Strengthening Properties and Wear Resistance of the Cu-xNi-yCo-Cr-Si Alloy by Varying Ni/Co and Zr Addition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Samples Preparations
2.2. Heat Treatments
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Surface Characterization
2.3.2. Hardness Test
2.4. Friction and Wear Test
3. Results and Discussion
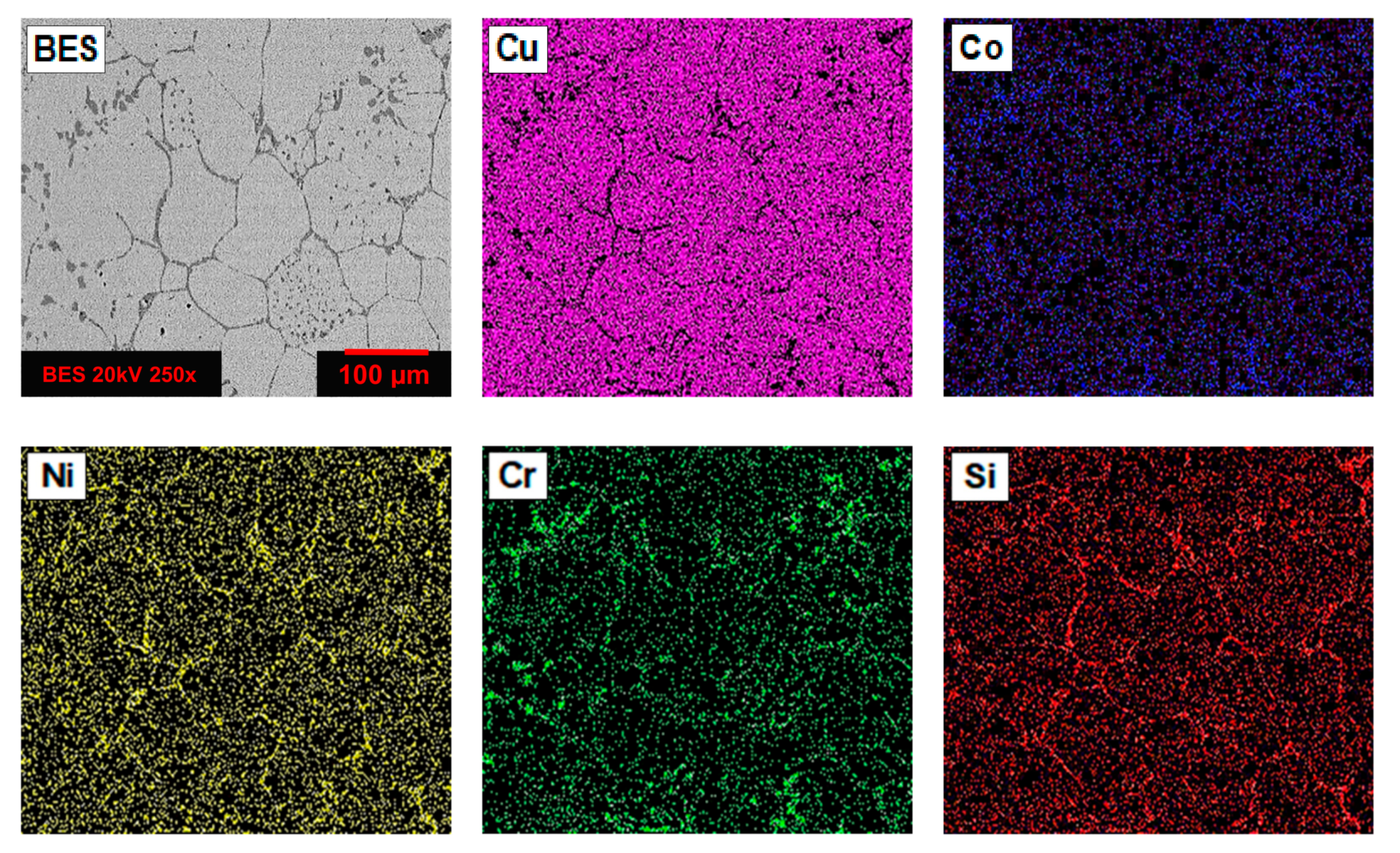
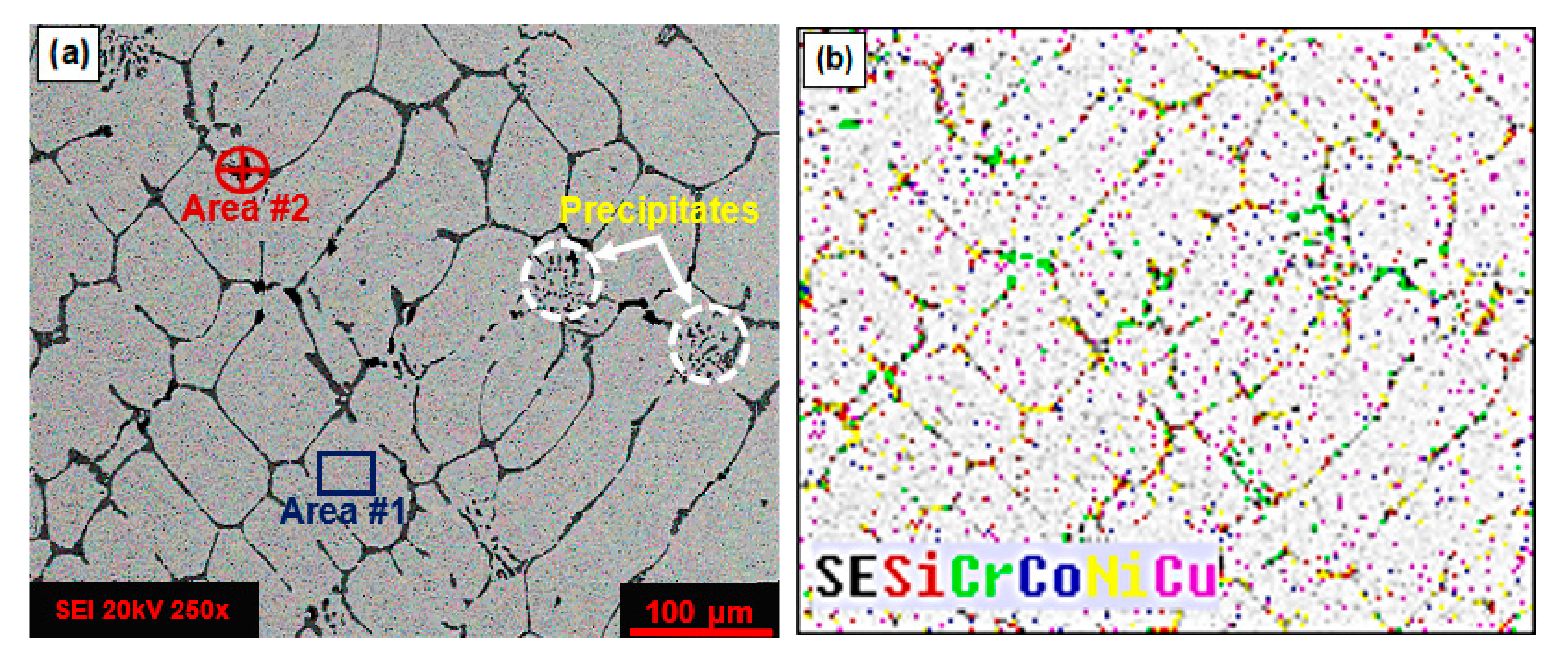
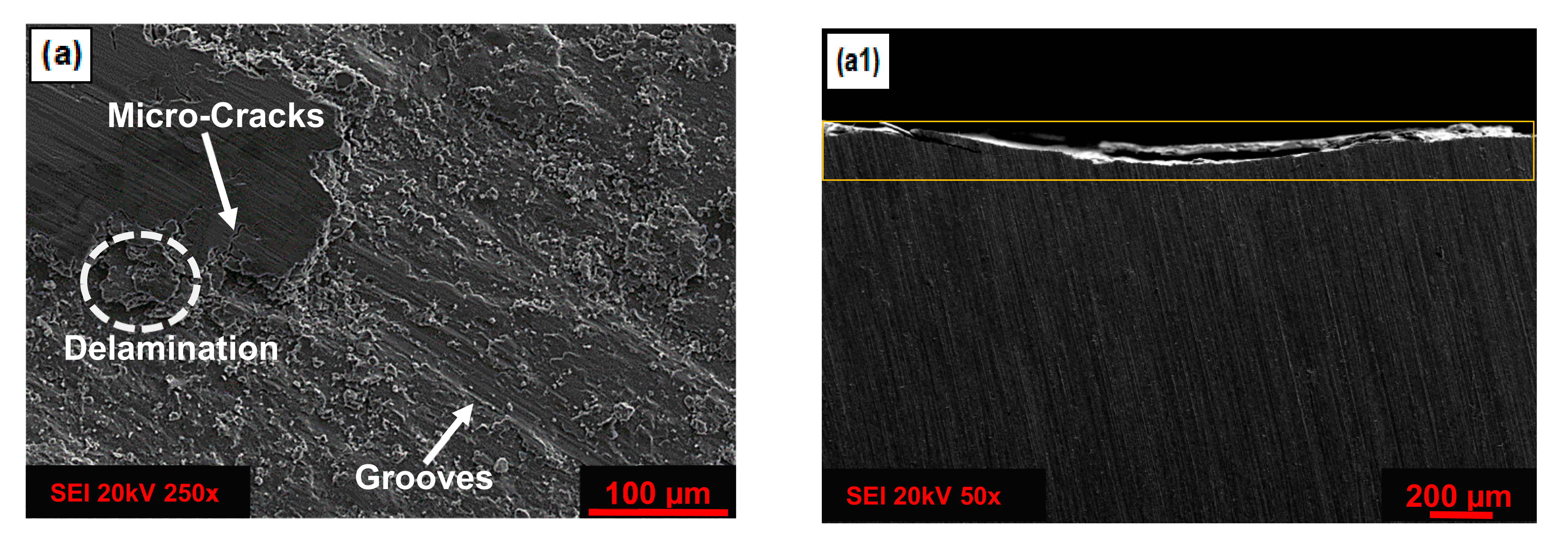
3.1. Microstructure Analysis by Scanning Electron Microscopy
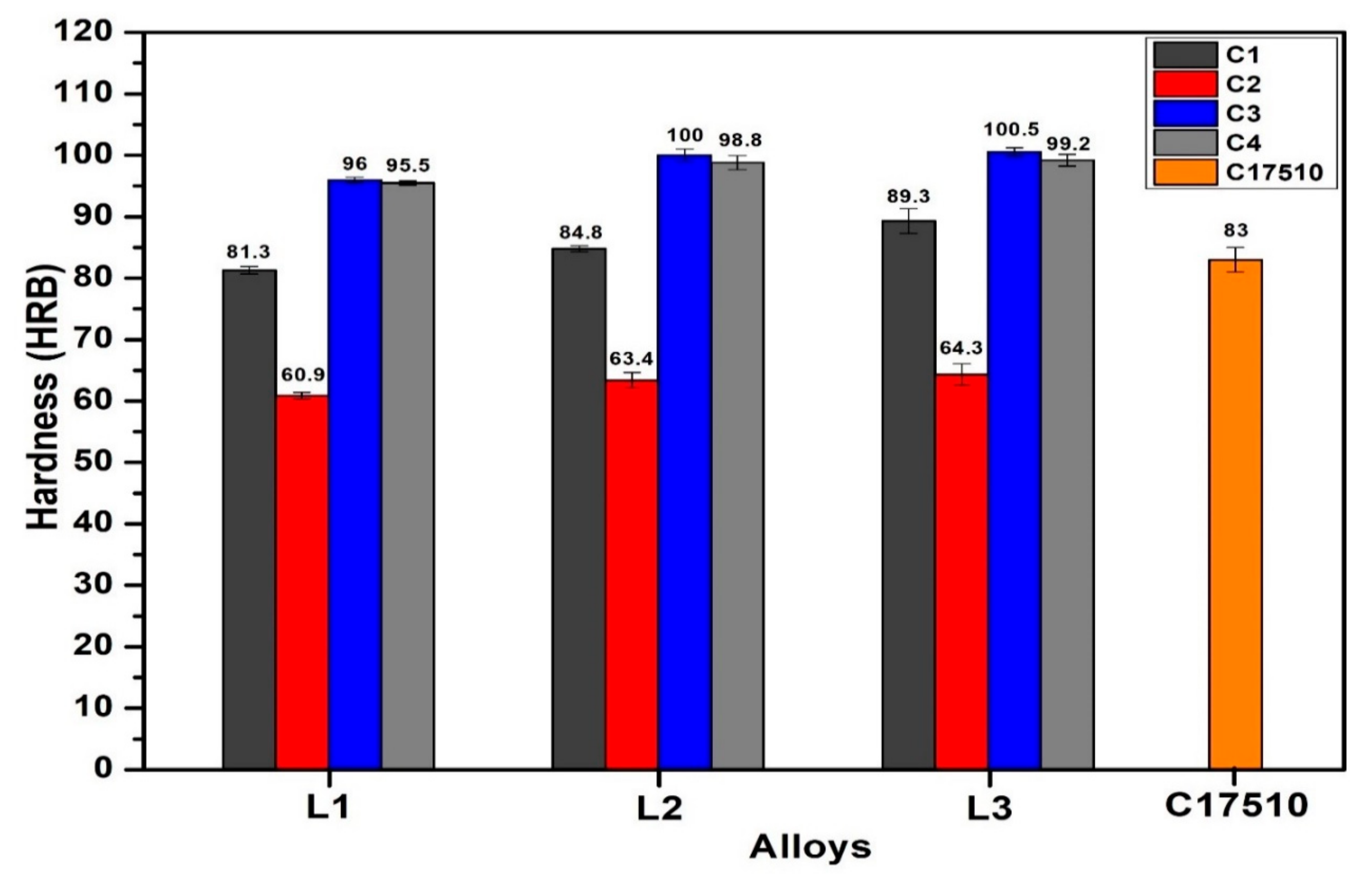
3.2. Hardness Analysis
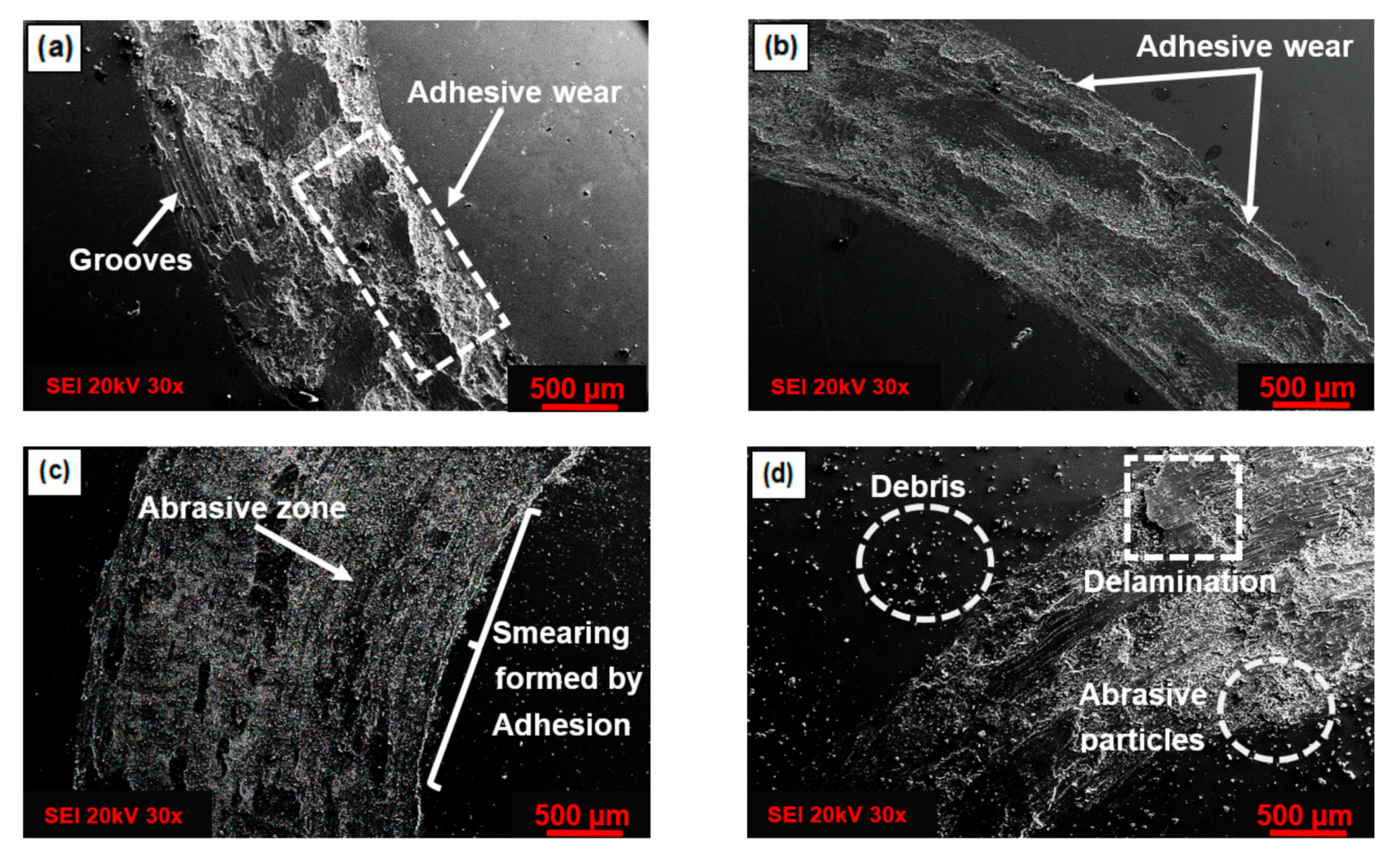
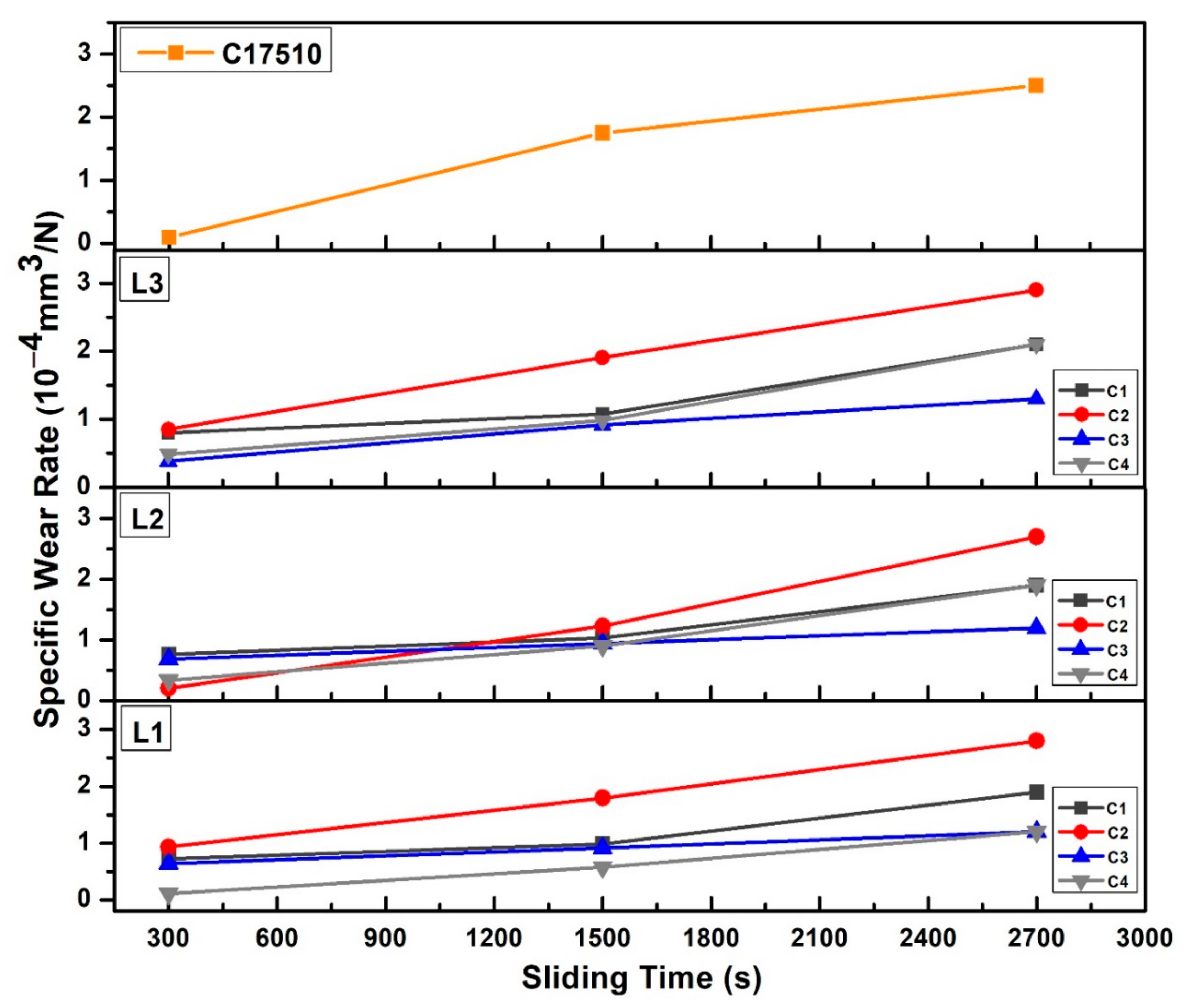
3.3. Friction and Wear Behavior
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, L.X.; Tao, N.R.; Lu, K. A high strength and high electrical conductivity bulk CuCrZr alloy with nanotwins. Scr. Mater. 2015, 99, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, B.; An, J.; Volinsky, A.A.