Rough Surface Contact Modelling—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Friction and Load Carrying Capacity of Lubricated Rough-Surface Contact
3. The Statistics of Rough Surfaces
4. Rough-Surface contact Models
4.1. Bowden and Tabor’s Model
4.2. Archard’s Work
4.3. The Greenwood–Williamson and Greenwood–Tripp Models
4.4. Bush, Gibson, Thomas Model
4.5. Models Due to Persson
4.6. Recent Work on Rough-Surface Contact Models
5. The Impact of Lubricant Additives
6. Experimental Data on Rough-Surface Friction
7. Application of Rough-Surface Models to the Prediction of Mixed/Boundary Friction
8. Discussion
9. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dowson, D. History of Tribology; Longman: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Hutchings, I.M. Leonardo da Vinci’s Studies of Friction. Wear 2016, 360–361, 51–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Betancourt-Parra, S. Leonardo da Vinci’s Tribological Intuitions. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, W.G. Leondardo da Vinci on Wear. Biotribology 2021, 26, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amontons, G. De la Resistance Cause’e Dans les Machines (About Resistance and Force in Machines), Mem l’Acedemie R A. 1699, 257–282. Available online: https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40544-015-0074-6.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Coulomb, C.A. Theorie des Machines Simples; Bachelier: Paris, French, 1821. [Google Scholar]
- Popova, E.; Popov, V.L. The Research Works of Coulomb and Amontons and Generalized Laws of Friction. Friction 2015, 3, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persson, B.N.J.; Sivebæk, I.M.; Samoilov, V.N.; Zhao, K.; Volokitin, A.I.; Zhang, Z. On the Origin of Amonton’s Friction Law. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2008, 20, 395006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Luedtke, W.D.; Gourdon, D.; Ruths, M.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Landman, U. Frictional Forces and Amonton’s Law: From the Molecular to the Microscopic Scale. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 3410–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.A. Sliding Friction: From Microscopic Contacts to Amontons’ Law. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Blau, P.J. The Significance and Use of the Friction Coefficient. Tribol. Int. 2001, 34, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbakh, M.; Klafter, J.; Gourdon, D.; Israelachvili, J. The Nonlinear Nature of Friction. Nature 2004, 430, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euler, L. Sur La Friction des Corps Solides. Mem. Acad. Sci. 1750, 4, 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Leslie, L. An Experimental Inquiry into the Nature and Propagation of Heat; Bell & Bradfute: Edinburgh, UK, 1804. [Google Scholar]
- Bowden, F.P.; Tabor, D. The Friction and Lubrication of Solids; Oxford Classics Series; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hertz, H. Ueber die Berűhrung fester elastischer Kőrper. J. Reine Angew. Math. 1881, 92, 156–171. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Williamson, J.B.P. Contact of Nominally Flat Surfaces. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. 1966, 295, 300–319. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse, D.J.; Archard, J.F. The Properties of Random Surfaces of Significance in Their Contact. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. 1970, 316, 97–121. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, A.W.; Gibson, R.D.; Thomas, T.R. The Elastic Contact of a Rough Surface. Wear 1975, 35, 87–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Tripp, J.H. The Elastic Contact of Rough Spheres. J. Appl. Mech. 1967, 34, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Tripp, J.H. The Contact of Two Nominally Flat Rough Surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1970, 185, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J. Elastoplastic Contact between Randomly Rough Surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 116101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Persson, B.N.J. Contact Mechanics for Randomly Rough Surfaces. Surf. Sci. Rep. 2006, 61, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joe, J.; Scaraggi, M.; Barber, J. Effect of fine-scale roughness on the tractions between contacting bodies. Tribol. Int. 2017, 111, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Wu, J.J. Surface Roughness and Contact: An Apology. Meccanica 2001, 36, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, J.R. Multiscale Surfaces and Amontons’ Law of Friction. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 49, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afferrante, L.; Carbone, G.; Demelio, G. Interacting and Coalescing Hertzian Aperities: A New Multiasperity Model. Wear 2012, 278–279, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Contact and Rubbing of Flat Surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1957, 24, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F.; Hirst, W. An Examination of a Mild Wear Process. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. 1957, 238, 515–528. [Google Scholar]
