Is Neonatal Viremia a Possible Predictor of the Timing of Maternal Infection in Asymptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection? A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Timing of Maternal Infection and Gestational Age Determination
2.3. Diagnosis of Neonatal Infection
2.4. Real-Time PCR Assay on Plasma
2.5. Standard Immunoglobulins Administration and Neonatal PVLs
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Plasma Viral Load in Relation to the Trimester of Maternal Infection
3.2. Plasma Viral Load in Relation to Gestational Age at Birth
3.3. Neonatal PVLs in Relation to Maternal Immunoglobulin Administration During Pregnancy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| acCMV | Asymptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus |
| cCMV | Congenital cytomegalovirus |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| GA | Gestational age |
| IQR | Interquartile Range |
| IUGR | Intrauterine Growth Restriction |
| LoD | Limit of Detection |
| LoQ | Limit of Quantification |
| NPP | Negative Predictive Value |
| PPV | Positive Predictive Value |
| PVLs | Plasma Viral Loads |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| sIVIG | Standard Intravenous Immunoglobulins |
| SNHL | Sensorineural hearing loss |
| TMI | Timing of maternal infection |
References
- Leruez-Ville, M.; Foulon, I.; Pass, R.; Ville, Y. Cytomegalovirus infection during pregnancy: State of the science. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 330–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smiljkovic, M.; Le Meur, J.-B.; Malette, B.; Boucoiran, I.; Minsart, A.-F.; Lamarre, V.; Tapiero, B.; Renaud, C.; Kakkar, F. Blood Viral Load in the Diagnostic Workup of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2020, 122, 104231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppana, S.B.; Fowler, K.B.; Pass, R.F.; Rivera, L.B.; Bradford, R.D.; Lakeman, F.D.; Britt, W.J. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection: Association between Virus Burden in Infancy and Hearing Loss. J. Pediatr. 2005, 146, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanari, M.; Lazzarotto, T.; Venturi, V.; Papa, I.; Gabrielli, L.; Guerra, B.; Landini, M.P.; Faldella, G. Neonatal Cytomegalovirus Blood Load and Risk of Sequelae in Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Congenitally Infected Newborns. Pediatrics 2006, 117, e76–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, G.; Abate, D.; Mengoli, C.; Palù, G.; Gussetti, N. High Cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNAemia Predicts CMV Sequelae in Asymptomatic Congenitally Infected Newborns Born to Women With Primary Infection During Pregnancy. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.A.; Novak, Z.; Fowler, K.B.; Arora, N.; Britt, W.J.; Boppana, S.B. Cytomegalovirus Blood Viral Load and Hearing Loss in Young Children with Congenital Infection. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2009, 28, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, R.D.; Cloud, G.; Lakeman, A.D.; Boppana, S.; Kimberlin, D.W.; Jacobs, R.; Demmler, G.; Sanchez, P.; Britt, W.; Soong, S.; et al. Detection of Cytomegalovirus (CMV) DNA by Polymerase Chain Reaction Is Associated with Hearing Loss in Newborns with Symptomatic Congenital CMV Infection Involving the Central Nervous System. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 191, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure-Bardon, V.; Magny, J.-F.; Parodi, M.; Couderc, S.; Garcia, P.; Maillotte, A.