High-Throughput Genotyping of Common Chromosomal Inversions in the Afrotropical Malaria Mosquito Anopheles Funestus
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Illumina Whole Genome Sequencing and Ascertainment of Candidate Tag SNPs
2.1.1. Mosquito Sampling and Sequencing
2.1.2. Tag SNP Discovery
2.2. Mosquito Samples for Validation of Tag SNPs
2.3. TaqMan OpenArray Assay Design and Workflow for Genotyping of Inversions 3Ra and 3Rb
2.4. Amplicon Sequencing Assay Design and Workflow for Genotyping of Inversions 2Ra, 3Ra, and 3Rb
2.5. Converting Genotypes at Individual Tags to Multilocus Inversion Genotypes
2.6. Code and Data Availability
3. Results
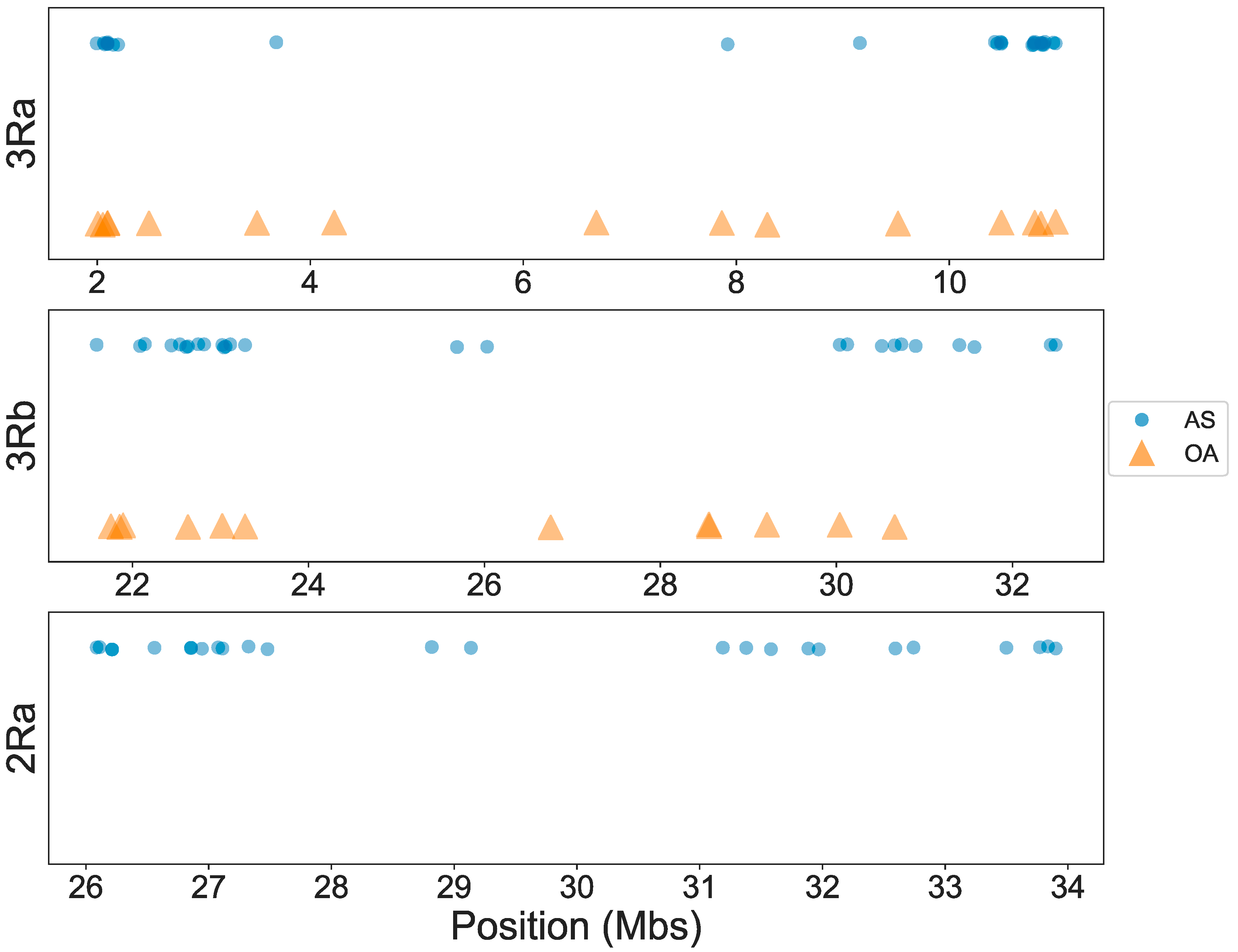
3.1. OA Genotyping
3.2. AS Genotyping
3.3. Concordance among Cytogenetic and Molecular Inversion Genotyping Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wellenreuther, M.; Bernatchez, L. Eco-Evolutionary Genomics of Chromosomal Inversions. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2018, 33, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkpatrick, M. How and Why Chromosome Inversions Evolve. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoffmann, A.A.; Rieseberg, L.H. Revisiting the Impact of Inversions in Evolution: From Population Genetic Markers to Drivers of Adaptive Shifts and Speciation? Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2008, 39, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhimulev, I.; Koryakov, D.E. Polytene Chromosomes; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, P.H.; Cheke, R.A.; Post, R.J. Evolution, epidemiology, and population genetics of black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2010, 10, 846–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krimbas, C.B.; Powell, J.R. Drosophila Inversion Polymorphism; CRC Press: London, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Coluzzi, M.; Sabatini, A.; Petrarca, V.; Di Deco, M. Chromosomal differentiation and adaptation to human environments in the Anopheles gambiae complex. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1979, 73, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, M.; Barton, N. Chromosome Inversions, Local Adaptation and Speciation. Genetics 2005, 173, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coluzzi, M. Spatial distribution of chromosomal inversions and speciation in Anopheline mosquitoes. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1982, 96, 143–153. [Google Scholar]
- Coluzzi, M.; Sabatini, A.; Della Torre, A.; Di Deco, M.A.; Petrarca, V. A Polytene Chromosome Analysis of the Anopheles gambiae Species Complex. Science 2002, 298, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organisation. World Malaria Report: 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/malaria/publications/world-malaria-report-2018/report/en/ (accessed on 20 August 2020).
