Effect of Trap Color on Captures of Bark- and Wood-Boring Beetles (Coleoptera; Buprestidae and Scolytinae) and Associated Predators
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Trap Type, Trap Color and Trap Height
2.3. Experimental Scheme and Attractive Lures
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
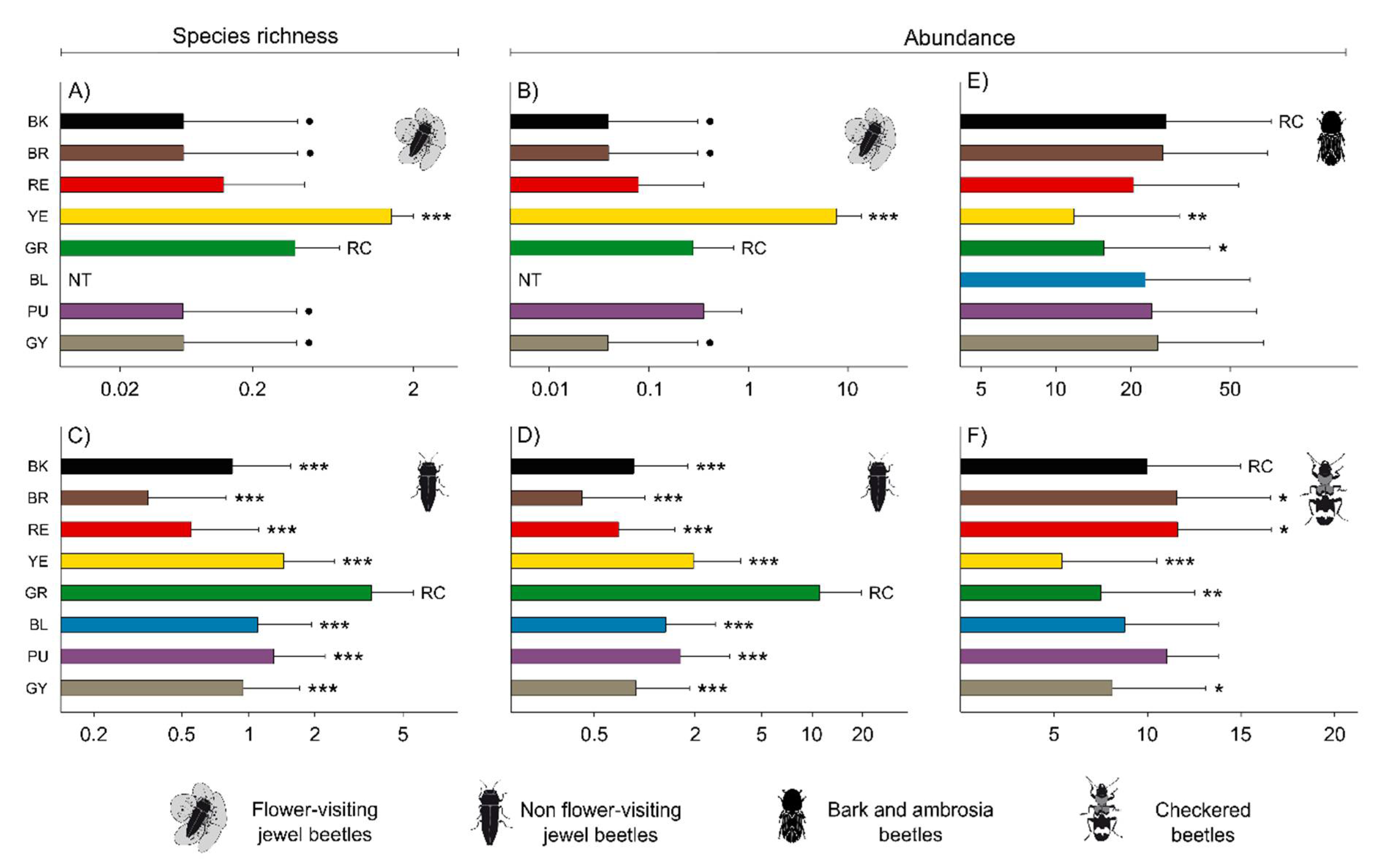
3.1. General Results
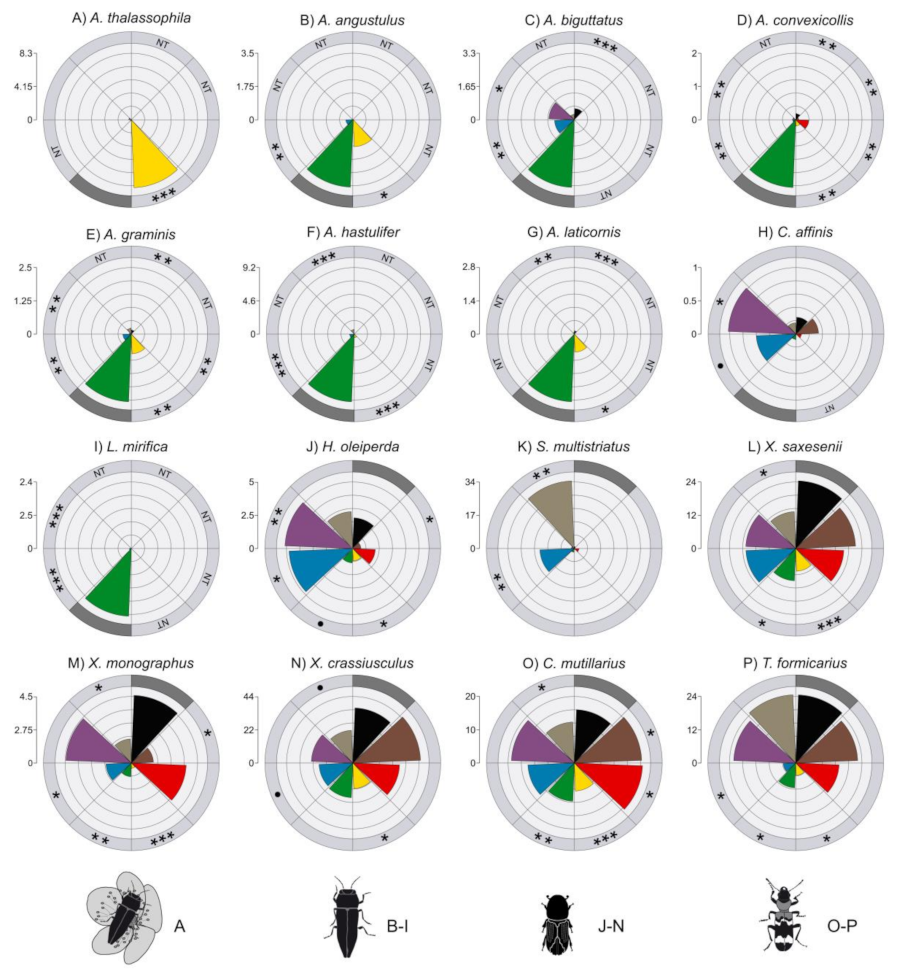
3.2. Effect of Trap Color on Jewel Beetles
3.3. Effect of Trap Color on Bark Beetles, Ambrosia Beetles and Checkered Beetles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haack, R.A. Exotic bark- and wood-boring Coleoptera in the United States: Recent establishments and interceptions. Can. J. For. Res. 2006, 36, 269–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnankutty, S.; Nadel, H.; Taylor, A.M.; Wiemann, M.C.; Wu, Y.; Lingafelter, S.W.; Myers, S.W.; Ray, A.M. Identification of tree genera used in the construction of solid wood-packaging materials that arrived at U.S. ports infested with live wood-boring insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurisse, N.; Rassati, D.; Hurley, B.P.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Haack, R.A. Common pathways by which non-native forest insects move internationally and domestically. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rassati, D.; Haack, R.A.; Knížek, M.; Faccoli, M. National trade can drive range expansion of bark- and wood-boring beetles. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vannini, A.; Contarini, M.; Faccoli, M.; Valle, M.D.; Rodriguez, C.M.; Mazzetto, T.; Guarneri, D.; Vettraino, A.M.; Speranza, S. First report of the ambrosia beetle Xylosandrus compactus and associated fungi in the Mediterranean maquis in Italy, and new host–pest associations. EPPO Bull. 2017, 47, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galko, J.; Dzurenko, M.; Ranger, C.M.; Kulfan, J.; Kula, E.; Nikolov, C.; Zubrick, M.; Zach, P. Distribution, habitat preference, and management of the invasive ambrosia beetle Xylosandrus germanus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Scolytinae) in European forests with an emphasis on the West Carpathians. Forests 2019, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovacs, K.F.; Haight, R.G.; McCullough, D.G.; Mercader, R.J.; Siegert, N.W.; Liebhold, A.M. Cost of potential emerald ash borer damage in US communities, 2009–2019. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassati, D.; Lieutier, F.; Faccoli, M. Alien wood-boring beetles in Mediterranean regions. In Insects and Diseases of Mediterranean Forest Systems; Payne, T.D., Lieutier, F., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 293–327. [Google Scholar]
- Rabaglia, R.J.; Cognato, A.I.; Hoebeke, E.R.; Johnson, C.W.; LaBonte, J.R.; Carter, M.E.; Vlach, J.J. Early detection and rapid response: A 10-Year summary of the USDA forest service program of surveillance for non-native bark and ambrosia beetles. Am. Entomol. 2019, 65, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockerhoff, E.G.; Jones, D.C.; Kimberley, M.O.; Suckling, D.M.; Donaldson, T. Nationwide survey for invasive wood-boring and bark beetles (Coleoptera) using traps baited with pheromones and kairomones. For. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 228, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassati, D.; Faccoli, M.; Petrucco Toffolo, E.; Battisti, A.; Marini, L. Improving the early detection of alien wood-boring beetles in ports and surrounding forests. J. Appl. Ecol. 2015, 52, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassati, D.; Faccoli, M.; Marini, L.; Haack, R.A.; Battisti, A.; Petrucco Toffolo, E. Exploring the role of wood waste landfills in early detection of non-native wood-boring beetles. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, J.; Hughes, C.; Webster, V.; Kostanowicz, C.; Webster, R.; Mayo, P.; Allison, J.D. Impact of horizontal edge–interior and vertical canopy–understory gradients on the abundance and diversity of bark and woodboring beetles in survey traps. Insects 2020, 11, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, J.D.; Redak, R.A. The impact of trap type and design features on survey and detection of bark and woodboring beetles and their associates: A review and meta-analysis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 127–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flaherty, L.; Gutowski, J.M.G.; Hughes, C.; Mayo, P.; Mokrzycki, T.; Pohl, G.; Silk, P.; Van Rooyen, K.; Sweeney, J. Pheromone-enhanced lure blends and multiple trap heights improve detection of bark and wood-boring beetles potentially moved in solid wood packaging. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchioro, M.; Rassati, D.; Faccoli, M.; Van Rooyen, K.; Kostanowicz, C.; Webster, V.; Mayo, P.; Sweeney, J. Maximizing bark and ambrosia beetle catches in trapping surveys for longhorn and jewel beetles. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aukema, B.H.; Dahlsten, D.L.; Raffa, K.F. Exploiting behavioral disparities among predators and prey to selectively remove pests: Maximizing the ratio of bark beetles to predators removed during semiochemically based trap-out. Environ. Entomol. 2000, 29, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, A.; Etxebeste, I.; Pérez, G.; Álvarez, G.; Sánchez, E.; Pajares, J. Modified pheromone traps help reduce bycatch of bark-beetle natural enemies. Agric. For. Entomol. 2013, 15, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, W.P.; Sullivan, B.T. Spatial displacement of a lure component can reduce catches of two nontarget species during spring monitoring of southern pine beetle. J. Insect Sci. 2018, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavaletto, G.; Faccoli, M.; Marini, L.; Spaethe, J.; Giannone, F.; Moino, S.; Rassati, D. Exploiting trap color to improve surveys of longhorn beetles. J. Pest Sci. 2020. Under review. [Google Scholar]
- Rassati, D.; Marini, L.; Marchioro, M.; Rapuzzi, P.; Magnani, G.; Poloni, R.; Di Giovanni, F.; Mayo, P.; Sweeney, J. Developing trapping protocols for wood-boring beetles associated with broadleaf trees. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, H.F.; Moraal, L.G.; Pajares, J.A. Biology, ecology and economic importance of Buprestidae and Cerambycidae. In Bark and Wood Boring Insects in Living Trees in Europe, a Synthesis; Lieutier, F., Day, K.R., Battisti, A., Gregoire, J.C., Evans, H.F., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 447–474. [Google Scholar]