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Song, K. Effects of Ce addition on the Cu-Mg-Fe alloy hot deformation behavior. Vacuum 2018, 155, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H.G.; Gu, J.W.; Hsu, C.E.; Wu, C.Y. Improvement in strength and thermal conductivity of powder metallurgy produced Cu-Ni-Si-Cr alloy by adjusting Ni/Si weight ratio and hot forging. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 633, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsa-Ngam, J.; Langdon, T.G. Microstructural evolution and grain refinement in a Cu-Zr alloy processed by high-pressure torsion. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2014, 783, 2635–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, G.; Yang, G.; Li, L.; Li, Q. Modeling constitutive relationship of Cu-0.4 Mg alloy during hot deformation. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1770–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Narayana Murty, S.V.; Sharma, S.C.; Mondal, K. Constitutive modeling of hot deformation behavior of vacuum hot pressed Cu-8Cr-4Nb alloy. Mater. Des. 2015, 75, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, G.; Mi, X.; Peng, L.J.; Xie, H.F.; Kang, Y. Effect of Co addition on microstructure and properties of Cu-Ni-Si alloy. Adv. Mater. Process. 2018, 1, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, A.; Watanabe, C.; Monzen, R. Influence of Co on Strength of Cu-Ni-Co-Si Alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2014, 783, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Gu, J.; Hsu, C.; WU, C. Effects of heat treatment processes on the microstructures and properties of powder metallurgy produced Cu–Ni–Si–Cr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. 2014, 619, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Salgado, D.A.; Juárez-Hernández, A.; Medina-Ortíz, F.; Banda, M.L.; Hernández-Rodríguez, M.A.L. Influence of B and Nb additions and heat treatments on the mechanical properties of Cu-Ni-Co-Cr-Si alloy for high pressure die casting applications. Metals 2020, 10, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, S.; Criado, A.J.; Castro, L.; Fosca, C. Influencia de distintos recubrimientos en alguna propiedades de aleaciones Cu-Be. Efecto de los tratamientos térmicos. Gandía 2002, 125–132. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Q.