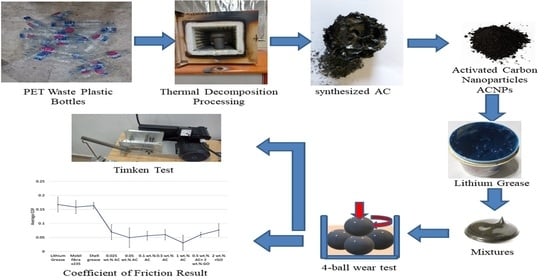
Activated Carbon Nano-Particles from Recycled Polymers Waste as a Novel Nano-Additive to Grease Lubrication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Activated Carbon (AC) from Waste Plastic
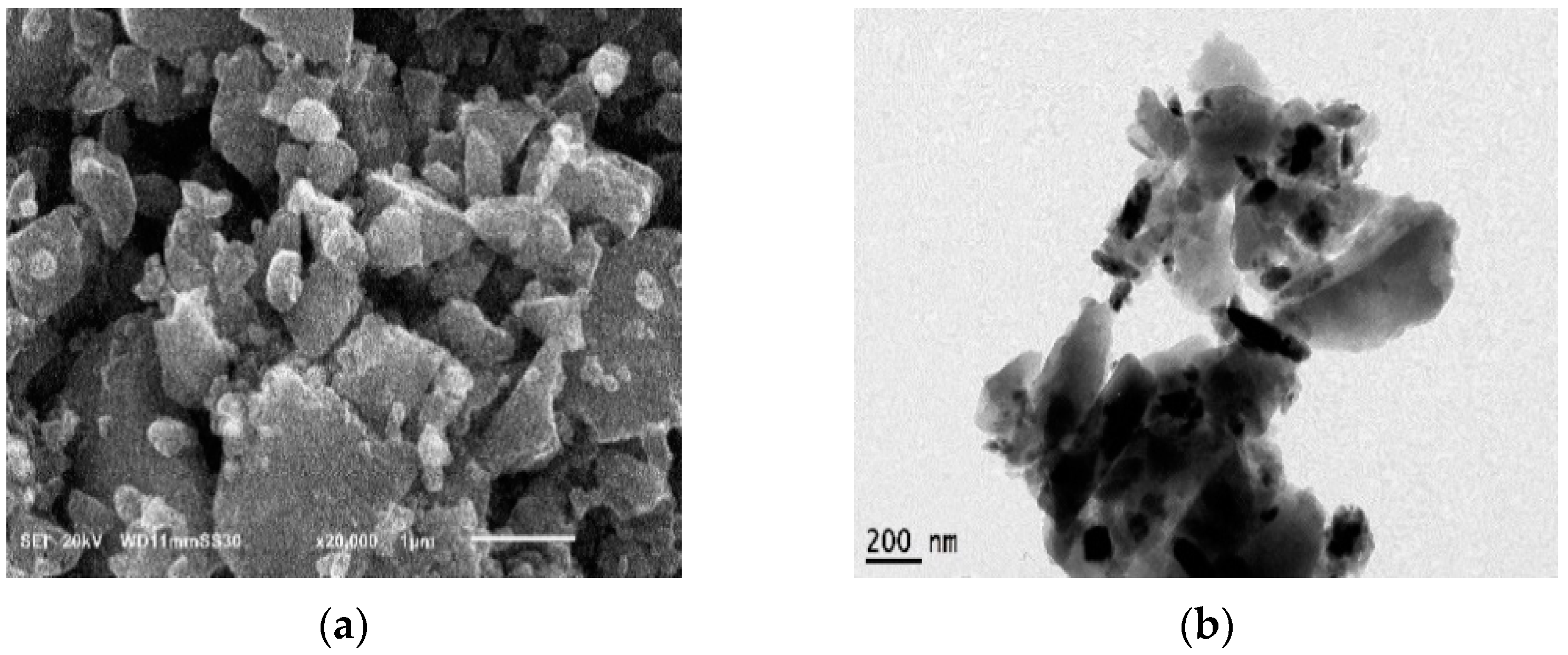
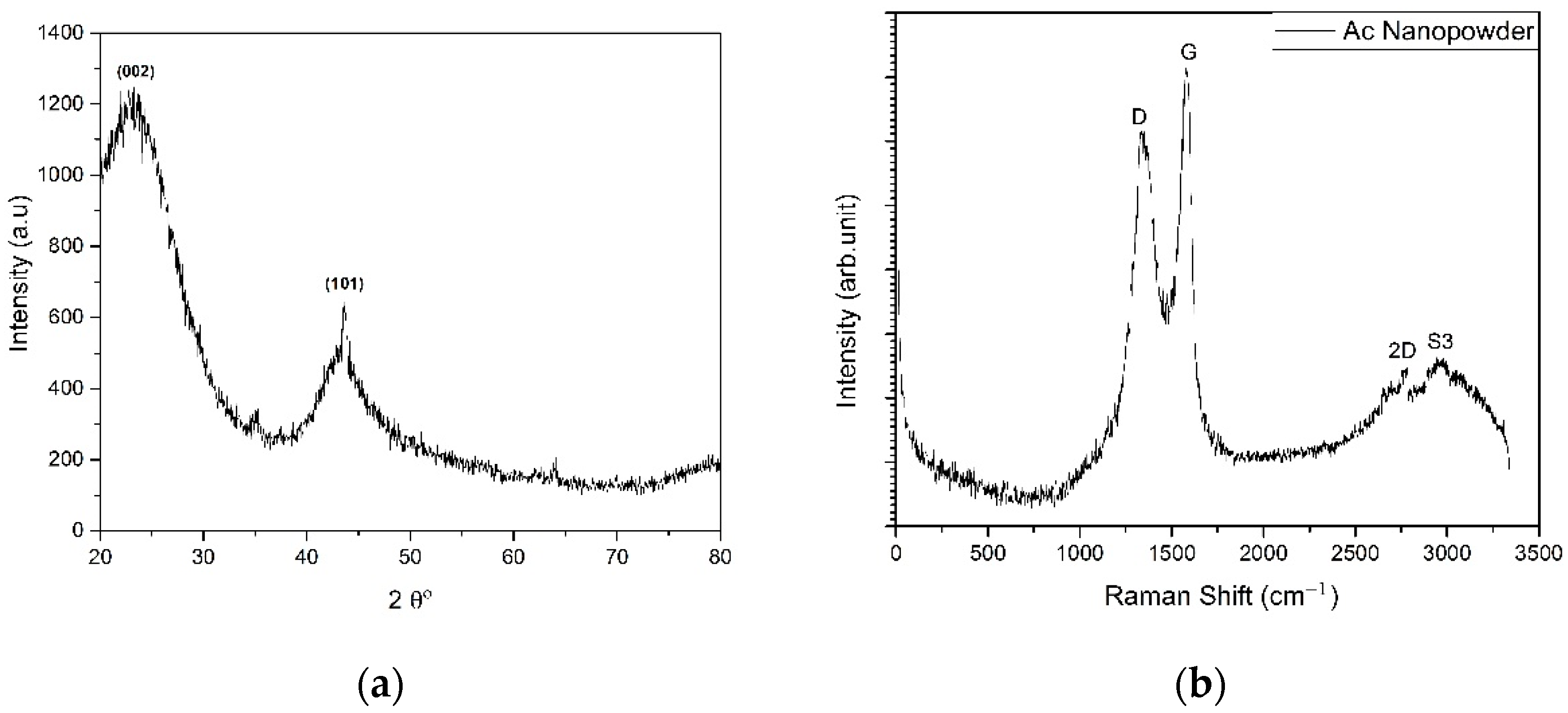
2.2. Characterization of the Synthetic AC
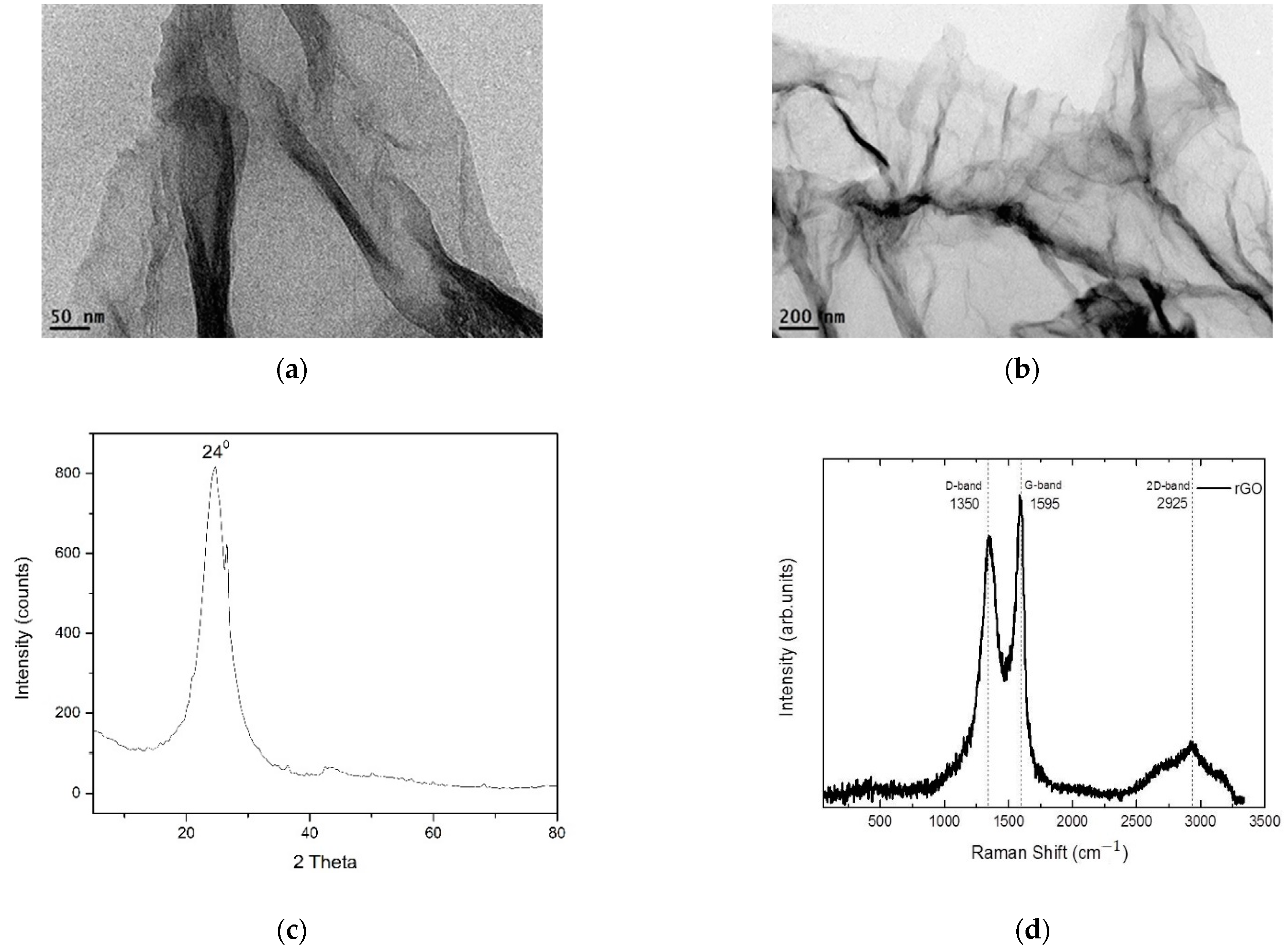
2.3. Characterization of the rGO
2.4. Type of Used Grease
2.5. Four Ball Wear Test
2.6. Load Carrying Capacity Test
3. Results
3.1. Nano-Additive Material Characterization
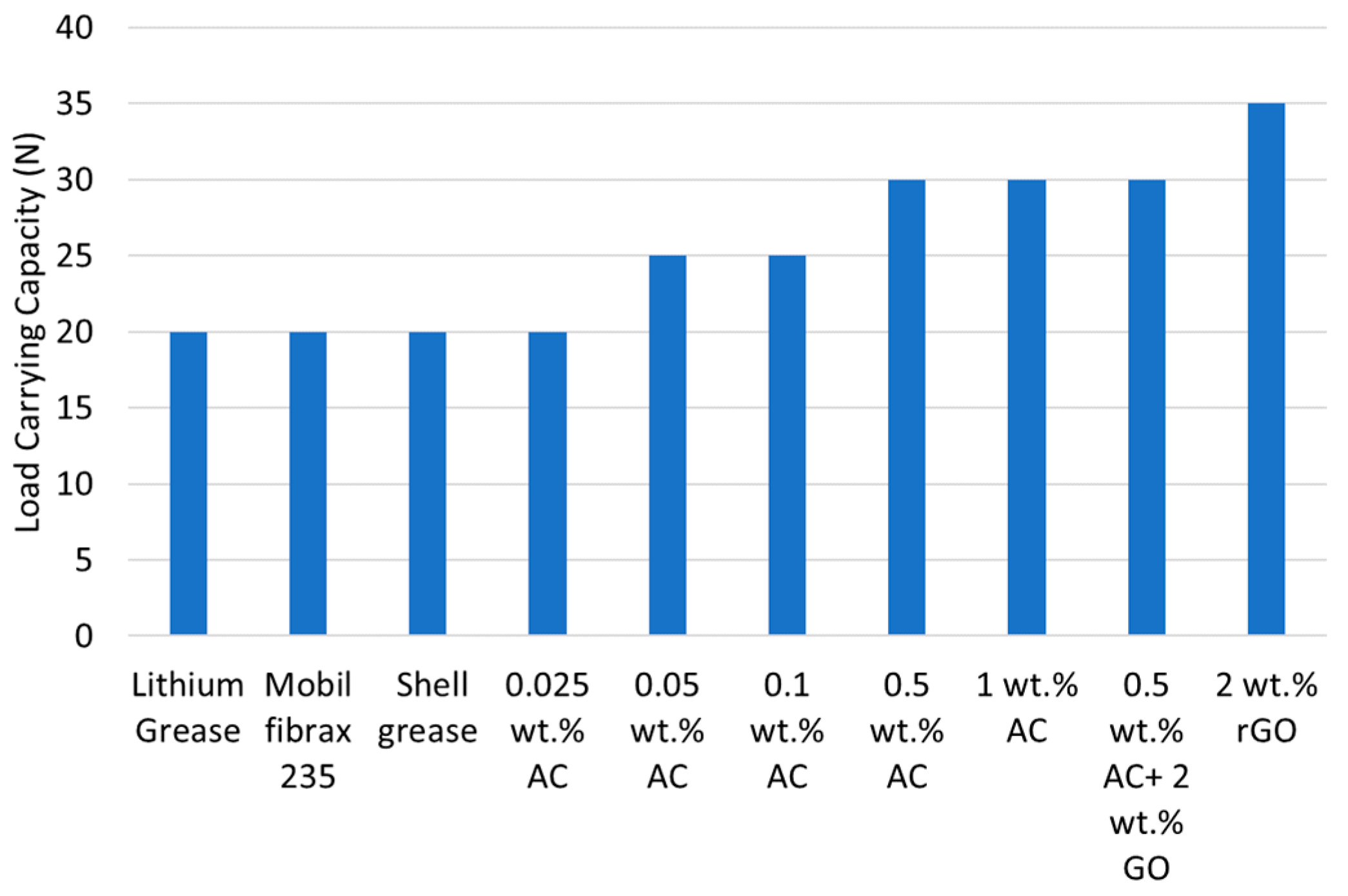
3.2. Load Carrying Capacity Results
3.3. Wear Properties and Coefficient of Friction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Activated nanoparticles enhanced the tribological properties of commercial lithium grease in terms of WSD, COF, and load carrying capacity. Increasing the AC concentration in grease leads to lower power losses due to friction.
- The highly porous structure of AC promotes its absorption properties leading to the deposition of more stable tribofilm layers to protect the contact surfaces in comparison with rGO (2 wt.%) which is manifested by lower mass loss values. However, rGO shows higher load carrying capacity than AC due to its higher modulus of elasticity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, F.; Xie, G.; Luo, J. Electrical bearing failures in electric vehicles. Friction 2020, 8, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Erdemir, A. Influence of tribology on global energy consumption, costs and emissions. Friction 2017, 5, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, K.; Andersson, P.; Nylund, N.O.; Mäkelä, K.; Erdemir, A. Global energy consumption due to friction in trucks and buses. Tribol. Int. 2014, 78, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, H.P. Tribology Micro Macro Economics: A Road to Economic Savings. Tribol. Lubr. Technol. 