- Archard, J.F. Elastic Deformation and the Laws of Friction. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. 1957, 243, 190–205. [Google Scholar]
- Archard, J.F. Single Contacts and Multiple Encounters. J. Appl. Phys. 1961, 32, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, J.; Hirst, W. The True Contact Area between Solids. Proc. Phys. Soc. B 1954, 67, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoln, B. Elastic Deformation and the Laws of Friction. Nature 1953, 172, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.R. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Blau, P.J. On the Nature of Running-In. Tribol. Int. 2008, 38, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, J.I. Comparison of Models for the Contact of Rough Surfaces. Wear 1986, 107, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Contact Mechanics of Rough Surfaces in Tribology: Multiple Asperity Contacts. Tribol. Lett. 1998, 4, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Wang, Q.J.; Lin, C. A Survey of Current Models for Simulating the Contact between Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 1999, 42, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, G.G.; Nosonovsky, M. Contact Modelling—Forces. Tribol. Int. 2000, 33, 431–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakis, A.; Yastrebov, V.; Scheibert, J.; Nicola, L.; Dini, D.; Minfray, C.; Almqvist, A.; Paggi, M.; Lee, S.; Limbert, G.; et al. Modelling and Simulation in Tribology Across Scales: An Overview. Tribol. Int. 2018, 125, 169–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A. Engineering Tribology; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Stachowiak, G.W.; Batchelor, A.W. Engineering Tribology; Tribology Series, 24; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Halling, J. (Ed.) Principles of Tribology; The MacMillan Press Ltd.: London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Olver, A.V.; Spikes, H.A. Prediction of Traction in Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 1998, 212, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.R. Rough Surfaces, 2nd ed.; Imperial College Press: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehouse, D. Surfaces and Their Measurement; Taylor & Francis, Books, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, P.R. Random Process Model of Rough Surfaces. J. Lubr. Technol. (ASME) 1971, 93, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.R. Some Aspects of Surface Roughness Measurement. Wear 1973, 26, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.R. Random Process Model of Rough Surfaces in Plastic Contact. Wear 1973, 26, 305–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A. A Note on Nayak’s Third Paper. Wear 2007, 262, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A. A Unified Theory of Surface Roughness. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1984, 393, 133–157. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, J.A. Problems with Surface Roughness, 57–76 of Fundamentals of Friction: Macroscopic and Microscopic Processes; Singer, I.L., Pollock, H.M., Eds.; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.S. The Statistical Analysis of a Random Moving Surface. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 1957, 249, 321–387. [Google Scholar]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.S. Statistical Properties of an Isotropic Random Surface. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. 1957, 250, 157–174. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, J.A. Contact of Rough Surfaces: The Greenwood and Williamson/Tripp, Fuller and Tabor Theories, Encyclopedia of Tribology; Wang, Q.J., Chung, Y.-W., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Longuet-Higgins, M.S. The Statistical Distribution of the Curvature of a Random Gaussian Surface. Math. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1958, 54, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayles, R.S.; Thomas, T.R. Measurements of the Statistical Microgeometry of Engineering Surfaces. J. Lubr. Technol. 1979, 101, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayles, R.S.; Thomas, T.R. Surface Topography as a Nonstationary Random Process. Nature 1978, 271, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.R.; Sayles, R.S. Some Problems in the Tribology of Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Int. 1978, 11, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayles, R.S. Basic Principles of Rough Surface Contact Analysis Using Numerical Methods. Tribol. Int. 1996, 29, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peklenik, J. New Developments in Surface Characterization and Measurements by Means of Random Process Analysis. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Conf. Proc. 1967, 182, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gujrati, A.; Khanal, S.R.; Pastewka, L.; Jacobs, T.D.B. Combining TEM, AFM, and Profilometry for Quantitative Topography Characterization across All Scales. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 26169–29178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desaguliers, J.T. A Course of Experimental Philosophy; W. Innys Publisher, 1734; Volume 1, Available online: https://books.google.co.uk/books/about/A_Course_of_Experimental_Philosophy.html?id=P5MPAAAAQAAJ&redir_esc=y (accessed on 10 March 2022).