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, Z. Microstructural evolution, phase transition, and physics properties of a high strength Cu–Ni–Si–Al alloy. Mater. Charact. 2018, 147, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Q.; Li, Z.; Xiao, T.; Pang, Y.; Xiang, Z.Q.; Qiu, W.T.; Xiao, Z. A new ultrahigh strength Cu-Ni-Si alloy. Intermetallics. 2013, 42, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Chen, Z.; Kang, H.; Li, R.; Wnag, W.; Zou, C.; Wang, T. Effects of Nb addition on the microstructures and mechanical properties of a precipitation hardening Cu-9Ni-6Sn alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 715, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Han, S.; Euh, K.; Lim, S.; Kim, S. Effect of Ti Addition on Tensile Properties of Cu-Ni-Si Alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 2011, 17, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnakwo, K.C.; Mbah, C.N.; Nnuka, E.E. Influence of trace additions of titanium on grain characteristics, conductivity and mechanical properties of copper-silicon-titanium alloys. Heliyon 2019, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tian, K.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Volinsky, A.A. Aging Strengthening Mechanism of the Cu-1.0Zr Alloy. Metall. Mater. Trans A 2017, 48, 5628–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Guo, E.; Chen, Z.; Kang, H.; Chen, Z.; Zou, C.; Li, R.; Yin, G.; Wan, T. Correlation beween microstuues and mechanical poperties of cryolled CuNiSi alloys with Cr and Zr alloying. Mat. Charact. 2018, 144, 532–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.Z.; Gu, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Que, Z.P.; Shin, J.H.; Lim, S.H.; Kim, S.S. Effect of V Addition on Hardness and Electrical Conductivity in Cu-Ni-Si Alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 2013, 19, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Cheng, J.; Feng, G.; Xie, J.; Yu, F. Effect of V Addition on Microstructure and Properties of Cu-1.6Ni-1.2Co-0.65Si alloys. Metals 2019, 9, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Li, X.; Zhou, W.; Dong, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, Q. Minor-alloyed Cu-Ni-Si alloys with high hardness and electric conductivity designed by a cluster formula approach. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2017, 27, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobrawa, J.; Rdzawski, Z.; Gluchowski, W.; Malec, W. Microstructure and properties of CuNi2Si1 alloy processed by continuous RCS method,” J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2009, 37, 466–479. [Google Scholar]
- Rdzawski, Z.; Stobrawa, J. Thermomechanical processing of Cu–Ni–Si–Cr–Mg. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1993, 9, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Aging Behavior and Precipitation Analysis of Cu-Ni-Co-Si alloy. Crystals 2018, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, P.; Tian, B.; Jia, S.G.; Liu, Y. Aging treatment of Cu-Ni-Si-Ag alloy. Procedia Eng. 2012, 27, 1789–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Kang, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zou, C.; Li, R.; Yin, G.; Wang, T. Effects of Cr and Zr additions on microstructure and properties of Cu-Ni-Si alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 673, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, B.; Jia, Y.; Liu, Y. Co effects on Cu-Ni-Si alloys microstructure and physical properties. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 797, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, G.; Mi, X.; Peng, L.; Xie, H.; Kang, Y. Influence of the Ni/Co Mass Ratio on the Microstructure and Properties of Quaternary Cu-Ni-Co-Si Alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Huang, G.; Mi, X.; Peng, L.; Xie, H.; Kang, Y. Effect of Ni/Si Mass Ratio and Thermomechanical Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of Cu-Ni-Si Alloys. Materials 2019, 12, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.R.; Associates, D. Wear-Resistant and Corrosion-Resistant Copper Alloy Coatings. Copper and Copper Alloys. ASM Int. 2001, 1, 150. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, M.; Mariano, A.; Maffía, E.G. Efecto del Solubilizado en la Estructura de la Aleación CuCrZr. 2017. Available online: http://prointec.ing.unlp.edu.ar/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/2017.04.05-JornadasITE-Efecto-del-solubilizado-en-la-estructura-de-la-aleaci%C3%B3n-CuCrZr.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2021).
