An Experimental Investigation of the Electrical Tribological Characteristics of a Copper–Silver Alloy Contact Wire/Novel Pure Carbon Slider
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Apparatus and Test Parameters
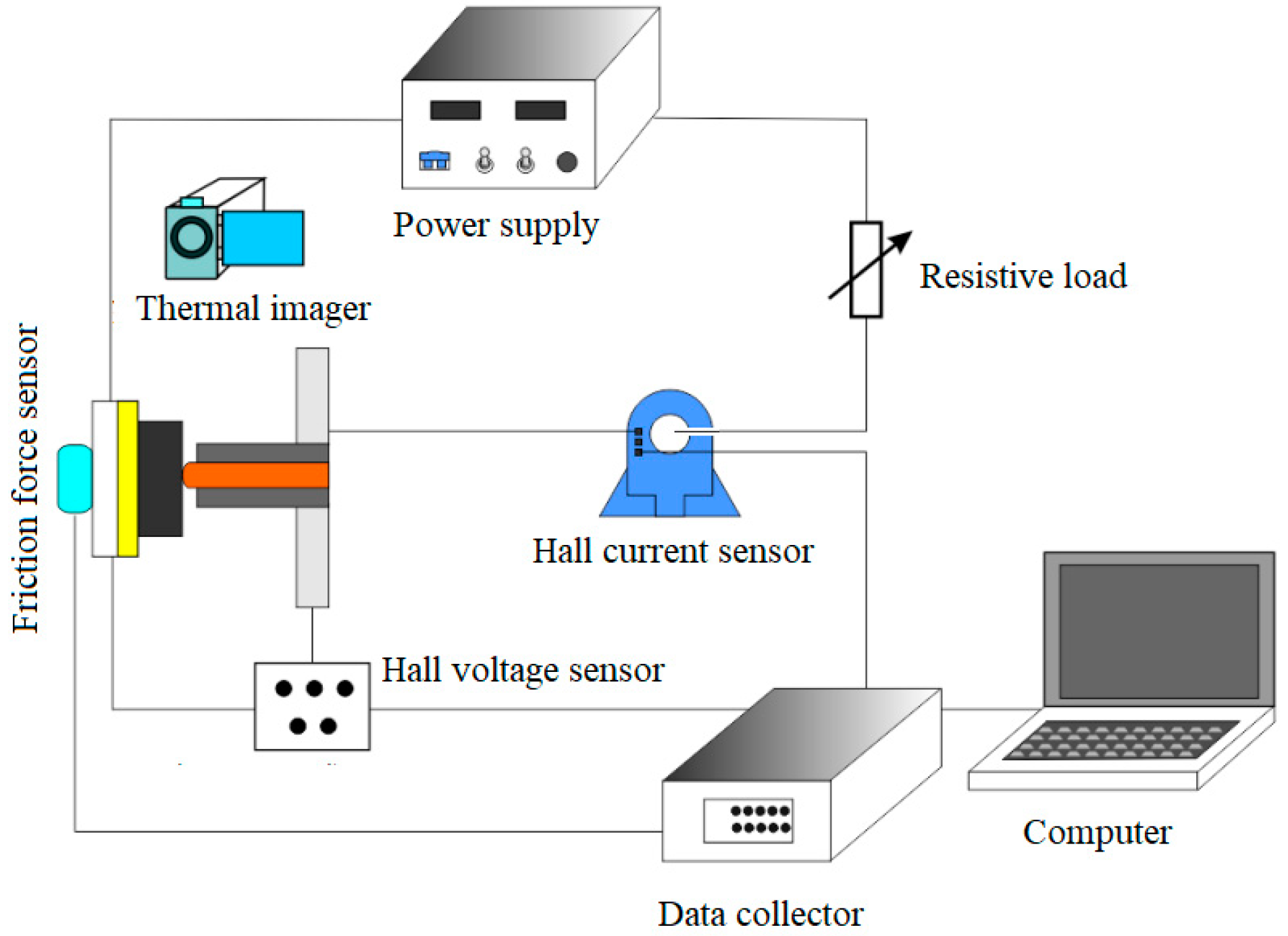
2.1. Experimental Apparatus
2.1.1. Experimental Machine
2.1.2. Data Measurement System and Passing Current Circuit
