Fundamental Parameters and Evolutionary Scenario of HD 327083
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. RV Variations
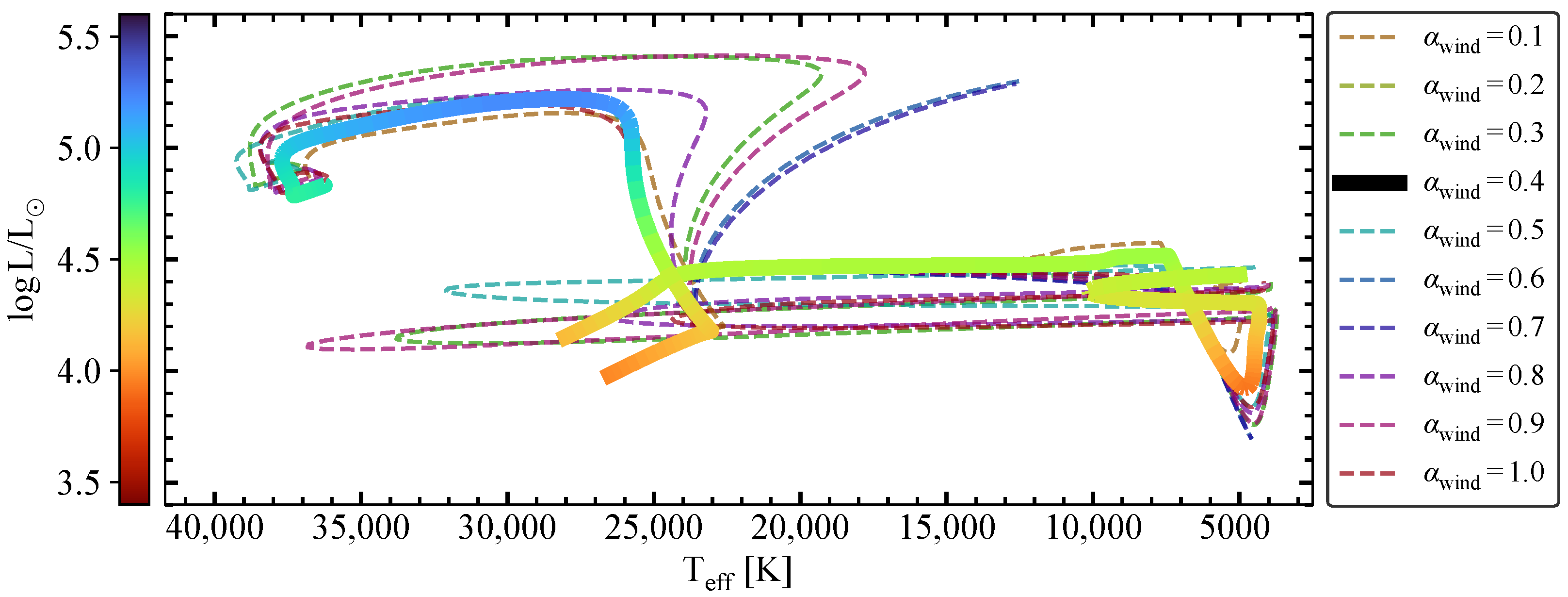
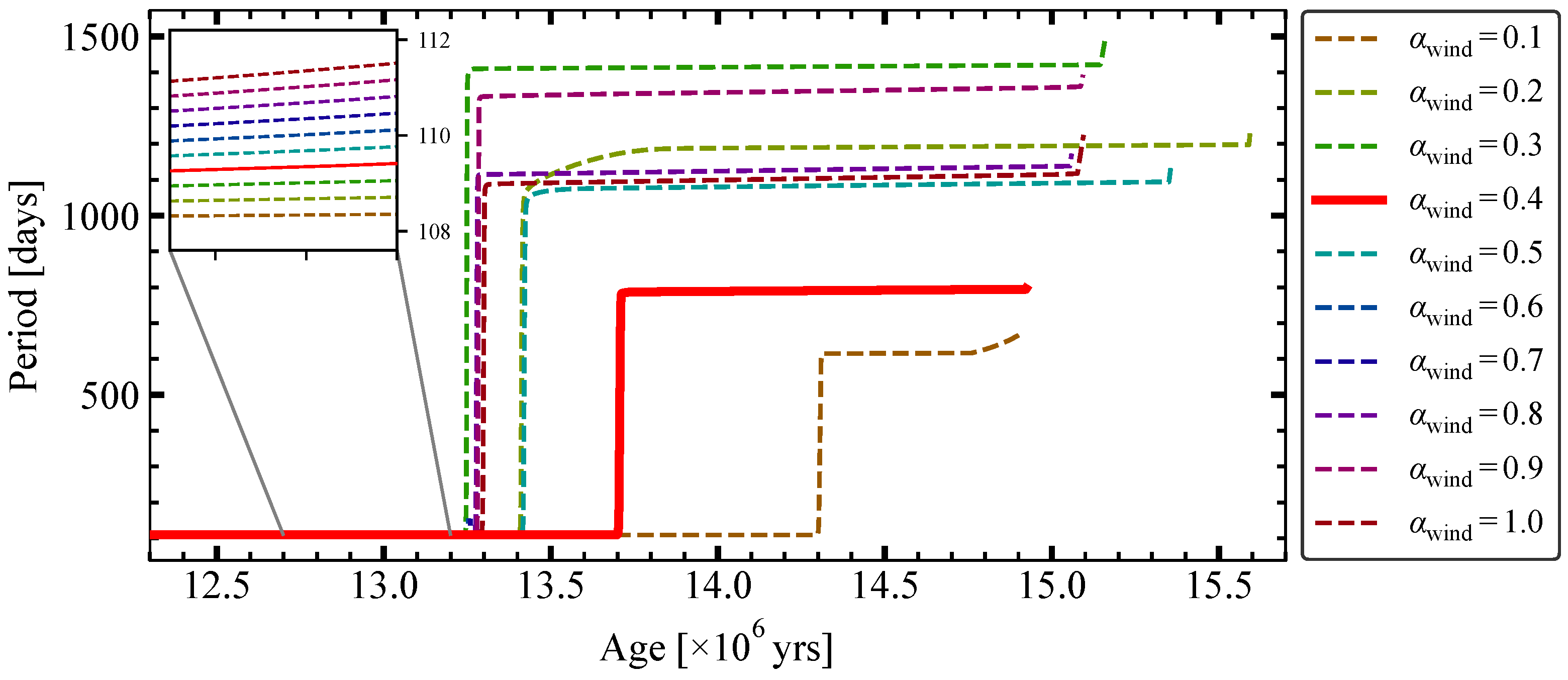
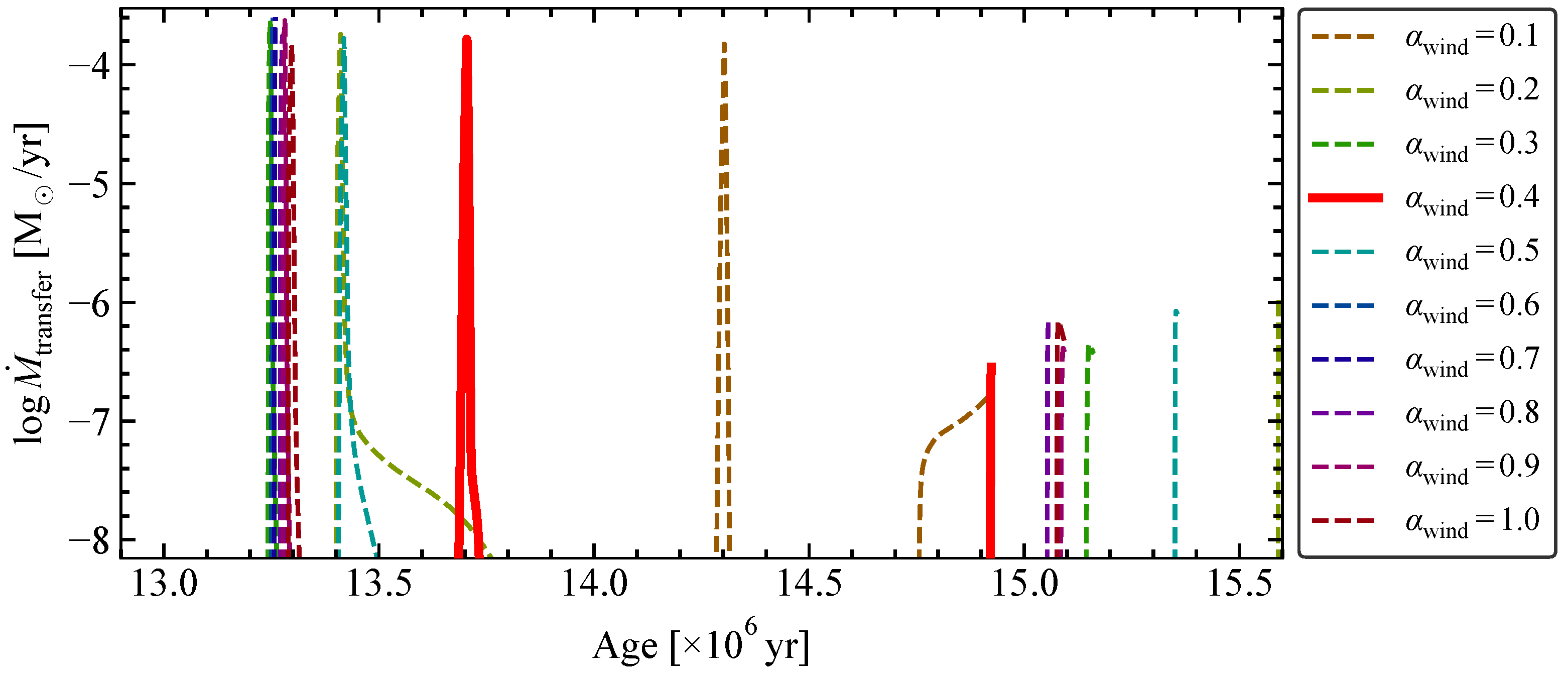
3. System Evolution
4. Conclusions
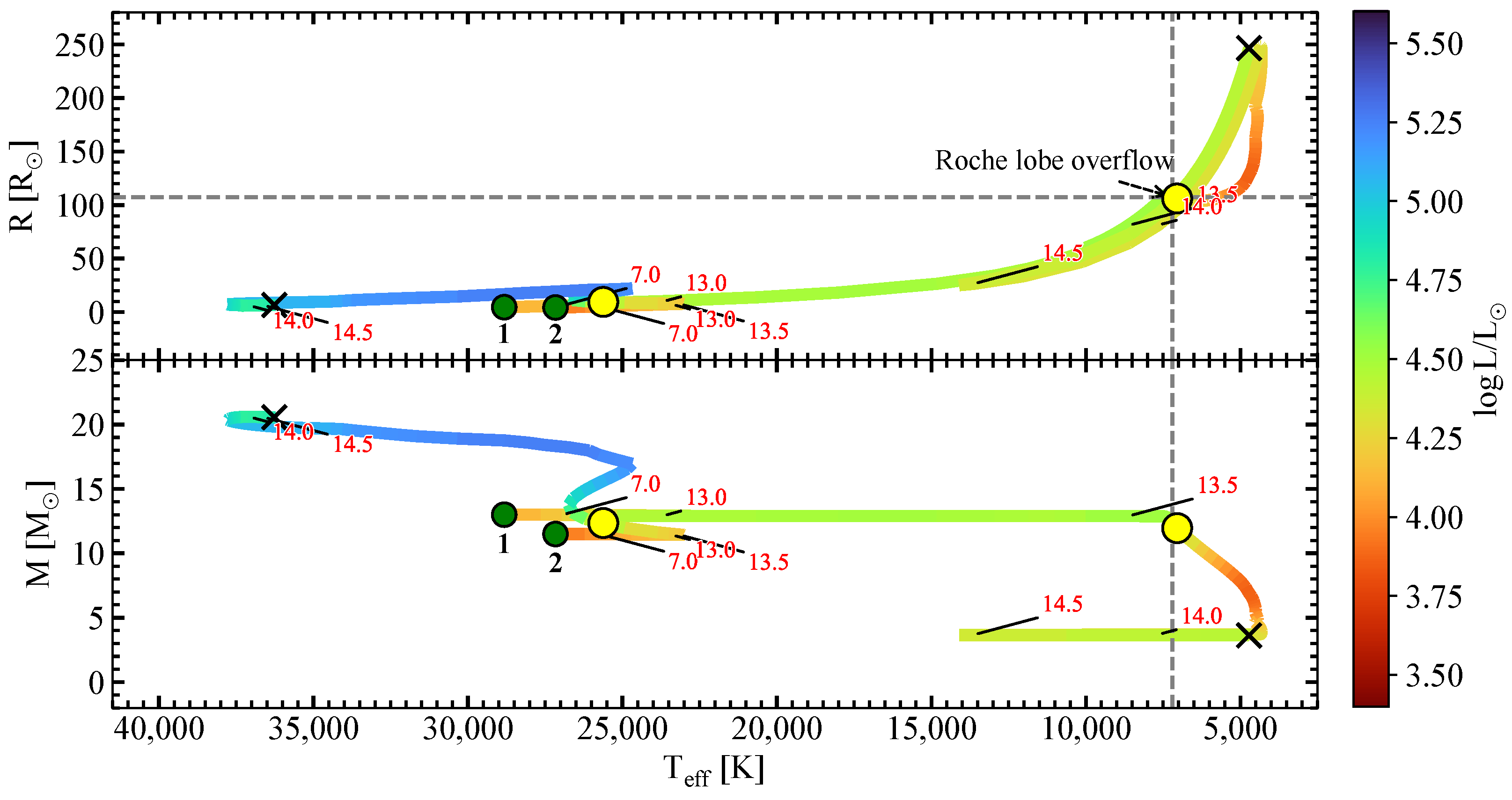
- We ascertained that the system evolved from a binary with an initial orbital period of days, in which the primary component’s mass was 13.00 and the secondary component’s mass was . The initial rotational velocity of both stars were found to be , and .
- Currently, the system’s age is Myr, when the more massive cold component closes to fill or fills its Roche lobe and begins a mass-transfer stage. The mass-transfer event occurred in a very short time of ≲0.1 Myr. After that, the mass of the post-primary drops to ≈5 and that of the post-secondary grows to ≈20 , and the binary evolves into a detached system with a long orbital period of ≈700 days.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 1 | Hereafter, we consider mass transfer from the initially more massive or “primary” component onto the initially less massive or “secondary” component. Hence, we use subscript “1” for the primary and subscript “2” for the secondary component. Equivalently, the primary (secondary) and donor (accretor) references are used. |
| 2 | Research Center “Data Science in Astrophysics” https://astro.kaznu.info/Computingcluster.html (accessed on 21 April 2025). |
| 3 | corresponds to the Vink_scaling_factor and de_Jager_scaling_factor in MESA, which control the strength of stellar winds. See MESA documentation https://docs.mesastar.org (accessed on 21 April 2025). |
References