- Klement, J.F.; Ingerson, Q.F. Method of Heat-Treating Copper Base Alloy. U.S. Patent No. 3,072,508, 8 January 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Gorson, M.G. Copper Alloy and Process of Producing and Treating the Same. U.S. Patent No. 1,658,186, 7 February 1928. [Google Scholar]
- Edens, W.W.; Ingenson, Q.F. Copper-Nickel-Silicon-Chromium Alloys Having Improved Electrical Conductivity. Amped-Pittsburgh Corporation. U.S. Patent No. 4,191.601, 4 March 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Connétable, D.; Thomas, O. First-principles study of nickel-silicides ordered phases. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 2639–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, J.; Lu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liu, X. Thermodynamic Description of the Cu-Ni-Si System. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2014, 35, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, R.; Adams, J.H.; Ammons, M.; Avery, H.S.; Barnhurst, R.J. Introduction to Copper and Copper Alloys. Properties and Selection: Nonferrous Alloys and Special-Purpose Materials; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1992; Volume 2, pp. 760–790. [Google Scholar]
- Dossett, J.L.; Boyer, H.E. Heat Treating of Nonferrous Alloys. Practical Heat Treating, 2nd ed.; Copyring; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2006; pp. 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingerson, Q.F. Copper-Nickel-Silicon-Chromium Alloy. U.S. Patent 5028391, 2 July 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Vander voort, G.F. Metallography Principles and Practice. Macroetchants for Copper and Copper Alloys; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2007; Volume 4, pp. 515–516. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM standard E407-07. Standard Practice for Microetching Metals and Alloys; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2007; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E18-15. Standard Test Methods for Rockwell Hardness of Metallic Materials; Copyring; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G 99-95a. Standard Test Method for Wear Testing with a Pin-On-Disk; Copyright; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.J.K.; Pamkumar, P.; Wang, L.; Wang, T.J..; Nelson, K.; Yamaguchi, E.S.; Harrison, J.J.; Harrison, J.J.; Powrie, H.E.G.; Otin, N. Electrostatic monitoring of the effects of carbon black on lubricated steel/steel sliding contacts. Tribol. Interface Eng. Series Elvesier 2005, 48, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Elements (wt%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alloy Name | Ni | Co | Cr | Si | Fe | Zr | Be | Cu |
| L1 | 8.0 | 2.0 | 1.6 | 2.0 | --- | --- | --- | Balance |
| L2 | 8.5 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 2.0 | --- | --- | --- | Balance |
| L3 | 9.0 | 1.0 | 1.6 | 2.0 | 0.18 | 0.30 | --- | Balance |
| C17510 | 1.8 | --- | --- | --- | --- | 0.6 | Balance | |
| Sample | C/HT | Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Experimental Conditions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C | 1275 to 1300 | --- | C |
| C2 | ST | 925 | 120 | C + ST |
| C3 | HT1 | 550 | 100 | C + ST + HT1 |
| C4 | HT2 | 450 | 180 | C + ST + HT1 + HT2 |
| Alloy | Surface Roughness, Ra (Micron) |
|---|---|
| L1 | 0.0223 |
| L2 | 0.0237 |
| L3 | 0.0222 |
| C17510 | 0.0252 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avila-Salgado, D.A.; Juárez-Hernández, A.; Cabral-Miramontes, J.; Camacho-Martínez, J.L. Strengthening Properties and Wear Resistance of the Cu-xNi-yCo-Cr-Si Alloy by Varying Ni/Co and Zr Addition. Lubricants 2021, 9, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants9100096
Avila-Salgado DA, Juárez-Hernández A, Cabral-Miramontes J, Camacho-Martínez JL. Strengthening Properties and Wear Resistance of the Cu-xNi-yCo-Cr-Si Alloy by Varying Ni/Co and Zr Addition. Lubricants. 2021; 9(10):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants9100096
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvila-Salgado, Denis Ariel, Arturo Juárez-Hernández, José Cabral-Miramontes, and José Luis Camacho-Martínez. 2021. "Strengthening Properties and Wear Resistance of the Cu-xNi-yCo-Cr-Si Alloy by Varying Ni/Co and Zr Addition" Lubricants 9, no. 10: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants9100096
APA StyleAvila-Salgado, D. A., Juárez-Hernández, A., Cabral-Miramontes, J., & Camacho-Martínez, J. L. (2021). Strengthening Properties and Wear Resistance of the Cu-xNi-yCo-Cr-Si Alloy by Varying Ni/Co and Zr Addition. Lubricants, 9(10), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants9100096








