The Effects of Different Diets and Transgenerational Stress on Acyrthosiphon pisum Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Aphid Lines
2.2. Developmental Trials on Three Different Diets
2.3. Effects of Plant Age
2.4. Effects of Transgenerational Stress on Aphid Development
2.5. Statistical Analysis of Developmental Events
2.6. Fitness and Morphometric Measurements
3. Results
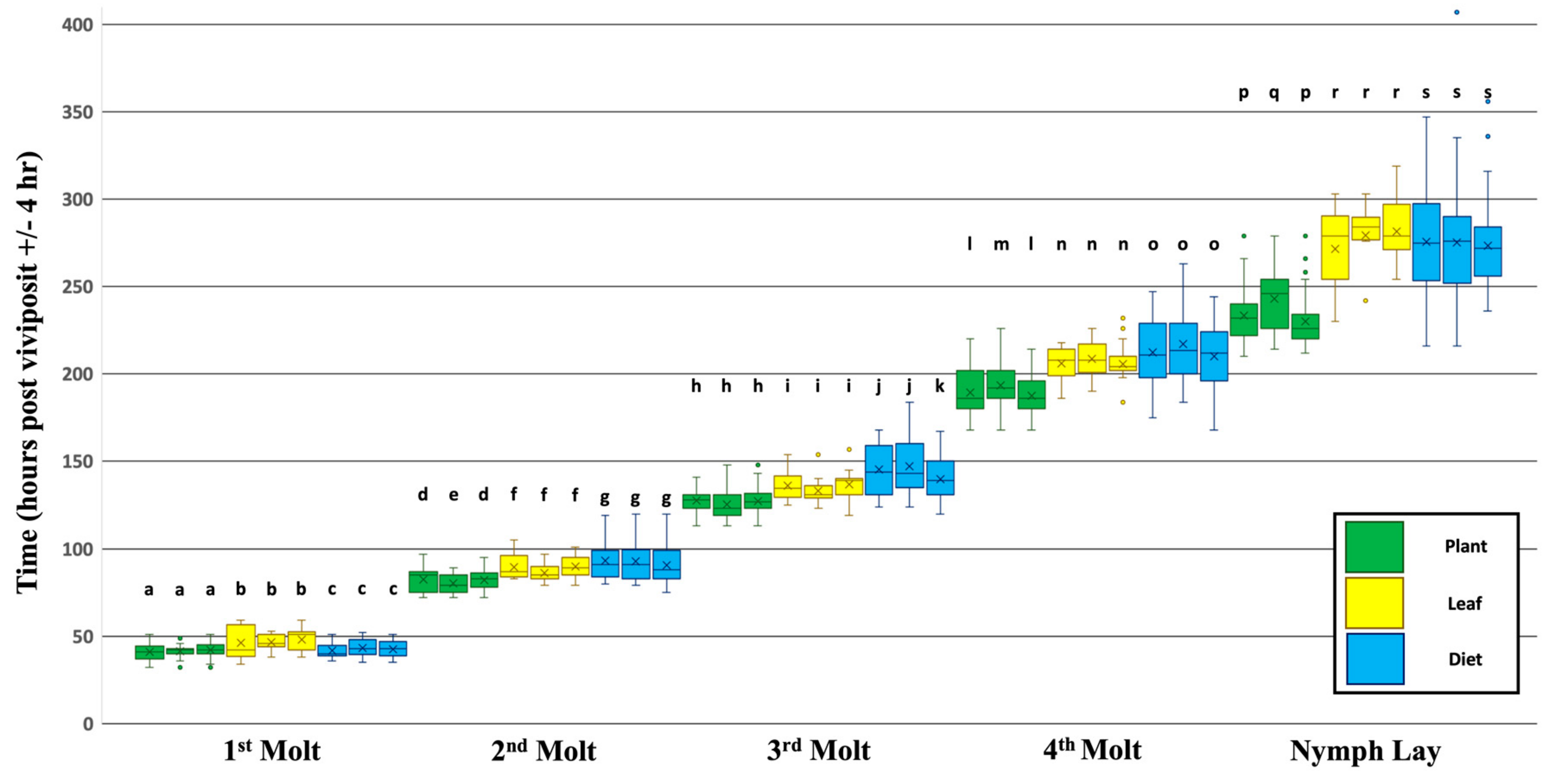
3.1. Dietary Effects on the Timing of Developmental Events
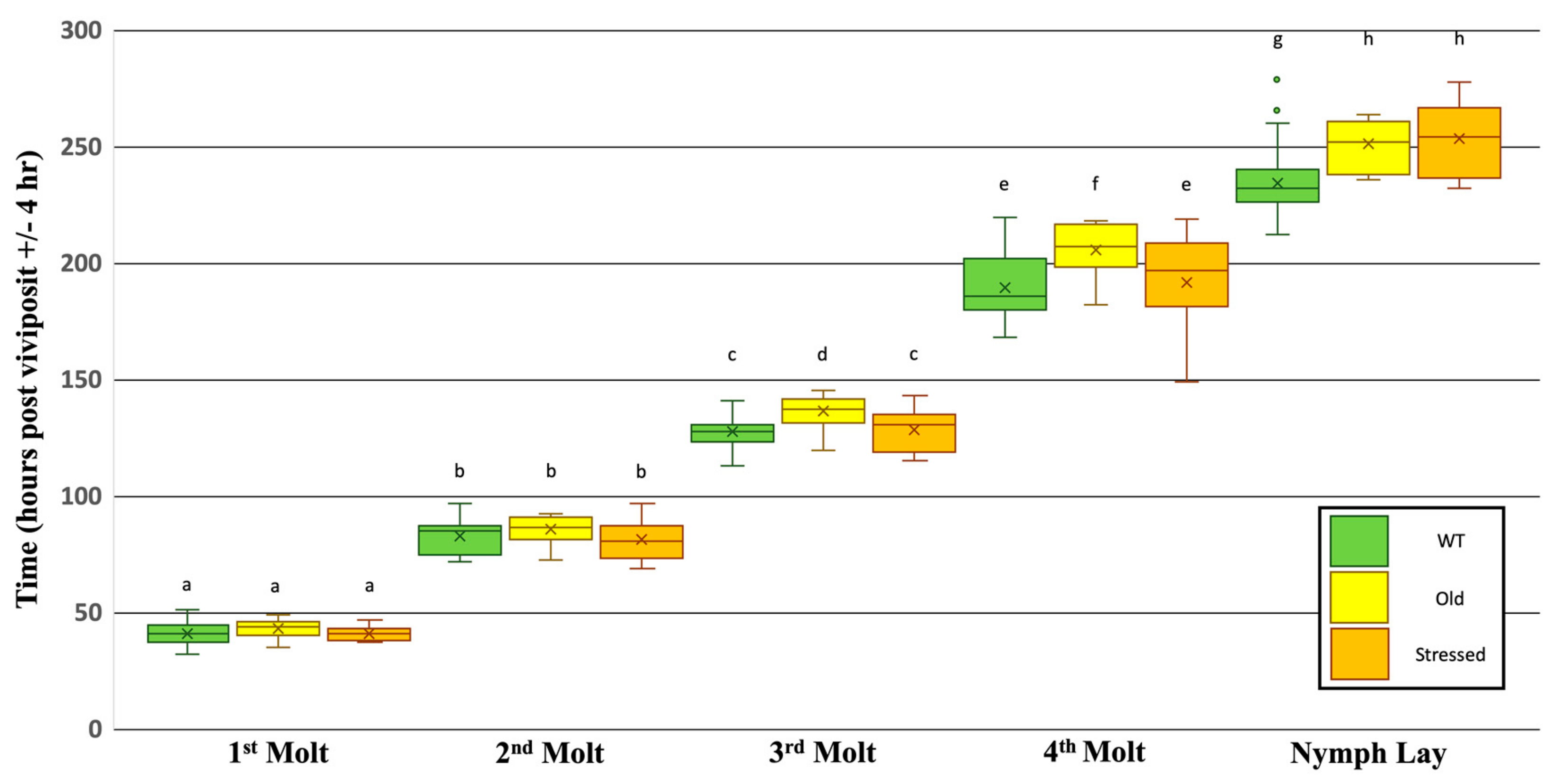
3.2. Effects of Plant Age and Transgenerational Stress on the Timing of Developmental Events
3.3. Effects of Wing Morph on the Timing of Developmental Events
3.4. Fitness and Morphometric Measurements at Each Developmental Stage
4. Discussion
4.1. Possible Sources of Inter- and Intra-Treatment Variation
4.2. Developmental Effects of Plant Age, Transgenerational Responses to Environmental Cues, and Morphotype
4.3. Siphunculus Length: A Proxy for Determining Developmental Age
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chougule, N.P.; Bonning, B.C. Toxins for Transgenic Resistance to Hemipteran Pests. Toxins 2012, 4, 405–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The International Aphid Genomics Consortium. Genome Sequence of the Pea Aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, J.A.; Stern, D.L. The pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum: An emerging genomic model system for ecological, developmental and evolutionary studies. BioEssays 2006, 28, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Miura, T. Aphid polyphenisms: Trans-generational developmental regulation through viviparity. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanoth, N.; Purba Gupta, V.; Hall, T.A.; Brisson, J.A. Ecdysone signaling underlies the pea aphid transgenerational wing polyphenism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, B.J.; Brisson, J.A. A Laterally Transferred Viral Gene Modifies Aphid Wing Plasticity. Curr. Boil. 2019, 29, 2098–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braendle, C.; Miura, T.; Bickel, R.; Shingleton, A.W.; Kambhampati, S.; Stern, D.L. Developmental Origin and Evolution of Bacteriocytes in the Aphid–Buchnera Symbiosis. PLoS Biol. 2003, 1, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Braendle, C.; Shingleton, A.; Sisk, G.; Kambhampati, S.; Stern, D.L. A comparison of parthenogenetic and sexual embryogenesis of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera: Aphidoidea). J. Exp. Zool. 2003, 295, 59–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, R.; Meng, X.-Y.; Tsuchida, T.; Fukatsu, T. Cellular mechanism for selective vertical transmission of an obligate insect symbiont at the bacteriocyte–embryo interface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1230–E1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, T.C.; Mugford, S.T.; Percival-Alwyn, L.; Chen, Y.; Kaithakottil, G.; Swarbreck, D.; Hogenhout, S.A.; van Oosterhout, C. Sex-specific changes in the aphid DNA methylation landscape. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.F.G. Aphid Ecology: Life Cycles, Polymorphism, and Population Regulation. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1977, 8, 329–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, D.G.; Brisson, J.A. Aphids: A Model for Polyphenism and Epigenetics. Genet. Res. Int. 2012, 2012, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brisson, J.A. Aphid wing dimorphisms: Linking environmental and genetic control of trait variation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallot, A.; Shigenobu, S.; Hashiyama, T.; Jaubert-Possamai, S.; Tagu, D. Sexual and asexual oogenesis require the expression of unique and shared sets of genes in the insect Acyrthosiphon pisum. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickel, R.D.; Cleveland, H.C.; Barkas, J.; Jeschke, C.C.; Raz, A.A.; Stern, D.L.; Davis, G.K. The pea aphid uses a version of the terminal system during oviparous, but not viviparous, development. EvoDevo 2013, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, N.; Kanbe, T.; Akimoto, S.-I.; Numata, H. Transgenerational seasonal timer for suppression of sexual morph production in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 101, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, N.A.; Yun, Y. Experimental replacement of an obligate insect symbiont. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2093–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouvaine, S.; Faure, M.-L.; Grebenok, R.J.; Behmer, S.T.; Douglas, A.E. A Dietary Test of Putative Deleterious Sterols for the Aphid Myzus persicae. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febvay, G.; Rahbé, Y.; Rynkiewicz, M.; Guillaud, J.; Bonnot, G. Fate of dietary sucrose and neosynthesis of amino acids in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum, reared on different diets. J. Exp. Biol. 1999, 202, 202. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, T.; Hayashi, H.; Ishikawa, H. Growth and Reproduction of the Symbiotic and Aposymbiotic Pea Aphids, Acyrthosiphon pisum Maintained on Artificial Diets. J. Insect Physiol. 1999, 37, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E.; Minto, L.B.; Wilkinson, T.L. Quantifying nutrient production by the microbial symbionts in an aphid. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Puterka, G.J.; Nicholson, S.J.; Cooper, W.R. Survival and Feeding Rates of Four Aphid Species (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on Various Sucrose Concentrations in Diets. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.H.; Jing, X.; Luo, Y.; Douglas, A.E. Targeting symbiosis-related insect genes by RNAi in the pea aphid- Buchnera symbiosis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 95, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackauer, M. The population growth of the pea aphid biotype R1 on broad bean and pea (Homoptera: Aphididae). Z. fü Angew. Entomol. 1973, 74, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Hardie, J. Melatonin and the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. J. Insect Physiol. 1997, 43, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wale, M.; Jembere, B.; Seyoum, E. Biology of the Pea Aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harr.) (Homoptera: Aphididae) on Cool-Season Legumes. Insect Sci. Applic. 2000, 20, 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Sandstrom, J.; Pettersson, J. Amino acid composition of phloem sap and the relation to intraspecific variation in pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) performance. J. Insect Physiol. 1994, 40, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, B.D. Life tables and intrinsic rates of increase of the apterous black bean aphids and pea aphids, on broad bean (Homoptera: Aphididae). Can. Entomol. 1972, 104, 1717–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, P.A.; Wellington, W.G. A comparison of the reproductive patterns of apterous and alate virginoparous Acyrthosiphon pisum (Homoptera: Aphididae). Can. Entomol. 