Agri-Food Side-Stream Inclusions in the Diet of Alphitobius diaperinus Part 1: Impact on Larvae Growth Performance Parameters
Abstract
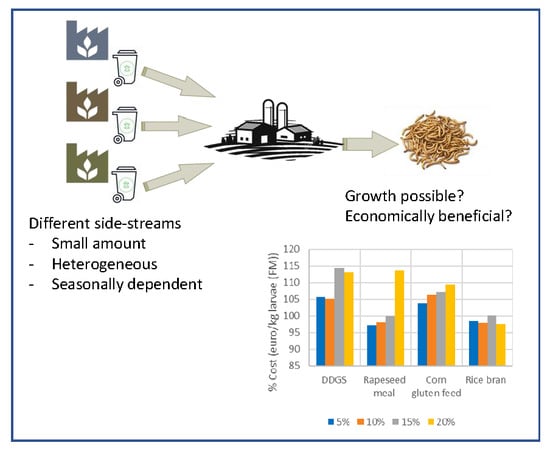
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Pure Side-Streams
3.2. Reference Diet
3.3. Mixed Side-Streams
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| 0% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 25% | 50% | 100% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| means | means | means | means | means | means | means | means | |
| DDGS | ||||||||
| % larval yield | 100.0 ± 2.0 | 96.2 ± 3.5 | 98.3 ± 3.7 | 91.8 ± 7.5 (−) | 94.3 ± 7.9 | 97.1 ± 3.4 | 95.3 ± 2.3 | 79.8 ± 3.7 (−) |
| % BE | 100.0 ± 2.0 | 96.1 ± 3.5 | 98.1 ± 3.7 | 91.5 ± 7.4 (−) | 93.9 ± 7.9 | 96.6 ± 3.4 | 94.3 ± 2.3 | 78.1 ± 3.6 (−) |
| % LM weigh after 14 days | 100.0 ± 10.2 | 99.2 ± 13.1 | 106.9 ± 9.2 | 95.5 ± 8.9 | 88.0 ± 10.7 | 89.4 ± 6.3 | 92.9 ± 6.6 | 90.5 ± 5.5 |
| % LM weight after 28 days | 100.0 ± 3.9 | 100.1 ± 3.0 | 105.3 ± 4.8 | 107.0 ± 4.0 (+) | 105.2 ± 3.7 | 93.1 ± 4.2 (−) | 91.9 ± 3.9 (−) | 91.3 ± 5.2 |
| Rapeseed meal | ||||||||
| % larval yield | 100.0 ± 2.3 | 104.9 ± 1.6 (+) | 105.9 ± 2.6 (+) | 105.9 ± 2.6 (+) | 95.0 ± 2.8 (−) | |||
| % BE | 100.0 ± 2.3 | 104.9 ± 1.6 (+) | 105.8 ± 2.6 (+) | 105.8 ± 2.6 (+) | 94.7 ± 2.8 (−) | |||
| % LM weigh after 14 days | 100.0 ± 8.6 | 117.9 ± 9.1 | 123.0 ± 9.6 | 119.9 ± 14.2 | 82.4 ± 33.8 | |||
| % LM weight after 28 days | 100.0 ± 1.8 | 102.7 ± 4.3 | 99.8 ± 3.8 | 100.1 ± 4.9 | 97.7 ± 2.7 | |||
| Corn gluten feed | ||||||||
| % larval yield * | 100.0 ± 2.6 | 97.4 ± 2.7 | 96.1 ± 2.3 | 96.2 ± 2.1 | 95.1 ± 3.1 | 92.0 ± 5.0 (−) | 91.4 ± 2.5 (−) | 79.4 ± 2.7 (−) |
| % BE * | 99.9 ± 2.7 | 97.3 ± 2.7 | 95.3 ± 2.3 | 95.9 ± 2.1 | 94.7 ± 3.1 | 91.4 ± 5.0 (−) | 90.3 ± 2.5 (−) | 77.6 ± 2.7 (−) |
| % LM weigh after 14 days | 100.0 ± 9.5 | 102.3 ± 6.0 | 90.9 ± 5.7 | 92.8 ± 7.4 | 105.2 ± 17.4 | 79.2 ± 7.4 (−) | 84.1 ± 8.5 (−) | 77.3 ± 7.3 |
| % LM weight after 28 days | 100.0 ± 2.3 | 96.5 ± 2.8 | 108.2 ± 5.8 (+) | 112.4 ± 6.2 (+) | 114.2 ± 5.5 | 99.8 ± 2.5 | 98.3 ± 1.8 | 85.9 ± 2.7 |
| Rice bran | ||||||||
| % larval yield | 100.0 ± 2.0 | 101.2 ± 2.2 | 101.1 ± 2.8 | 98.4 ± 1.3 | 100.5 ± 2.4 | 38.1 ± 1.8(−) | ||
| % BE | 100.1 ± 2.0 | 101.04 ± 2.1 | 100.8 ± 2.8 | 97.9 ± 1.3 | 99.9 ± 2.4 | 89.1 ± 4.1 | ||
| % LM weigh after 14 days | 100.0 ± 9.2 | 109.4 ± 12.6 | 108.0 ± 6.6 | 97.1 ± 12.0 | 102.0 ± 4.5 | / | ||
| % LM weight after 28 days | 100.0 ± 2.6 | 99.3 ± 1.2 | 100.5 ± 3.5 | 96.9 ± 2.4 | 98.7 ± 3.9 | 43.5 ± 3.0 |
References
- European Commission EC COMMUNICATION. Roadmap to a Resource Efficient Europe; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2011; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- DeFoliart, G.R. The human use of insects as food and as animal feed. Bull. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1989, 35, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Broekhoven, S.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; van Huis, A.; van Loon, J.J.A. Growth performance and feed conversion efficiency of three edible mealworm species (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) on diets composed of organic by-products. J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; Van Broekhoven, S.; Van Huis, A.; Van Loon, J.J.A. Feed conversion, survival and development, and composition of four insect species on diets composed of food by-products. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0222043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Huis, A.; Van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects. Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; FAO: Rome, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Veldkamp, T.; van Duinkerken, G.; van Huis, A.; Lakemond, C.M.M.; Ottevanger, E.; Bosch, G.; van Boekel, T. Insects As a Sustainable Feed Ingredient in Pig and Poultry Diets—A Feasibility Study; Wageningen University: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Varelas, V. Food wastes as a potential new source for edible insect mass production for food and feed: A review. Fermentation 2019, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosen, M.; Rahman Khan, A.; Hossain, M. Growth and Development of the Lesser Mealworm, Alphitobius diaperinus (Panzer) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) on Cereal Flours. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2004, 7, 1505–1508. [Google Scholar]
