Research on Debris Characteristics and Wear Mechanism of Gear Material 18CrNiMo7-6 Used in Mining Reducer Under Dust-Contaminated Lubrication
Abstract
:1. Introduction
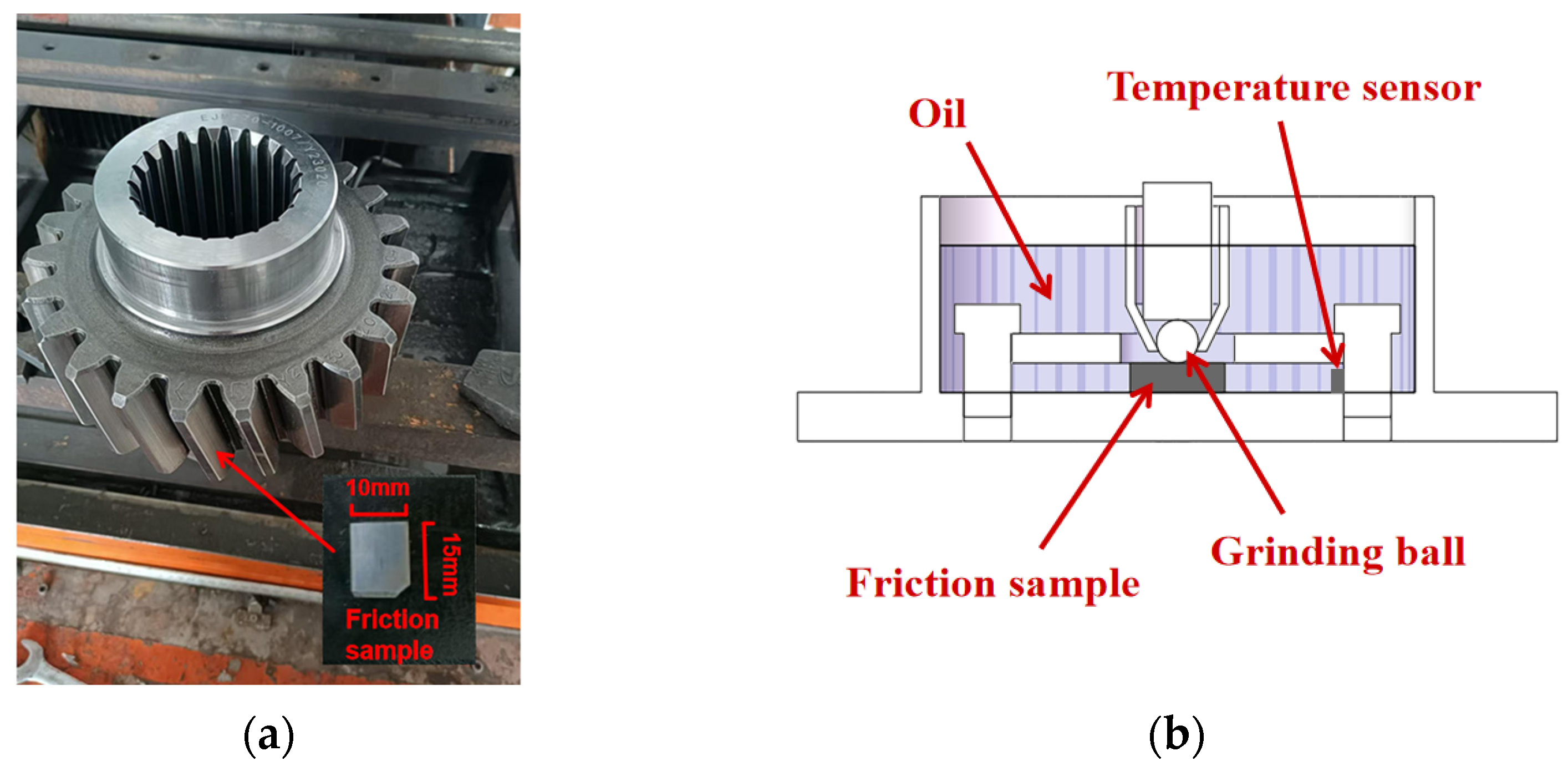
2. Investigation Test Setup
3. Test Result Observations
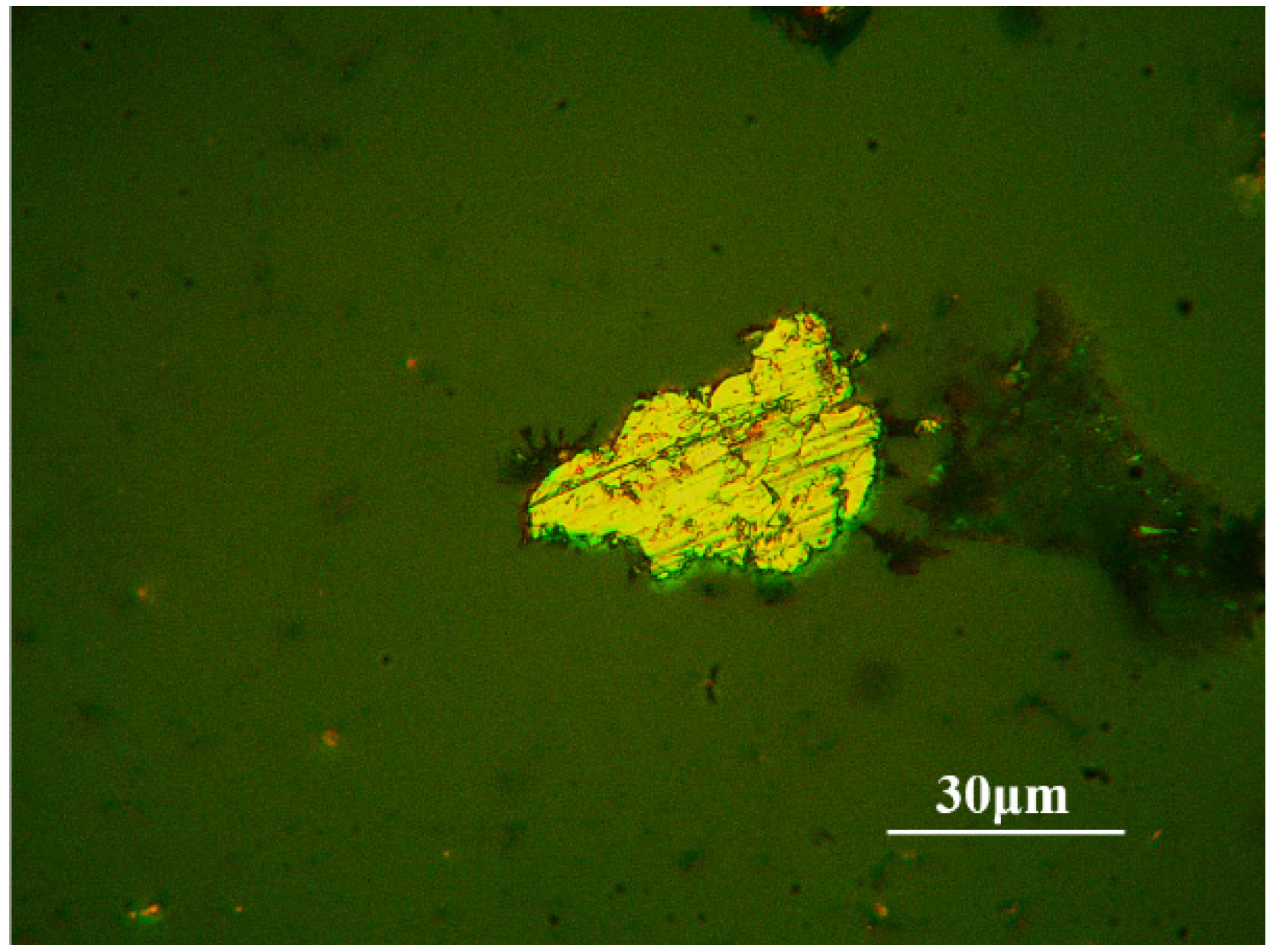
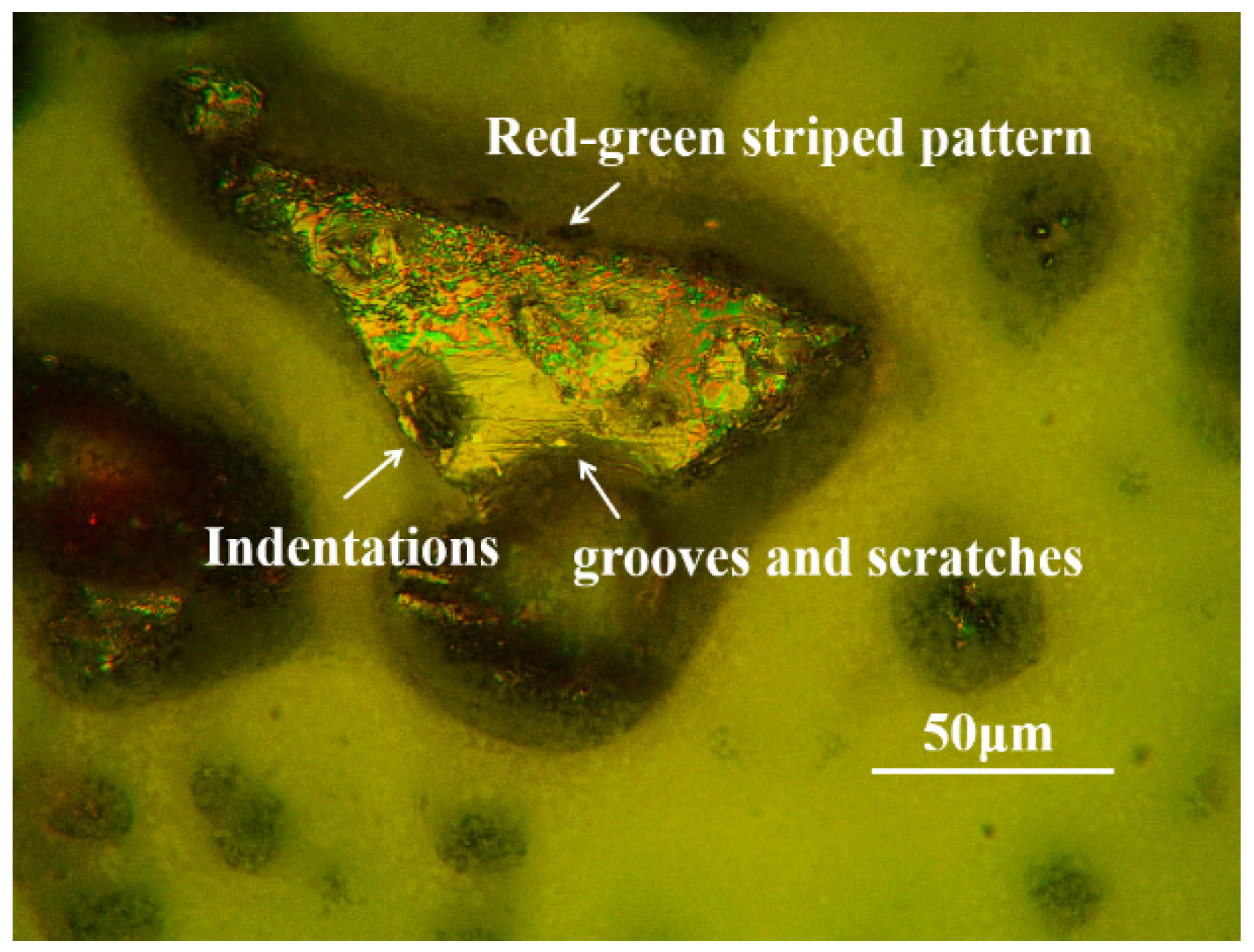
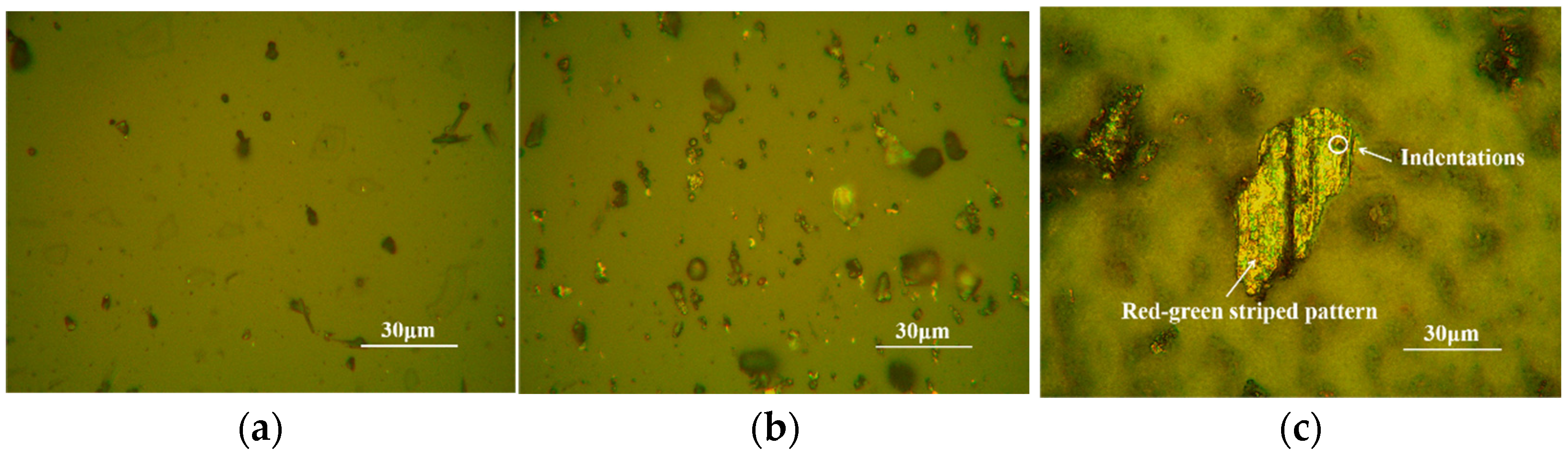
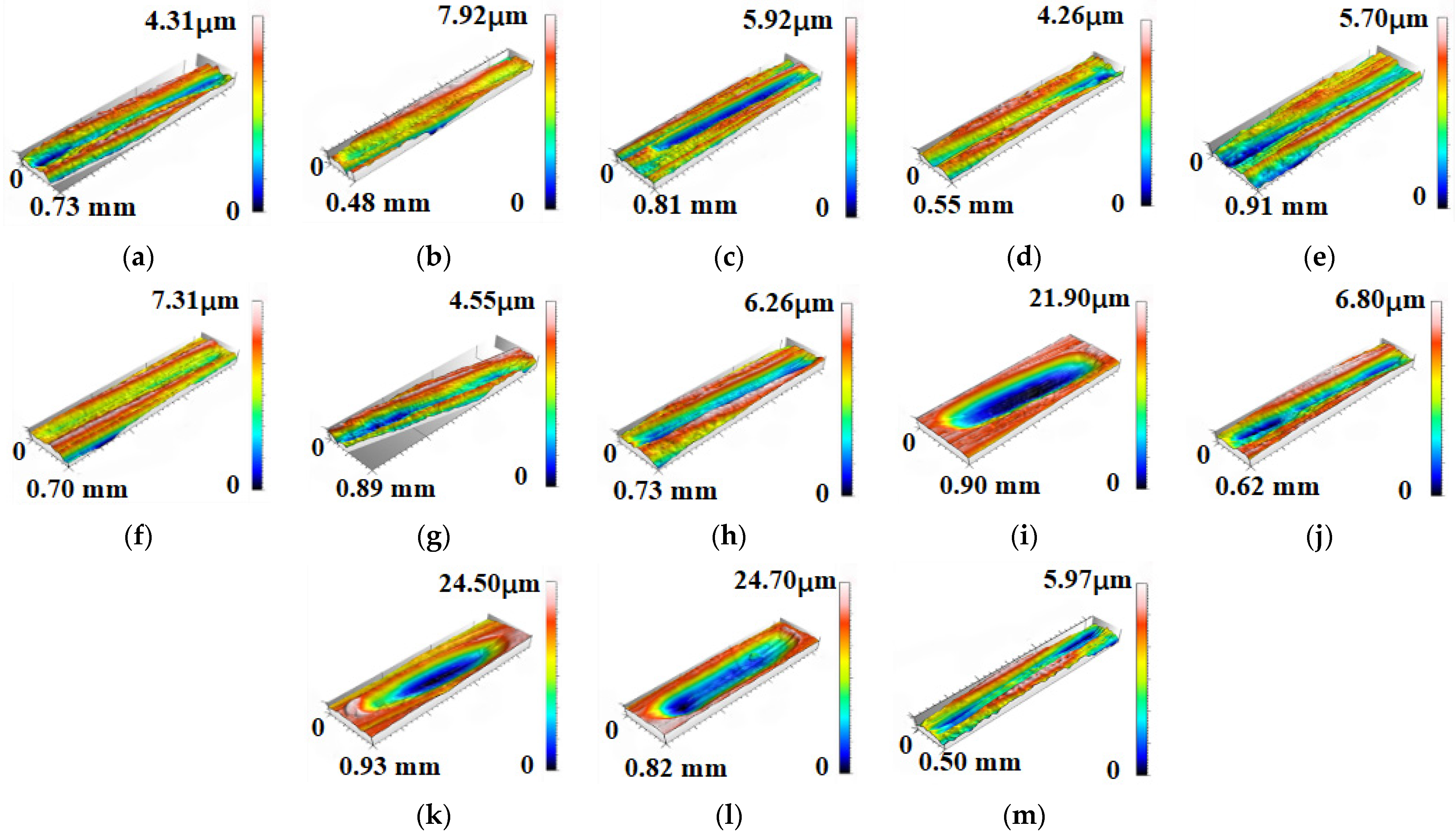
3.1. Contaminant-Free Debris Grain Characteristics
3.2. Characterization of Debris Particles Under Coal Dust Contamination
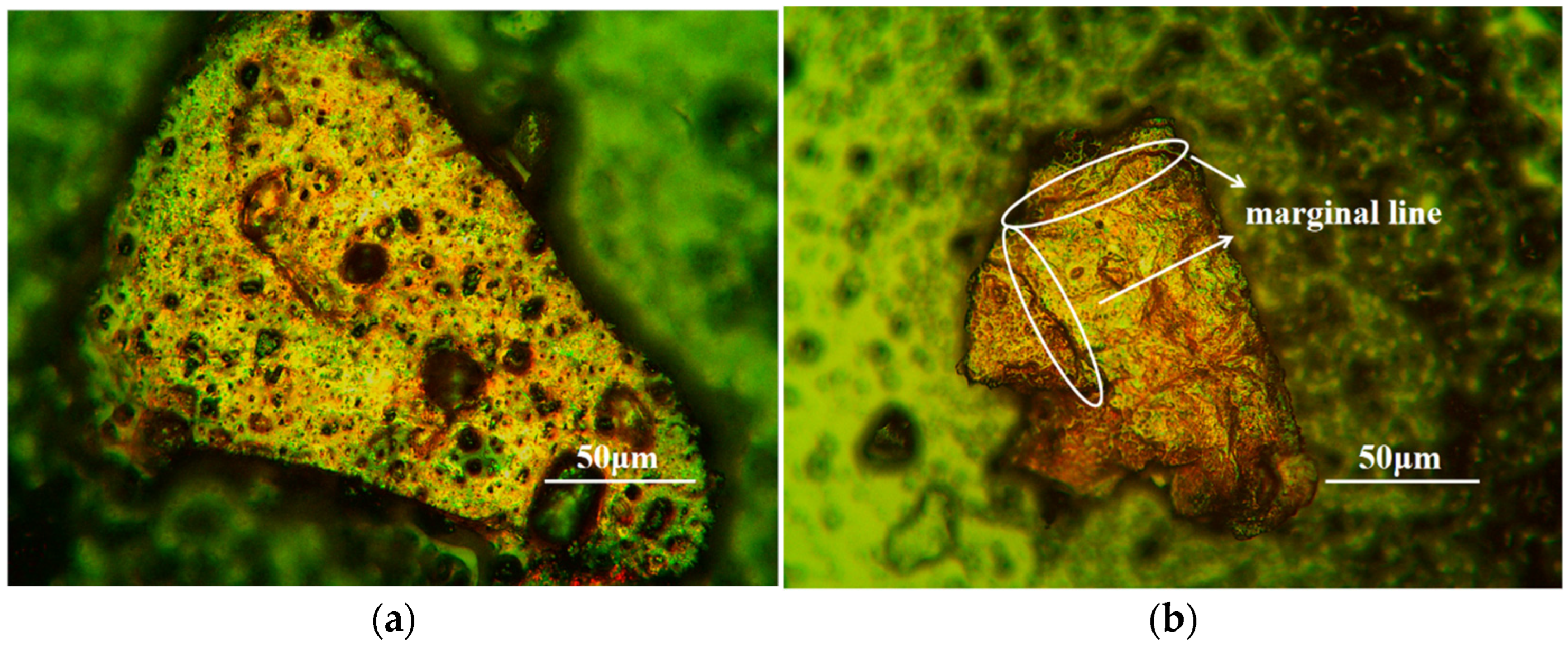
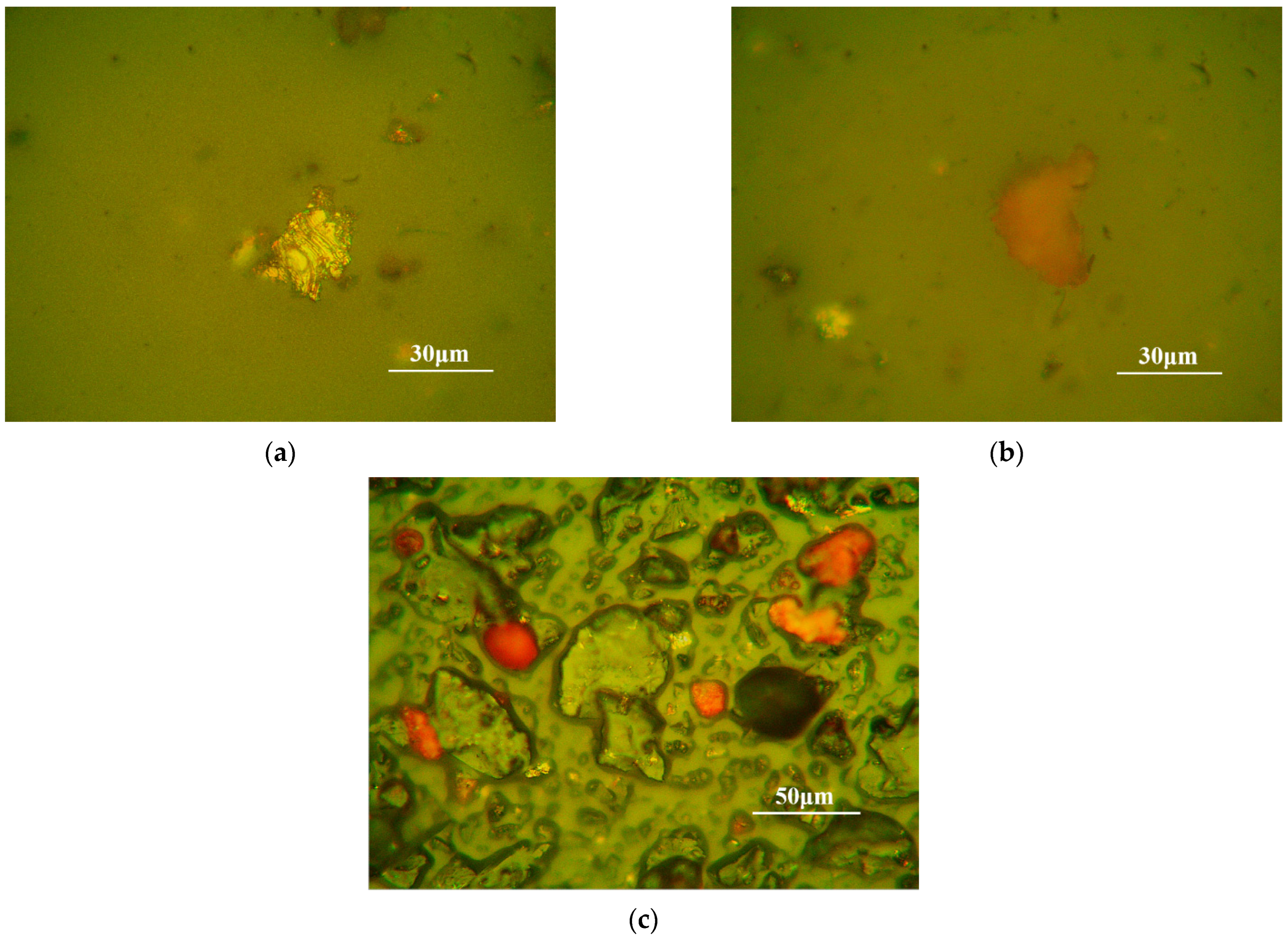
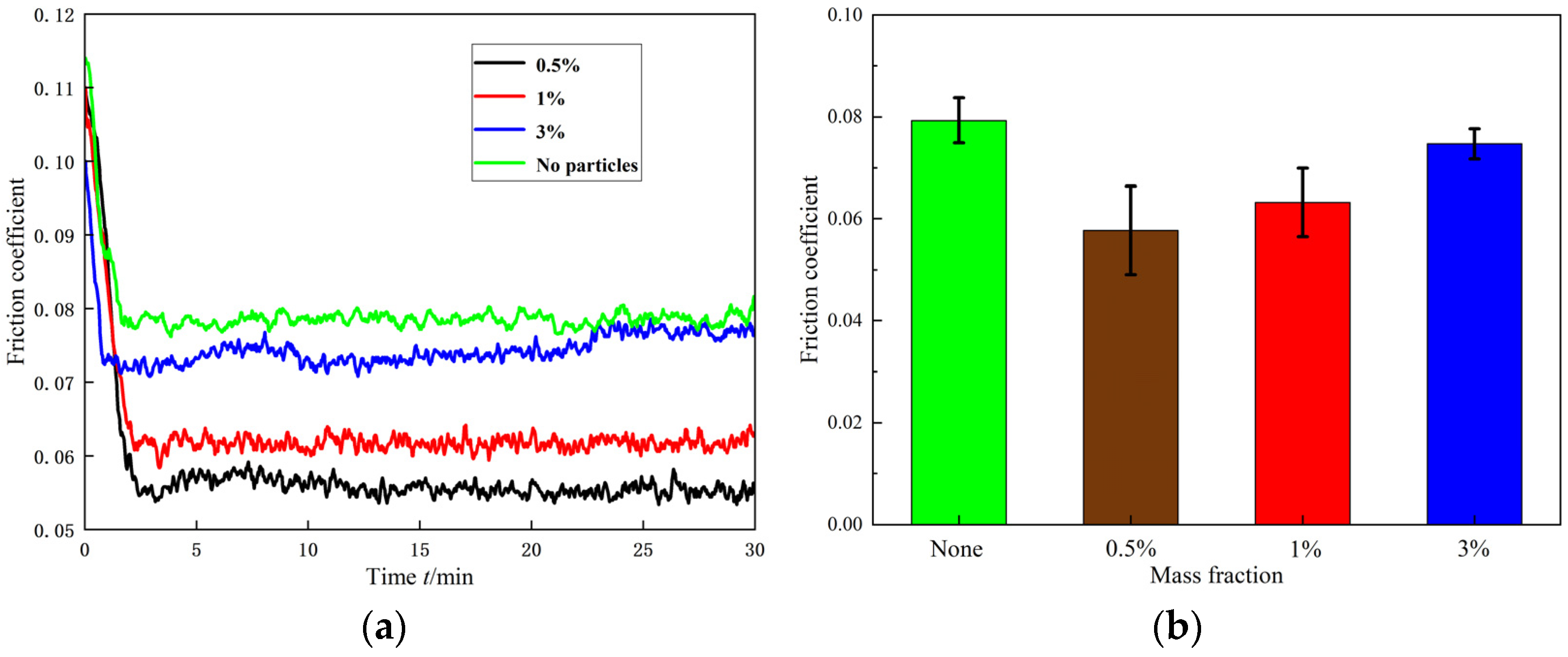
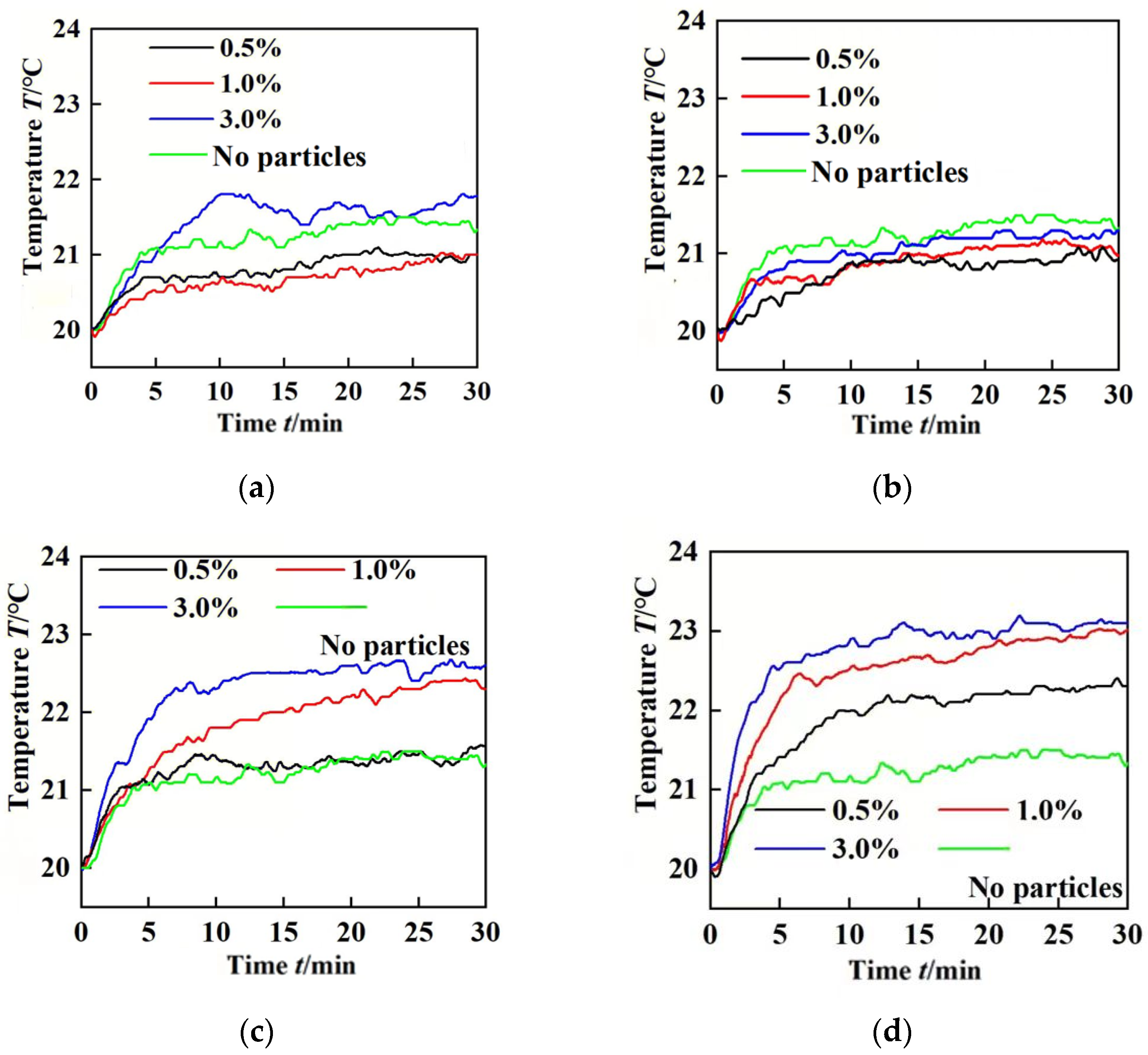
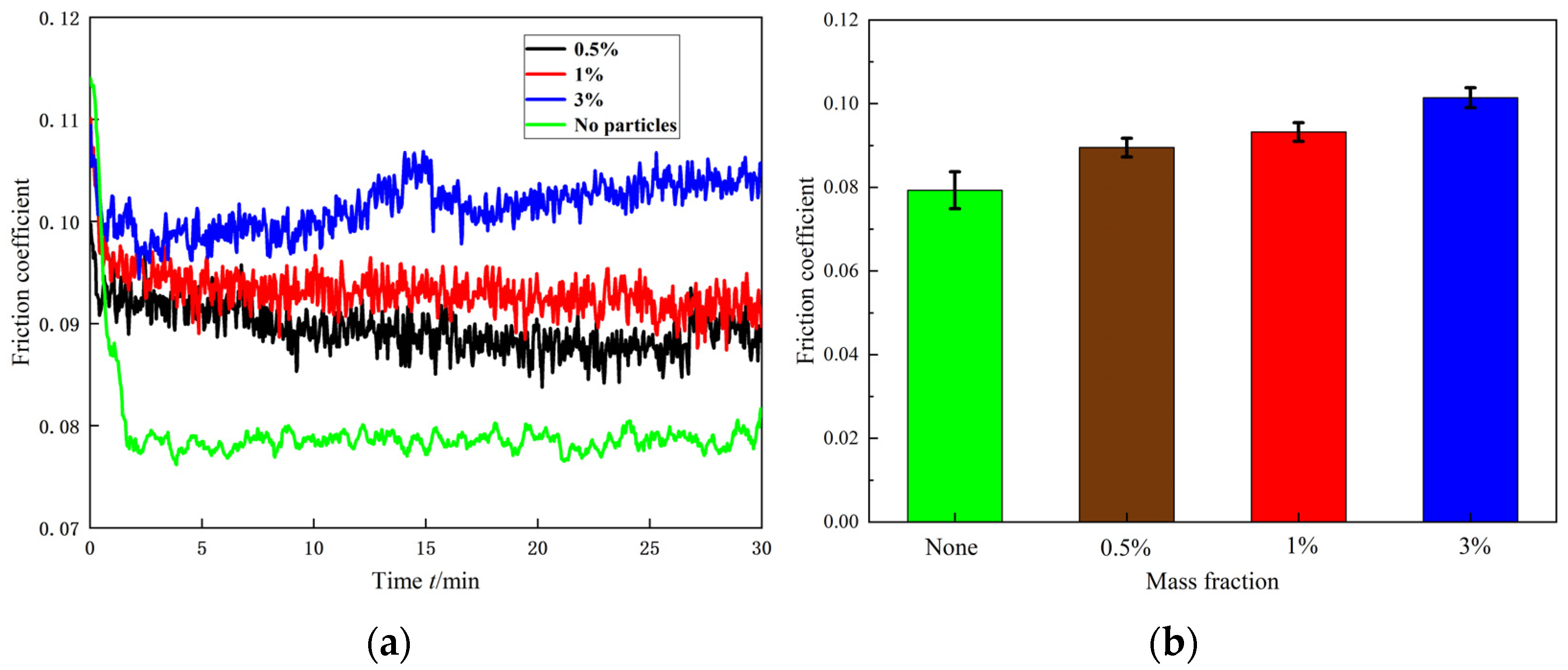
3.2.1. The 80-Mesh Coal Dust
3.2.2. The 200-Mesh Coal Dust
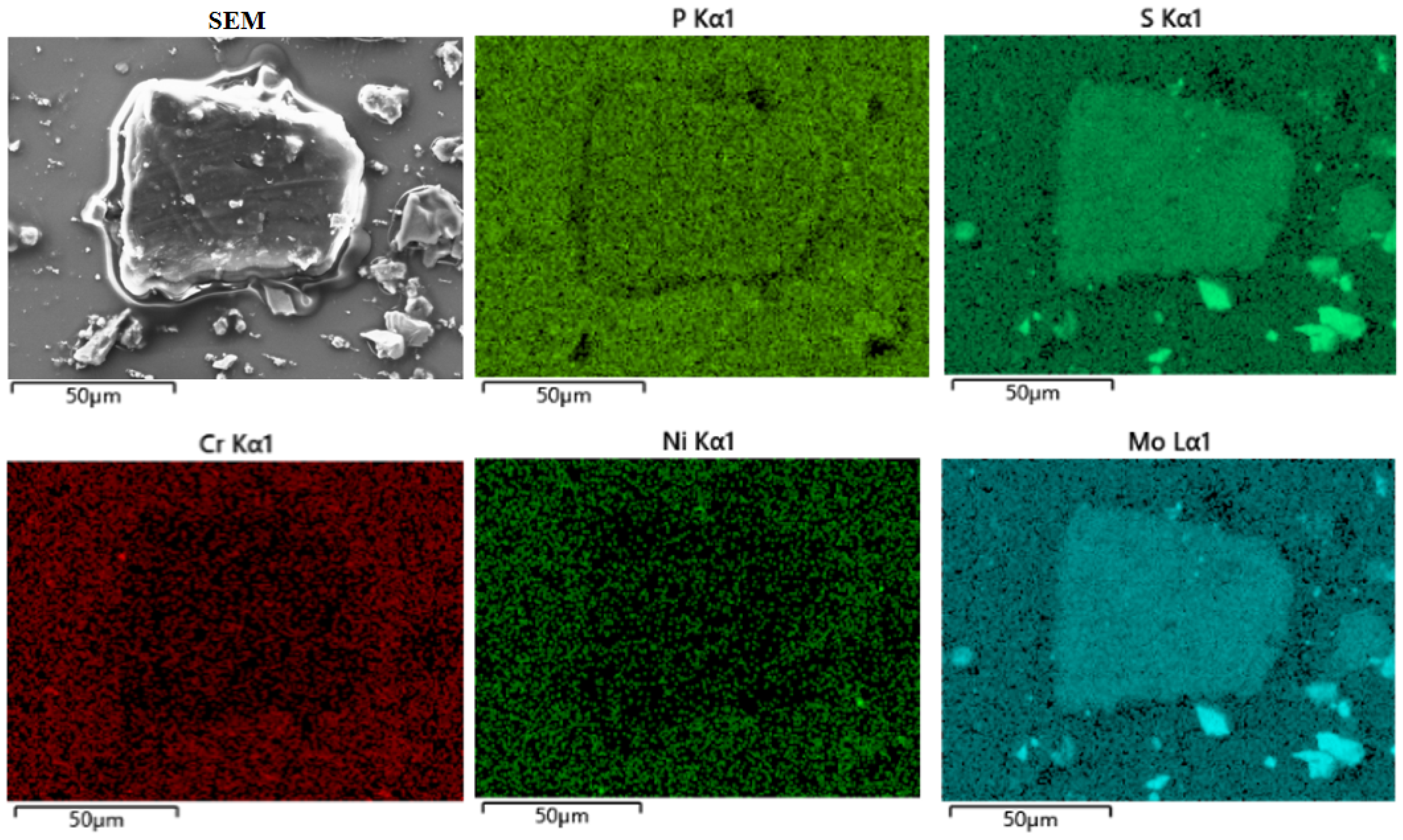
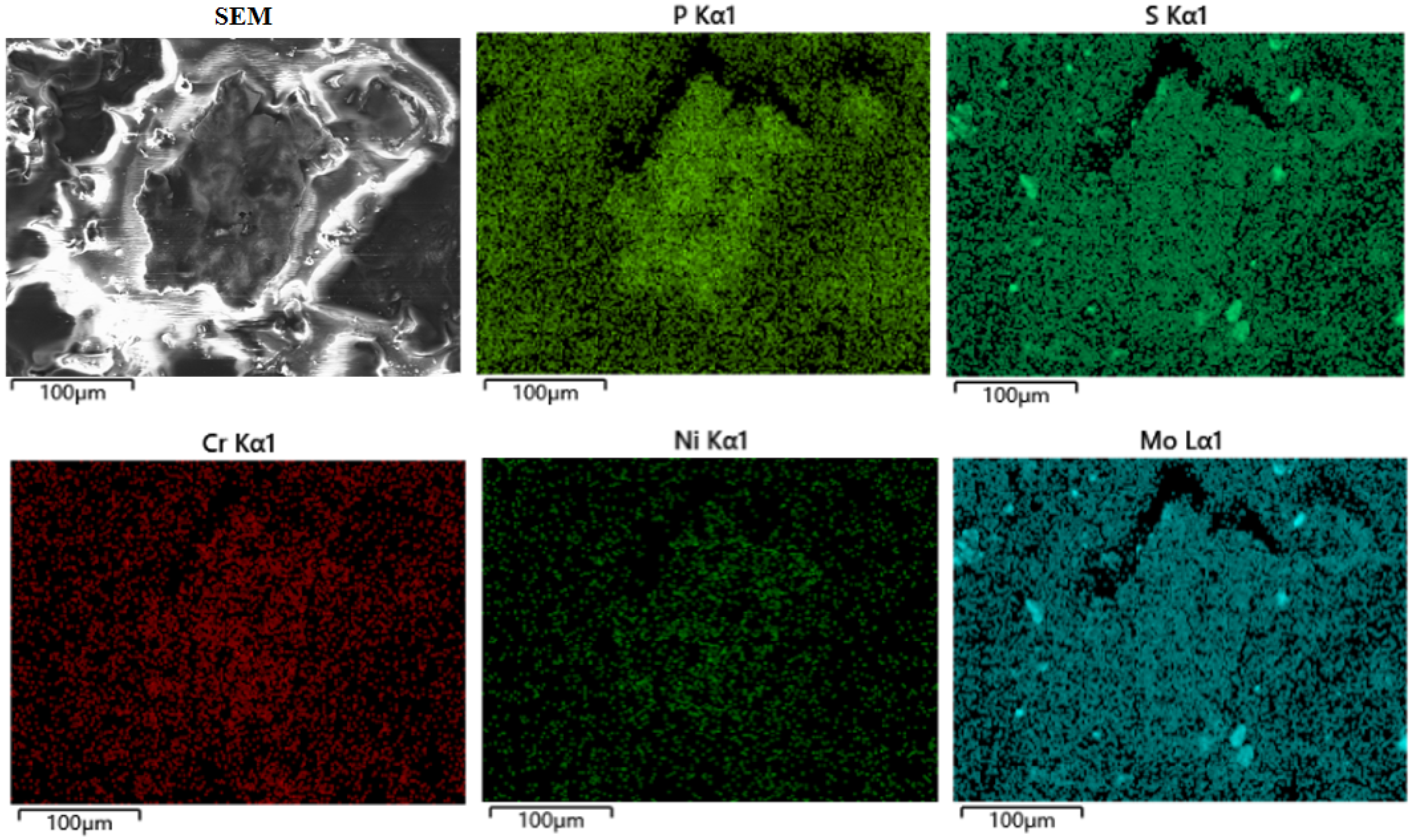
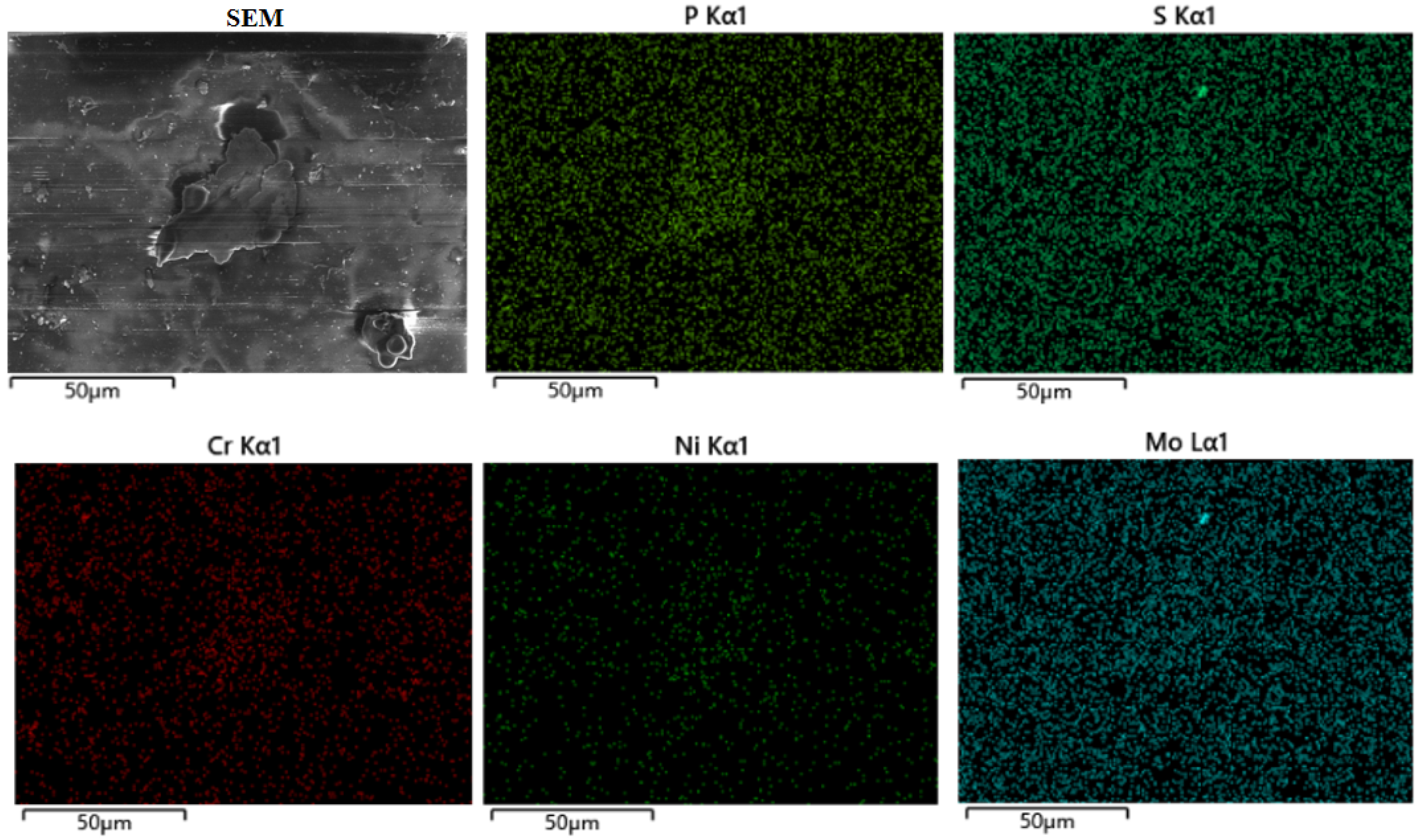
3.3. Characterization of Debris Grains Under Rock Dust Contamination
3.4. Characterization of Debris Grains Under Mixed Contamination
4. Wear Mechanism Analysis
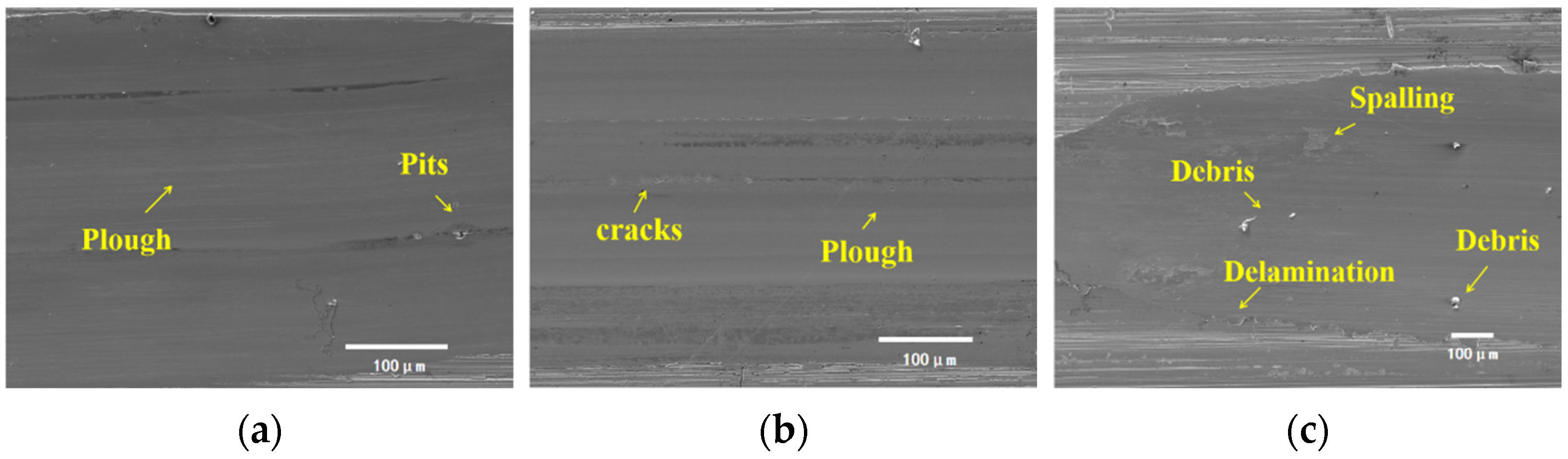
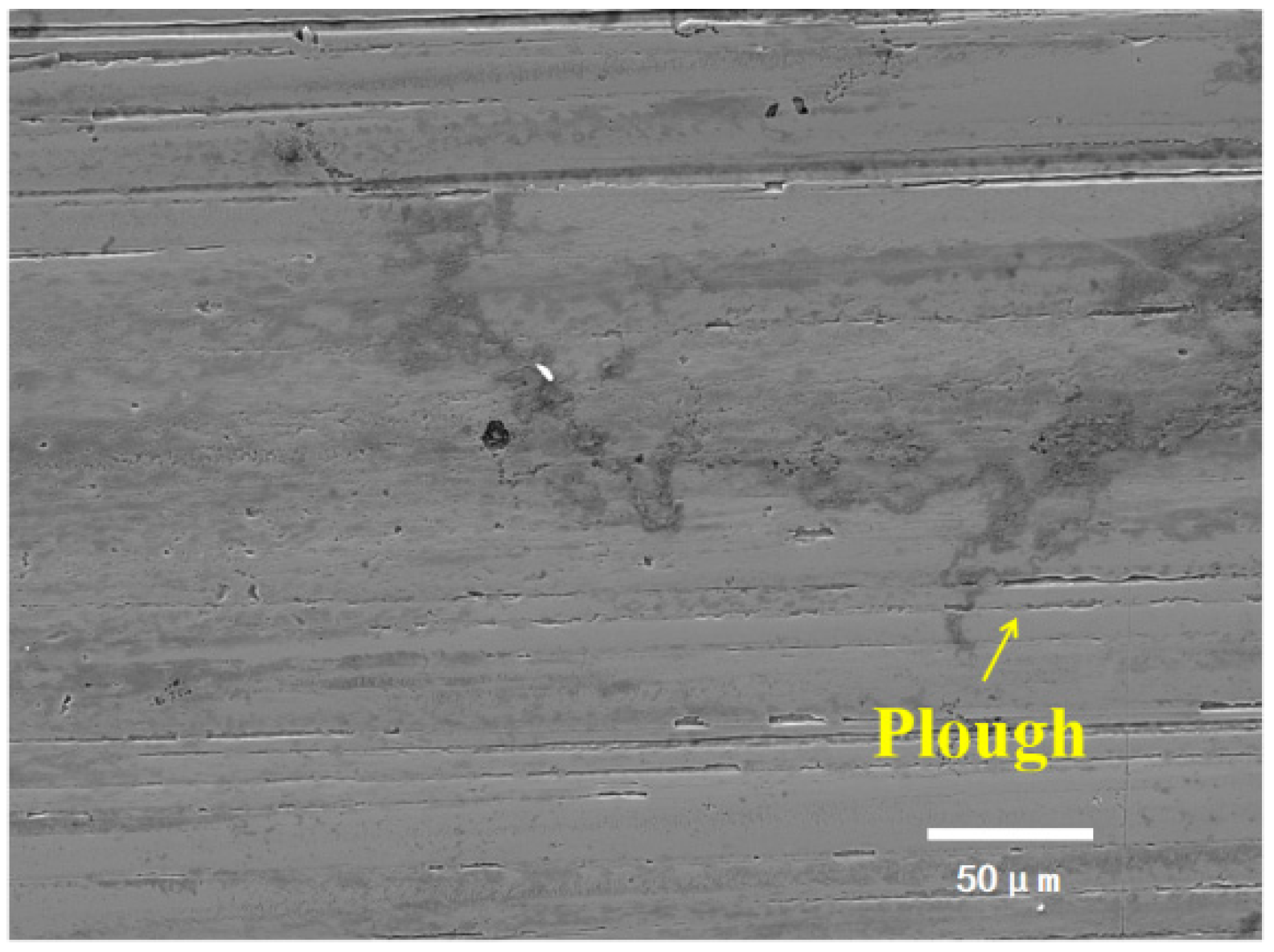
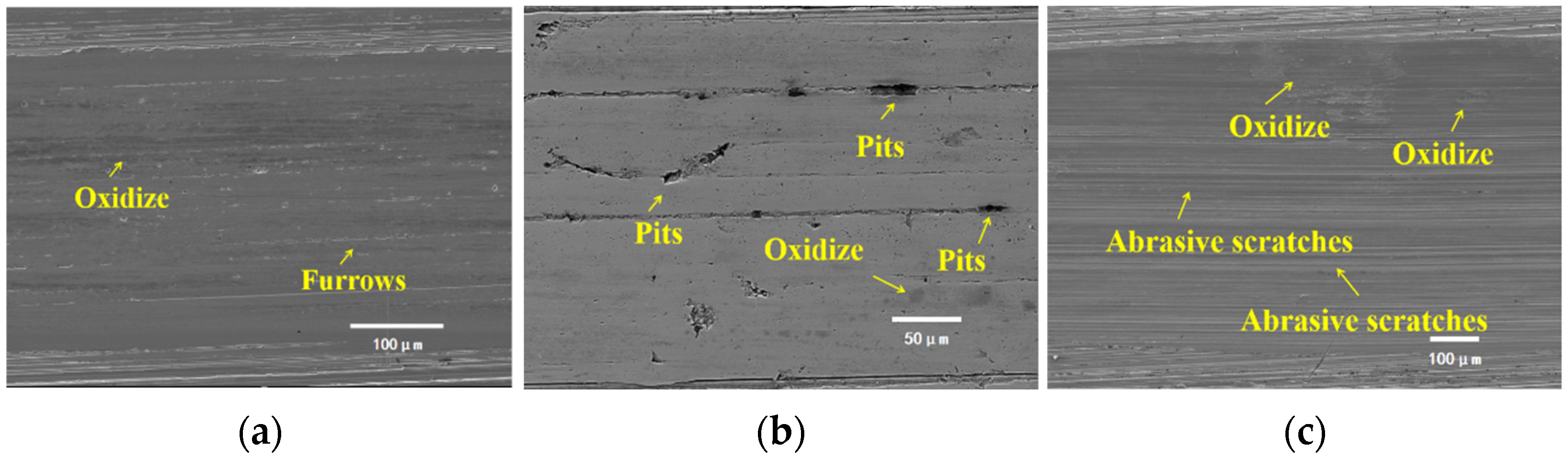
4.1. Wear Mechanism Under Coal Dust Contamination
4.2. Wear Mechanism Under Rock Dust Contamination
4.3. Wear Mechanism Under Mixed Contamination
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duan, D.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, J. Fatigue crack propagation behavior of 18CrNiMo7-6 gear steel. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2022, 43, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, X. Research Progress of Gear Steel for Automobiles. J. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2011, 29, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gu, X.; Pan, H. Cyclic Quenching Treatment to Improve Strength–Ductility Combinations in 18CrNiMo7-6 Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2023, 33, 10446–10454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wu, G.; Zhang, X.; Fu, W.; Huang, X. Gradient microstructure and microhardness in a nitrided 18CrNiMo7-6 gear steel. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. IOP Publ. 2017, 219, 012047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Han, X.; Wang, G.; Xu, G. Determination of the mechanical properties of surface-modified layer of 18CrNiMo7-6 steel alloys after carburizing heat treatment. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 2018, 148, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Hu, X.; Liu, T.; Fang, L.; Dearn, K.D.; Xu, H. The role of soot particles in the tribological behavior of engine lubricating oils. Wear 2013, 304, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motamen Salehi, F.; Khaemba, D.; Morina, A.; Neville, A. Corrosive–abrasive wear induced by soot in boundary lubrication regime. Tribol. Lett. 2016, 63, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, F.M.; Morina, A.; Neville, A. The effect of soot and diesel contamination on wear and friction of engine oil pump. Tribol. Int. 2017, 115, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.A. Friction and wear of sand-contaminated lubricated sliding. Friction 2018, 6, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.K.A.; Ezzat, F.M.H.; El-Gawwad, K.A.A.; Salem, M.M.M. Effect of lubricant contaminants on tribological characteristics during boundary lubrication reciprocating sliding. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.04448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.R.; Ville, F.; Haiahem, A.; Flamand, L. Effect of lubricant contamination on friction and wear in an EHL sliding contact. Mechanics 2010, 82, 43–49. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, N.; Wu, N.; Wang, S.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z. Tribological Properties of Friction Pairs in Lubricant Contaminated with Particles under High Temperature. Tribol. Trans. 2017, 60, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.K.; Shindhe, M.; Rawat, P.; Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, G.K.; Verma, R.; Bhutto, J.K.; Hussein, H.S. The Effect of Various Contaminants on the Surface Tribological Properties of Rail and Wheel Materials: An Experimental Approach. Coatings 2023, 13, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wang, J.; Wei, A.; Feng, W.; Yu, Y. Analysis on Wear Resistance of Hydraulic Oil under Pollution State. Lubr. Eng. 2024, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Boldyrev, S.; Budarova, O. Experimental study of wear of model friction pairs lubricated with contaminated oil. J. Frict. Wear 2016, 37, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. Research on friction and wear state analysis of coal mine electromechanical equipment based on iron spectrum analysis. Inn. Mong. Coal Econ. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X. Design of On-line Rotary Ferrograph and Study on the Image Acquisition Method of Wear Debris. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Ma, X.; Liu, T.; Liu, S.; You, K. Quantitative Analysis Method of Wear Particles for Ferrogram of Rotary Ferrograph. Lubr. Eng. 2019, 44, 115–119+125. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G. Study on Quantitative Analysis Method for Qualitative Ferrography of Equipment Wear Condition. Master’s Thesis, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, Q. Comprehensive evaluation method of wear state of mechanical equipment based on ferrography analysis. Ordnance Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 45, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, B.; Jia, T.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Prediction of the formation of carbide network on grain boundaries in carburizing of 18CrNiMo7-6 steel alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 421, 127348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalczewski, R.; Kalbarczyk, M.; Mańkowska-Snopczyńska, A.; Osuch-Słomka, E.; Piekoszewski, W.; Snarski-Adamski, A.; Szczerek, M.; Tuszyński, W.; Wulczyński, J.; Wieczorek, A. The Effect of a Gear Oil on Abrasion, Scuffing, and Pitting of the DLC-Coated 18CrNiMo7-6 Steel. Coatings 2019, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuszyński, W.; Michalczewski, R.; Osuch-Słomka, E.; Snarski-Adamski, A.; Kalbarczyk, M.; Wieczorek, A.N.; Nędza, J. Abrasive Wear, Scuffing and Rolling Contact Fatigue of DLC-Coated 18CrNiMo7-6 Steel Lubricated by a Pure and Contaminated Gear Oil. Materials 2021, 14, 7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z. Recrystallization Mechanism and Processing Map of 18CrNiMo7-6 Alloy Steel during Hot Deformation. Metals 2022, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, A.; Ji, V. Contact Fatigue Behavior Evolution of 18CrNiMo7-6 Gear Steel Based on Surface Integrity. Metals 2023, 13, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, V.; Momin, V.; Patil, P. Investigation and optimization of hypoid gear micro-geometry parameters and axle deflections to improve the contact stress distribution and fatigue life of hypoid gears. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, 72, 1950–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Sang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, G.; Zhao, M.; Peng, Z. Surface integrity and corrosion resistance of 18CrNiMo7-6 gear steel subjected to combined carburized treatment and wet shot peening. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 484, 130862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tang, L.; Zhou, C.; Shi, Z. Wear life prediction method of crowned double helical gear drive in point contact mixed elastohydrodynamic lubrication. Wear 2021, 484, 204041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Luo, J.; Lu, F.; Wang, G.; Liu, H.; Zhao, M. Characterization of fracture toughness for surface-modified layer of 18CrNiMo7-6 alloy steel after carburizing heat treatment by indentation method. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 269, 108508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, W.; Che, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Wang, M. The Effect of Cyclic Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 18CrNiMo7-6 Gear Steel. Materials 2024, 17, 5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J.; Yang, H. Mechanical and Heterogeneous Properties of Coal and Rock Quantified and Mapped at the Microscale. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epshtein, S.A.; Borodich, F.M.; Bull, S.J. Evaluation of elastic modulus and hardness of highly inhomogeneous materials by nanoindentation. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 119, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomas, H.; Roest, R.; Thorley, T.; Wells, A.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z.; Sakurovs, R.; Wotherspoon, S.; Pearson, R.A.; Mahoney, M.R. Fuels, Tribological testing of metallurgical coke: Coefficient of friction and relation to coal properties. Energy Fuels 2018, 32, 12021–12029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Jia, C.; Wu, T. Mechanism-guided wear severity assessment of worn surfaces with multiple damages. Wear 2025, 205875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, P.J.; Grejtak, T.; Qu, J. The characterization of wear-causing particles and silica sand in particular. Wear 2023, 530, 204872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, K.S.; Kanagaraj, A.; Gopal, P.M. Dry sliding wear characterization of Al 6061/rock dust composite. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3893–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycerz, P.; Olver, A.; Kadiric, A. Propagation of surface initiated rolling contact fatigue cracks in bearing steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2017, 97, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, V.A.; Furlong, O.J. Stick-slip friction: A Monte Carlo study. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heshmat, H.J.W. Wear reduction systems for coal-fueled diesel engines II. Experimental results and hydrodynamic model of powder lubrication. Wear 1993, 162, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonazzi, D.; Massi, F.; Baillet, L.; Culla, A.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Berthier, Y.J.M. Experimental and numerical analysis of frictional contact scenarios: From macro stick–slip to continuous sliding. Meccanica 2015, 50, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Li, B.; Wu, T. Wear characterization under sliding–rolling contact using friction-induced vibration features. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2022, 236, 634–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Espejel, G.E.; Rycerz, P.; Kadiric, A. Prediction of micropitting damage in gear teeth contacts considering the concurrent effects of surface fatigue and mild wear. Wear 2018, 398, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrica, M.; Badisch, E.; Peinsitt, T. Abrasive wear mechanisms and their relation to rock properties. Wear 2013, 308, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












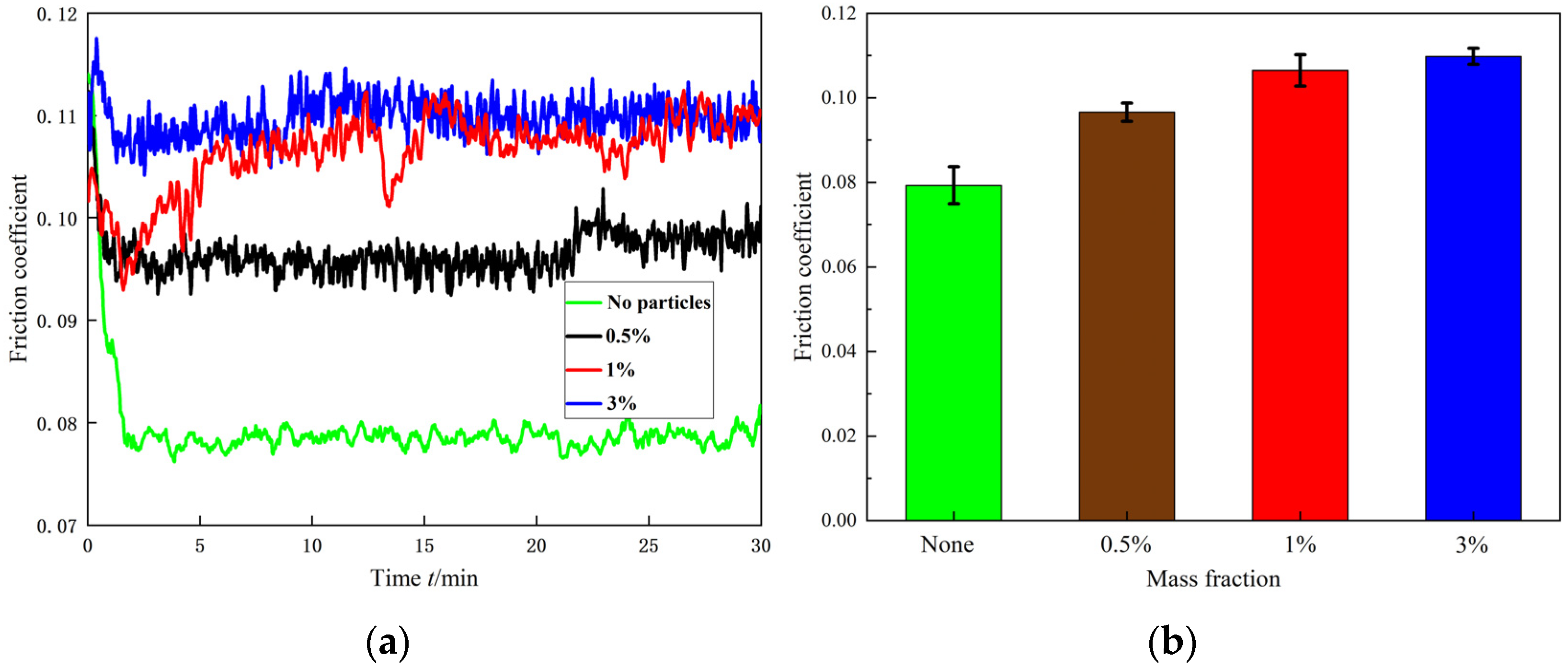
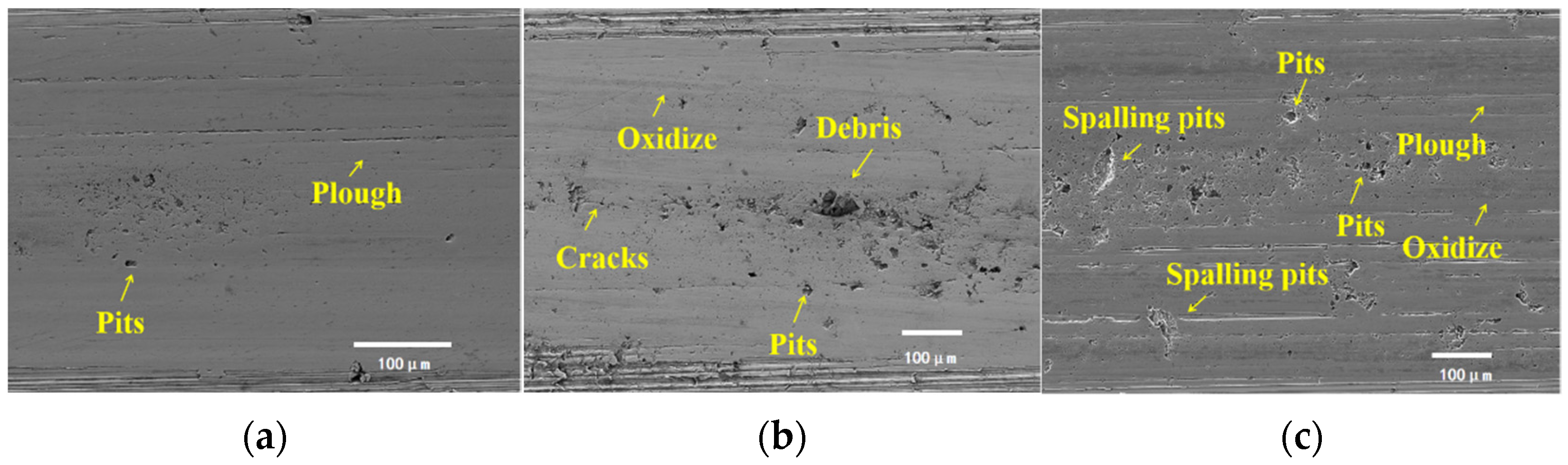
| Elemental | Quantity Contained (%) |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.15–0.21 |
| Silicon (Si) | ≤0.40 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.50–0.90 |
| Barium (Cr) | 1.50–1.80 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 1.40–1.70 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.25–0.35 |
| Phosphorus (P) | ≤0.025 |
| Sulphur (S) | ≤0.035 |
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density (15 °C) | 0.88~0.92 g/cm3 |
| 40 °C Kinematic Viscosity | 198~242 cSt |
| 100 °C Kinematic Viscosity | 18~22 cSt |
| Viscosity Index (VI) | ≥90 |
| Flash Point | ≥220 °C |
| Pour Point | ≤−6 °C~−12 °C |
| Heat Capacity | 1.7~2.0 J/(g·K) |
| Thermal Conductivity (m·K) | 0.12~0.15 W/(m·K) |
| Groups | Particulate Matter | Granularity | Mass Fraction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1–3 | pulverized coal | 80 mesh | 0.5%, 1%, 3% |
| 4–6 | pulverized coal | 200 mesh | 0.5%, 1%, 3% |
| 7–9 | silicon dioxide (SiO2) | 200 mesh | 0.5%, 1%, 3% |