-M.; Benard, M.; Pinquier, D.; Astruc, D.; Patural, H.; et al. Sequelae of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Following Maternal Primary Infections Are Limited to Those Acquired in the First Trimester of Pregnancy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 69, 1526–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulon, I.; De Brucker, Y.; Buyl, R.; Lichtert, E.; Verbruggen, K.; Piérard, D.; Camfferman, F.A.; Gucciardo, L.; Gordts, F. Hearing Loss With Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Pediatrics 2019, 144, e20183095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzakis, C.; Ville, Y.; Makrydimas, G.; Dinas, K.; Zavlanos, A.; Sotiriadis, A. Timing of primary maternal cytomegalovirus infection and rates of vertical transmission and fetal consequences. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 223, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leruez-Ville, M.; Chatzakis, C.; Lilleri, D.; Blazquez-Gamero, D.; Alarcon, A.; Bourgon, N.; Foulon, I.; Fourgeaud, J.; Gonce, A.; Jones, C.E.; et al. Consensus recommendation for prenatal, neonatal and postnatal management of congenital cytomegalovirus infection from the European congenital infection initiative (ECCI). Lancet Reg Health Eur 2024, 40, 100892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, J.K.E.; Chakraborty, P.; Reuvers, E.; Gallagher, L.; Kernohan, K.D.; Lacaria, M.; Barton, M.; Leifso, K.; Pernica, J.M.; Santander, E.; et al. Outcomes of a Population-Based Congenital Cytomegalovirus Screening Program. JAMA Pediatr. 2025, 179, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revello, M.G.; Lazzarotto, T.; Guerra, B.; Spinillo, A.; Ferrazzi, E.; Kustermann, A.; Guaschino, S.; Vergani, P.; Todros, T.; Frusca, T.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Hyperimmune Globulin to Prevent Congenital Cytomegalovirus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawlinson, W.D.; Boppana, S.B.; Fowler, K.B.; Kimberlin, D.W.; Lazzarotto, T.; Alain, S.; Daly, K.; Doutré, S.; Gibson, L.; Giles, M.L.; et al. Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection in Pregnancy and the Neonate: Consensus Recommendations for Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e177–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, S.E.; Wieringa, J.W.; Blázquez-Gamero, D.; Henneke, P.; Schuster, K.; Butler, K.; Capretti, M.G.; Cilleruelo, M.J.; Curtis, N.; Garofoli, F.; et al. Congenital Cytomegalovirus: A European Expert Consensus Statement on Diagnosis and Management. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natale, F.; De Curtis, M.; Bizzarri, B.; Orlando, M.P.; Ralli, M.; Liuzzi, G.; Caravale, B.; Franco, F.; Gaeta, A.; Giancotti, A.; et al. Isolated Auditory Neuropathy at Birth in Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2020, 46, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polilli, E.; Parruti, G.; D’Arcangelo, F.; Tracanna, E.; Clerico, L.; Savini, V.; D’Antonio, F.; Rosati, M.; Manzoli, L.; D’Antonio, D.; et al. Preliminary evaluation of the safety and efficacy of standard intravenous immunoglobulins in pregnant women with primary cytomegalovirus infection. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1991–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsico, C.; Aban, I.; Kuo, H.; James, S.H.; Sanchez, P.J.; Ahmed, A.; Arav-Boger, R.; Michaels, M.G.; Ashouri, N.; Englund, J.A.; et al. Blood Viral Load in Symptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preiksaitis, J.K.; Hayden, R.T.; Tong, Y.; Pang, X.L.; Fryer, J.F.; Heath, A.B.; Cook, L.; Petrich, A.K.; Yu, B.; Caliendo, A.M. Are We There Yet? Impact of the First International Standard for Cytomegalovirus DNA on the Harmonization of Results Reported on Plasma Samples. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alari, K.; Goyal, M. Retrospective studies—Utility and caveats. J. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 2020, 50, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourgeaud, J.; Magny, J.