- Domingue, M.J.; Lelito, J.P.; Myrick, A.J.; Csóka, G.; Szöcs, L.; Imrei, Z.; Baker, T.C. Differences in spectral selectivity between stages of visually guided mating approaches in a buprestid beetle. J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 219, 2837–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lelito, J.P.; Fraser, I.; Mastro, V.C.; Tumlinson, J.H.; Böröczky, K.; Baker, T.C. Visually mediated ‘paratrooper copulations’ in the mating behavior of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), a highly destructive invasive pest of North American ash trees. J. Insect Behav. 2007, 20, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lelito, J.P.; Domingue, M.J.; Fraser, I.; Mastro, V.C.; Tumlinson, J.H.; Baker, T.C. Field investigation of mating behaviour of Agrilus cyanescens and Agrilus subcinctus. Can. Entomol. 2011, 143, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingue, M.J.; Csóka, G.; Tóth, M.; Vétek, G.; Pénzes, B.; Mastro, V.; Baker, T.C. Field observations of visual attraction of three European oak buprestid beetles toward conspecific and heterospecific models. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2011, 140, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imrei, Z.; Lohonyai, Z.; Csóka, G.; Muskovits, J.; Szanyi, S.; Vétek, G.; Fail, J.; Toth, M.; Domingue, M.J. Improving trapping methods for buprestid beetles to enhance monitoring of native and invasive species. For. Int. J. For. Res. 2020, 93, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakalian, V.; Langourov, M. Colour trap a method for distributional and ecological investigations of Buprestidae (Coleoptera). Acta Soc. Zool. Bohem. 2004, 68, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.W.; Hanula, J.L. Efficiency of Malaise traps and colored pan traps for collecting flower visiting insects from three forested ecosystems. J. Insect Conserv. 2007, 11, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varandi, H.B.; Kalashian, M.; Barari, H.; Taleshi, S.R. The diversity of wood-boring beetles caught by different traps in northern forests of Iran. Trop. Drylands 2018, 2, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francese, J.A.; Crook, D.J.; Fraser, I.; Lance, D.R.; Sawyer, A.J.; Mastro, V.C. Optimization of trap color for emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrice, T.R.; Haack, R.A.; Poland, T.M. Attraction of Agrilus planipennis (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) and other buprestids to sticky traps of various colors and shapes. Great Lakes Entomol. 2013, 46, 13–30. [Google Scholar]
- Crook, D.J.; Khrimian, A.; Cossé, A.; Fraser, I.; Mastro, V.C. Influence of trap color and host volatiles on capture of the emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Francese, J.A.; Rietz, M.L.; Mastro, V.C. Optimization of multifunnel traps for emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae): Influence of size, trap coating and color. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 2415–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skvarla, M.J.; Dowling, A.P. A comparison of trapping techniques (Coleoptera: Carabidae, Buprestidae, Cerambycidae, and Curculionoidea excluding Scolytinae). J. Insect Sci. 2017, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstenau, B.; Quero, C.; Riba, J.M.; Rosell, G.; Guerrero, A. Field trapping of the flathead oak borer Coroebus undatus (Coleoptera: Buprestidae) with different traps and volatile lures. Insect Sci. 2015, 22, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, D.J.; Francese, J.A.; Zylstra, K.E.; Fraser, I.; Sawyer, A.J.; Bartels, D.W.; Lance, D.R.; Mastro, V.C. Laboratory and field response of the emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae), to selected regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 2160–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francese, J.A.; Fraser, I.; Rietz, M.L.; Crook, D.J.; Lance, D.R.; Mastro, V.C. Relation of color, size, and canopy placement of prism traps in determining capture of emerald ash borer (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). Can. Entomol. 2010, 142, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, T.M.; Petrice, T.R.; Ciaramitaro, T.M. Trap designs, colors, and lures for emerald ash borer detection. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2019, 2, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haack, R.A.; Jendek, E.; Liu, H.; Marchant, K.R.; Petrice, T.R.; Poland, T.M.; Ye, H. The emerald ash borer: A new exotic pest in North America. Newslett. Mich. Entomol. Soc. 2002, 47, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rhainds, M.; Kimoto, T.; Galko, J.; Nikolov, C.; Ryall, K.; Brodersen, G.; Webster, V. Survey tools and demographic parameters of Slovakian Agrilus associated with beech and poplar. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2017, 162, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingue, M.J.; Imrei, Z.; Lelito, J.P.; Muskovits, J.; Janik, G.; Csóka, G.; Mastro, V.C.; Baker, T.C. Trapping of European buprestid beetles in oak forests using visual and olfactory cues. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2013, 148, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.; Jeger, M.; Kirk, S.; Williams, D.; Xu, X.; Pautasso, M.; Denman, S. Acute oak decline and Agrilus biguttatus: The co-occurrence of stem bleeding and D-shaped emergence holes in Great Britain. Forests 2017, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, S.A.; Borden, J.H. Additive and synergistic integration of multimodal cues of both hosts and non-hosts during host selection by woodboring insects. Oikos 2009, 118, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.A.; Borden, J.H. Integration of visual and olfactory cues of hosts and non-hosts by three bark beetles (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Ecol. Entomol. 2006, 31, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayfield, A.E., III; Brownie, C. The redbay ambrosia beetle (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae) uses stem silhouette diameter as a visual hostfinding cue. Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, S.A.; Borden, J.H. Bark reflectance spectra of conifers and angiosperms: Implications for host discrimination by coniferophagous bark and timber beetles. Can. Entomol. 2005, 137, 719–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, B.L.; Roton, L.M.; Goyer, R.A.; Meeker, J.R. Visual and semiochemical disruption of host finding in the southern pine beetle. Ecol. Appl. 1999, 9, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.A.; Borden, J.H. Close-range, in-flight integration of olfactory and visual information by a host-seeking bark beetle. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2006, 120, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, B.L.; Goyer, R.A. Effect of silhouette color on trap catches of Dendroctonus frontalis (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2001, 94, 948–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubbel, V.; Kerck, K.; Sohrt, M.; Mangold, S. Influence of trap color on the efficiency of bark beetle pheromone traps. J. Appl. Entomol. 1985, 99, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Q.H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.T.; Zhou, X.; Niu, J.; Schlyter, F. Catching Ips duplicatus (Sahlberg) (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) with pheromone-baited traps: Optimal trap type, colour, height and distance to infestation. Pest Manag. Sci. Former. Pestic. Sci. 2010, 66, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanula, J.L.; Ulyshen, M.D.; Horn, S. Effect of trap type, trap position, time of year, and beetle density on captures of the redbay ambrosia beetle (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2011, 104, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, J.L.; Kelly, D.; Bader, M.K.F.; Brockerhoff, E.G. Olfactory cues, visual cues, and semiochemical diversity interact during host location by invasive forest beetles. J. Chem. Ecol. 2017, 43, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werle, C.T.; Bray, A.M.; Oliver, J.B.; Blythe, E.K.; Sampson, B.J. Ambrosia beetle (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae) captures using colored traps in southeast Tennessee and south Mississippi. J. Entomol. Sci. 2014, 49, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbasi, Q.D.; Jan, N.D.; Maher, A.N.; Khuhro, R.D.; Nizamani, S.M.; Panhwar, A. Monitoring of ambrosia bark beetle through installation of sticky color traps at different heights in mango trees. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2007, 7, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzlancyk, A.M.; Held, D.W.; Kim, D.J.; Ranger, C.M. Capture of Xylosandrus crassiusculus and other scolytinae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in response to visual and volatile cues. Fla. Entomol. 2013, 96, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzlancyk, A.M.; Held, D.W.; Ranger, C.M.; Barwary, Z.; Kim, D.J. Capture of Cnestus mutilatus, Xylosandrus crassiusculus, and other Scolytinae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in response to green light emitting diodes, ethanol, and conophthorin. Fla. Entomol. 2014, 97, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herms, D.A.; Haack, R.A.; Ayres, B.D. Variation in semiochemical-mediated prey-predator interaction: Ips pini (Scolytidae) and Thanasimus dubius (Cleridae). J. Chem. Ecol. 1991, 17, 1705–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, L.M. Differences in responses to α-pinene and ethanol, and flight periods between the bark beetle predators Thanasimus femoralis and T. formicarius (Col.: Cleridae). For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 177, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, B.L.; Goyer, R.A.; Shea, P.J. Visual and olfactory disruption of orientation by the western pine beetle to attractant-baited traps. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2001, 100, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goyer, R.A.; Lenhard, G.J.; Strom, B.L. The influence of silhouette color and orientation on arrival and emergence of Ips pine engravers and their predators in loblolly pine. For. Ecol. Manag. 2004, 191, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Reeve, J.D. Upwind flight response of the bark beetle predator Thanasimus dubius towards olfactory and visual cues in a wind tunnel. Agric. For. Entomol. 2011, 13, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, T.D.; Phillips, A.D.G.; Gregoire, J. Turbulence, trees, and semiochemicals: Wind-tunnel orientation of the predator, Rhizophagus grandis, to its bark beetle prey, Dendroctonus micans. Physiol. Entomol. 1993, 18, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, S.L.; Negrón, J.F.; Jacobi, W.R. Traps and attractants for wood-boring insects in ponderosa pine stands in the Black Hills, South Dakota. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 101, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, J.D.; Graham, E.E.; Poland, T.M.; Strom, B.L. Dilution of fluon before trap surface treatment has no effect on longhorned beetle (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) captures. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulyshen, M.D.; Sheehan, T.N. Trap height considerations for detecting two economically important forest beetle guilds in southeastern US forests. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, T.N.; Ulyshen, M.D.; Horn, S.; Hoebeke, E.R. Vertical and horizontal distribution of bark and woodboring beetles by feeding guild: Is there an optimal trap location for detection? J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balachowsky, A. Faune de France: Coléoptéres Scolytides; Librairie de la Faculté des Sciences: Paris, France, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Curletti, G.; Rastelli, M.; Rastelli, S.; Tassi, F. Coleotteri Buprestidi d’Italia; Piccole Faune. Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Carmagnola (Torino) e Progetto Biodiversità Comitato Parchi—Centro Studi (Roma); Rastelli: Torino, Italy, 2003; ISBN 88-901201-9-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gertsmeier, R. Checkered Beetles, Illustrated Key to the Cleridae of the Western Palaeartic; Magraf: Weikersheim, Germany, 1998; p. 258. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.T.; Denux, O.; Courtin, C.; Bernard, A.; Javal, M.; Millar, J.G.; Hanks, L.M.; Roques, A. Multi-component blends for trapping native and exotic longhorn beetles at potential points-of-entry and in forests. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S.; Christensen, R.H.B.; Singmann, H.; Grothendieck, G. Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using ‘Eigen’ and S4. R Package, Version 1.1–15.1–117. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/lme4/index.html (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Reeve, J.D.; Strom, B.L. Statistical problems encountered in trapping studies of scolytids and associated insects. J. Chem. Ecol. 2004, 30, 1575–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartig, F. Package ‘DHARMa’ Residual Diagnostics for Hierarchical (Multi-Level/Mixed) Regression Models. Version 0.1.5. 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/DHARMa/DHARMa.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2020).
