chien-Hua, Kun-Ta Chou, Diahn-Warng Perng, Yi-Han Hsiao, and Chien-Wen Huang. 2024. "Using Machine Learning with Impulse Oscillometry Data to Develop a Predictive Model for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Asthma" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 4: 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040398
APA StyleHuang, C.-H., Chou, K.-T., Perng, D.-W., Hsiao, Y.-H., & Huang, C.-W. (2024). Using Machine Learning with Impulse Oscillometry Data to Develop a Predictive Model for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Asthma. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(4), 398. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040398