-F.; Couderc, S.; Garcia, P.; Maillotte, A.-M.; Benard, M.; Pinquier, D.; Minodier, P.; Astruc, D.; Patural, H.; et al. Clinical Value of Serial Quantitative Analysis of Cytomegalovirus DNA in Blood and Saliva Over the First 24 Months of Life in Congenital Infection: The French Cymepedia Cohort. J. Pediatr. 2023, 253, 197–204.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzarotto, T.; Chiereghin, A.; Piralla, A.; Gibertoni, D.; Piccirilli, G.; Turello, G.; Campanini, G.; Gabrielli, L.; Costa, C.; Comai, G.; et al. Kinetics of cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus DNA in whole blood and plasma of kidney transplant recipients: Implications on management strategies. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, Y.; Morioka, I.; Kakei, Y.; Fujioka, K.; Kakimoto, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Yoshikawa, T.; Moriuchi, H.; Oka, A.; Ito, Y. Correlation of Cytomegalovirus Viral Load between Whole Blood and Plasma of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection under Valganciclovir Treatment. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huygens, A.; Dauby, N.; Vermijlen, D.; Marchant, A. Immunity to Cytomegalovirus in Early Life. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizić, I.; Hiršl, L.; Britt, W.J.; Krmpotić, A.; Jonjić, S. Immune Responses to Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. Microbes Infect. 2018, 20, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGovern, N.; Shin, A.; Low, G.; Low, D.; Duan, K.; Yao, L.J.; Msallam, R.; Low, I.; Shadan, N.B.; Sumatoh, H.R.; et al. Human Fetal Dendritic Cells Promote Prenatal T-Cell Immune Suppression through Arginase-2. Nature 2017, 546, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.F.; Holmes, T.H.; Slifer, T.; Ramachandran, V.; Mackey, S.; Hebson, C.; Arvin, A.M.; Lewis, D.B.; Dekker, C.L. Longitudinal Kinetics of Cytomegalovirus-Specific T-Cell Immunity and Viral Replication in Infants With Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Pediatric Infect. Dis. Soc. 2016, 5, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pass, R.F.; Stagno, S.; Britt, W.J.; Alford, C.A. Specific Cell-Mediated Immunity and the Natural History of Congenital Infection with Cytomegalovirus. J. Infect. Dis. 1983, 148, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbou Ould, M.A.; Luton, D.; Yadini, M.; Pedron, B.; Aujard, Y.; Jacqz-Aigrain, E.; Jacquemard, F.; Sterkers, G. Cellular Immune Response of Fetuses to Cytomegalovirus. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 55, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Liang, X.-N.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Li, T.-J.; Huang, S.; Qin, X.; Li, S. Effects of Storage Time on Cytomegalovirus DNA Stability in Plasma Determined by Quantitative Real-Time PCR. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 207, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Buller, R.S.; Gaudreault-Keener, M.; Sternhell, K.E.; Garlock, K.; Singer, G.G.; Brennan, D.C.; Storch, G.A. Effects of Storage Temperature and Time on Qualitative and Quantitative Detection of Cytomegalovirus in Blood Specimens by Shell Vial Culture and PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 2224–2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatzakis, C.; Sotiriadis, A.; Dinas, K.; Ville, Y. Neonatal and long-term outcomes of infants with congenital cytomegalovirus infection and negative amniocentesis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2023, 61, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leruez-Ville, M.; Magny, J.