1975, 107, 1161–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, L.; Nielson, M.W. Differential Effects of Temperature on the Biological Activity of Four Biotypes of the Pea Aphid. J. Econ. Entomol. 1971, 64, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, R.J.; MacKay, P.A.; Gerber, G.H. Are development and growth of pea aphids, Acyrthosiphon pisum, in North America adapted to local temperatures? Oecologia (Berlin) 1987, 72, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A.; Frazer, B.D.; Gilbert, N.; Gutierrez, A.P.; Mackauer, M. Temperature Requirements of Some Aphids and Their Parasites. J. Appl. Ecol. 1974, 11, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, W.H.; Barlow, C.A.; Randolph, P.A. Effects of some constant and alternating temperatures on population growth of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Homoptera: Aphididae). Can. Entomol. 1973, 105, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchison, W.D.; Hogg, D.B. Demographic Statistics for the Pea Aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Wisconsin and a Comparison with Other Populations. Environ. Entomol. 1984, 13, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, A.E. Requirement of pea aphids (Acyrthosiphon pisum) for their symbiotic bacteria. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1992, 65, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, A.; Barbosa, P. Pea Aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) Fecundity, Rate of Increase, and Within-Plant Distribution Unaffected by Plant Morphology. Environ. Entomol. 2000, 29, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartier, J.J. Growth, Reproduction and Longevity in one Biotype of the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harr.) (Homoptera: Aphididae). Can. Entomol. 1960, 92, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-N.; Kuo, M.-H. Life table and heat tolerance of Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera: Aphididae) in subtropical Taiwan. Entomol. Sci. 2008, 11, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.N.; Auclair, J.L. Effect of Amino Acid Concentration on Diet Uptake and Performance by the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Homoptera: Aphididae). Can. Entomol. 1974, 106, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieri, M.; Baumgartner, J.; Bianchi, G.; Delucchi, V.; von Arx, R. Development and fecundity of pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum Harris) as affected by constant temperatures and by pea varieties. Bull Soc. Entomol. Suisse. 1983, 56, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, A. Seasonal Changes in Abundance of the Pea Aphid and its Associated Parasites in the Southern Interior of British Columbia. Ph.D. Thesis, Simon Fraser University, Burnaby, BC, Canada, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Prosser, W.; Douglas, A. The aposymbiotic aphid: An analysis of chlortetracycline-treated pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. J. Insect Physiol. 1991, 37, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair, J.L. Feeding and nutrition of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Homoptera: Aphididae), on chemically defined diets of various pH and nutrient levels. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1965, 58, 855–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair, J.L.; Boisvert, J.M. Besoins qualitatifs en vitamins hydrosolubles chez deux biotypes du puceron du pois, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1980, 28, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.N.; Auclair, J.L. An Improved Chemically Defined Diet for the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum1. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1971, 64, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.N.; Auclair, J.L. Influence of Sucrose Concentration on Diet Uptake and Performance by the Pea Aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum1. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1971, 64, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auclair, J.L.; Cartier, J.J. Pea Aphid: Rearing on a Chemically Defined Diet. Science 1963, 142, 1068–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akey, D.H.; Beck, S.D. Continuous rearing of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum, on a synthetic diet. Ann. Ent. Soc. Am. 1971, 64, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrovsky, A.; Ledger, T.N.; Engler, G.; Robichon, A. Using the pea aphid Acrythociphon pisum as a tool for screening biological responses to chemicals and drugs. BMC Res. Notes 2009, 2, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, K.J.; Moran, N.A. Sources of variation in dietary requirements in an obligate nutritional symbiosis. Proc. R. Soc. B 2011, 278, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadd, R.H.; Mittler, T.E. Permanent culture of an aphid on a totally synthetic diet. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 1966, 22, 832–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Minhas, B.F.; Li-Byarlay, H.; Hansen, A.K. Key Transport and Ammonia Recycling Genes Involved in Aphid Symbiosis Respond to Host-Plant Specialization. G3 (Bethesda) 2018, 8, 2433–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, A.R. Novel Approaches for the Chromatographic and Electrophoretic Separation of Molecules. Ph.D. Thesis, Kansas State University, Manhattan, KS, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Schoonhoven, L.M.; van Loon, J.J.A.; Dicke, M. Insect-Plant Biology, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press Inc.: New York, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Marquis, R.J. Plant architecture, sectoriality and plant tolerance to herbivores. Vegetatio 1996, 127, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.A.; Casper, B.B. Morphogenetic Constraints on Patterns of Carbon Distribution in Plants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1984, 15, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, C.A.; Clegg, J.M. Escape behaviour of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) in response to alarm pheromone and vibration. Can. J. Zool. 1982, 60, 2245–2252. [Google Scholar]
- Chau, A.; Mackauer, M. Dropping of pea aphids from feeding site: A consequence of parasitism by the wasp, Monoctonus paulensis. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1997, 83, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, L.M.; Fraser, A.H.G.; Roitberg, B.D. The economics of escape behaviour in the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Oecologia 1990, 83, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losey, J.E.; Denno, R.F. The escape response of pea aphids to foliar-foraging predators: Factors affecting dropping behavior. Ecol. Entomol. 1997, 23, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilska, A.; Francikowski, J.; Wyglenda, A.; Masłowski, A.; Kaszyca, N.; Depa, Ł. Aphids Playing Possum—Defensive or Mutualistic Response? J. Insect Behav. 