Comparison of Nasal Dimensions According to the Facial and Nasal Indices Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Method
2.2.1. CBCT Data
2.2.2. Mimics 3D Modeling
- (1)
- Cranial 3D modeling
- (2)
- Nasal cavity 3D modeling
- (3)
- Soft tissue 3D modeling
2.2.3. Measurement Parameters
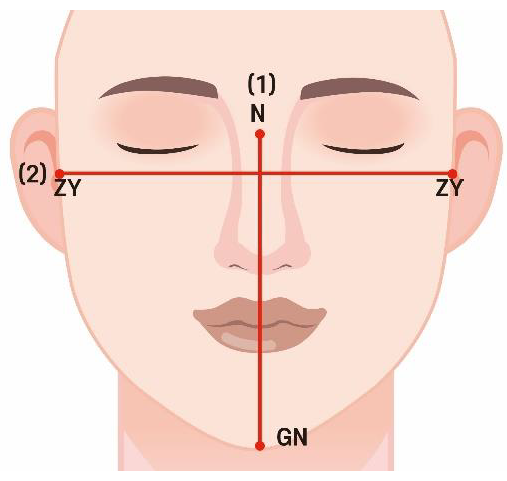
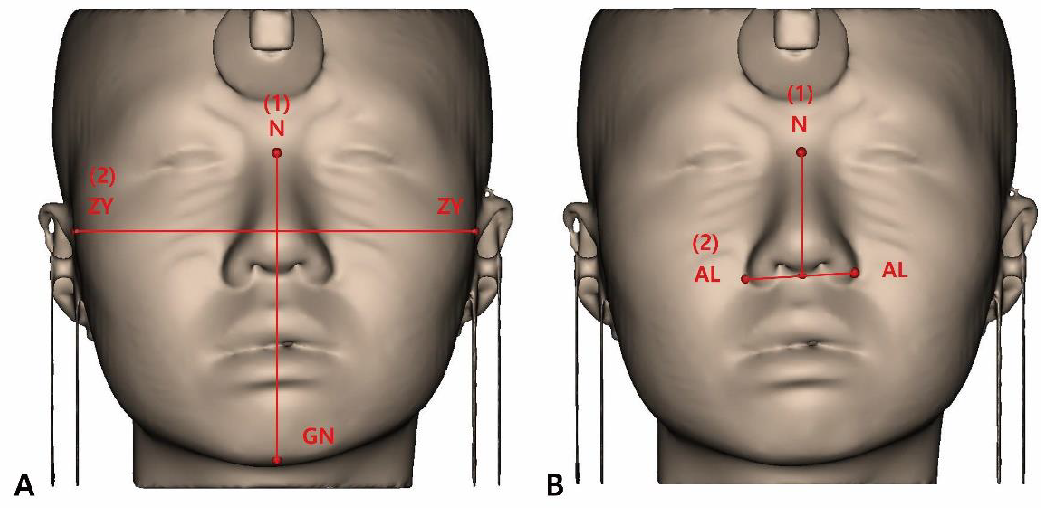
- (1)
- Facial index (FI)
- (2)
- NI
- (3)
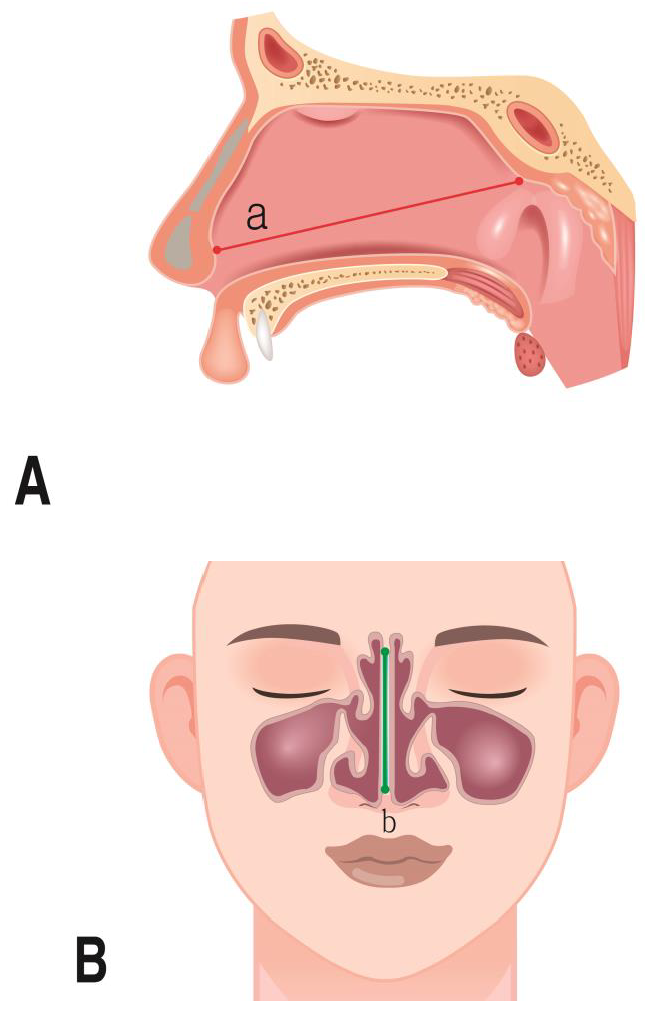
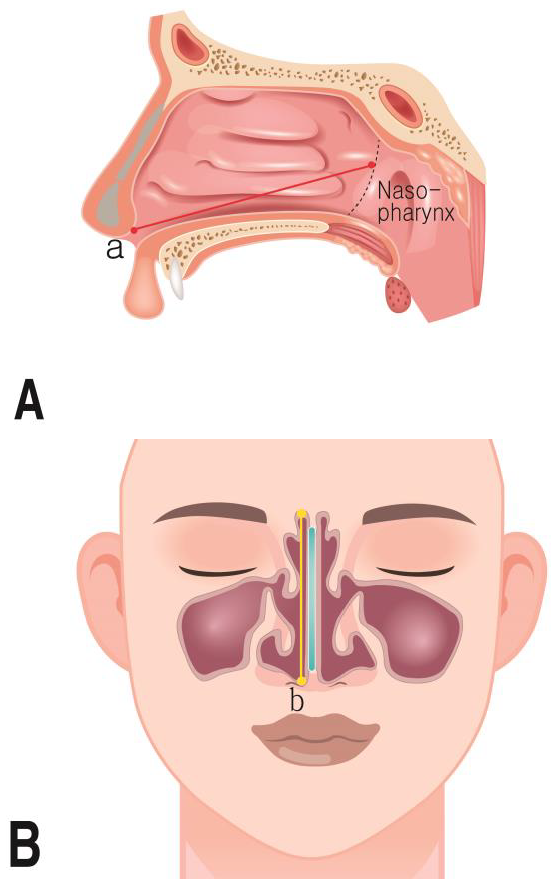
- Measurement parameters
2.2.4. Three-Dimensional Model Measurement in Mimics Software
2.2.5. Statistics
3. Results
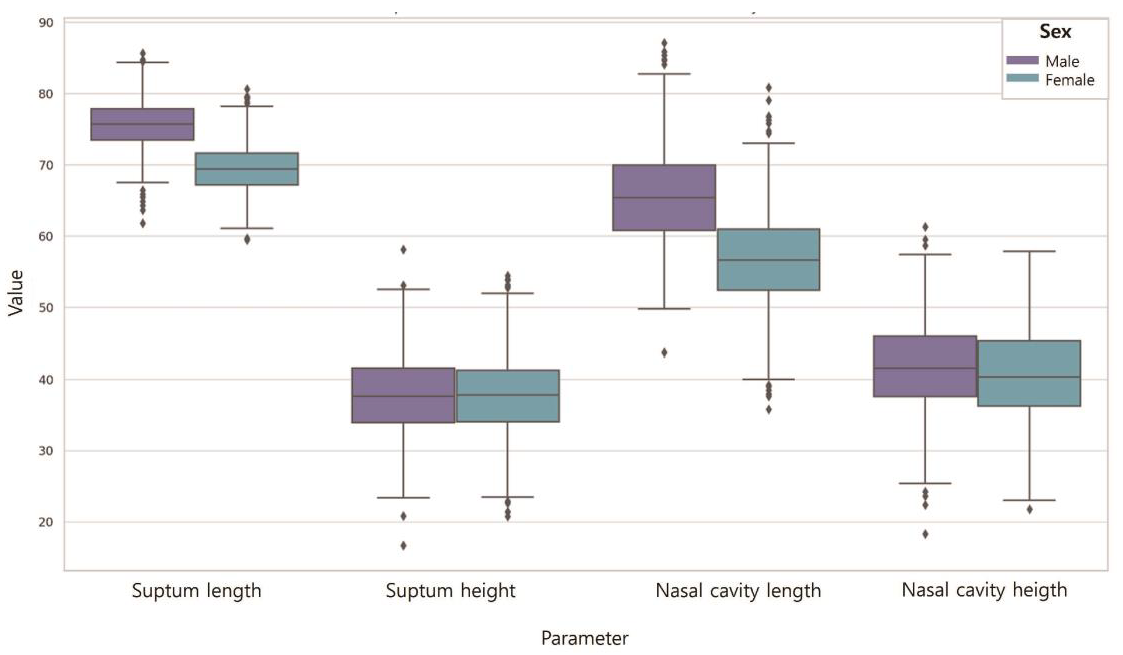
3.1. Nasal Dimensions According to Sex
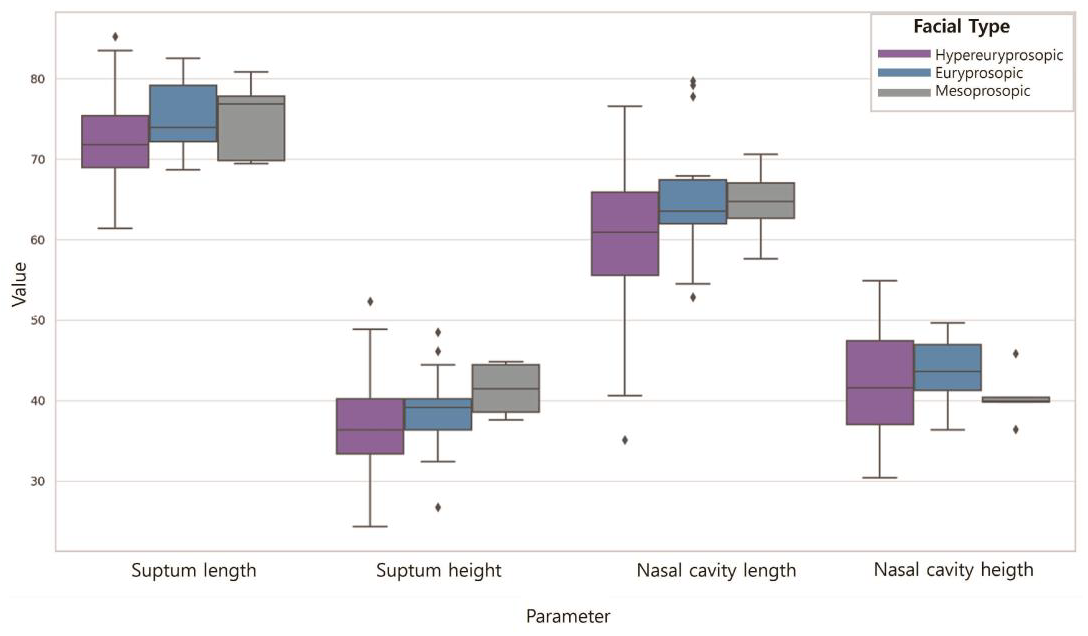
3.2. Nasal Dimensions According to the FI
3.3. Nasal Dimensions According to the NI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, L.; Dong, J.; Shang, Y.; Tu, J. Detailed comparison of anatomy and airflow dynamics in human and cynomolgus monkey nasal cavity. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 141, 105150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, S.; Heo, G.E.; Jeon, Y.J.; Sung, H.J.; Kim, S.K. Tomographic PIV measurements of flow patterns in a nasal cavity with geometry acquisition. Exp. Fluids 2014, 55, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Mi, C. The application of frontal sinus index and frontal sinus area in sex estimation based on lateral cephalograms among Han nationality adults in Xinjiang. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2018, 56, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, C.M. Facial reconstruction—Anatomical art or artistic anatomy? J. Anat. 2010, 216, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, J.H.; Cottrell, G. Two fixations suffice in face recognition. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 19, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyomarc’h, P.; Stephan, C.N. The validity of ear prediction guidelines used in facial approximation. J. Forensic Sci. 2012, 57, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyomarc’h, P.; Dutailly, B.; Charton, J.; Santos, F.; Desbarats, P.; Coqueugniot, H. Anthropological facial approximation in three dimensions (AFA 3D): Computer-assisted estimation of the facial morphology using geometric morphometrics. J. Forensic Sci. 2014, 59, 1502–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, C.N. Facial approximation: An evaluation of mouth-width determination. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2003, 121, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, T.L. Determining the sex of human remains through cranial morphology. J. Forensic Sci. 2005, 50, JFS2003385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.A.; Rogers, T.L. Evaluating the accuracy and precision of cranial morphological traits for sex determination. J. Forensic Sci. 2006, 51, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishan, K.; Chatterjee, P.M.; Kanchan, T.; Kaur, S.; Baryah, N.; Singh, R.K. A review of sex estimation techniques during examination of skeletal remains in forensic anthropology casework. Forensic Sci. Int. 2016, 261, 165-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scendoni, R.; Kelmendi, J.; Arrais Ribeiro, I.L.; Cingolani, M.; De Micco, F.; Cameriere, R. Anthropometric analysis of orbital and nasal parameters for sexual dimorphism: New anatomical evidences in the field of personal identification through a retrospective observational study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0284219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Qiang, Y.; Liu, M.; Fulton, D.; Chen, T. Age and sex related measurement of craniofacial soft tissue thickness and nasal profile in the Chinese population. Forensic Sci. Int. 2011, 212, 272-e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, U.Y.; Kim, H.; Song, J.K.; Kim, D.H.; Ahn, K.J.; Kim, Y.S. Assessment of nasal profiles for forensic facial approximation in a modern Korean population of known age and sex. Leg. Med. 2020, 42, 101646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakrishnan, J.M.; Reddy, J.; Kumar, R.V. Role of forensic odontology and anthropology in the identification of human remains. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2021, 25, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, A.; Chatra, L.; Shenai, P.K.; VeenaK, M.; Prabhu, R.V.; Shetty, P. Dental age estimation by pulp/tooth volume ratio based on cbct tooth images: A forensic study. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 7. Available online: https://www.worldwidejournals.com/paripex/article/dental-age-estimation-by-pulp-tooth-volume-ratio-based-on-cbct-tooth-images-a-forensic-study/ODU5NQ==/?is=1 (accessed on 1 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, S.; Azmi, S.R.; Devi, B.K.; Shwetha, V.; Kumar, T.P. CBCT-the newfangled in forensic radiology. J. Dent. Orofac. Res. 2017, 13, 47–55. [Google Scholar]
- Denny, C.; Bhoraskar, M.; Shaikh, S.A.A.; Bastian, T.S.; Sujir, N.; Natarajan, S. Investigating the link between frontal sinus morphology and craniofacial characteristics with sex: A 3D CBCT study on the South Indian population. F1000Research 2023, 12, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doni, R.P.; Janaki, C.S.; Vijayaraghavan, V.; Raj, U.D. A study on measurement and correlation of cephalic and facial indices in male of South Indian population. Int. J. Med. Res. Health Sci. 2013, 2, 439–446. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, H.; Azam, A.; Tandon, R.; Chandra, P.; Kulshrestha, R.; Gupta, A. Correlation between morphological facial index and canine relationship in adults—An anthropometric study. J. Orofac. Sci. 2017, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalman, R.S.E.; Abaidoo, C.S.; Darko, N.D.; Tetteh, J. Facial types and morphology: A study among Sisaala and Dagaaba adult population in the Upper West Region, Ghana. Sci. Afr. 2019, 3, e00071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.P.; Olson, K.L. Analysis of the African American female nose. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2003, 111, 627–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlum, C.S.; Rosenberg, T.; Dyrvig, A.K.; Groentved, A.M.; Kjaergaard, T.; Godballe, C. Can the Ni classification of vessels predict neoplasia? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alex, F.R.; Steven, B.; Timothy, G.L. Human Body Composition, 4th ed.; Human Kinetics Publishers: Champaign, IL, USA, 1996; pp. 167–172. [Google Scholar]
