Lubrication Characteristics of a Warhead-Type Irregular Symmetric Texture on the Stator Rubber Surfaces of Screw Pumps
Abstract
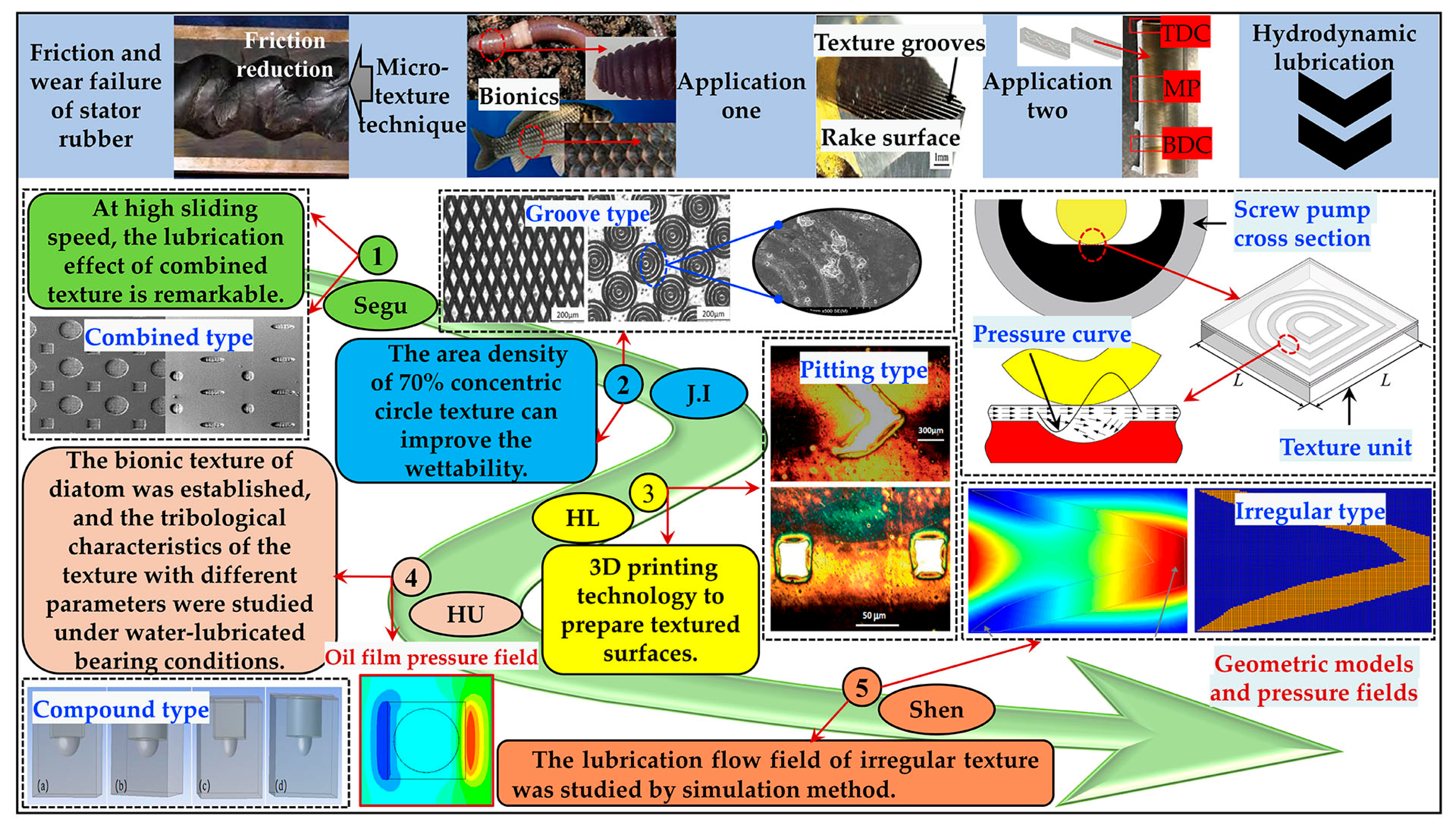
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model of the Textured Surface of the Stator Rubber
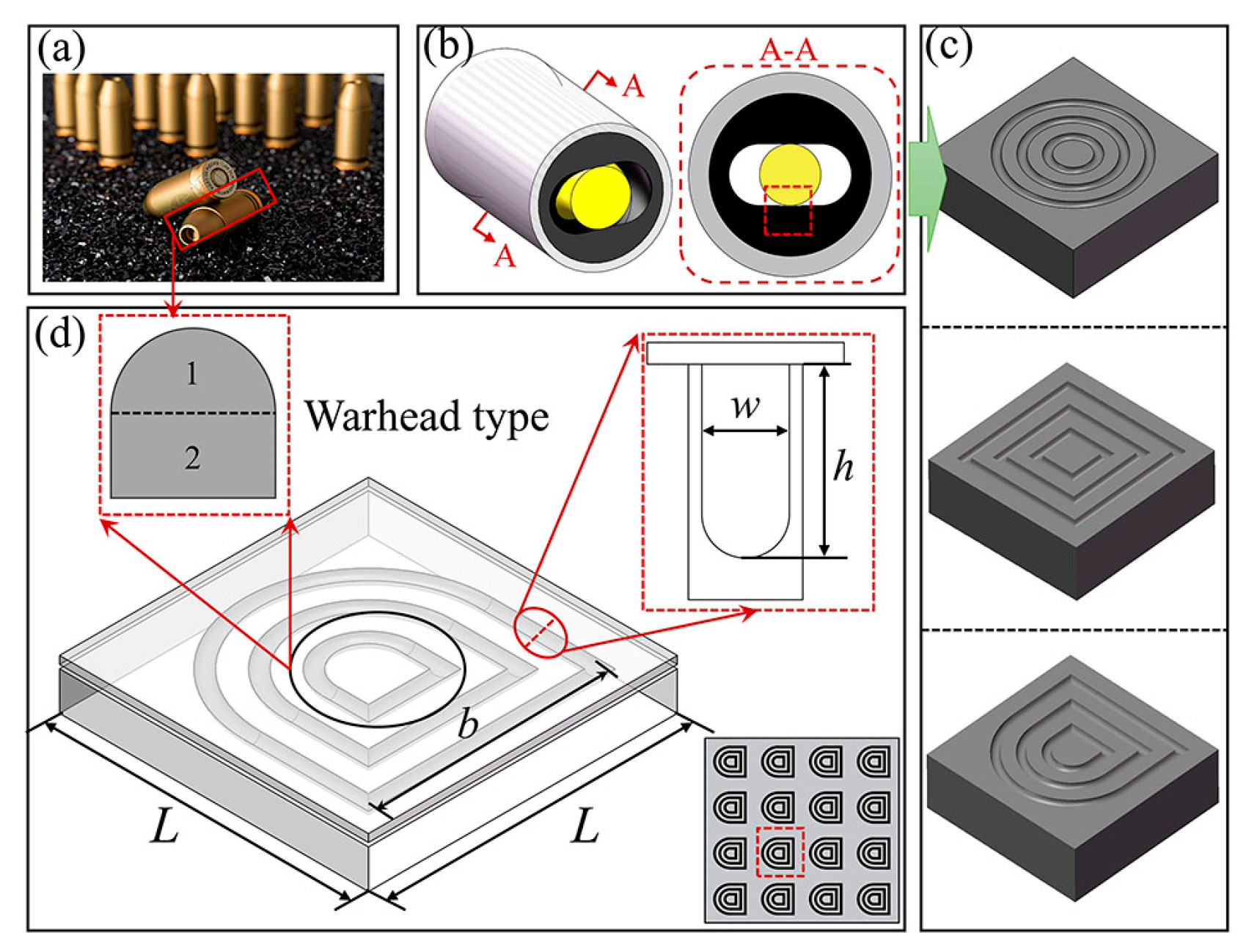
2.1. Geometric Modeling of the Stator Rubber Textured Surface
2.2. Mathematical Modeling of the Stator Rubber Textured Surface