-F.; Couderc, S.; Pichon, C.; Parodi, M.; Bussières, L.; Guilleminot, T.; Ghout, I.; Ville, Y. Risk Factors for Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection Following Primary and Nonprimary Maternal Infection: A Prospective Neonatal Screening Study Using Polymerase Chain Reaction in Saliva. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussi-Pinhata, M.M.; Yamamoto, A.Y. Natural History of Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection in Highly Seropositive Populations. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, S15–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, C.; Breuer, J. Cytomegalovirus Genetic Diversity and Evolution: Insights into Genotypes and Their Role in Viral Pathogenesis. Pathogens 2025, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
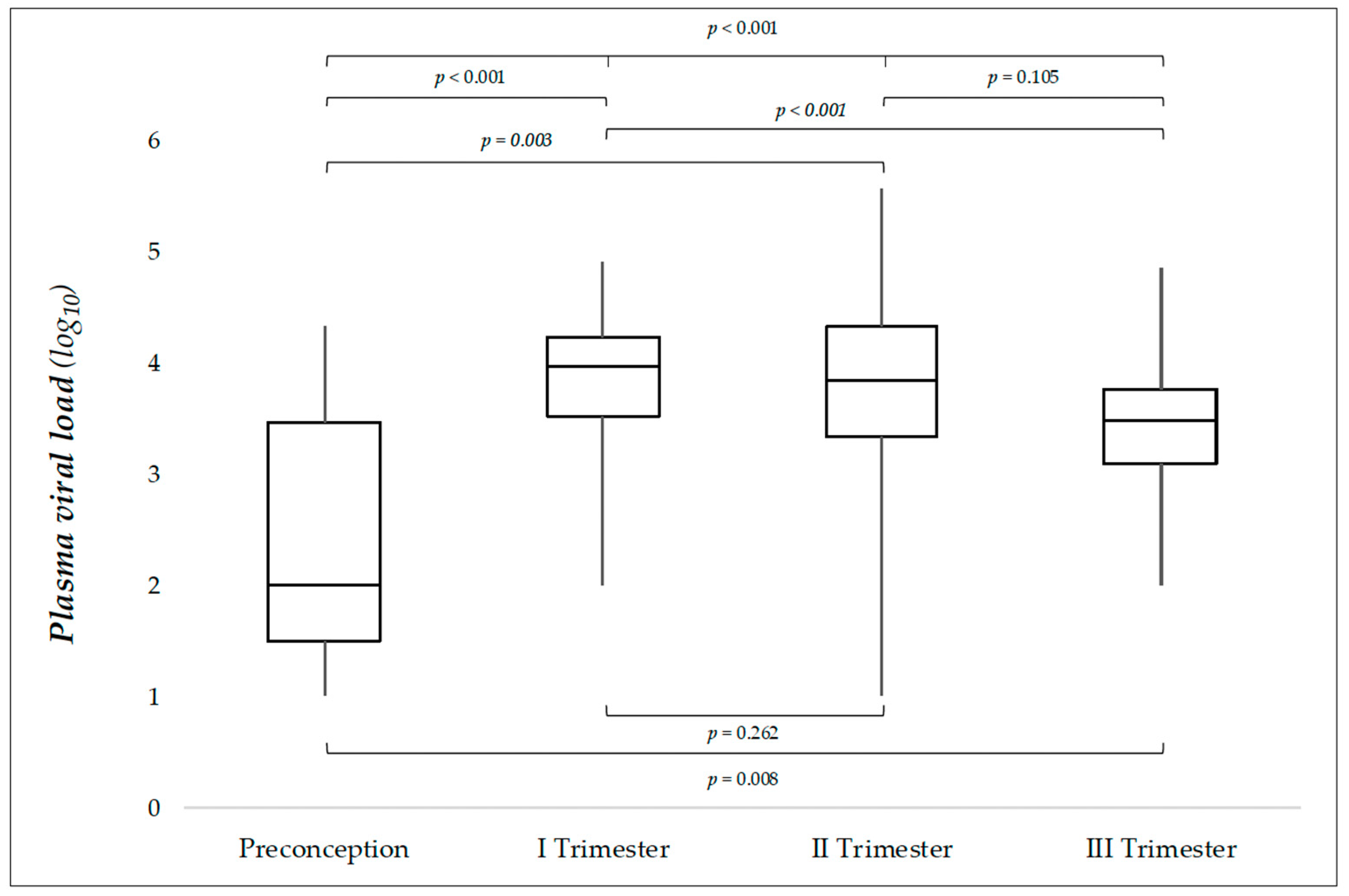

| Characteristic Cases (%) | Preconception 7 (6.4) | I Trimester 30 (27.3) | II Trimester 42 (38.2) | III Trimester 31 (28.2) | Total 110 (100) | p Value a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||||
| Female/Total | 5/7 | 13/37 | 20/42 | 16/31 | 54/110 | 0.259 b |
| (%) | (71.4) | (35.1) | (47.6) | (51.1) | (49.1) | |
| Birth weight (grams) | ||||||
| Median | 3190 | 3140 | 3215 | 3170 | 3200 | |
| IQR | 3020–3140 | 2525–3415 | 2900–3460 | 2980–3500 | 2870–3460 | 0.102 c |
| Min–Max | 2350–4280 | 1890–3980 | 2680–4180 | 2550–4210 | 1890–4280 | |
| Gestational age (weeks) | ||||||
| Median | 39 | 38 | 38 | 39 | 38 | |
| IQR | 39–41 | 38–39 | 37–40 | 37–40 | 37–40 | 0.197 c |
| Min–Max | 37–41 | 33–40 | 35–41 | 37–41 | 33–41 | |
| PVL sampling (days) | ||||||
| Median | 15.0 | 12.5 | 11.5 | 16.0 | 13.0 | |
| IQR | 10.0–22.0 | 6.0–17.0 | 6.0–17.0 | 11.0–21.0 | 8.5–18.5 | 0.394 b |
| Min–Max | 4.0–30.0 | 1.0–30.0 | 1.0–30.0 | 1.0–30.0 | 1.0-30.0 | |
| PVL gEq/mL log10 | ||||||
| Median | 2.00 | 3.97 | 3.83 | 3.47 | 3.67 | <0.001 c * |
| IQR | 1.00–4.15 | 3.51–4.22 | 3.32–4.32 | 3.03–3.77 | 3.27–4.17 | |
| Min–Max | 1.00–4.31 | 2.00–4.89 | 1.00–5.56 | 2.00–4.84 | 1.00–5.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Natale, F.; Boscarino, G.; Liuzzi, G.; Bonci, F.; Albanese, G.M.; Cellitti, R.; Giancotti, A.; Franco, F.; Caravale, B.; Turchetta, R.; et al. Is Neonatal Viremia a Possible Predictor of the Timing of Maternal Infection in Asymptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection? A Retrospective Study. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050165
Natale F, Boscarino G, Liuzzi G, Bonci F, Albanese GM, Cellitti R, Giancotti A, Franco F, Caravale B, Turchetta R, et al. Is Neonatal Viremia a Possible Predictor of the Timing of Maternal Infection in Asymptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection? A Retrospective Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(5):165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050165
Chicago/Turabian StyleNatale, Fabio, Giovanni Boscarino, Giuseppina Liuzzi, Fabrizia Bonci, Giuseppe Maria Albanese, Raffaella Cellitti, Antonella Giancotti, Francesco Franco, Barbara Caravale, Rosaria Turchetta, and et al. 2025. "Is Neonatal Viremia a Possible Predictor of the Timing of Maternal Infection in Asymptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection? A Retrospective Study" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 5: 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050165
APA StyleNatale, F., Boscarino, G., Liuzzi, G., Bonci, F., Albanese, G. M., Cellitti, R., Giancotti, A., Franco, F., Caravale, B., Turchetta, R., Turriziani, O., Conti, M. G., & Terrin, G. (2025). Is Neonatal Viremia a Possible Predictor of the Timing of Maternal Infection in Asymptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection? A Retrospective Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(5), 165. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15050165