- Ayala, D.; Acevedo, P.; Pombi, M.; Dia, I.; Boccolini, D.; Costantini, C.; Simard, F.; Fontenille, D. Chromosome inversions and ecological plasticity in the main African malaria mosquitoes. Evolution 2017, 71, 686–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rishikesh, N.; Di Deco, M.A.; Petrarca, V.; Coluzzi, M. Seasonal variations in indoor resting Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles arabiensis in Kaduna, Nigeria. Acta Trop. 1985, 42, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; White, B.J.; Kamdem, C.; Mockaitis, K.; Costantini, C.; Hahn, M.W.; Besansky, N.J. Ecological Genomics of Anopheles gambiae Along a Latitudinal Cline: A Population-Resequencing Approach. Genetics 2011, 190, 1417–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fouet, C.; Gray, E.; Besansky, N.J.; Costantini, C. Adaptation to Aridity in the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles gambiae: Chromosomal Inversion Polymorphism and Body Size Influence Resistance to Desiccation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gray, E.M.; Rocca, K.A.; Costantini, C.; Besansky, N.J. Inversion 2La is associated with enhanced desiccation resistance in Anopheles gambiae. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rocca, K.A.; Gray, E.M.; Costantini, C.; Besansky, N.J. 2La chromosomal inversion enhances thermal tolerance of Anopheles gambiae larvae. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cassone, B.J.; Molloy, M.J.; Cheng, C.; Tan, J.C.; Hahn, M.W.; Besansky, N.J. Divergent transcriptional response to thermal stress by Anopheles gambiae larvae carrying alternative arrangements of inversion 2La. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 2567–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ayala, D.; Zhang, S.; Chateau, M.; Fouet, C.; Morlais, I.; Costantini, C.; Hahn, M.W.; Besansky, N.J. Association mapping desiccation resistance within chromosomal inversions in the African malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 28, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.; Tan, J.C.; Hahn, M.W.; Besansky, N.J. A systems genetic analysis of inversion polymorphisms in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7005–E7014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petrarca, V.; Beier, J.C. Intraspecific Chromosomal Polymorphism in the Anopheles Gambiae Complex as a Factor Affecting Malaria Transmission in the Kisumu Area of Kenya. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1992, 46, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehle, M.M.; Bukhari, T.; Gneme, A.; Guelbeogo, W.M.; Coulibaly, B.; Fofana, A.; Pain, A.; Bischoff, E.; Renaud, F.; Beavogui, A.H.; et al. The Anopheles gambiae 2La chromosome inversion is associated with susceptibility to Plasmodium falciparum in Africa. eLife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Main, B.J.; Lee, Y.; Eferguson, H.; Kreppel, K.S.; Kihonda, A.; Govella, N.J.; Collier, T.C.; Cornel, A.J.; Eskin, E.; Kang, E.Y.; et al. The Genetic Basis of Host Preference and Resting Behavior in the Major African Malaria Vector, Anopheles arabiensis. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontenille, D.; Lochouarn, L.; Diagne, N.; Sokhna, C.; Lemasson, J.-J.; Diatta, M.; Konate, L.; Faye, F.; Rogier, C.; Trape, J.-F. High Annual and Seasonal Variations in Malaria Transmission by Anophelines and Vector Species Composition in Dielmo, a Holoendemic Area in Senegal. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1997, 56, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coetzee, M.; Koekemoer, L.L. Molecular Systematics and Insecticide Resistance in the Major African Malaria VectorAnopheles funestus. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dia, I.; Guelbeogo, M.W.; Ayala, D. Advances and Perspectives in the Study of the Malaria Mosquito Anopheles funestus. In Anopheles Mosquitoes—New Insights into Malaria Vectors; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Boccolini, D.; Sagnon, N.; Toure, Y.T. Chromosomal polymorphism in Anopheles funestus and description of new inversions in Burkina Faso and Mali. Parassitologia 1998, 40, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Lochouarn, L.; Dia, I.; Boccolini, D.; Coluzzi, M.; Fontenille, D. Bionomical and cytogenetic heterogeneities of Anopheles funestus in Senegal. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1998, 92, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, C.A.; Hunt, R.H. Interpretation of variation in ovarian polytene chromosomes of Anopheles Funestus Giles, A. Parensis Gillies, and A. Aruni? Genetics 1980, 51, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharakhov, I.; Braginets, O.; Grushko, O.; Cohuet, A.; Guelbeogo, W.M.; Boccolini, D.; Weill, M.; Costantini, C.; Sagnon, N.; Fontenille, D.; et al. A microsatellite map of the African human malaria vector Anopheles funestus. J. Hered. 2004, 95, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waterhouse, R.M.; Aganezov, S.; Anselmetti, Y.; Lee, J.; Ruzzante, L.; Reijnders, M.J.M.F.; Feron, R.; Bérard, S.; George, P.; Hahn, M.W.; et al. Evolutionary superscaffolding and chromosome anchoring to improve Anopheles genome assemblies. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayala, D.; Fontaine, M.C.; Cohuet, A.; Fontenille, D.; Vitalis, R.; Simard, F. Chromosomal Inversions, Natural Selection and Adaptation in the Malaria Vector Anopheles funestus. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 28, 745–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayala, D.; Guerrero, R.F.; Kirkpatrick, M. Reproductive Isolation and Local Adaptation Quantified For A Chromosome Inversion In A Malaria Mosquito. Evolution 2012, 67, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, D.; Caro-Riaño, H.; Dujardin, J.-P.; Rahola, N.; Simard, F.; Fontenille, D. Chromosomal and environmental determinants of morphometric variation in natural populations of the malaria vector Anopheles funestus in Cameroon. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2011, 11, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costantini, C.; Sagnon, N.; Ilboudo-Sanogo, E.; Coluzzi, M.; Boccolini, D. Chromosomal and bionomic heterogeneities suggest incipient speciation in Anopheles funestus from Burkina Faso. Parassitologia 1999, 41, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guelbeogo, W.M.; Grushko, O.; Boccolini, D.; Ouedraogo, P.A.; Besansky, N.J.; Sagnon, N.F.; Costantini, C. Chromosomal evidence of incipient speciation in the Afrotropical malaria mosquito Anopheles funestus. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2005, 19, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guelbéogo, W.M.; Sagnon, N.; Grushko, O.; Yameogo, M.A.; Boccolini, D.; Besansky, N.J.; Costantini, C. Seasonal distribution of Anopheles funestus chromosomal forms from Burkina Faso. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guelbéogo, W.M.; Sagnon, N.; Liu, F.; Besansky, N.J.; Costantini, C. Behavioural divergence of sympatric Anopheles funestus populations in Burkina Faso. Malar. J. 2014, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Della Torre, A. Polytene Chromosome Preparation from Anopheline Mosquitoes; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Berlin, Germany, 1997; pp. 329–336. [Google Scholar]
- Love, R.R.; Redmond, S.N.; Pombi, M.; Caputo, B.; Petrarca, V.; Della Torre, A.; Besansky, N.J.; The Anopheles gambiae 1000 Genomes Consortium. In Silico Karyotyping of Chromosomally Polymorphic Malaria Mosquitoes in the Anopheles gambiae Complex. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2019, 9, 3249–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miles, A.; Harding, N.J.; Bottà, G.; Clarkson, C.S.; Antão, T.; Kozak, K.; Schrider, D.R.; Kern, A.D.; Redmond, S.; Sharakhov, I.; et al. Genetic diversity of the African malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Nature 2017, 552, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, R.R.; Pombi, M.; Guelbeogo, M.W.; Campbell, N.R.; Stephens, M.T.; Dabire, R.K.; Costantini, C.; Della Torre, A.; Besansky, N.J. Inversion Genotyping in the Anopheles gambiae Complex Using High-Throughput Array and Sequencing Platforms. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghurye, J.; Koren, S.; Small, S.T.; Redmond, S.N.; Howell, P.; Phillippy, A.M.; Besansky, N.J. A chromosome-scale assembly of the major African malaria vector Anopheles funestus. GigaScience 2019, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, A.P.; Grushko, O.; Guelbeogo, W.M.; Lobo, N.F.; Sagnon, N.; Costantini, C.; Besansky, N.J. Divergence with Gene Flow in Anopheles funestus From the Sudan Savanna of Burkina Faso, West Africa. Genetics 2006, 173, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koekemoer, L.L.; Kamau, L.; Coetzee, M.; Hunt, R.H. A cocktail polymerase chain reaction assay to identify members of the Anopheles funestus (Diptera: Culicidae) group. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2002, 66, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.S.; Hunt, R.H.; Koekemoer, L.K. Simultaneous identification of the Anopheles funestus group and Anopheles longipalpis type C by PCR-RFLP. Malar. J. 2010, 9, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Rangasamy, M.; Tan, S.Y.; Wang, H.; Siegfried, B.D. Evaluation of Five Methods for Total DNA Extraction from Western Corn Rootworm Beetles. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miles, A.; Harding, N.J. A Python Package for Exploring and Analysing Genetic Variation Data. Available online: http://github.com/cggh/scikit-allel (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Smit, A.F.A.; Hubley, R.; Green, P. RepeatMasker Open-4.0. Available online: http://www.repeatmasker.org (accessed on 27 January 2019).