2005, 61, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, B.; Kumar, N.; Panda, K.; Dash, S.; Tyagi, A.K. Energy efficient reduced graphene oxide additives: Mechanism of effective lubrication and antiwear properties. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepika, S. Nanotechnology implications for high performance lubricants. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, L.R. Lubricant Additives: Chemistry and Applications, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Townsend, D.; Zaretsky, E.; Scibbe, H. Lubricant and additive effects on spur gear fatigue life. J. Synth. Lubr. 1986, 6, 83–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soul, D.M. 10 Lubricant Additives, Their Application, Performance and Limitations. Tribol. Int. 1983, 8, 242–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassef, B.G.; Nassef, G.A.; Daha, M.A. Graphene and Its Industrial Applications–A Review. Int. J. Mater. Eng. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Wang, A.; Edwards, B.J.; Yin, H.; Li, Z.; Ding, Y. Improvement of the Tribological Properties of a Lithium-Based Grease by Addition of Graphene. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2018, 18, 7163–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A.; Osman, T.A.; Khattab, A.; Zaki, M. Tribological Behavior of Carbon Nanotubes as an Additive on Lithium Grease. J. Tribol. 2014, 137, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, S.S.; Harsha, A.P.; Khatri, O.P.; Wäsche, R. Pristine, Reduced, and Alkylated Graphene Oxide as Additives to Paraffin Grease for Enhancement of Tribological Properties. J. Tribol. 2020, 143, 021903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Liu, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, L. 2D nano-materials beyond graphene: From synthesis to tribological studies. Appl. Nanosci. 