3. Simulation Analysis of Stator Micro-Texture Surface Lubrication Flow Field
3.1. Simulation Model of the Rubber Texture Surface Flow Field of a Screw Pump Stator
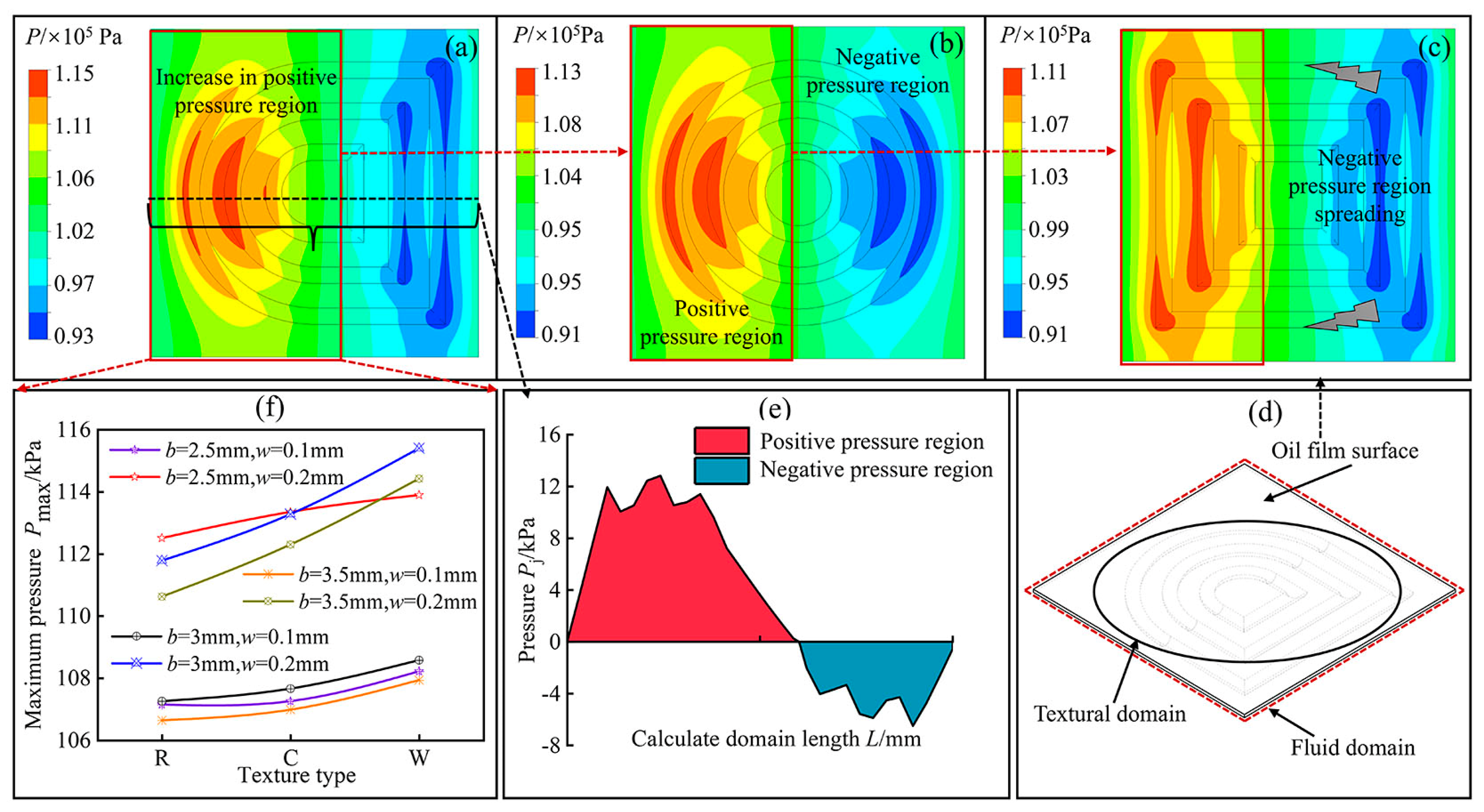
3.2. Influence of Texture Morphology on the Lubricating Properties of Stator Rubber Surfaces
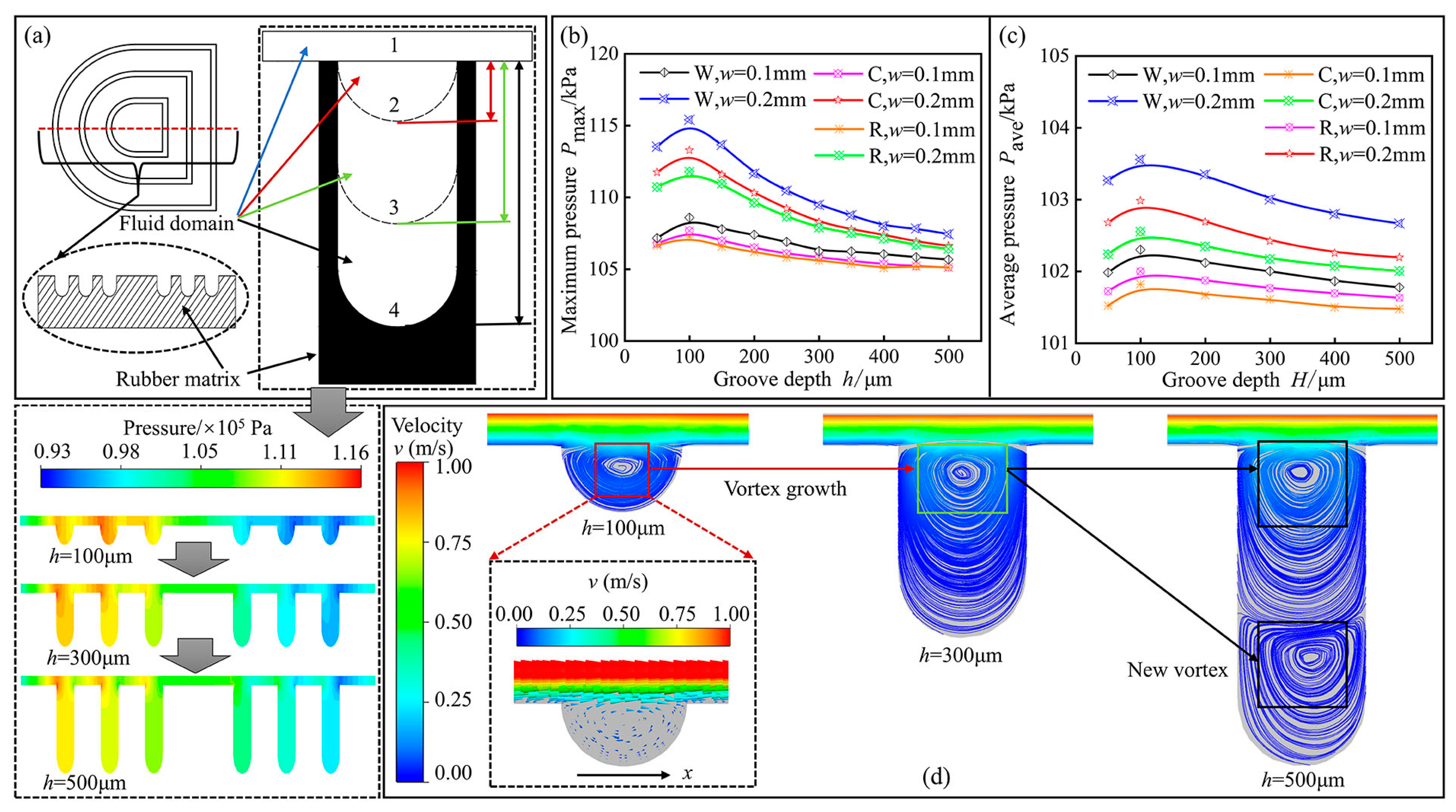
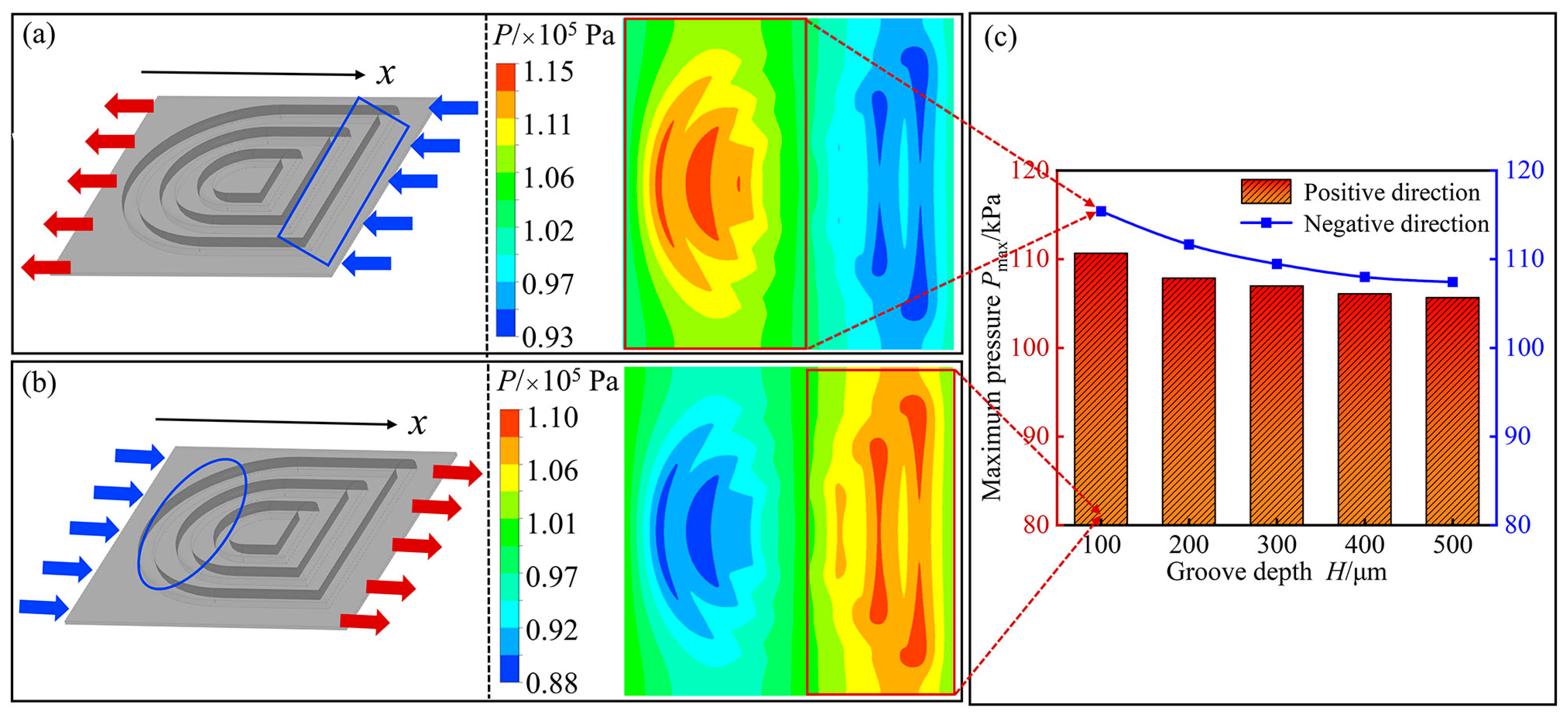