- Wegensteiner, R.; Wermelinger, B.; Herrmann, M. Natural enemies of bark beetles: Predators, parasitoids, pathogens, and nematodes. In Bark Beetles. Biology and Ecology of Native and Invasive Species; Vega, F., Hofstetter, R.W., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 247–304. [Google Scholar]
- Poland, T.M.; Rassati, D. Improved biosecurity surveillance of non-native forest insects: A review of current methods. J. Pest Sci. 2019, 92, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurali, G.S.; Edison, A.; Somanathan, H.; Kodandaramaiah, U. Spontaneous colour preferences and colour learning in the fruit-feeding butterfly, Mycalesis mineus. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2019, 73, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, H.M.; Schaefer, V.; Levey, D.J. How plant-animal interactions signal new insights in communication. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2004, 19, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meglič, A.; Ilić, M.; Quero, C.; Arikawa, K.; Belušič, G. Two chiral types of randomly rotated ommatidia are distributed across the retina of the flathead oak borer, Coraebus undatus (Coleoptera: Buprestidae). J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb225920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imrei, Z.; Lohonyai, Z.; Muskovits, J.; Matula, E.; Vuts, J.; Fail, J.; Gould, P.J.L.; Birkett, M.A.; Tóth, M.; Domingue, M.J. Developing a non-sticky trap design for monitoring jewel beetles. J. Appl. Entomol. 2020, 144, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pureswaran, D.S.; Borden, J.H. Primary attraction and kairomonal host discrimination in three species of Dendroctonus (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Agric. For. Entomol. 2005, 7, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranger, C.M.; Reding, M.E.; Addesso, K.; Ginzel, M.; Rassati, D. Semiochemical-mediated host selection by Xylosandrus spp. ambrosia beetles (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) attacking horticultural tree crops: A review of basic and applied science. Can. Entomol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streinzer, M.; Roth, N.; Paulus, H.F.; Spaethe, J. Color preference and spatial distribution of glaphyrid beetles suggest a key role in the maintenance of the color polymorphism in the peacock anemone (Anemone pavonina, Ranunculaceae) in Northern Greece. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2019, 205, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Buprestidae | BK | BR | RE | YE | GR | BL | PU | GY | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flower visitors | |||||||||
| Acmaeoderella flavofasciata | - | - | - | 3 | - | - | - | - | 3 |
| Anthaxia cichorii | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | - | 2 |
| Anthaxia croesus | 1 | - | - | 12 | - | - | - | - | 13 |
| Anthaxia fulgurans | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Anthaxia hungarica | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Anthaxia manca | - | - | - | 1 | 2 | - | - | - | 3 |
| Anthaxia millefolii polychloros | - | - | - | 9 | 1 | - | - | - | 10 |
| Anthaxia nitidula | - | - | - | 19 | - | - | - | - | 19 |
| Anthaxia thalassophila | - | - | 1 | 150 | 3 | - | 9 | 1 | 164 |
| Coraebus elatus | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | 5 |
| Total | 1 | 1 | 2 | 200 | 7 | 0 | 9 | 1 | 221 |
| Non flower visitors | |||||||||
| Agrilus angustulus | - | - | - | 9 | 21 | 2 | - | - | 32 |
| Agrilus ater | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Agrilus auricollis | - | - | 1 | 2 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 15 |
| Agrilus biguttatus | 5 | - | - | - | 26 | 7 | 9 | 2 | 49 |
| Agrilus convexicollis | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 21 | 1 | 1 | - | 32 |
| Agrilus derasofasciatus | - | - | - | 5 | 1 | - | 1 | - | 7 |
| Agrilus graminis | 2 | - | - | 11 | 49 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 71 |
| Agrilus hastulifer | - | - | - | 3 | 62 | 4 | - | 4 | 73 |
| Agrilus laticornis | 2 | - | - | 17 | 40 | - | - | 1 | 60 |
| Agrilus obscuricollis | - | - | 1 | 1 | 2 | - | - | 1 | 5 |