- Olotu, J.E.; Eroje, A.; Oladipo, G.S.; Ezon-Ebidor, E. Anthropometric study of the facial and nasal length of adult Igbo ethnic group in Nigeria. Int. J. Biol. Anthropol. 2009, 2, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Esomonu, U.G.; Ude, R.A.; Lukpata, P.U.; Nandi, E.M. Anthropometric study of the nasal index of Bekwara ethnic group of Cross River state, Nigeria. Int. Res. J. Appl. Basic. Sci. 2013, 5, 1262–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Peter, F.; Jorgen, T.J. Anatomy in Diagnostic Imaging; Blackwell: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2001; pp. 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Pandeya, A.; Atreya, A. Variations in the facial dimensions and face types among the students of a Medical College. JNMA J. Nepal Med. Assoc. 2018, 56, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanifard, M.; Hassanzadeha, G. Anthropometric study of nasal index in Hausa ethnic population of northwestern Nigeria. J. Contemp. Med. Sci. 2018, 4, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Johnson, M.R.; Matida, E.A.; Kherani, S.; Marsan, J. Creation of a standardized geometry of the human nasal cavity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 106, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russel, S.M.; Frank-Ito, D.O. Gender differences in nasal anatomy and function among Caucasians. Facial Plast. Surg. 2023, 25, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Chiang, Y.F.; Jiang, R.S. Influence of Age and Gender on Nasal Airway Patency as Measured by Active Anterior Rhinomanometry and Acoustic Rhinometry. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoliński, B.K.; Grzanka, A.; Gotlib, T. Changes in nasal cavity dimensions in children and adults by gender and age. Laryngoscope 2007, 117, 1429–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoMauro, A.; Aliverti, A. Sex differences in respiratory function. Breathe 2018, 14, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butaric, L.N.; McCarthy, R.C.; Broadfield, D.C. A preliminary 3D computed tomography study of the human maxillary sinus and nasal cavity. Am. J. Biol. Anthropol. 