2.2. Specimen
2.2.1. Physical Parameters and Composition of the Cu-Ag Line
2.2.2. Physical Parameters and Components of the Pure Carbon Slider
2.3. Specimen Preparation Method
2.4. Arc Energy Calculation Method
2.5. Test Parameters
2.6. Test Procedures
3. Test Results
3.1. Change in Sliding Coefficient of Friction with Sliding Speed
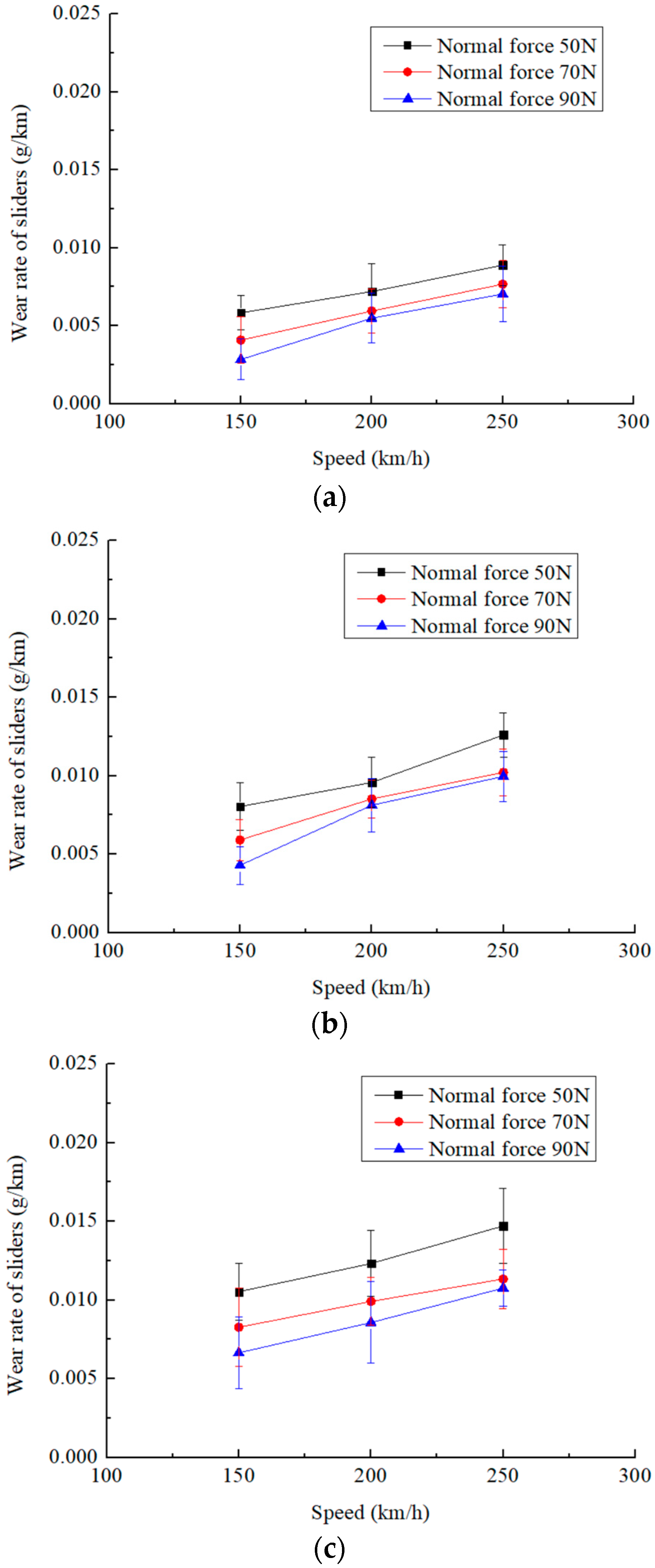
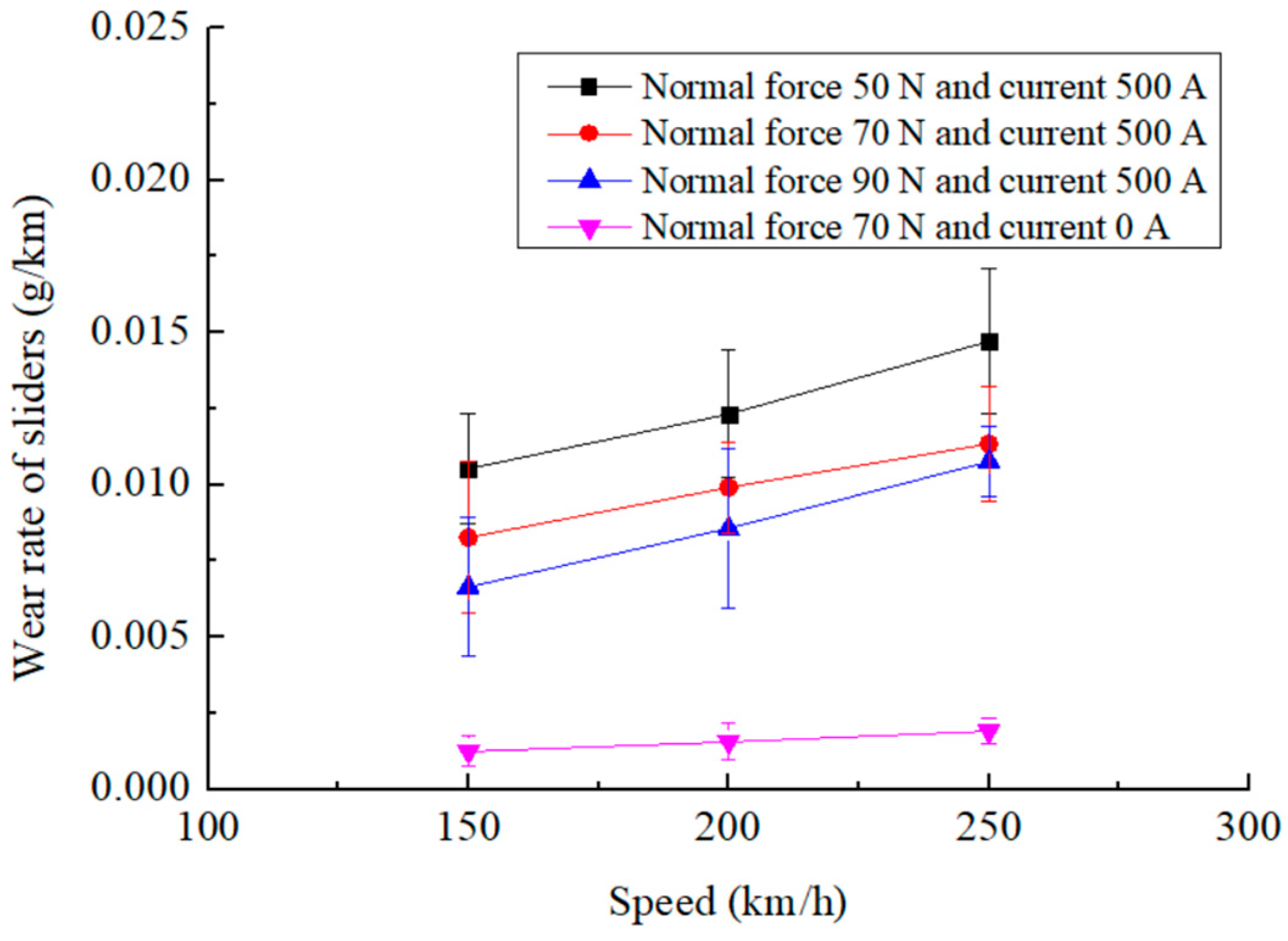
3.2. Changes in Wear Rate of Sliders with Slip Speed
3.3. Variations in Wear Rate of Sliders with Electric Current
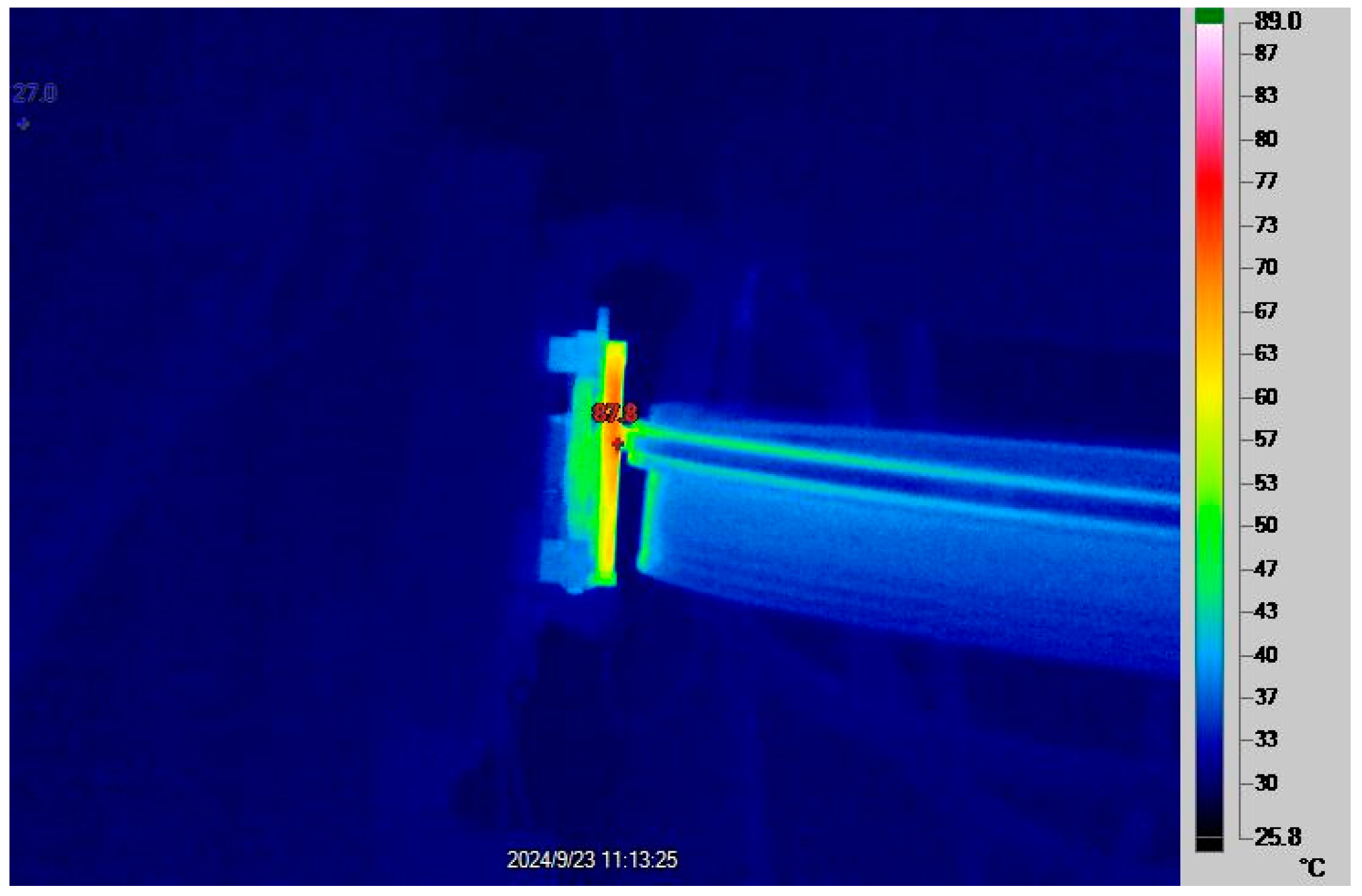
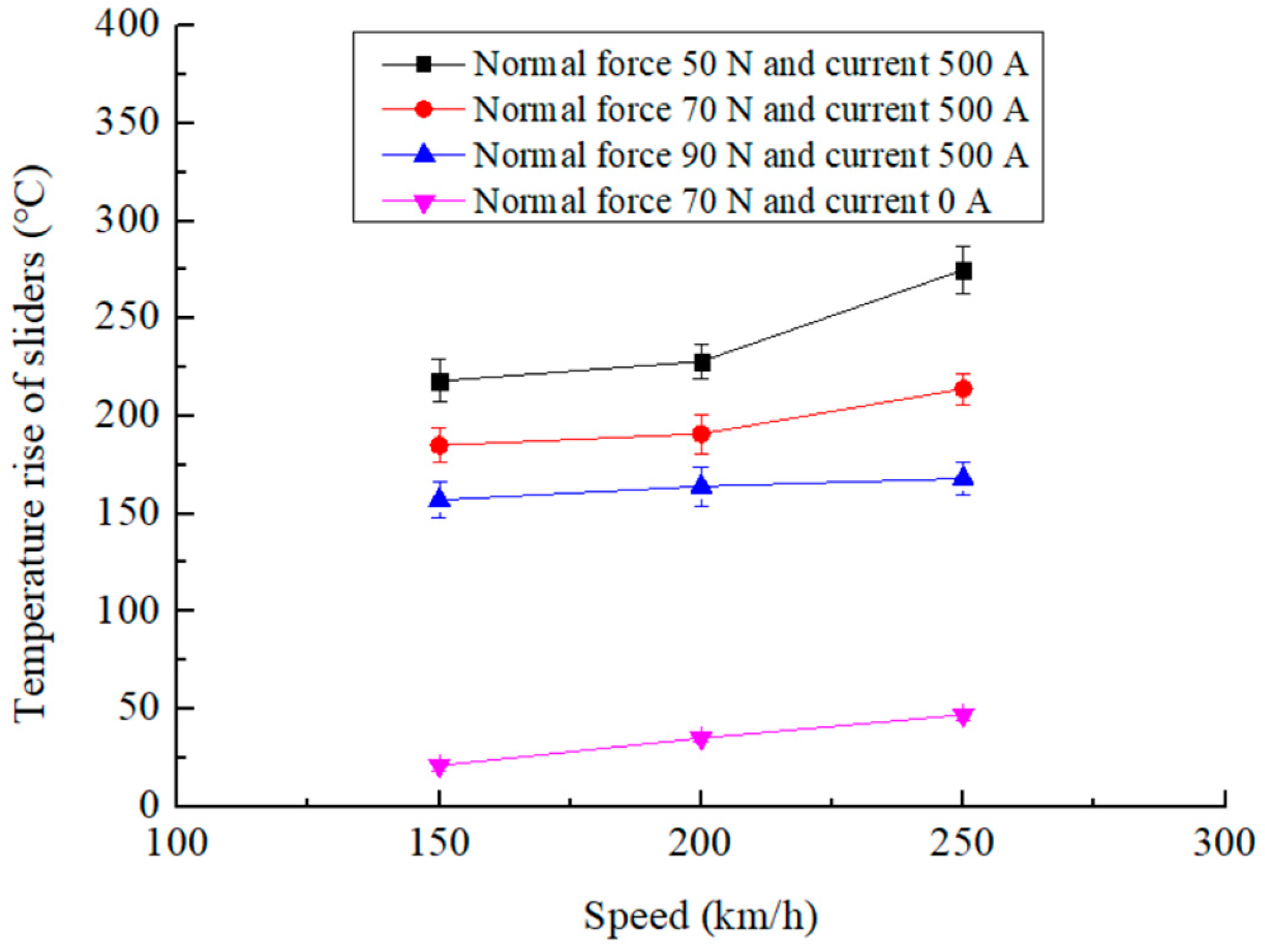
3.4. Changes in Temperature Rise of Sliders as a Function of Electric Current