- Tabor, D. Indentation Hardness: Fifty Years on a Personal View. Philos. Mag. A 1996, 74, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. The Temperature of Rubbing Surfaces. Wear 1958, 2, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication of Real Surfaces. Tribology 1973, 6, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Surface Topography and Tribology. Tribology 1974, 7, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archard, J.F. Friction between Metal Surfaces. Wear 1986, 113, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedynak, R. Exact and Approximate Solutions of the Infinite Integrals of the Asperity Height Distribution for the Greenwood-Williamson and the Greenwood-TriAsperity Contact Models. Tribol. Int. 2019, 130, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. (Eds.) Handbook of Mathematical Functions; Dover Publications, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.L.; Green, I. On the Modeling of Elastic Contact between Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 2011, 54, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venner, C.H.; Couhier, F.A.A.; Lubrecht; Greenwood, J.A. Amplitude Reduction of Waviness in Transient EHL Line Contacts. Tribol. Ser. 1997, 32, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Biboulet, N.; Venner, C.H.; Lubrecht, A.A. Prediction of the Stribeck Curve under Full-Film Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2020, 149, 105569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Jackson, R.L. Statistical Models of Nearly Complete Elastic Rough Surface Contact—Comparison with Numerical Solutions. Tribol. Int. 2017, 105, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J. Relationship between Interfacial Separation and Load: A General Theory of Contact Mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 125502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCool, J.I. Elastic Contact of Coated Rough Surfaces. Proc. Leeds-Lyon Symp. Mech. Coat. 1990, 17, 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, S.J.; Sayles, R.S. A Numerical Model for the Contact of Layered Elastic Bodies with Real Rough Surfaces. ASME J. Tribol. 1992, 114, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasaribu, H.R.; Schipper, D.J. Deterministic Friction Model of a Rough Surface Sliding against a Flat Layered Surface. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddad, Y.; Magnier, V.; Dufrénoy, P.; De Saxcé, G. A New Contact Model for Multilayered Solids with Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finkin, E.F. Applicability of Greenwood-Williamson Theory to Film Covered Surfaces. Wear 1970, 15, 291–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blencoe, K.A.; Williams, J.A. Friction of Sliding Surfaces Carrying Boundary Films. Tribol. Lett. 1997, 3, 121–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A. The Behaviour of Sliding Contacts between Non-Conformal Rough Surfaces Protected by ‘Smart’ Films. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Zhang, H.; Lococo, J. Effects of Boundary Films on the Frictional Behaviour of Rough-Surface Contacts in Incipient Sliding. Proc. Inst. Mech. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2006, 220, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakis, A.I.; Polycarpou, A.A. An Advanced Rough Surface Continuum-Based Contact and Sliding Model in the Presence of Molecularly Thin Lubricant. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 49, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wei, C. Research on the Friction Behaviours of Two Rough Surfaces Covered with Boundary Film. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 53, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, J.I. Non-Gaussian Effects in Microcontact. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 1992, 32, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilamakuri, S.K.; Bhushan, B. Contact Analysis of Non-Gaussian Random Surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 1998, 212, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, J.I. Extending the Capability of the Greenwood Williamson Microcontact Model. ASME J. Tribol. 2000, 122, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Bhushan, B.; Cho, Y.J. The Contact Behaviour of Elastic/Plastic Non-Gaussian Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2006, 22, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, M.; Morris, N.; Gore, M.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H.; King, P.D. Boundary Interactions of Rough Non-Gaussian Surfaces. Proc. Inst. Mech. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2016, 230, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomota, T.; Kondoh, Y.; Ohmori, T. Modeling Solid Contact between Smooth and Rough Surfaces with Non-Gaussian Distributions. Tribol. Trans. 2018, 62, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Bhushan, B. Role of Fractal Geometry in Roughness Characterization and Contact Mechanics of Surfaces. ASME J. Tribol. 1991, 112, 205–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumdar, A.; Bhushan, B. Fractal Model of Elastic-Plastic Contact between Rough Surfaces. ASME J. Tribol. 1991, 113, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Komvopoulos, K. Contact Analysis of Elastic-Plastic Fractal Surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, M.; Demelio, G.; Barber, J.R.; Jang, Y.H. Elastic Contact of the Weierstrass Profile. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 2000, 456, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciavarella, M.; Demelio, G. Elastic Multiscale Contact of Rough Surfaces: Archard’s Model Revisited and Comparisons with Modern Fractal Models. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 2001, 68, 496–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, R.L.; Streator, J.L. A Multi-Scale Model for Contact between Rough Surfaces. Wear 2006, 261, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogut, L.; Jackson, R.L. A Comparison of Contact Modeling Utilizing Statistical and Fractal Approaches. ASME J. Tribol. 2006, 128, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosonovsky, M.; Bhushan, B. Multiscale Friction Mechanisms and Hierarchical Surfaces in Nano- and Bio-Tribology. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2007, 58, 162–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.L. An Analytical Solution to an Archard-Type Fractal Rough Surface Contact Model. Tribol. Trans. 2010, 53, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goedecke, A.; Jackson, R.L.; Mock, R. A Fractal Expansion of a Three-Dimensional Elastic-Plastic Multi-Scale Rough Surface Contact Model. Tribol. Int. 2013, 59, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Huang, X. A Complete Contact Model of a Fractal Rough Surface. Wear 2014, 309, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, I. Exact Spectral Moments and Differentiability of the Weierstrass-Mandelbrot Fractal Function. Tribology 2020, 142, 041501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Gan, L.; Liu, K.; Yang, X. Elastoplastic Contact Mechanics Model of Rough Surface Based on Fractal Theory. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2017, 30, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, M.N.; Sayles, R.S. A Numerical Model for the Elastic Frictionless Contact of Real Rough Surfaces. ASME J. Tribol. 