2020, 10, 3353–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, M.; Berman, D.; Rota, A.; Jackson, R.; Rosenkranz, A. Layered 2D Nanomaterials to Tailor Friction and Wear in Machine Elements—A Review. Adv. Mater. 2022, 9, 2101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; Hong, H.; D’Urso, V.; Younes, H. Tribological Behavior of Novel CNTs-Based Lubricant Grease in Steady-State and Fretting Sliding Conditions. Lubricants 2021, 9, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Xie, Z.; Gu, L.; Song, B.; Wang, L. Investigation of the tribological behavior of graphene oxide nanoplates as lubricant additives for ceramic/steel contact. Tribol. Int. 2018, 128, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, B.M.; Mohamed, A.; El Sherbiny, M.; Abed, K.A.; Abd-Rabou, M. Tribological properties of graphene nanosheets as an additive in calcium grease. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 2017, 38, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.; Ocvirk, F.W. Principles of Lubrication. J. Lubr. Tech. 1967, 89, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yamabe, T.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, I.S.; Enomoto, Y. Lubricating Characteristic of Grease Composites with CNT Additive. Tribol. Online 2011, 6, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- El-Adly, R.; Hussein, M.F.; Mohamed, A. Preparation and evaluation of lubricating greases based on carbon nanotube. Int. J. Adv. Pharm. Biol. Chem. 2015, 4, 675–684. [Google Scholar]