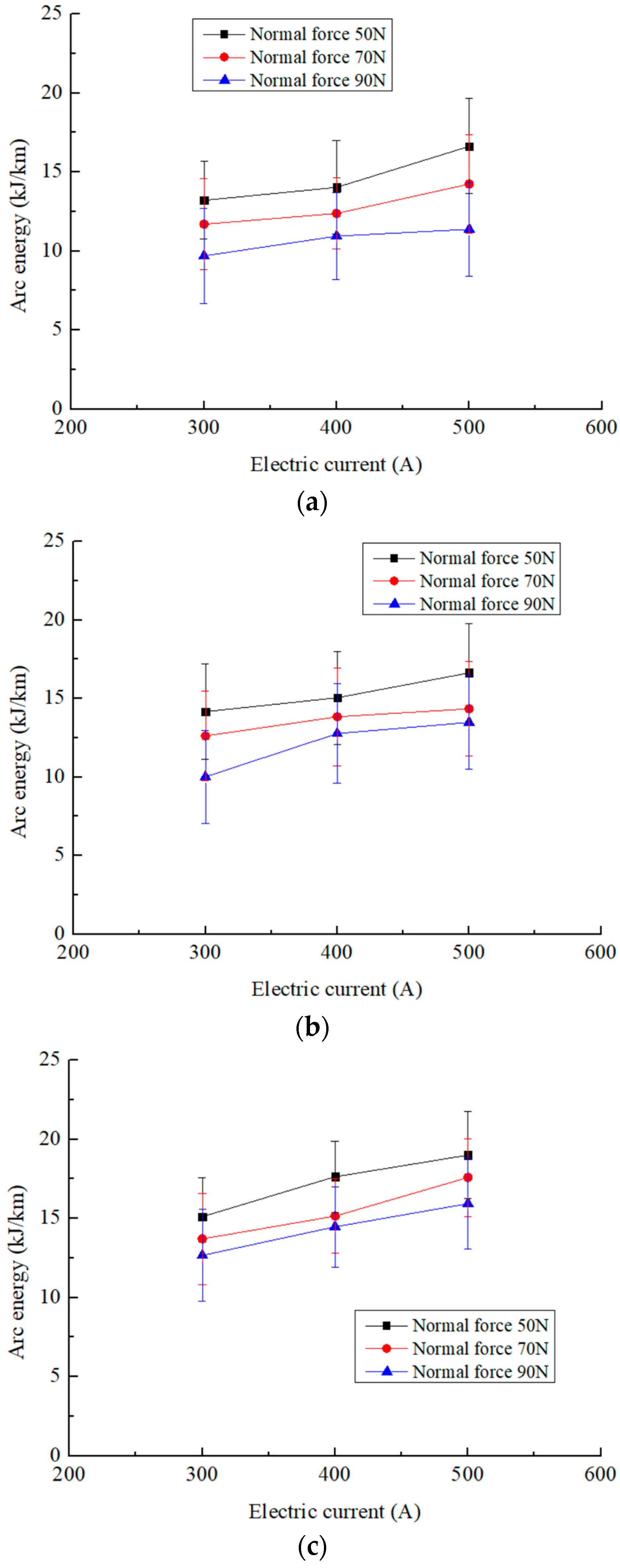
3.5. Changes in Arc Energy with Electric Current
4. Discussion
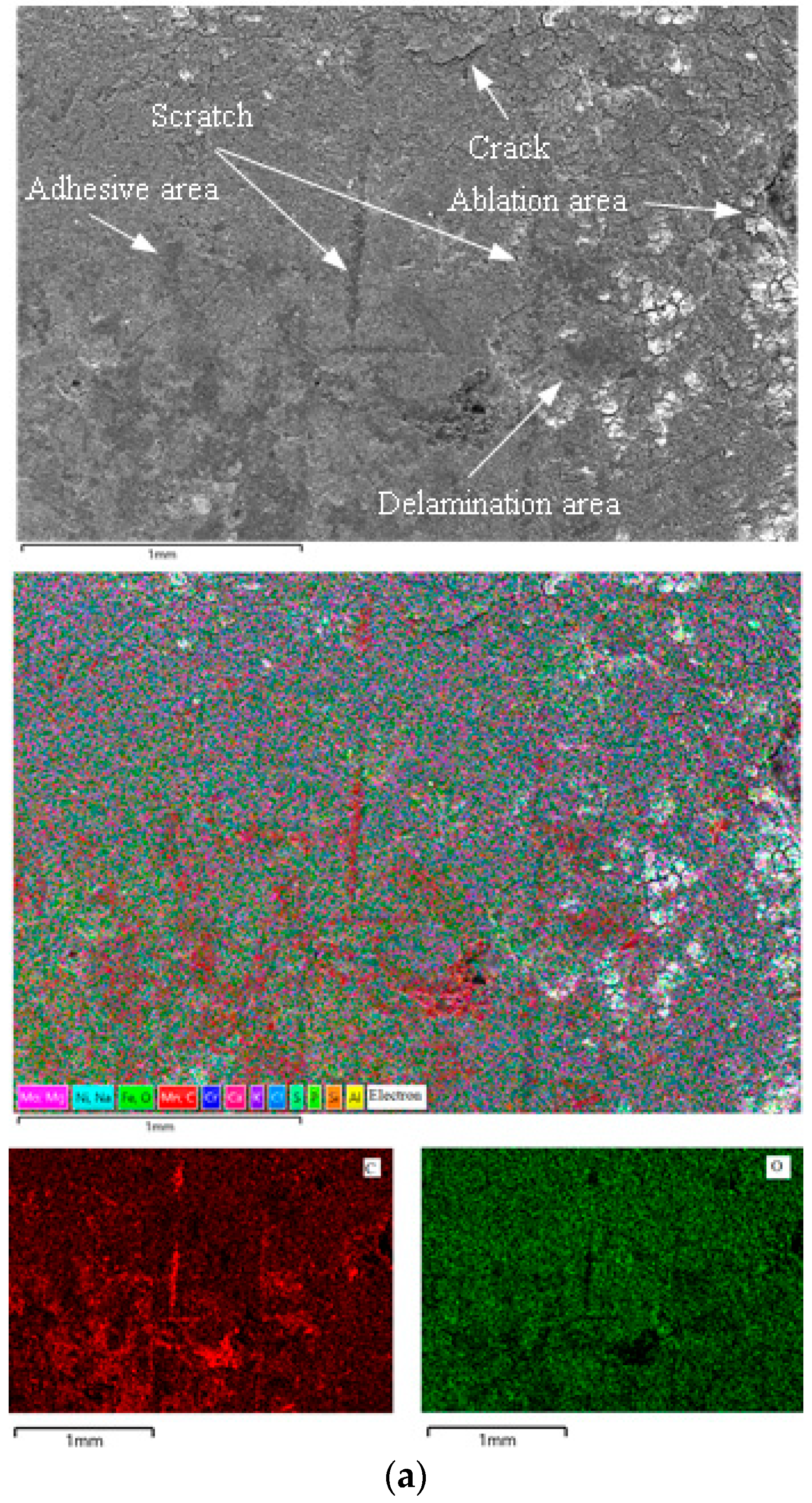
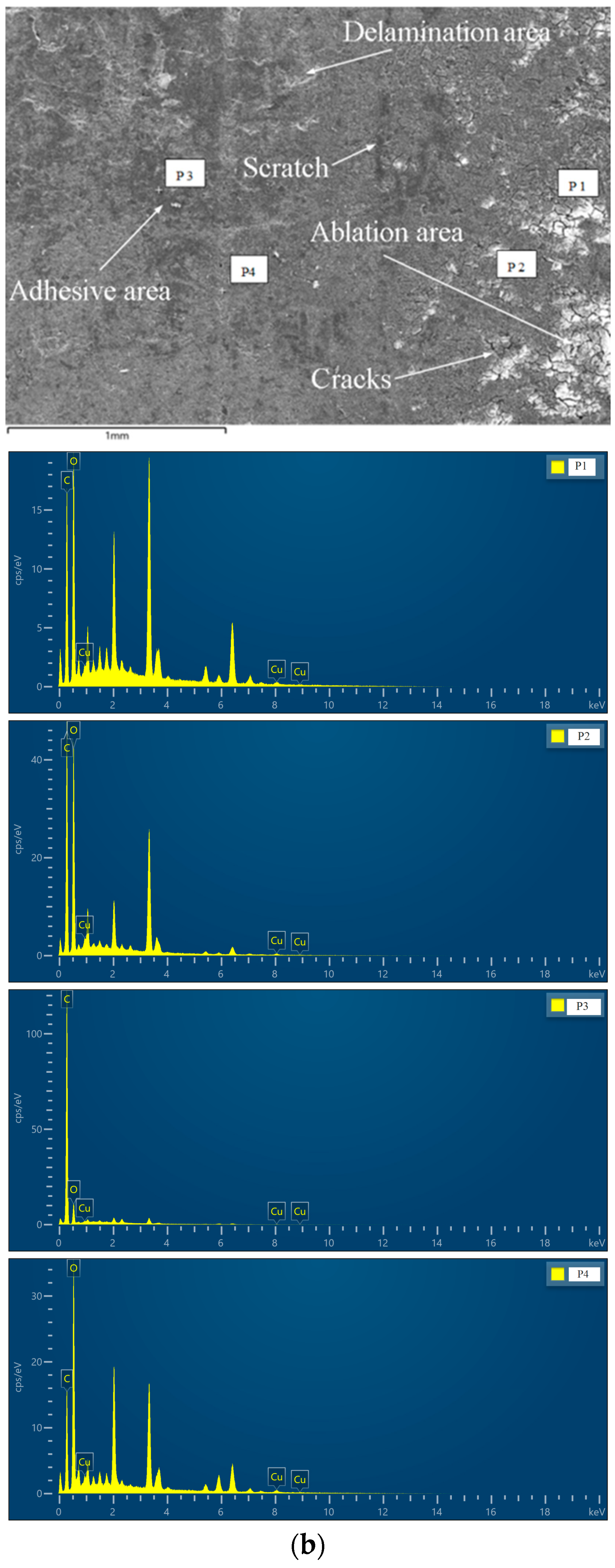
4.1. Wear Mechanism of Sliders with Current
4.2. Impact of Electric Current on the Wear Rate of Sliders
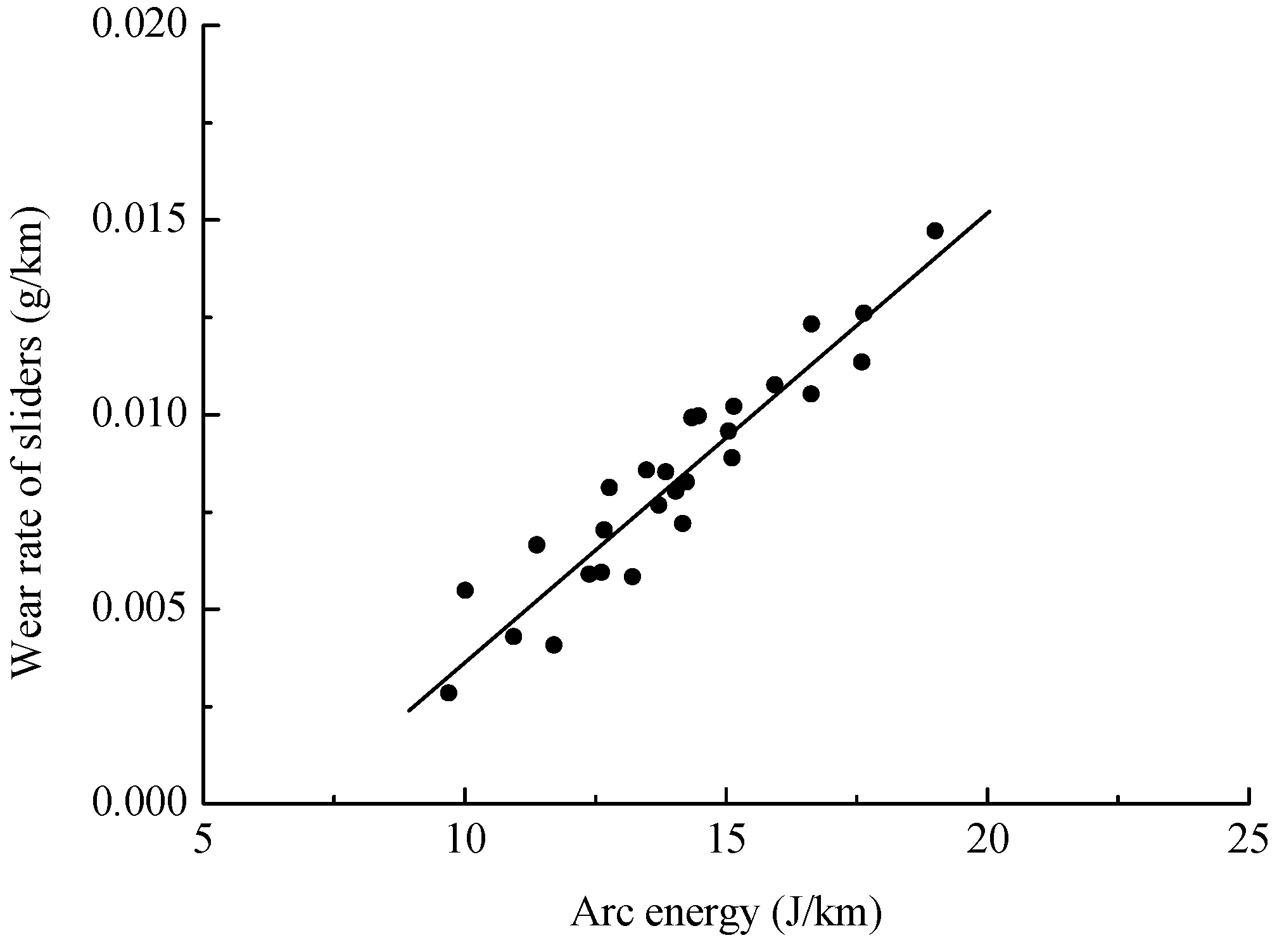
4.3. Effect of Arc Energy on the Slider Wear Rate
5. Conclusions
- When the new pure carbon slider is sliding on a Cu-Ag line with a current, the abrasion mechanisms of sliders are mainly arc ablation, adhesive abrasion, abrasive abrasion, and delamination abrasion. Among these wear mechanisms, arc ablation stands out as the predominant wear mechanism affecting the sliders.
- The coefficient of friction of the new pure carbon slider sliding on a Cu-Ag line in the presence of an electric current decreases with the sliding speed when other test parameters remain unchanged. Within the range of the test parameters, the coefficient of friction varies from 0.20 to 0.28.
- The wear rate of the pure carbon slider increases with the electric current when the other test parameters remain unchanged. Within the range of the test parameters, the slider wear rate varies from 0.0028 g/km to 0.0147 g/km.
- When the other test parameters remain unchanged, the temperature of the pure carbon slider increases with the electric current. Within the range of the test parameters, the temperature rise of the slider varies from 89.4 °C to 269.2 °C.