1986, 108, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, H.M.; Kato, T. An FFT-Based Method for Rough Surface Contact. ASME J. Tribol. 1997, 119, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Z.; Barber, G.C.; Zhu, D. Numerical Analysis for the Elastic Contact of Real Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 1999, 42, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borri-Brunetto, M.; Chiaia, B.; Ciavarella, M. Incipient Sliding of Rough Surfaces in Contact: A Multiscale Numerical Analysis. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 2001, 190, 6053–6073.zs. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.J.; Wang, W.Z.; Hu, Y.Z.; Wang, H. A Numerical Elastic-Plastic Contact Model for Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Trans. 2010, 53, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, N. Advanced Modeling of Mixed Lubrication and Its Mechanical and Biomedical Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ghaednia, H.; Wang, X.; Saha, S.; Xu, Y.; Sharma, A.; Jackson, R.L. A Review of Elastic-Plastic Contact Mechanics. ASME Appl. Mech. Rev. 2017, 69, 060804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yastrebov, V.A.; Durand, J.; Proudhon, H.; Cailletaud, G. Rough Surface Contact Analysis by Means of the Finite Element Method and of a New Reduced Model. Comptes Rendus Mécanique 2011, 339, 473–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yastrebov, V.A.; Anciaux, G.; Molinari, J.F. Contact between Representative Rough Surfaces. Phys. Rev. E 2012, 86, 035601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Putignano, C.; Afferrante, L.; Carbone, G.; Demelio, G. A New Efficient Numerical Method for Contact Mechanics of Rough Surfaces. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2012, 49, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tysoe, W.T.; Spencer, N.D. Contact-Mechanics Challenge. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. 2015, 71, 96. [Google Scholar]
- McGhee, A.J.; Pitenis, A.A.; Bennett, A.I.; Harris, K.L.; Schulze, K.D.; Urueña, J.M.; Ifju, P.G.; Angelini, T.E.; Müser, M.H.; Sawyer, W.G. Contact and Deformation of Randomly Rough Surfaces with Varying Root-Mean-Square Gradient. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-J. Numerical Simulation on the Adhesive Contact between Rough Surfaces with Bi-Conjugate Gradient Stabilized Method. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.I.; Harris, K.L.; Schulze, K.; Urueña, J.M.; McGhee, A.J.; Pitenis, A.A.; Müser, M.H.; Angelini, T.E.; Sawyer, W.G. Contact Measurements of Randomly Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, A.I.; Rohde, S.; Harris, K.L.; Schulze, K.D.; Urueña, J.M.; Pitenis, A.A.; Ifju, P.G.; Angelini, T.E.; Müser, M.H.; Sawyer, W.G. Deformation Measurements of Randomly Rough Surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müser, M.H.; Dapp, W.B.; Bugnicourt, R.; Sainsot, P.; Lesaffre, N.; Lubrecht, T.A.; Persson, B.N.; Harris, K.; Bennett, A.; Schulze, K.; et al. Meeting the Contact-Mechanics Challenge. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Müser, M.H. Gauging Persson Theory on Adhesion. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afferrante, L.; Bottiglione, F.; Putignano, C.; Persson, B.N.J.; Carbone, G. Elastic Contact Mechanics of Randomly Rough Surfaces: An Assessment of Advanced Asperity Models and Persson’s Theory. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugnicourt, R.; Sainsot, P.; Dureisseix, D.; Gauthier, C.; Lubrecht, A.A. FFT-Based Methods for Solving a Rough Adhesive Contact: Description and Convergence Study. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.I. Tribology and Energy Efficiency: From Molecules to Lubricated Contacts to Complete Machines. Faraday Trans. 2012, 156, 361–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spikes, H. The History and Mechanisms of ZDDP. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 469–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawczyk, J.; Morgan, N.; Russo, J.; Spikes, H. Film Thickness and Friction of ZDDP Tribofilms. Tribol. Lett. 2019, 67, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spikes, H. Friction Modifier Additives. Tribol. Lett. 2015, 60, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bec, S.; Tonck, A.; Georges, J.M.; Coy, R.C.; Bell, J.C.; Roper, G.W. Relationship between Mechanical Properties and Structures of Zinc Dithiophosphate Anti-Wear Films. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 1999, 455, 4181–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, B.J.; Scruton, B.; Willis, F.R. The Shear Strength of Thin Lubricant Films. Proc. R. Soc. A 1973, 333, 99–114. [Google Scholar]
- Timsit, R.S.; Pelow, C.V. Shear Strength and Tribological Properties of Stearic Acid Films—Part I: On Glass and Aluminium-Coated Glass. Tribology 1992, 114, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazirisereshk, M.R.; Martini, A.; Strubbe, D.A.; Baykara, M.Z. Solid Lubrication with MoS2: A Review. Lubricants 2019, 7, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Spikes, H. On the Mechanism of ZDDP Antiwear Film Formation. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 63, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shahnazar, S.; Bagheri, S.; Hamid, S.B.A. Enhancing Lubricant Properties by Nanoparticle Additives. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 3153–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Kheireddin, B.; Gao, H.; Liang, H. Roles of Nanoparticles in Oil Lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Qiu, F.; Barber, G.C.; Zou, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, Q. Role of Nano-Sized Materials as Lubricant Additives in Friction and Wear Reduction: A Review. Wear 2022, 490–491, 204206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, Y.; Sayles, R.S.; Kadiric, A. Film Formation and Friction in Grease Lubricated Rolling-Sliding Non-Conformal Contacts. Tribol. Int. 2017, 105, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.J. Experimental and Numerical Investigations of the Stribeck Curve for Lubricated Counterformal Contacts. ASME J. Tribol. 2017, 139, 021505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, Q.; Lian, Z.; Li, L. Theoretical Model and Experimental Research on Friction and Torque Characteristics of Hydro-Viscous Drive in Mixed Friction Stage. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 32, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taylor, R.I.; Sherrington, I. A Simplified Approach to the Prediction of Mixed and Boundary Friction. Tribol. Int. 2022; paper submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Stribeck, R. Die Wesentlichen Eigenschaften der Gleit-und Rollenlager. VDI-Z 1902, 46, 1341–1348, 1432–1438, 1463–1470. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, S.A. The Effect of Running-In on Journal Bearing Performance. ASME Trans. 1927, 49, 1335. [Google Scholar]
- Hersey, M.D. Theory of Lubrication; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Lenning, R.L. The Transition from Boundary to Mixed Friction. Lubr. Eng. 1960, 16, 575–582. [Google Scholar]