3.3. Influence of Texture Depth on the Lubricating Properties of the Stator Rubber Surface
3.4. Influence of Irregular Symmetry on the Lubrication Performance of Stator Rubber Surface
4. Screw Pump Textured Stator Rubber Friction Test
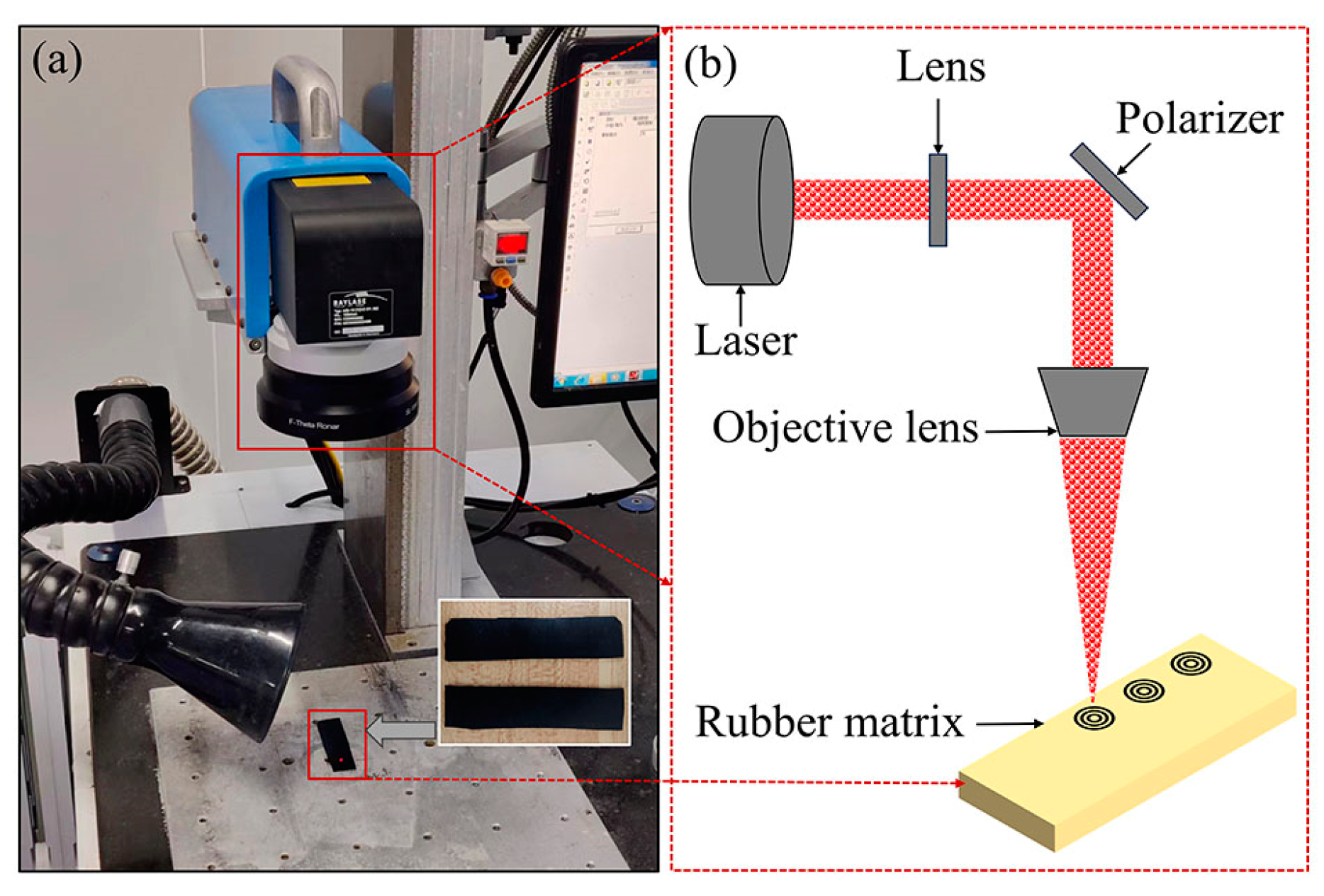
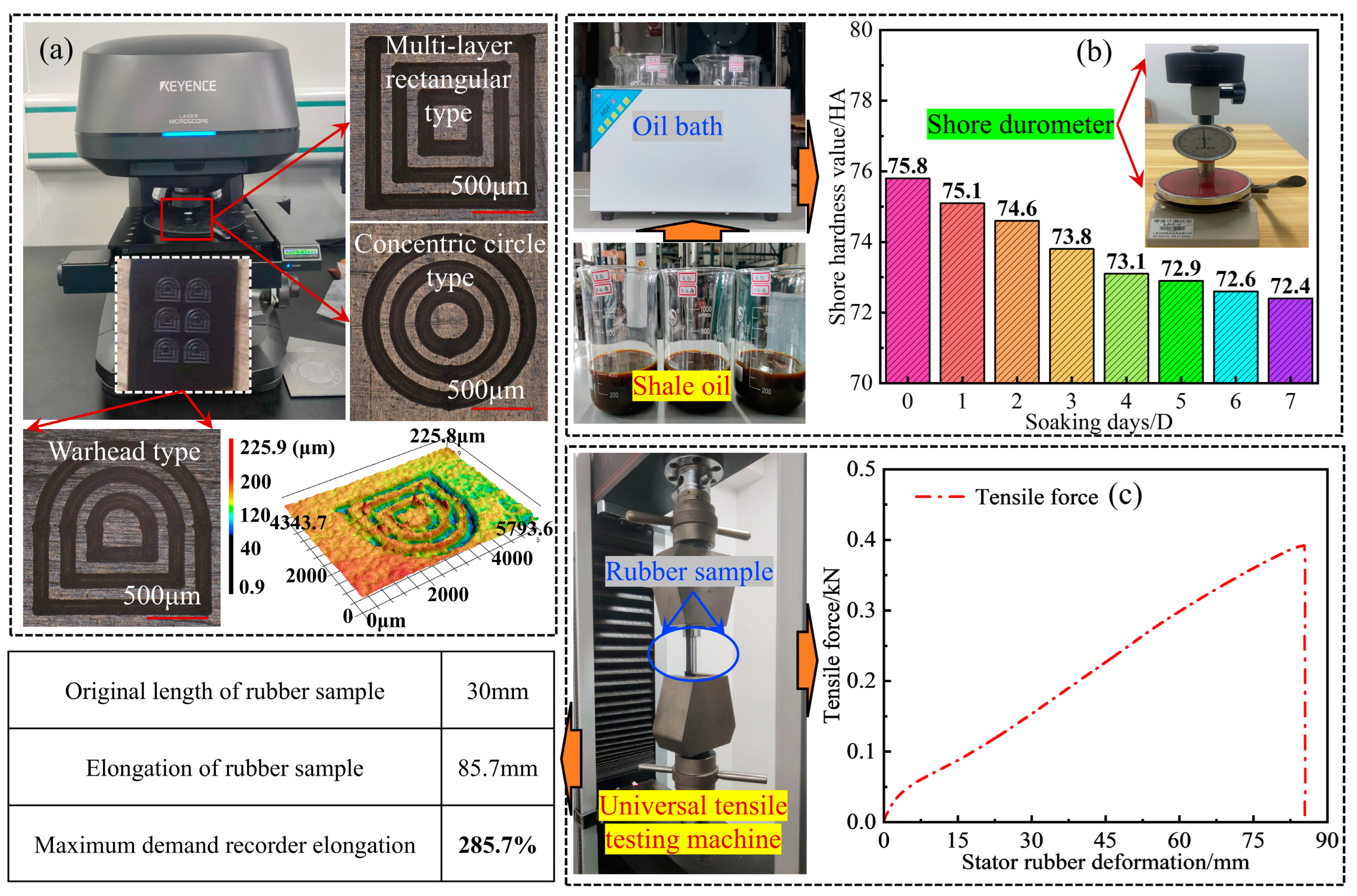
4.1. Preparation of the Textured Rubber Surface
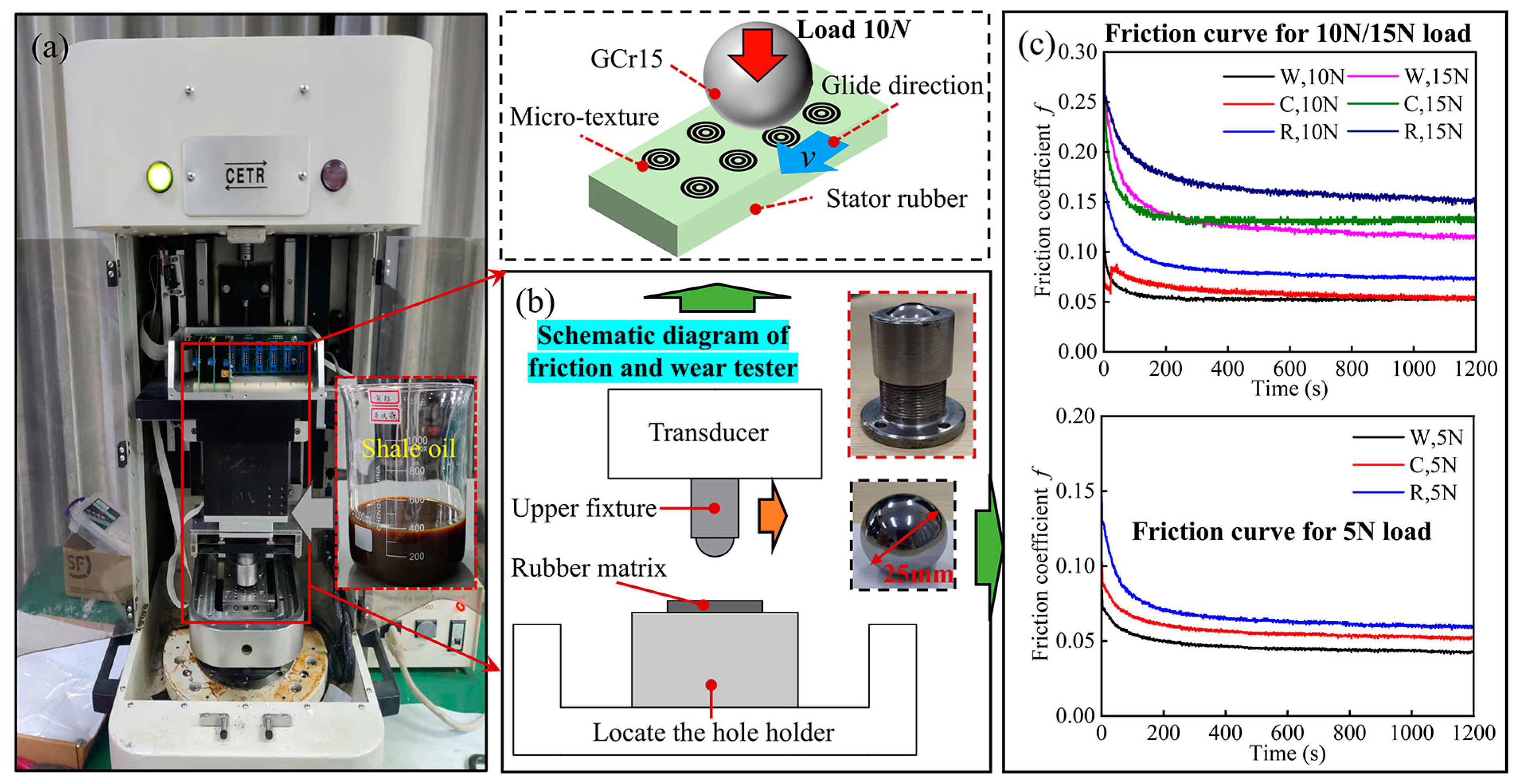
4.2. Actual Complex Well Fluid Textured Rubber Friction Test
5. Conclusions
- The friction performance of the warhead-type micro-texture was superior compared with the concentric circle and multilayer rectangular micro-textures. The head of the warhead-type texture featured a sharp converging wedge along the flow direction, with its irregular symmetry enhancing the hydrodynamic lubrication effect within the texture groove. This improvement significantly enhanced the lubrication characteristics between the stator rubber and the rotor of the screw pumps.
- The hydrodynamic lubrication performance of the textured stator rubber surface was highly influenced by the groove width. As the groove width increased, the pressure distribution on the upper wall of the oil film changed significantly, leading to an increase in additional net bearing capacity. This effectively enhanced the film pressure between the stator and rotor friction pairs.
- Under different textured morphology conditions, the maximum pressure on the wall surface of the textured stator rubber oil film initially increased with depth, followed by a decrease. As depth increased, the vortex volume within the grooves increased, which was accompanied by energy changes that further diminished the effect of dynamic pressure lubrication.