| Agrilus olivicolor | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | - | 2 |
| Agrilus roscidus | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 14 |
| Agrilus sulcicollis | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | 1 | 3 |
| Agrilus viridicaerulans rubi | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 | 2 |
| Buprestis haemorrhoidalis | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| Buprestis novemmaculata | - | - | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | 2 |
| Capnodis tenebrionis | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Chrysobothris affinis | 3 | 4 | 1 | - | 1 | 7 | 12 | 2 | 30 |
| Dicerca aenea | 2 | 3 | 3 | - | - | 1 | 3 | 2 | 14 |
| Dicerca berolinensis | 1 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 2 |
| Lamprodila mirifica | - | - | - | - | 65 | 2 | 1 | - | 68 |
| Meliboeus fulgidicollis | - | 1 | 4 | 1 | 5 | - | - | - | 11 |
| Trachypteris picta decostigma | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 |
| Total | 20 | 10 | 16 | 53 | 308 | 32 | 36 | 21 | 496 |
| Scolytinae | |||||||||
| Ambrosiophilus atratus * | 1 | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | 3 |
| Anisandrus dispar | 11 | 15 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 10 | 12 | 10 | 80 |
| Cyrtogenius luteus * | 2 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | - | 9 |
| Dryocoetes villosus | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | 1 |
| Hylesinus oleiperda | 16 | 6 | 12 | 7 | 8 | 32 | 37 | 22 | 140 |
| Orthotomicus erosus | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | 1 | 2 |
| Scolytus intricatus | 7 | 9 | 14 | 9 | 3 | 2 | 36 | 80 | |
| Scolytus multistriatus | 3 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 37 | 5 | 69 | 129 |
| Scolytus pygmaeus | - | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | - | 2 | 13 |
| Scolytus rugulosus | 8 | 4 | 4 | 23 | 11 | 10 | 23 | 12 | 95 |
| Taphrorychus hirtellus | 1 | - | 1 | - | - | - | 1 | - | 3 |
| Xyleborinus saxesenii | 1177 | 1408 | 804 | 434 | 678 | 1086 | 734 | 696 | 7017 |
| Xyleborus dryographus | 24 | 4 | 11 | 6 | 6 | 11 | 13 | 9 | 84 |
| Xyleborus monographus | 27 | 12 | 20 | 2 | 6 | 10 | 24 | 9 | 110 |
| Xylosandrus crassiusculus * | 665 | 1270 | 610 | 264 | 541 | 697 | 420 | 353 | 4820 |
| Xylosandrus germanus * | 4 | 20 | 8 | 16 | 4 | 19 | 20 | 16 | 107 |
| Total | 1946 | 2754 | 1501 | 774 | 1269 | 1922 | 1328 | 1199 | 12693 |
| Cleridae | |||||||||
| Clerus mutillarius | 467 | 553 | 520 | 228 | 312 | 379 | 544 | 329 | 3332 |
| Denops albofasciatus | - | - | - | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | 3 |
| Thanasimus formicarius | 12 | 11 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 10 | 11 | 60 |
| Tilloidea unifasciata | - | 2 | 2 | 5 | 1 | - | - | - | 10 |
| Total | 479 | 566 | 529 | 237 | 318 | 382 | 554 | 340 | 3405 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cavaletto, G.; Faccoli, M.; Marini, L.; Spaethe, J.; Magnani, G.; Rassati, D. Effect of Trap Color on Captures of Bark- and Wood-Boring Beetles (Coleoptera; Buprestidae and Scolytinae) and Associated Predators. Insects 2020, 11, 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110749
Cavaletto G, Faccoli M, Marini L, Spaethe J, Magnani G, Rassati D. Effect of Trap Color on Captures of Bark- and Wood-Boring Beetles (Coleoptera; Buprestidae and Scolytinae) and Associated Predators. Insects. 2020; 11(11):749. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110749
Chicago/Turabian StyleCavaletto, Giacomo, Massimo Faccoli, Lorenzo Marini, Johannes Spaethe, Gianluca Magnani, and Davide Rassati. 2020. "Effect of Trap Color on Captures of Bark- and Wood-Boring Beetles (Coleoptera; Buprestidae and Scolytinae) and Associated Predators" Insects 11, no. 11: 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110749
APA StyleCavaletto, G., Faccoli, M., Marini, L., Spaethe, J., Magnani, G., & Rassati, D. (2020). Effect of Trap Color on Captures of Bark- and Wood-Boring Beetles (Coleoptera; Buprestidae and Scolytinae) and Associated Predators. Insects, 11(11), 749. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11110749