- Pape, F.; Poll, G. Investigations on Graphene Platelets as Dry Lubricant and as Grease Additive for Sliding Contacts and Rolling Bearing Application. Lubricants 2020, 8, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassef, B.G.; Labban, H.; Al-Oufy, A.; Daha, M.A. Effect of Graphene Addition to Lithium-Based Grease on the Performance of Rolling Element Bearings. Key Eng. Mater. 2022, 913, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talib, N.; Jamaluddin, N.A.; Sheng, T.K.; Kiow, L.W.; Haslina, A.; Said, A.; Aslinda, S. Tribological Study of Activated Carbon Nanoparticle in Nonedible Nanofluid for Machining Application. Evergreen. J. Nov. Carbon Resour. Sci. Green Asia Strategy 2021, 8, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, K.; Mahmoud, H.; Fujii, M.; Shokry, H. Upcycling of Polystyrene Waste Plastics to High Value Carbon by Thermal Decomposition. Key Eng. Mater. 2021, 897, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.M.; Alvim-Ferraz, M.C.M.; Almeida, M.F.; Rivera-Utrilla, J.; Sánchez-Polo, M. Waste materials for activated carbon preparation and its use in aqueous-phase treatment: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 833–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, K.; Mahmoud, H.; Fujii, M.; Shokry, H. Novel nano-ferromagnetic activated graphene adsorbent extracted from waste for dye decolonization. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisebois, P.P.; Siaj, M. Harvesting graphene oxide—Years 1859 to 2019: A review of its structure, synthesis, properties and exfoliation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 1517–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Kaur, H.; Kukkar, D. Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide using modified Hummer’s method. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1953, 030180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawant, S.Y.; Somani, R.S.; Panda, A.B.; Bajaj, H.C. Formation and characterization of onions shaped carbon soot from plastic wastes. Mater. Lett. 2013, 94, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares-Solano, A.; Lillo-Rodenas, M.A.; Marco Lozar, J.P.; Kunowsky, M.; Romero Anaya, A.J. NaOH and KOH for preparing activated carbons used in energy and environmental applications. Int. J. Energy Environ. Econ. 2012, 20, 59–92. [Google Scholar]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daud, W.M.A.W.; Ali, W.S.W.; Sulaiman, M.Z. Effect of carbonization temperature on the yield and porosity of char produced from palm shell. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2001, 76, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Essawy, N.A.; Ali, S.M.; Farag, H.A.; Konsowa, A.H.; Elnouby, M.; Hamad, H.A. Green synthesis of graphene from recycled PET bottle wastes for use in the adsorption of dyes in aqueous solution. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 145, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, V.G. Upcycling: Converting waste plastics into paramagnetic, conducting, solid, pure carbon microspheres. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 4753–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Lua, A.C. A facile method for the large-scale continuous synthesis of graphene sheets using a novel catalyst. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokry, H.; Elkady, M.; Hamad, H. Nano activated carbon from industrial mine coal as adsorbents for removal of dye from simulated textile wastewater: Operational parameters and mechanism study. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 4477–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.; Singh, K.P. Valorization of Poly (ethylene) terephthalate (PET) wastes into magnetic carbon for adsorption of antibiotic from water: Characterization and application. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 207, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Veerapandian, M.; Mohan, R.; Kim, S.J. Investigation of Raman and photoluminescence studies of reduced graphene oxide sheets. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 106, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, S.; Karak, N. Green reduction of graphene oxide by aqueous phytoextracts. Carbon 2012, 50, 5331–5339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, M.J.-Y. Green synthesis of reduced graphene oxide using green tea extract. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 2045, 020032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Cao, Z.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, L.; Fang, Z.; Fu, S. Fabrication of exfoliated graphene-based polypropylene nanocomposites with enhanced mechanical and thermal properties. Polymer 2011, 52, 4001–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayah, N. Comparison on graphite, graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide: Synthesis and characterization. AIP Conf. Proc. 2017, 1892, 150002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 2007, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuinstra, F.; Koenig, J.L. Raman spectrum of graphite. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 53, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Meyer, J.C.; Scardaci, V.; Casiraghi, C.; Lazzeri, M.; Mauri, F.; Piscanec, S.; Jiang, D.; Novoselov, K.S.; Roth, S.; et al. Raman Spectrum of Graphene and Graphene Layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 97, 187401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Kumar, N.; Panda, K.; Kanan, V.; Joshi, S.; Visoly-Fisher, I. Role of oxygen functional groups in reduced graphene oxide for lubrication. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassef, M.G.A.; Soliman, M.; Nassef, B.G.; Daha, M.A.; Nassef, G.A. Impact of Graphene Nano-Additives to Lithium Grease on the Dynamic and Tribological Behavior of Rolling Bearings. Lubricants 2022, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vyavhare, K.; Aswath, P.B. Tribological Properties of Novel Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes and Phosphorus Containing Ionic Liquid Hybrids in Grease. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; D’Agostino, V.; Petrone, V.; Ciambelli, P.; Sarno, M. Graphene Oxide Nanosheets as Effective Friction Modifier for Oil Lubricant: Materials, Methods, and Tribological Results. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 9, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, A.H.; Ramli, N.; Nordin, A.N.; Abd. Wahab, M.F. Supercapacitor performance with activated carbon and graphene nanoplatelets composite electrodes, and insights from the equivalent circuit model. Carbon Trends 2021, 5, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



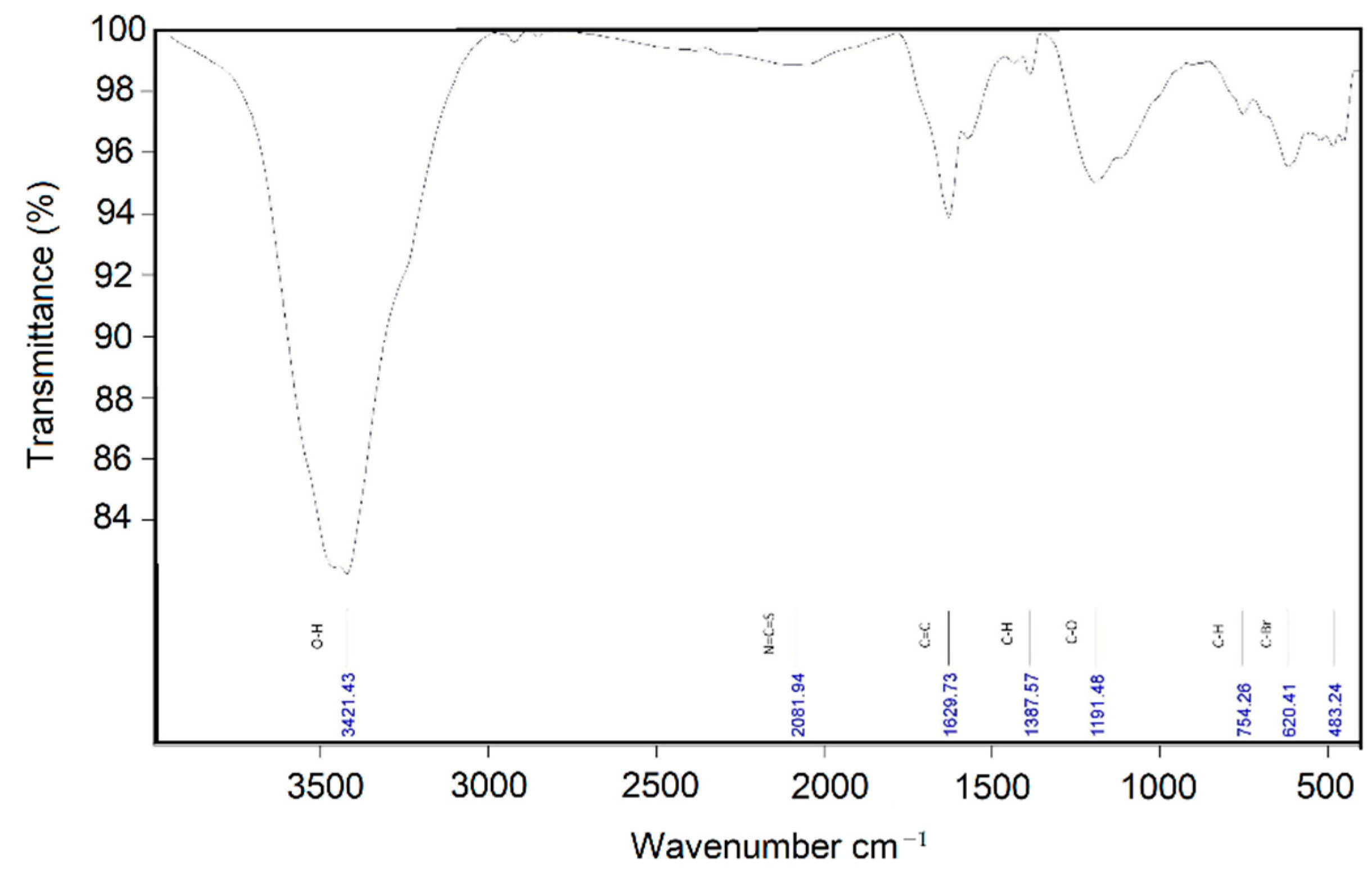



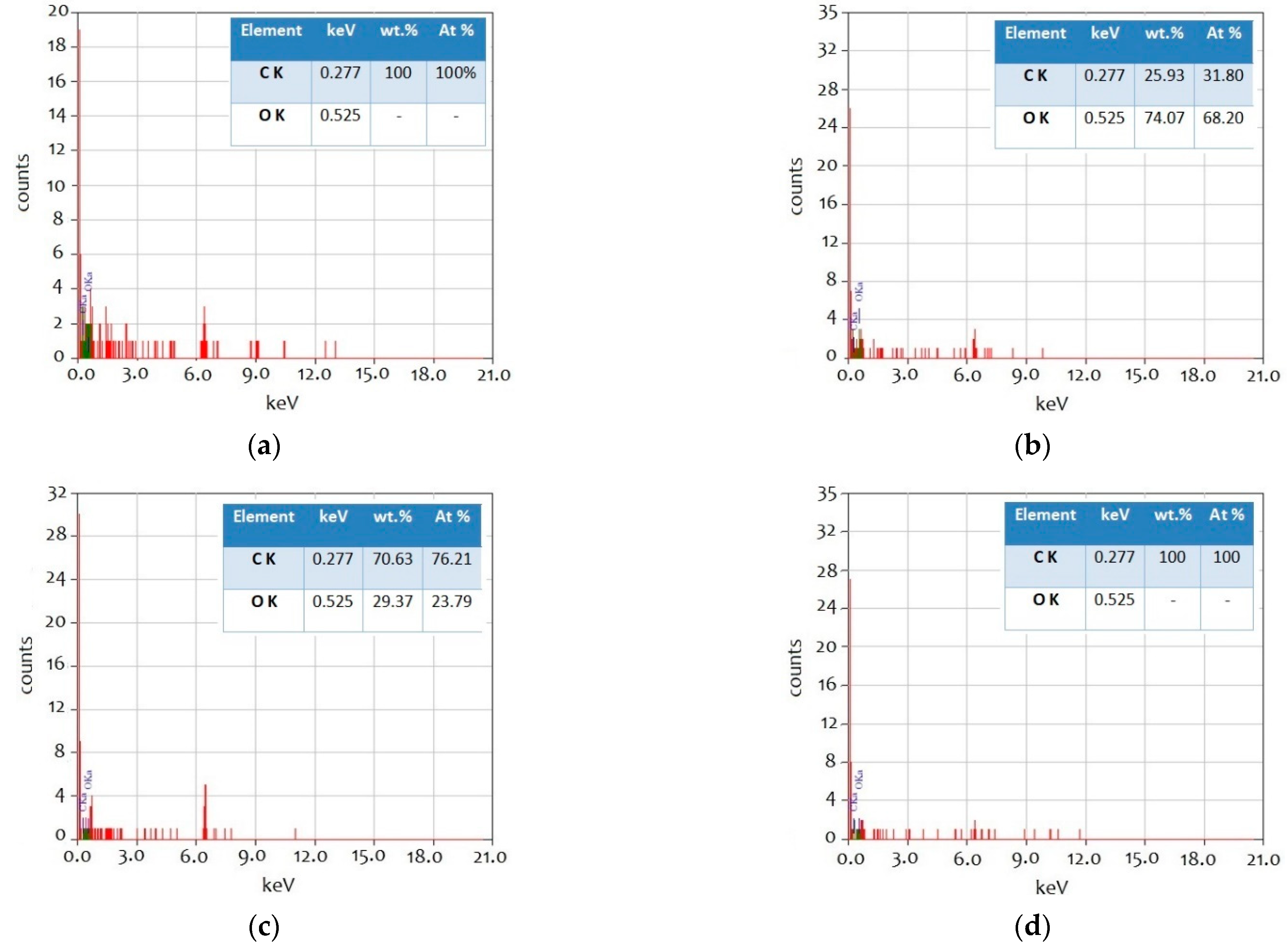

| Sample | BET Surface Area (m2 g−1) | Total Pore Volume (cm3 g−1) | Mean Pore Diameter (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 448.88 | 0.2029 | 1.808 |
| Sample | Test Grease | Average WSD (mm) | Relative Reduction in WSD (%) | Wear Scar Area (mm2) | Relative Reduction in Wear Scar Area (%) | Mass Loss (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lithium Grease | 0.73 | 100% | 0.418 | 100.00 | 0.0633 |
| 2 | Mobil fibrax 235 | 0.73 | 100% | 0.418 | 100.00 | 0.065 |
| 3 | Shell grease | 0.675 | 92.47% | 0.357 | 85.50 | 0.0587 |
| 4 | 0.025 wt.% AC | 0.485 | 66.44% | 0.185 | 44.14 | 0.0087 |
| 5 | 0.05 wt.% AC | 0.48 | 65.75% | 0.180 | 43.24 | 0.019 |
| 6 | 0.1 wt.% AC | 0.465 | 63.70% | 0.169 | 40.58 | 0.0199 |
| 7 | 0.5 wt.% AC | 0.465 | 63.70% | 0.169 | 40.58 | 0.0195 |
| 8 | 1 wt.% AC | 0.495 | 67.81% | 0.192 | 45.98 | 0.0174 |