- Lamers, H.J.G.L.M.; Zickgraf, F.J.; de Winter, D.; Houziaux, L.; Zorec, J. An improved classification of B[e]-type stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1998, 340, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Merrill, P.W.; Burwell, C.G. Second Supplement to the Mount Wilson Catalogue and Bibliography of Stars of Classes B and a whose Spectra have Bright Hydrogen Lines. Astrophys. J. 1949, 110, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henize, K.G. Six Peculiar Hα-Emission Stars. Astrophys. J. 1952, 115, 133–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozok, J.R. Photometric observations of emission B-stars in the southern Milky Way. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1985, 61, 387–405. [Google Scholar]
- Whitelock, P.A.; Feast, M.W.; Roberts, G.; Carter, B.S.; Catchpole, R.M. Circumstellar CO emission at 2.3 μm in BI Cru, He 3-1138 and He 3-1359. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1983, 205, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.F.; Damineli Neto, A.; de Freitas Pacheco, J.A. A spectroscopic study of luminous peculiar B-type stars. Astron. Astrophys. 1992, 261, 482–492. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, M.A.D.; de Araújo, F.X.; Lorenz-Martins, S. The peculiar B-type supergiant HD 327083. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 368, L29–L33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, A.S.; Levato, H.; Bjorkman, K.S.; Grosso, M. Properties of galactic B[e] supergiants II. HDE 327083. Astron. Astrophys. 2003, 406, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, A.S.; Chari, R.; Danford, S.; Prendergast, P.; Aarnio, A.N.; Andronov, I.L.; Chinarova, L.L.; Lytle, A.; Amantayeva, A.; Gabitova, I.A.; et al. Searching for Phase-Locked Variations of the Emission-Line Profiles in Binary Be Stars. Galaxies 2023, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelwright, H.E.; de Wit, W.J.; Oudmaijer, R.D.; Vink, J.S. VLTI/AMBER observations of the binary B[e] supergiant HD 327083. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 538, A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelwright, H.E.; de Wit, W.J.; Weigelt, G.; Oudmaijer, R.D.; Ilee, J.D. AMBER and CRIRES observations of the binary sgB[e] star HD 327083: Evidence of a gaseous disc traced by CO bandhead emission. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 543, A77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, A.S.; Zharikov, S.V.; Manset, N.; Khokhlov, S.A.; Nodyarov, A.S.; Klochkova, V.G.; Danford, S.; Kuratova, A.K.; Mennickent, R.; Chojnowski, S.D.; et al. Recent Progress in Finding Binary Systems with the B[e] Phenomenon. Galaxies 2023, 11, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodyarov, A.S.; Miroshnichenko, A.S.; Khokhlov, S.A.; Zharikov, S.V.; Agishev, A.T.; Gabitova, I.A.; Vaidman, N.L.; Manset, N. Properties of Galactic B[e] Supergiants. X. Refined Orbit and Fundamental Parameters of the HD 327083 Binary System. Astrophys. J. 2024, 968, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailer-Jones, C.A.L.; Rybizki, J.; Fouesneau, M.; Demleitner, M.; Andrae, R. Estimating Distances from Parallaxes. V. Geometric and Photogeometric Distances to 1.47 Billion Stars in Gaia Early Data Release 3. Astron. J. 2021, 161, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, B.; Bildsten, L.; Dotter, A.; Herwig, F.; Lesaffre, P.; Timmes, F. Modules for Experiments in Stellar Astrophysics (MESA). Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2011, 192, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, B.; Cantiello, M.; Arras, P.; Bildsten, L.; Brown, E.F.; Dotter, A.; Mankovich, C.; Montgomery, M.H.; Stello, D.; Timmes, F.X.; et al. Modules for Experiments in Stellar Astrophysics (MESA): Planets, Oscillations, Rotation, and Massive Stars. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2013, 208, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, B.; Marchant, P.; Schwab, J.; Bauer, E.B.; Bildsten, L.; Cantiello, M.; Dessart, L.; Farmer, R.; Hu, H.; Langer, N.; et al. Modules for Experiments in Stellar Astrophysics (MESA): Binaries, Pulsations, and Explosions. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2015, 220, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, B.; Schwab, J.; Bauer, E.B.; Bildsten, L.; Blinnikov, S.; Duffell, P.; Farmer, R.; Goldberg, J.A.; Marchant, P.; Sorokina, E.; et al. Modules for Experiments in Stellar Astrophysics (MESA): Convective Boundaries, Element Diffusion, and Massive Star Explosions. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2018, 234, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxton, B.; Smolec, R.; Schwab, J.; Gautschy, A.; Bildsten, L.; Cantiello, M.; Dotter, A.; Farmer, R.; Goldberg, J.A.; Jermyn, A.S.; et al. Modules for Experiments in Stellar Astrophysics (MESA): Pulsating Variable Stars, Rotation, Convective Boundaries, and Energy Conservation. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2019, 243, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermyn, A.S.; Bauer, E.B.; Schwab, J.; Farmer, R.; Ball, W.H.; Bellinger, E.P.; Dotter, A.; Joyce, M.; Marchant, P.; Mombarg, J.S.G.; et al. Modules for Experiments in Stellar Astrophysics (MESA): Time-dependent Convection, Energy Conservation, Automatic Differentiation, and Infrastructure. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2023, 265, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foreman-Mackey, D.; Hogg, D.W.; Lang, D.; Goodman, J. emcee: The MCMC Hammer. Publ. Astron. Soc. Pac. 2013, 125, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmakhametova, S.T.; Vaidman, N.L.; Miroshnichenko, A.S.; Khokhlov, A.A.; Agishev, A.T.; Yermekbayev, B.S.; Danford, S.; Aarnio, A.N. HR 4049: A Spectroscopic Analysis of a Post-AGB Object. Galaxies 2025, 13, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meynet, G.; Maeder, A. Stellar evolution with rotation. V. Changes in all the outputs of massive star models. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 361, 101–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, J.S.; de Koter, A.; Lamers, H.J.G.L.M. Mass-loss predictions for O and B stars as a function of metallicity. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 369, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jager, C.; Nieuwenhuijzen, H.; van der Hucht, K.A. Mass loss rates in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser. 1988, 72, 259–289. [Google Scholar]
- Björklund, R.; Sundqvist, J.O.; Singh, S.M.; Puls, J.; Najarro, F. New predictions for radiation-driven, steady-state mass-loss and wind-momentum from hot, massive stars. III. Updated mass-loss rates for stellar evolution. Astron. Astrophys. 2023, 676, A109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beasor, E.R.; Davies, B.; Smith, N.; van Loon, J.T.; Gehrz, R.D.; Figer, D.F. A new mass-loss rate prescription for red supergiants. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 492, 5994–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, P.A.; Lennon, D.J.; Walborn, N.R. Physical parameters and wind properties of galactic early B supergiants. Astron. Astrophys. 