- Friction tests on the textured stator rubber of a progressive cavity pump show that under a load of 5 N, 10 N and 15 N, a friction frequency of 3 Hz, and an oil-rich condition, the average friction coefficient of the three types of textured stator rubber initially decreased and then gradually stabilized over time. The warhead texture exhibited an enhanced lubrication effect. Given all texture parameters, the optimal combination included a warhead-type texture size of 3 mm, a groove width of 0.2 mm, and a depth of 0.1 mm, resulting in an excellent dynamic pressure lubrication effect.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, H. A review of experiments and modeling of gas-liquid flow in electrical submersible pumps. Energies 2018, 11, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Zhu, S.; Pei, X.; Huang, P.; Tong, Z.; Wang, B.; Li, D. Submersible direct-drive progressing cavity pump rodless lifting technology. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Zhu, H.; Hu, B. Performance Research and Structure Optimization of Labyrinth Screw Pump. Micromachines 2021, 12, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishlyannikov, D.; Zverev, V.; Ivanchenko, A.; Zvonarev, I. Increasing the Time between Failures of Electric Submersible Pumps for Oil Production with High Content of Mechanical Impurities. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nie, D.; Cai, Z. The performance analysis of screw pump stator elastomers: Polyamide 6/hydrogenated nitrile blends: Mechanical, oil resistance and tribological properties. Polym. Test. 2023, 128, 108–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segu, D.Z.; Hwang, P. Friction control by multi-shape textured surface under pin-on-disc test. Tribol. Int. 2015, 91, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, H.L.; Hutchings, I.M. Some innovative surface texturing techniques for tribological purposes. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2014, 229, 429–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.; Masjuki, H.H.; Kalam, M.; Varman, R.A.; Mufti, M.H.; Mosarof, L.S. Surface texture manufacturing techniques and tribological effect of surface texturing on cutting tool performance: A review. Crit. Rev. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2016, 41, 447–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuir-Torres, J.I.; Arenas, M.A.; Perrie, W.; Dearden, G.; de Damborenea, J. Surface texturing of aluminium alloy AA2024-T3 by picosecond laser: Effect on wettability and corrosion properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 321, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Wood, R.J.K. Tribological performance of surface texturing in mechanical applications—A review. Surf. Topogr. Metrol. Prop. 2020, 8, 043001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.X.; Zhang, P.L.; Song, S.J.; Liu, Z.Y.; Yan, H.; Sun, T.Z.; Lu, Q.H.; Chen, Y. Research Status of Laser Surface Texturing on Tribological and Wetting Properties of Materials: A Review. Optik 2024, 298, 171581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, W.; Yin, H.; Jing, P.R. Research status of biomimetic surface texture in agriculture and forestry machinery. Agric. Mech. Res. 2024, 46, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zu, H.; Sun, J.; Ye, W.; Li, D. Study on dynamic mechanical characteristics and Fatigue life prediction of single progressing cavity pump. China Mech. Eng. 2024, 35, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Yu, X.; Zheng, X.; Hang, Q.; Yuan, T.; Li, D. Influence of recess shape on comprehensive lubrication performance of high speed and heavy load hydrostatic thrust bearing. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2019, 71, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Long, R. Effect of compound pit textures on the friction and wear of thrust cylindrical roller bearings under starved lubrication. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2023, 75, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Zhou, Z.; Yin, B.; Zhou, H.; Xu, B. Influence of microdimple on lubrication performance of textured plunger pump. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2021, 73, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Matsoukas, G. Numerical study of surface texturing for improving tribological properties of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene. Biosurface Biotribol. 2015, 1, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Q.; Bai, J.; Meng, X.; Ji, C.; Liang, Y. Drag reduction characteristics and flow field analysis of textured surface. Friction 2016, 4, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Liu, Y.; Yi, P.; Jia, H.; Zhang, N.; Sun, J. Anti-friction mechanism of sinusoidal texture with various intervals: The synergistic effect of dynamic pressure and tribofilm. Tribol. Int. 2022, 173, 107635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Fang, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Ge, H.; Zhu, H. Hydrodynamic lubrication of surfaces with asymmetric microdimple. Tribol. Trans. 2011, 54, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Khonsari, M. Numerical optimization of texture shape for parallel surfaces under unidirectional and bidirectional sliding. Tribol. Int. 2015, 82, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, Q.; Huang, Z.; Qian, W.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Lai, T. Influence of surface texture parameters of screw pump rotor on tribological properties of its friction pairs. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2021, 74, 964–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Huang, Z.; Qian, W.; Li, G. Study of the effect of laser textured rotors on the starting performance of metal–rubber mating pairs under different lubricating media environments. J. Eng. Tribol. 2024, 238, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Study on Surface Texturing Flow Field Characteristics and Anti-Friction Performance of Screw Pumped. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Petroleum University, Daqing, China, 2021. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Brizmer, V.; Kligerman, Y. A laser surface textured journal bearing. J. Tribol. 2012, 134, 031702-1–031702-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hua, M.; Dong, G.; Zhang, D.; Chin, K. A mixed lubrication model for studying tribological behaviors of surface texturing. Tribol. Int. 2016, 93, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Wood, R.J.K.; Gee, M.G.; Wang, L.; Pfleging, W. A novel surface texture shape for directional friction control. Tribol. Lett. 2018, 66, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vencl, A.; Ivanović, L.; Stojanović, B.; Zadorozhnaya, E.; Miladinović, S.; Svoboda, P. Surface texturing for tribological applications: A review. Proc. Eng. Sci. 2019, 1, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Shang, H.; Liao, C.; Huang, J.; Shi, B. Tribology performance of surface texturing plunger. Biomimetics 2019, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Lv, G.; Gao, Y. Research progress of improving surface friction properties by surface texture technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2021, 116, 2797–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, M.; Kumar, P.; Murtaza, Q. Surface texturing techniques to enhance tribological performance: A review. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 27, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Duan, J.; He, M.; Liu, Y.; Bao, Y. Study on antifriction mechanism of surface textured elliptical bearings. J. Tribol. 2023, 145, 011702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhao, B.; He, T.; Tu, L.; Lu, X.; Xu, H. Tribology and dynamic characteristics of textured journal-thrust coupled bearing considering thermal and pressure coupled effects. Tribol. Int. 2023, 180, 108292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, S.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, M. Feature-adaptive toolpath planning with enhanced surface texture uniformity for ultra-precision diamond milling of freeform optics. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2024, 323, 118220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, N.J.; Shahmohamadi, H.; Rahmani, R.; Rahnejat, H.; Garner, C.P. Combined experimental and multiphase computational fluid dynamics analysis of surface textured journal bearings in mixed regime of lubrication. Lubr. Sci. 2018, 30, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Wang, J.; Wei, S.; Hao, A.; Tao, J.; Chen, H. Non-symmetric distributions of solids deposition for solid-water stratified flow in deviated tubing strings. Pet. Sci. 2023, 20, 3048–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirubakaran, V.; Bhatt, D. Effect of different turbulence model on prediction of lean blowout limit for micro gas turbine combustor. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2020, 8, 1324–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheed, R.; Mohammadian, A.; Kheirkhah Gildeh, H. A comparison of standard k–ε and realizable k–ε turbulence models in curved and confluent channels. Env. Fluid Mech 2019, 19, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, X. Hydrodynamic lubrication of partial textured sliding journal bearing based on three-dimensional CFD. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2016, 68, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Puoza, J.; Zhang, P.; Yin, B.; Xie, X.; Din, J. Numerical simulation and experimental analysis of grease friction properties on textured surface. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Mech. Eng. 2019, 43, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ni, H.; Chen, H.; Wang, P. Numerical simulation and experimental investigation on tribological performance of micro-dimples textured surface under hydrodynamic lubrication. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2019, 163, 105095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Tang, H. Elastohydrodynamic lubrication characteristics of surface-textured slipper bearing in an axial piston pump. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2020, 42, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HU, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jian, G.; Zuo, M.; Fang, Y.; Mo, J. Study on lubrication properties of parallel slider surface with different shape compound texture. Surf. Technol. 2022, 51, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Hua, J.; Dong, G. Numerical optimization of asymmetric surface texturing under reciprocating sliding conditions. Tribol. Int. 2023, 180, 108310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Guo, S.; Wang, M. Tribological properties of surface microtexture friction pairs under different lubrication conditions. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1687814019881569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Cong, J.; Sun, J.; Shao, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, K.; Lv, G.; Yang, H. In Situ Microtexture Hydrodynamic Lubrication Characteristics of Ductile Cast Iron Crankshaft Surface. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 32, 7390–7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yang, J.; Gu, Q. Numerical study on the hydrodynamic lubrication performance improvement of bio-inspired peregrine falcon wing-shaped microtexture. Tribol. Int. 2024, 191, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Ji, J.; Tian, L. Numerical investigation of microtexture cutting tool on hydrodynamic lubrication. J. Tribol. 2017, 139, 054502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zeng, L.; Chen, X. Eccentric correction of piston based on bionic micro-texture technology for the gap seal hydraulic cylinder. Micro Nano Lett. 2019, 14, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Duan, J.; Bao, Y. Performance analysis of columnar convex-concave compound microtexture thrust bearing. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2024, 76, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Xing, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, D. Effect of composite bionic micro-texture on bearing lubrication and cavitation characteristics of slipper pair. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Niu, X.; Liu, C.; Shi, X.; Sun, Y.; Hao, Z.; Huang, S.; Wang, Y.; Tao, H. Study on the Tribological Properties of Multilayer Concentric Hexagonal Laser Texturing on Rubber Surfaces of Screw Pumps. Materials 2024, 17, 3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, X.; Niu, X.; Zheng, G.; Wei, W.; Wei, S.; Huang, S. Lubrication Characteristics of a Warhead-Type Irregular Symmetric Texture on the Stator Rubber Surfaces of Screw Pumps. Lubricants 2024, 12, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12110397
Liu X, Sun Y, Liu C, Shi X, Niu X, Zheng G, Wei W, Wei S, Huang S. Lubrication Characteristics of a Warhead-Type Irregular Symmetric Texture on the Stator Rubber Surfaces of Screw Pumps. Lubricants. 2024; 12(11):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12110397
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xinfu, Yi Sun, Chunhua Liu, Xiangzhi Shi, Xinglong Niu, Gang Zheng, Wei Wei, Songbo Wei, and Shouzhi Huang. 2024. "Lubrication Characteristics of a Warhead-Type Irregular Symmetric Texture on the Stator Rubber Surfaces of Screw Pumps" Lubricants 12, no. 11: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12110397
APA StyleLiu, X., Sun, Y., Liu, C., Shi, X., Niu, X., Zheng, G., Wei, W., Wei, S., & Huang, S. (2024). Lubrication Characteristics of a Warhead-Type Irregular Symmetric Texture on the Stator Rubber Surfaces of Screw Pumps. Lubricants, 12(11), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants12110397