- Bair, S.; Winer, W.O. Regimes of Traction in Concentrated Contact Lubrication. ASME J. Lubr. Technol. 1982, 104, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, C.R.; Johnson, K.L. The Influence of Surface Roughness on Elastohydrodynamic Traction. Proc. Inst. Mech. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1987, 201, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, D.J. Transitions in the Lubrication of Concentrated Contacts. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Schipper, D.J.; Vroegop, P.H.; de Gee, A.W.J. Prediction of Lubrication Regimes of Concentrated Contacts. Lubr. Sci. 1991, 3, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.W.; Choi, S.M.; Bae, C.S. Frictional Modes of Barrel Shaped Piston Rings under Flooded Lubrication. Tribol. Int. 2000, 33, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J.; Scaraggi, M. On the Transition from Boundary Lubrication to Hydrodynamic Lubrication in Soft Contacts. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2009, 21, 185002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Rao, Z.; Ta, N.; Liu, L. Investigations on Transitions of Lubrication States for Water Lubricated Bearing. Part I: Determination of Frictrion Coefficients and Film Thickness Ratios. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2016, 68, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Rao, Z.; Ta, N.; Liu, L. Investigations on Transitions of Lubrication States for Water Lubricated Bearing. Part II: Further Insight into the Film Thickness Ratio Lambda. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2016, 68, 416–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, W.W.; Hamdan, F.; Wong, S.H.K.J.; Yusup, S. Modelling Transitions in Regimes of Lubrication for Rough Surface Contact. Lubricants 2019, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, J.; Bjorling, M.; Larsson, R. Mapping of the Lubrication Regimes in Rough Surface EHL Contacts. Tribol. Int. 2019, 131, 637–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhu, W. Theoretical and Experimental Exploration on the Micro Asperity Contact Load Ratios and Lubrication Regimes Transition for Water-Lubricated Stern Tube Bearing. Tribol. Int. 2021, 164, 107105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coy, R.C. Practical Applications of Lubrication Models in Engines. Tribol. Int. 1998, 31, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patir, N.; Cheng, H.S. An Average Flow Model for Determining Effects of Three-Dimensional Roughness on Partial Hydrodynamic Lubrication. J. Tribol. 1978, 100, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patir, N.; Cheng, H.S. Application of Average Flow Model to Lubrication between Rough Sliding Surfaces. J. Tribol. 1979, 101, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Neville, A.; Reuben, R.L. Analyzing Elastic-Plastic Real Rough Surface Contact in Running In. Tribol. Trans. 2001, 44, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Moslehy, A.; Rice, S.L. A Model for Friction in Quasi-Steady-State Sliding Part I: Derivation. Wear 1991, 149, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Moslehy, A.; Rice, S.L. A Model for Friction in Quasi-Steady-State Sliding Part II: Numerical Results and Discussion. Wear 1991, 149, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.K.; Kapoor, A.; Williams, J.A. Shakedown Limits on Coated and Engineered Surfaces. Wear 1997, 203–204, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A.; Dyson, I.N.; Kapoor, A. Repeated Loading, Residual Stresses, Shakedown, and Tribology. J. Mater. Res. 1999, 14, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.A. The Influence of Repeated Loading, Residual Stresses and Shakedown