2006, 446, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N. Mass Loss: Its Effect on the Evolution and Fate of High-Mass Stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 487–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, S.; Podsiadlowski, P. Wind Roche-Lobe Overflow: A New Mass-Transfer Mode for Wide Binaries. In Proceedings of the 15th European Workshop on White Dwarfs, Leicester, UK, 7–11 August 2006; Napiwotzki, R., Burleigh, M.R., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2007; Volume 372, p. 397. [Google Scholar]
- Abate, C.; Pols, O.R.; Izzard, R.G.; Mohamed, S.S.; de Mink, S.E. Wind Roche-lobe overflow: Application to carbon-enhanced metal-poor stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 552, A26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm-Vitense, E. Über die Wasserstoffkonvektionszone in Sternen verschiedener Effektivtemperaturen und Leuchtkräfte. Mit 5 Textabbildungen. Z. Astrophys. 1958, 46, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Claret, A.; Torres, G. The Dependence of Convective Core Overshooting on Stellar Mass: A Semi-empirical Determination Using the Diffusive Approach with Two Different Element Mixtures. Astrophys. J. 2017, 849, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, U.; Ritter, H. A comparative study of the evolution of a close binary using a standard and an improved technique for computing mass transfer. Astron. Astrophys. 1990, 236, 385–392. [Google Scholar]
- Zahn, J.P. Tidal friction in close binary systems. Astron. Astrophys. 1977, 57, 383–394. [Google Scholar]