2010, 143, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomkinson, A.; Eccles, R. External facial dimensions and minimum nasal cross-sectional area. Clin. Otolaryngol. 1995, 20, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, S.C.; Eccles, R. A systematic review of the nasal index and the significance of the shape and size of the nose in rhinology. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2009, 34, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddux, S.D.; Butaric, L.N.; Yokley, T.R.; Franciscus, R.G. Ecogeographic variation across morphofunctional units of the humannose. Am. J. Biol. Anthropol. 2017, 162, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Facial Index | Range of FI | N |
|---|---|---|
| Hypereuryprosopic (very broad face) | 80% | 75 |
| Euryprosopic (broad face) | 80~85% | 20 |
| Mesoprosopic (round face) | 85~90% | 5 |
| Nasal Index | Range of FI | N |
|---|---|---|
| Leptorrhine (long and narrow) | 55~69.9% | 10 |
| Mesorrhine (moderate shape) | 70~84.9% | 76 |
| Platyrrhine (broad and short) | 85~99.9% | 14 |
| Parameter | Definition |
|---|---|
| Septum length | Width of the nasal septum in sagittal view |
| Septum height | Height of nasal septum in coronal view |
| Nasal cavity width | Width of nasal cavities in coronal view |
| Nasal cavity height | Height of nasal cavities in coronal view |
| Nasal cavity length | Width of nasal cavities in sagittal view |
| Parameter | N | Mean (SD) | F | T | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Septum length | Male | 50 | 75.72 (3.53) | 0.085 | 9.278 | 0.000 * |
| Female | 50 | 69.47 (3.20) | ||||
| Septum height | Male | 50 | 37.82 (5.48) | 0.000 | 0.264 | 0.793 |
| Female | 50 | 37.53 (5.46) | ||||
| Nasal cavity length | Male | 50 | 65.57 (6.46) | 0.001 | 6.864 | 0.000 * |
| Female | 50 | 56.64 (6.56) | ||||
| Nasal cavity height | Male | 50 | 41.82 (6.15) | 0.275 | 1.031 | 0.305 |
| Female | 50 | 40.51 (6.53) | ||||
| Parameter | N | Mean (SD) | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Septum length | Hypereuryprosopic | 75 | 71.71 (4.47) | 7.092 | 0.001 * |
| Euryprosopic | 20 | 75.82 (3.83) | |||