| 10–12 | pulverized coal + silicon dioxide (SiO2) (2:1) | 200 mesh | 0.5%, 1%, 3% |
| 13 | none | - | 0% |
| Type of Contamination | Surface Flatness | Smooth and Round Profile | Green Halo | Concave Depression | Red Oxidation | Scratch | Grain Size (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| non-contaminated | √ | √ | <60 | ||||
| 80-mesh coal powder | √ | √ | √ | <190 | |||
| 200-mesh coal powder | √ | √ | √ | √ | <140 | ||
| 200-mesh rock dust | √ | <210 | |||||
| 200-mesh mixture | √ | √ | √ | √ | <240 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, X.; He, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Luo, X.; Lv, K. Research on Debris Characteristics and Wear Mechanism of Gear Material 18CrNiMo7-6 Used in Mining Reducer Under Dust-Contaminated Lubrication. Lubricants 2025, 13, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13030107
Pang X, He Y, Chen X, Zhao J, Luo X, Lv K. Research on Debris Characteristics and Wear Mechanism of Gear Material 18CrNiMo7-6 Used in Mining Reducer Under Dust-Contaminated Lubrication. Lubricants. 2025; 13(3):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13030107
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Xinyu, Yixiang He, Xun Chen, Jiapeng Zhao, Xiting Luo, and Kaibo Lv. 2025. "Research on Debris Characteristics and Wear Mechanism of Gear Material 18CrNiMo7-6 Used in Mining Reducer Under Dust-Contaminated Lubrication" Lubricants 13, no. 3: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13030107
APA StylePang, X., He, Y., Chen, X., Zhao, J., Luo, X., & Lv, K. (2025). Research on Debris Characteristics and Wear Mechanism of Gear Material 18CrNiMo7-6 Used in Mining Reducer Under Dust-Contaminated Lubrication. Lubricants, 13(3), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13030107