- Tassoul, J.L. On Synchronization in Early-Type Binaries. Astrophys. J. 1987, 322, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, N. Presupernova Evolution of Massive Single and Binary Stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 50, 107–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadlowski, P.; Joss, P.C.; Hsu, J.J.L. Presupernova Evolution in Massive Interacting Binaries. Astrophys. J. 1992, 391, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mink, S.E.; Pols, O.R.; Langer, N.; Izzard, R.G. Massive binaries as the source of abundance anomalies in globular clusters. Astron. Astrophys. 2009, 507, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
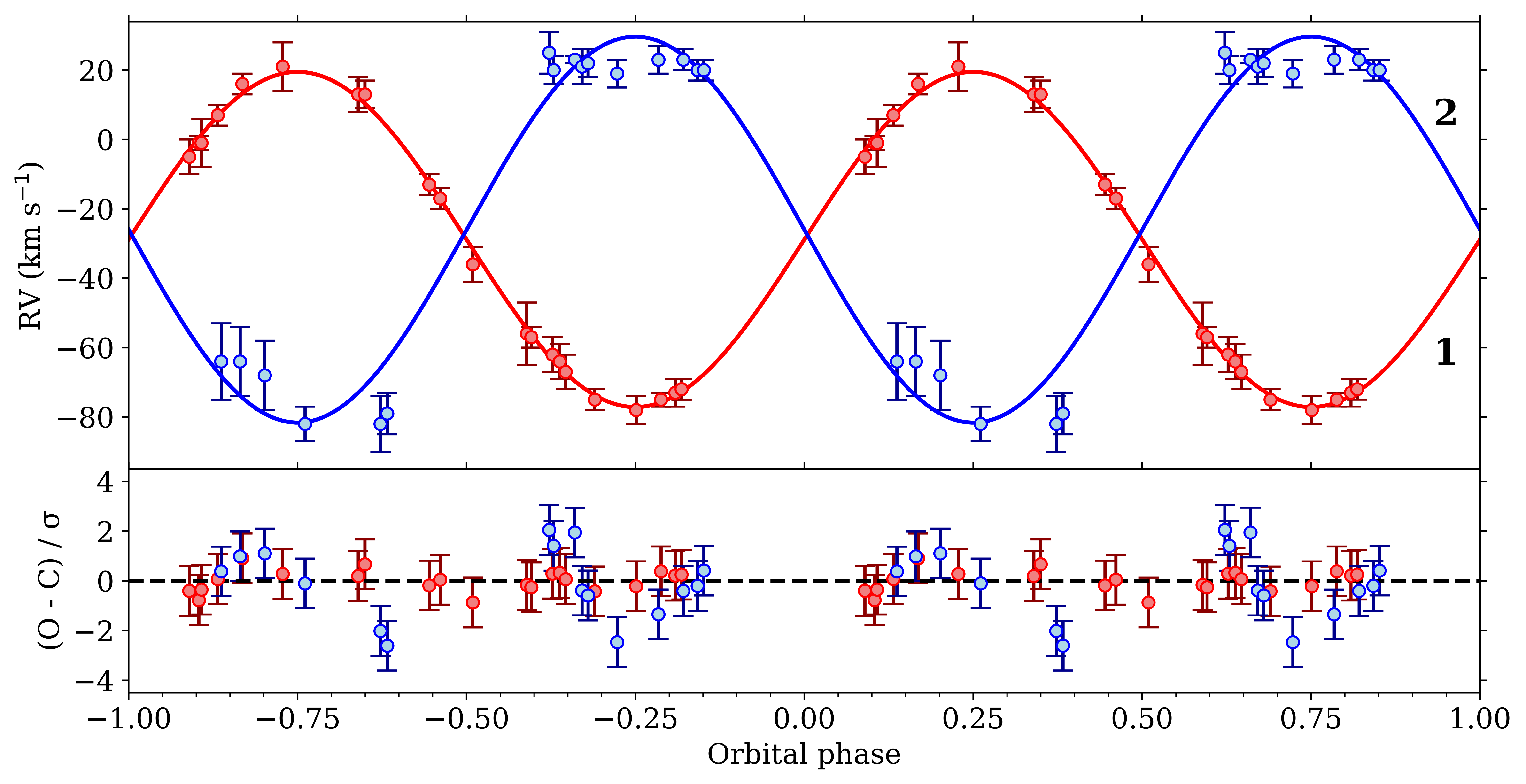
| Parameter | RVabs | RVem (Fe II) |
|---|---|---|
| (days) | ||
| (HJD—2450000) | ||
| e | ||
| (degrees) | ||
| (km ) | ||
| K (km ) | ||
| , | ||
| N | 20 | 16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaidman, N.L.; Miroshnichenko, A.S.; Zharikov, S.V.; Khokhlov, S.A.; Agishev, A.T.; Yermekbayev, B.S. Fundamental Parameters and Evolutionary Scenario of HD 327083. Galaxies 2025, 13, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13030047
Vaidman NL, Miroshnichenko AS, Zharikov SV, Khokhlov SA, Agishev AT, Yermekbayev BS. Fundamental Parameters and Evolutionary Scenario of HD 327083. Galaxies. 2025; 13(3):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13030047
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaidman, Nadezhda L., Anatoly S. Miroshnichenko, Sergey V. Zharikov, Serik A. Khokhlov, Aldiyar T. Agishev, and Berik S. Yermekbayev. 2025. "Fundamental Parameters and Evolutionary Scenario of HD 327083" Galaxies 13, no. 3: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13030047
APA StyleVaidman, N. L., Miroshnichenko, A. S., Zharikov, S. V., Khokhlov, S. A., Agishev, A. T., & Yermekbayev, B. S. (2025). Fundamental Parameters and Evolutionary Scenario of HD 327083. Galaxies, 13(3), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies13030047