- There is a significant correlation between the arc energy and slider wear. Suppressing the arc ablation can significantly decrease the wear of new pure carbon sliders sliding on a Cu-Ag line with an electric current.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, T.H.; Song, C.F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Niu, K.; Liu, Z.L.; Wang, L.; Sun, C.; Li, M.J.; Zhang, Y.Z. Current-carrying contact character and wear behavior of an elastic ring at different rolling speeds. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 131, 105825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, G.M. Tribological performance of rigid overhead lines against pantograph sliders under DC passage. Tribol. Int. 2020, 151, 106538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.J.; Chen, G.X.; Gao, G.Q.; Wu, G.N.; Zhang, W.H. Experimental research on the friction and wear properties of a contact strip of a pantograph–catenary system at the sliding speed of 350 km/h with electric current. Wear 2015, 332–333, 949–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senouci, A.; Frene, J.; Zaidi, H. Wear mechanism in graphite-copper electrical sliding contact. Wear 1999, 225–229, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, H.; Kato, K. Wear mechanism of copper alloy wire sliding against ironbase strip under electric current. Wear 1998, 216, 79–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.-S.; Liu, X.-L.; Peng, T.; Xiao, Q.; Shen, M.-X.; Zhang, D.; Cao, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, W.-B.; Chen, D.-Y. Study on the current-carrying friction and wear behaviors of a novel copper-impregnated carbon skateboard containing tungsten disulfide. Tribol. Int. 2025, 204, 110430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.-L.; Guan, X.; Zhong, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.-L.; Zhang, S.; Zheng, Y.-T.; Gao, M.-S.; Chen, D.-Y.; et al. Effect of different gaps in the conductor rail joints on the current-carrying wear performance of carbon skateboards/conductive rail contact. Wear 2024, 536–537, 205172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Song, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Hou, X.; Lu, H.; Zhang, Y. Current-carrying tribological properties of an elastic roll ring under different currents. Wear 2023, 514–515, 204590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Song, C.; Wu, H.; Lv, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Effect of relative humidity on the current-carrying tribological properties of Cu–C sliding contact pairs. Wear 2022, 492–493, 204219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Fu, L.; Jiang, G.; Cui, X.; Hu, B.; Wang, K. Study on the delamination wear and its influence on the conductivity of the carbon contact strip in pantograph-catenary system under high-speed current-carrying condition. Wear 2021, 477, 203823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Huang, P.; Cheng, C.; Zhang, M.; Ma, R. Influence of arc discharge on the temperature and wear behaviors of the contact strip in pantograph-rigid catenary systems under AC conditions. Wear 2024, 546–547, 205368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, G.M.; Fu, W.M.; Chen, G.X.; Zhang, W.H. Effect of high-density current on the wear of carbon sliders against Cu–Ag wires. Wear 2020, 452–453, 203275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Chen, G. Experimental study on the wear mechanism of the contact line in rigid pantograph-catenary systems. Tribol. Int. 2023, 187, 108739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucca, G.; Collina, A. A procedure for the wear prediction of collector strip and catenary wire in pantograph–catenary system. Wear 2009, 266, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, S.; Navik, P.; Collina, A.; Bucca, G.; Rønnquist, A. Contact point lateral speed effects on contact strip wear in pantograph-catenary interaction for railway operations under 15 kV 16.67 Hz AC systems. Wear 2021, 486–487, 204103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, S.; Kato, K. Effect of arc discharge on the wear rate and wear mode transition of a copper-impregnated metallized carbon strip sliding against a copper disk. Tribol. Int. 1999, 32, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, S.; Kato, K. Effect of arc discharge on wear rate of Cu-impregnated carbon strip in unlubricated sliding against Cu trolley under electric current. Wear 1998, 216, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.X.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, W.H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.D.; Zhou, Z.R. Experimental study on arc ablation occurring in a contact strip rubbing against a contact wire with electrical current. Tribol. Int. 2013, 61, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucca, G.; Collina, A. Electromechanical interaction between carbon-based pantograph strip and copper contact wire: A heuristic wear model. Tribol. Int. 2015, 92, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapas, D.; Benson, F.A.; Hackam, R.; Evison, P.R. Wear in simulated railway overhead current collection systems. Wear 1988, 126, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreivaitis, R.; Andriusis, A.; Treinyte, J.; Kupcinskas, A.; Jankauskas, V. Investigation of the lubricating conditions in a reciprocating sliding tribotest with applied electric voltage. Lubricants 2024, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Du, M.; Zuo, X. Influence of electric current on the temperature rise and wear mechanism of copper–graphite current-carrying friction pair. J. Tribol. 2022, 144, 101701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandin, M.; Wiklund, U. Wear phenomena and tribofilm formation of copper/copper-graphite sliding electrical contact materials. Wear 2018, 398–399, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Du, S.M.; Song, C.F.; Yang, Z.H.; Shangguan, B. Tribological properties of pure carbon strip affected by dynamic contact force during current-carrying sliding. Tribol. Int. 2018, 123, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argibay, N.; Sawyer, W.G. Low wear metal sliding electrical contacts at high current density. Wear 2012, 274, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Cu-Ag Line | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Ag | O | Bi | Pb | Other |
| 99.74 | 0.10 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.03 |
| Slider Material | Pure Carbon |
|---|---|
| Hardness(HRC) | 74 |
| Density(t·m−3) | 2.06 |
| Slider Material | Pure Carbon |
|---|---|
| Cu | 1.17 |
| C | 98.7 |
| Cr | <0.005 |
| Si | <0.088 |
| Ti | <0.005 |
| Sn | <0.005 |
| Fe | 0.06 |
| Al | 0.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, L.; Yang, C.; Xing, T.; Yu, Q. An Experimental Investigation of the Electrical Tribological Characteristics of a Copper–Silver Alloy Contact Wire/Novel Pure Carbon Slider. Lubricants 2025, 13, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13020087
Pan L, Yang C, Xing T, Yu Q. An Experimental Investigation of the Electrical Tribological Characteristics of a Copper–Silver Alloy Contact Wire/Novel Pure Carbon Slider. Lubricants. 2025; 13(2):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13020087
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Like, Caizhi Yang, Tong Xing, and Qun Yu. 2025. "An Experimental Investigation of the Electrical Tribological Characteristics of a Copper–Silver Alloy Contact Wire/Novel Pure Carbon Slider" Lubricants 13, no. 2: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13020087
APA StylePan, L., Yang, C., Xing, T., & Yu, Q. (2025). An Experimental Investigation of the Electrical Tribological Characteristics of a Copper–Silver Alloy Contact Wire/Novel Pure Carbon Slider. Lubricants, 13(2), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13020087