| Mesoprosopic | 5 | 72.95 (4.14) | |||
| Septum height | Hypereuryprosopic | 75 | 37.17 (5.36) | 1.285 | 0.281 |
| Euryprosopic | 20 | 39.10 (5.70) | |||
| Mesoprosopic | 5 | 39.49 (5.51) | |||
| Nasal cavity length | Hypereuryprosopic | 75 | 59.74 (7.53) | 5.297 | 0.007 * |
| Euryprosopic | 20 | 65.89 (7.75) | |||
| Mesoprosopic | 5 | 62.39 (7.25) | |||
| Nasal Cavity height | Hypereuryprosopic | 75 | 41.05 (6.55) | 0.688 | 0.505 |
| Euryprosopic | 20 | 40.79 (5.03) | |||
| Mesoprosopic | 5 | 44.39 (8.21) | |||
| Parameter | N | Mean (SD) | F | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Septum length | Leptorrhine | 10 | 72.28 (4.16) | 1.792 | 0.172 |
| Mesorrhine | 76 | 73.02 (3.77) | |||
| Platyrrhine | 14 | 70.53 (3.77) | |||
| Septum height | Leptorrhine | 10 | 39.93 (3.95) | 0.964 | 0.385 |
| Mesorrhine | 76 | 37.46 (5.69) | |||
| Platyrrhine | 14 | 37.22 (4.93) | |||
| Nasal cavity length | Leptorrhine | 10 | 61.53 (7.77) | 0.284 | 0.753 |
| Mesorrhine | 76 | 61.32 (8.41) | |||
| Platyrrhine | 14 | 59.63 (4.56) | |||
| Nasal cavity height | Leptorrhine | 10 | 39.71 (5.56) | 1.861 | 0.161 |
| Mesorrhine | 76 | 41.83 (6.57) | |||
| Platyrrhine | 14 | 38.60 (4.96) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.-S.; Park, J.-T. Comparison of Nasal Dimensions According to the Facial and Nasal Indices Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040415
Lee J-H, Kim H-S, Park J-T. Comparison of Nasal Dimensions According to the Facial and Nasal Indices Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(4):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040415
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jeong-Hyun, Hey-Suk Kim, and Jong-Tae Park. 2024. "Comparison of Nasal Dimensions According to the Facial and Nasal Indices Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 4: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040415
APA StyleLee, J.-H., Kim, H.-S., & Park, J.-T. (2024). Comparison of Nasal Dimensions According to the Facial and Nasal Indices Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(4), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040415