- Neafsey, D.E.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Abai, M.R.; Aganezov, S.S.; Alekseyev, M.A.; Allen, J.E.; Amon, J.; Arcà, B.; Arensburger, P.; Artemov, G.; et al. Highly evolvable malaria vectors: The genomes of 16 Anopheles mosquitoes. Science 2015, 347, 1258522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Amos, C.I. Investigation of Inversion Polymorphisms in the Human Genome Using Principal Components Analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Besansky, N.J.; Powell, J.R. Reassociation Kinetics of Anopheles gambiae (Diptera: Culicidae) DNA. J. Med. Entomol. 1992, 29, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, N.R.; Harmon, S.A.; Narum, S.R. Genotyping-in-Thousands by sequencing (GT-seq): A cost effective SNP genotyping method based on custom amplicon sequencing. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 15, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanez-Gonzalez, R.; Pichler, V.; Calzetta, M.; Love, R.R.; Vallera, A.; Schaecher, L.; Caputo, B.; Pombi, M.; Petrarca, V.; Della Torre, A.; et al. Highly specific PCR-RFLP assays for karyotyping the widespread 2Rb inversion in malaria vectors of the Anopheles gambiae complex. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, S.T.; Labbé, F.; Lobo, N.F.; Koekemoer, L.L.; Sikaala, C.H.; Neafsey, D.E.; Hahn, M.W.; Fontaine, M.C.; Besansky, N.J. Radiation with reticulation marks the origin of a major malaria vector. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, A.P.; Guelbeogo, W.M.; Grushko, O.; Schemerhorn, B.J.; Kern, M.; Willard, M.B.; Sagnon, N.; Costantini, C.; Besansky, N.J. Molecular differentiation between chromosomally defined incipient species of Anopheles funestus. Insect Mol. Biol. 2005, 14, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantini, C.; Ayala, D.; Guelbéogo, W.M.; Pombi, M.; Somé, Y.S.C.; Bassolé, I.H.N.; Ose, K.; Fotsing, J.-M.; Sagnon, N.; Fontenille, D.; et al. Living at the edge: Biogeographic patterns of habitat segregation conform to speciation by niche expansion in Anopheles gambiae. BMC Ecol. 2009, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simard, F.; Ayala, D.; Kamdem, G.C.; Etouna, J.; Ose, K.; Fotsing, J.-M.; Fontenille, D.; Besansky, N.J.; Costantini, C. Ecological niche partitioning between the M and S molecular forms of Anopheles gambiae in Cameroon: The ecological side of speciation. BMC Ecol. 2009, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Inversion | Genomic Coordinates |
|---|---|
| 2Ra | 25,967,767–33,984,223 |
| 3Ra | 1,866,360–11,289,547 |
| 3Rb | 20,512,400–33,000,000 |
| 3Ra | 3Rb | 2Ra | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concordance: | |||
| CYT + AS + OA | 211/229 (92.1%) | 183/225 (81.3%) | NA |
| CYT + AS | --- | --- | 195/226 (86.3%) |
| CYT + PCA | 151/158 (95.6%) | 145/155 (93.5%) | 134/143 (93.7%) |
| Discordance: | |||
| CYT vs. (AS + OA) | 17/229 (7.4%) | 21/225 (9.3%) | NA |
| (CYT + AS) vs. OA | 1/229 (0.4%) | 12/225 (5.3%) | NA |
| (CYT + OA) vs. AS | 0/229 (0%) | 7/225 (3.1%) | NA |
| CYT + AS + OA | 0/229 (0%) | 2/225 (0.9%) | NA |
| CYT vs. PCA | 7/158 (4.4%) | 10/155 (6.5%) | 9/143 (6.3%) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lukindu, M.; Love, R.R.; Guelbeogo, M.W.; Small, S.T.; Stephens, M.T.; Campbell, N.R.; Sagnon, N.; Costantini, C.; Besansky, N.J. High-Throughput Genotyping of Common Chromosomal Inversions in the Afrotropical Malaria Mosquito Anopheles Funestus. Insects 2020, 11, 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100693
Lukindu M, Love RR, Guelbeogo MW, Small ST, Stephens MT, Campbell NR, Sagnon N, Costantini C, Besansky NJ. High-Throughput Genotyping of Common Chromosomal Inversions in the Afrotropical Malaria Mosquito Anopheles Funestus. Insects. 2020; 11(10):693. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100693
Chicago/Turabian StyleLukindu, Martin, R. Rebecca Love, Moussa W. Guelbeogo, Scott T. Small, Melissa T. Stephens, Nathan R. Campbell, N’Fale Sagnon, Carlo Costantini, and Nora J. Besansky. 2020. "High-Throughput Genotyping of Common Chromosomal Inversions in the Afrotropical Malaria Mosquito Anopheles Funestus" Insects 11, no. 10: 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100693
APA StyleLukindu, M., Love, R. R., Guelbeogo, M. W., Small, S. T., Stephens, M. T., Campbell, N. R., Sagnon, N., Costantini, C., & Besansky, N. J. (2020). High-Throughput Genotyping of Common Chromosomal Inversions in the Afrotropical Malaria Mosquito Anopheles Funestus. Insects, 11(10), 693. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11100693