| 9 | 0.5 wt.% AC + 2 wt.% rGO | 0.45 | 61.64% | 0.158 | 38.00 | 0.0107 |
| 10 | 2 wt.% rGO | 0.55 | 75.34% | 0.24 | 56.76 | 0.0186 |
| Sample | Test Grease | Average COF | Relative Reduction in COF (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lithium Grease | 0.17 | 100.00 |
| 2 | Mobil fibrax 235 | 0.16 | 94.62 |
| 3 | Shell grease | 0.16 | 97.61 |
| 4 | 0.025 wt.% AC | 0.07 | 41.43 |
| 5 | 0.05 wt.% AC | 0.05 | 29.37 |
| 6 | 0.1 wt.% AC | 0.06 | 33.48 |
| 7 | 0.5 wt.% AC | 0.06 | 35.84 |
| 8 | 1 wt.% AC | 0.03 | 18.48 |
| 9 | 0.5 wt.% AC + 2 wt.% rGO | 0.06 | 35.71 |
| 10 | 2 wt.% rGO | 0.08 | 45.76 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nassef, M.G.A.; Hassan, H.S.; Nassef, G.A.; Nassef, B.G.; Soliman, M.; Elkady, M.F. Activated Carbon Nano-Particles from Recycled Polymers Waste as a Novel Nano-Additive to Grease Lubrication. Lubricants 2022, 10, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10090214
Nassef MGA, Hassan HS, Nassef GA, Nassef BG, Soliman M, Elkady MF. Activated Carbon Nano-Particles from Recycled Polymers Waste as a Novel Nano-Additive to Grease Lubrication. Lubricants. 2022; 10(9):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10090214
Chicago/Turabian StyleNassef, Mohamed G. A., Hassan Shokry Hassan, Galal A. Nassef, Belal Galal Nassef, Mina Soliman, and Marwa F. Elkady. 2022. "Activated Carbon Nano-Particles from Recycled Polymers Waste as a Novel Nano-Additive to Grease Lubrication" Lubricants 10, no. 9: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10090214
APA StyleNassef, M. G. A., Hassan, H. S., Nassef, G. A., Nassef, B. G., Soliman, M., & Elkady, M. F. (2022). Activated Carbon Nano-Particles from Recycled Polymers Waste as a Novel Nano-Additive to Grease Lubrication. Lubricants, 10(9), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10090214