2018, 31, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salyk, R.P.; Sullivan, D.J. Comparative feeding behavior of two aphid species: Bean aphid (Aphis fabae Scopoli) and pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris)) (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. New York Entomol. Soc. 1982, 90, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Prosser, W.; Douglas, A. A test of the hypotheses that nitrogen is upgraded and recycled in an aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) symbiosis. J. Insect Physiol. 1992, 38, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, T.E. Uptake Rates of Plant Sap and Synthetic Diet by the Aphid Myzus persicae1. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1970, 63, 1701–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjallingii, W.F.; Esch, T.H. Fine structure of aphid stylet routes in plant tissues in correlation with EPG signals. Physiol. Entomol. 1993, 18, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrys, B.; Tjallingii, W. The role of sinigrin in host plant recognition by aphids during initial plant penetration. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2002, 104, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hom, J.L.; Oechel, W.C. The photosynthetic capacity, nutrient content, and nutrient use efficiency of different needle age-classes of black spruce (Picea mariana) found in interior Alaska. Can. J. For. Res. 1983, 13, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volder, A.; Smart, D.R.; Bloom, A.J.; Eissenstat, D.M. Rapid decline in nitrate uptake and respiration with age in fine lateral roots of grapes: Implications for the root efficiency and competitive effectiveness. New Phytol. 2005, 165, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.B.; Liu, Y.Q.; Chen, D.Y.; Chen, F.Y.; Fang, X.; Hong, G.J.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, J.W.; Chen, X.Y. Jasmonate response decay and defense metabolite accumulation contributes to age-related dynamics of plant insect resistance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, D.; Levitis, D. Dichotomous Key to Pea Aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum) Apterous Parthenogenic Instars. Bates College Department of Biology. SCARAB Data Repos. 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Digilio, M. Rapid Identification of the nymphal stages of Acyrthosiphon pisum (Harris) (Homoptera Aphidoidea). Bollettino di Zoologia Agraria e di Bachicoltura 1995, 27, 111–116. [Google Scholar]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pers, D.; Hansen, A.K. The Effects of Different Diets and Transgenerational Stress on Acyrthosiphon pisum Development. Insects 2019, 10, 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10090260
Pers D, Hansen AK. The Effects of Different Diets and Transgenerational Stress on Acyrthosiphon pisum Development. Insects. 2019; 10(9):260. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10090260
Chicago/Turabian StylePers, Daniel, and Allison K. Hansen. 2019. "The Effects of Different Diets and Transgenerational Stress on Acyrthosiphon pisum Development" Insects 10, no. 9: 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10090260
APA StylePers, D., & Hansen, A. K. (2019). The Effects of Different Diets and Transgenerational Stress on Acyrthosiphon pisum Development. Insects, 10(9), 260. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects10090260