on the Behaviour of Tribological Contacts. Tribol. Int. 2005, 38, 786–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Marian, M.; Profito, F.J.; Aragon, N.; Shah, R. The Use of Artificial Intelligence in Tribology—A Perspective. Lubricants 2020, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, M.; Tremmel, S. Current Trends and Applications of Machine Learning in Tribology—A Review. Lubricants 2021, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghababaei, R.; Brink, T.; Molinari, J.F. Asperity-Level Origins of Transition from Mild to Severe Wear. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 186105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, J.; Zou, Q. Evolution of Contact Characteristics during a Scuffing Process. Tribol. Trans. 2013, 56, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roper, G.W.; Bell, J.C. Review and Evaluation of Lubricated Wear in Simulated Valve Train Contact Conditions. SAE Pap. 1995, 104, 1478–1494. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, J.C.; Willemse, P.J. Mid-Life Scuffing Failure in Automotive Cam-Follower Contacts. Proc. Inst. Mech. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 1998, 212, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patir, N. A Numerical Procedure for Random Generation of Rough Surfaces. Wear 1978, 47, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leighton, M.; Morris, N.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H. Surface Specific Asperity Model for Prediction of Friction in Boundary and Mixed Regimes of Lubrication. Meccanica 2017, 52, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
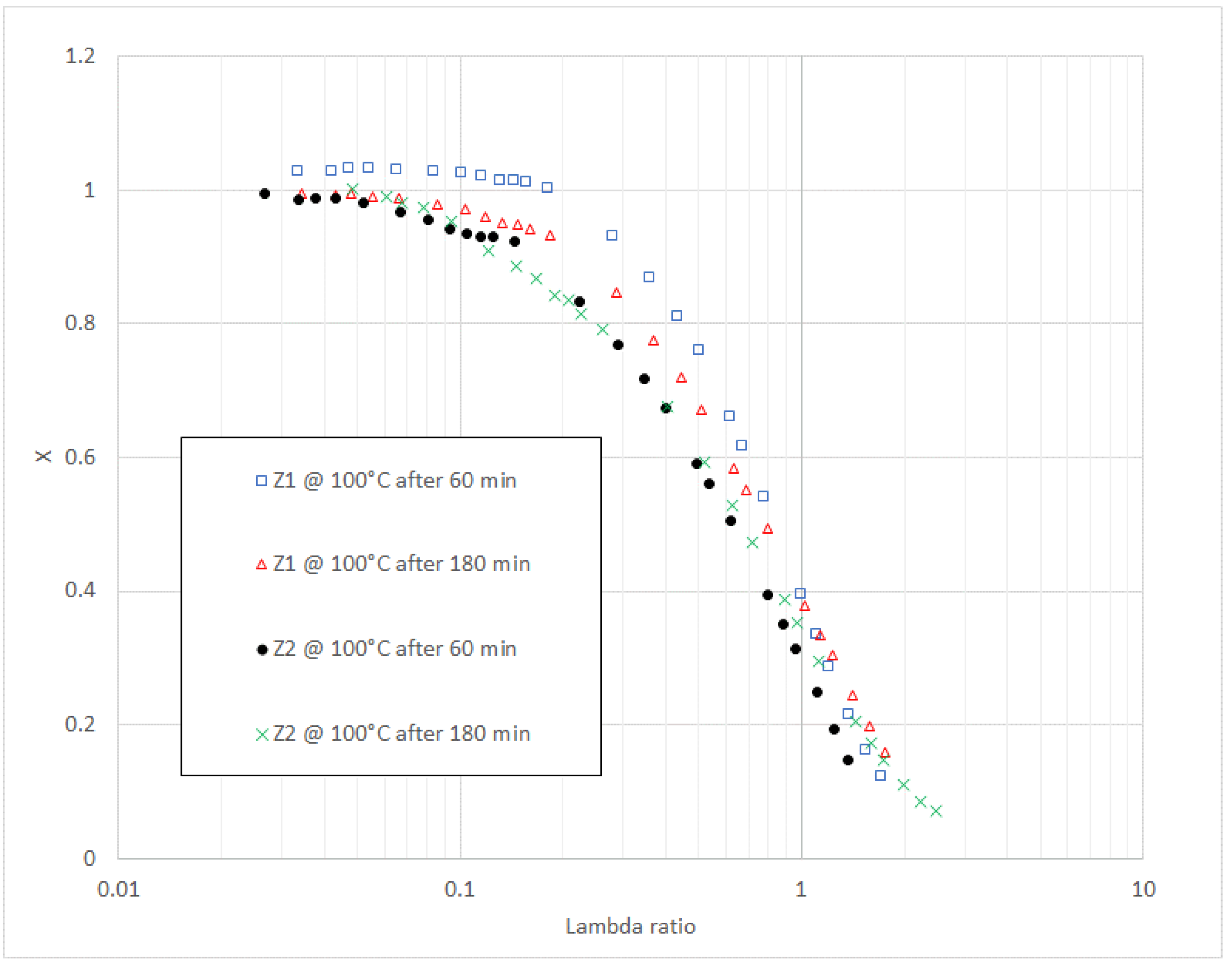
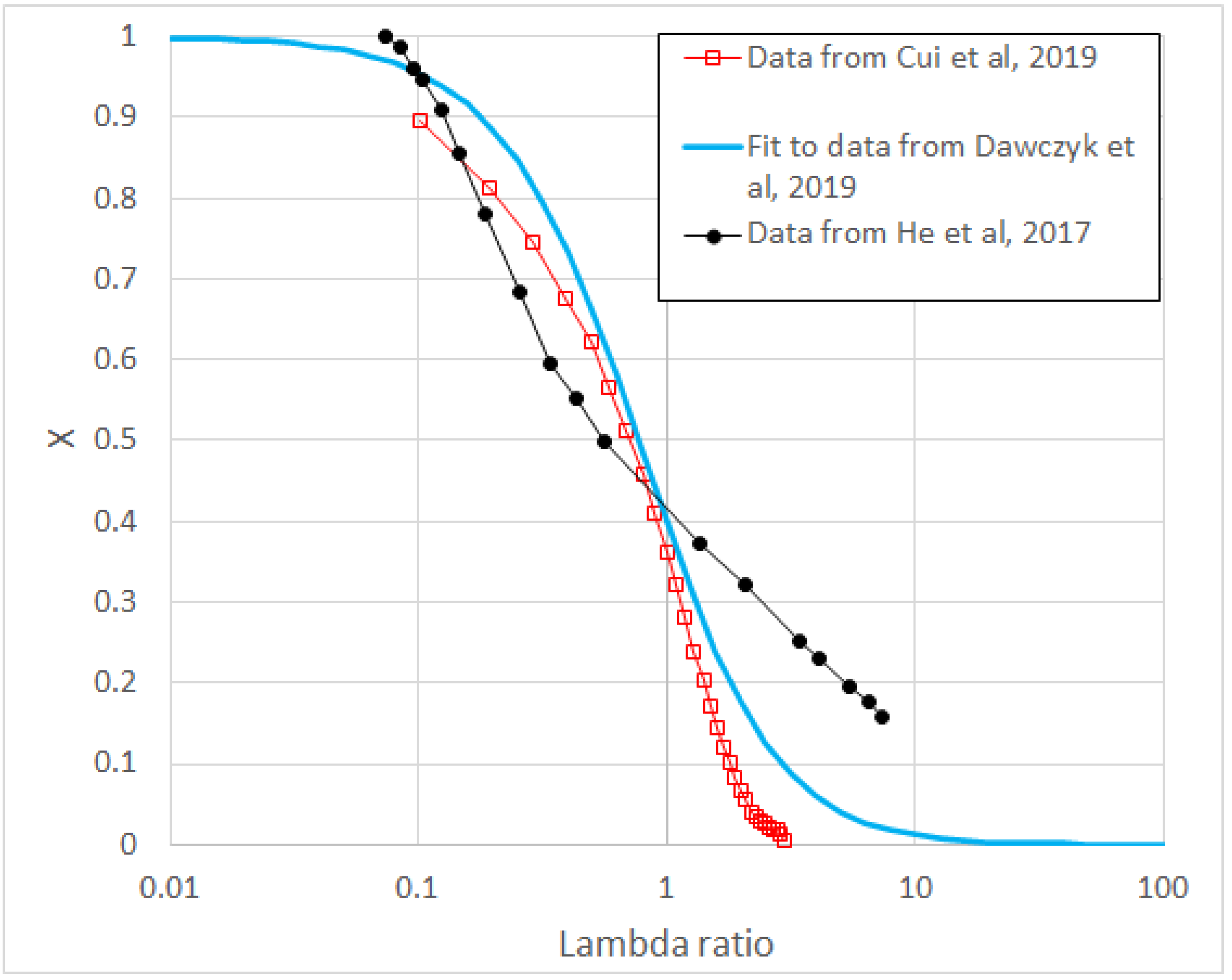
| λ | F0(λ) | F1/2(λ) | F1(λ) | F3/2(λ) | F2(λ) | F5/2(λ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 0.50000 | 0.41109 | 0.39894 | 0.43002 | 0.50000 | 0.61664 |
| 0.5 | 0.30854 | 0.22534 | 0.19780 | 0.19520 | 0.20964 | 0.24024 |
| 1.0 | 0.15865 | 0.10415 | 0.08332 | 0.07567 | 0.07534 | 0.08056 |
| 1.5 | 0.06681 | 0.03988 | 0.02931 | 0.02464 | 0.02285 | 0.02286 |
| 2.0 | 0.02275 | 0.01248 | 0.00849 | 0.00665 | 0.00577 | 0.00542 |
| 2.5 | 0.00621 | 0.00316 | 0.00200 | 0.00147 | 0.00120 | 0.00106 |
| 3.0 | 0.00135 | 0.00064 | 0.00038 | 0.00026 | 0.00020 | 0.00017 |
| 3.5 | 0.00023 | 0.00010 | 0.00006 | 0.00004 | 0.00003 | 0.00002 |
| 4.0 | 0.00003 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| X | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| λ | k = 3/2, a ≈ 4/3 | exp(−λ) | Linear fit (Equation (38)) | Olver and Spikes [44] (Equation (36)) | Greenwood-Tripp [21] | Bush, Gibson, Thomas [19] |
| 3 | 0.0879 | 0.0498 | 0 | 0.0625 | 0.00028 | 0.0027 |
| 2 | 0.167 | 0.135 | 0.333 | 0.111 | 0.0088 | 0.0455 |
| 1 | 0.397 | 0.368 | 0.667 | 0.25 | 0.131 | 0.317 |
| 0.5 | 0.668 | 0.607 | 0.833 | 0.444 | 0.390 | 0.617 |
| 0.2 | 0.892 | 0.819 | 0.933 | 0.694 | 0.698 | 0.895 |
| 0.1 | 0.959 | 0.905 | 0.967 | 0.826 | 0.838 | 0.920 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taylor, R.I. Rough Surface Contact Modelling—A Review. Lubricants 2022, 10, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10050098
Taylor RI. Rough Surface Contact Modelling—A Review. Lubricants. 2022; 10(5):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10050098
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaylor, Robert Ian. 2022. "Rough Surface Contact Modelling—A Review" Lubricants 10, no. 5: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10050098
APA StyleTaylor, R. I. (2022). Rough Surface Contact Modelling—A Review. Lubricants, 10(5), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10050098