- Offenberg, J. Oecophylla smaragdina food conversion efficiency: Prospects for ant farming. J. Appl. Entomol. 2011, 135, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zanten, H.H.E.; Bikker, P.; Mollenhorst, H.; Meerburg, B.G.; De Boer, I.J.M. Environmental impact of replacing soybean meal with rapeseed meal in diets of finishing pigs. Animal 2015, 9, 1866–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramos-Elorduy, J.; González, E.A.; Hernández, A.R.; Pino, J.M. Use of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) to Recycle Organic Wastes and as Feed for Broiler Chickens. J. Econ. Entomol. 2002, 95, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, S.; Fratini, F.; Turchi, B.; Mattioli, S.; Bosco, A.D.; Tuccinardi, T.; Nozic, S.; Paci, G. Former Foodstuff Products in Tenebrio Molitor Rearing: Effects on Growht, Chemical Composition, Microbiomogical Load, and Antioxidant Status. Animals 2019, 9, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smetana, S.; Palanisamy, M.; Mathys, A.; Heinz, V. Sustainability of insect use for feed and food: Life Cycle Assessment perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 137, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetana, S.; Schmitt, E.; Mathys, A. Sustainable use of Hermetia illucens insect biomass for feed and food: Attributional and consequential life cycle assessment. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 144, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federatie Nederlandse Diervoederketen. CVB-Veevoedertabel 2018—Chemische Samenstelling van Nutritionele Waarden van Voedermiddelen; Federatie Nederlandse Diervoederketen: Rijswijk, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, G.; Oonincx, D.G.A.B.; Jordan, H.R.; Zhang, J.; van Loon, J.J.A.; van Huis, A.; Tomberlin, J.K. Standardisation of quantitative resource conversion studies with black soldier fly larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Shelomi, M. Review of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Animal Feed and Human Food. Foods 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rho, M.S.; Lee, K.P. Balanced intake of protein and carbohydrate maximizes lifetime reproductive success in the mealworm beetle, Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J. Insect Physiol. 2016, 91–92, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.P.; Li, P.L.; Li, Z.C.; Stein, H.H.; Liu, L.; Xia, T.; Yang, Y.Y.; Ma, Y.X. Effects of post-harvest storage duration and variety on nutrient digestibility and energy content wheat in finishing pigs. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waldbauer, G.P. The consumption and utilization of food by insects. Adv. Insect Physiol. 1968, 5, 229–288. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Tang, H.; Chen, G.; Qiao, L.; Li, J.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, X. Growth performance and nutritional profile of mealworms reared on corn stover, soybean meal, and distillers’ grains. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 2631–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pracros, P.; Couranjou, C.; Moreau, R. Effects on growth and respiration due to the ingestion of the rapeseed meal glucosinolates in young larvae of Tenebrio molitor. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1992, 103, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Cost Price (€/ton) 1 | DM (%) 2 | Protein Content on Dry Base (%) 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn DDGS | 200 | 90.3 | 29.3 |
| Rice Bran | 102 | 89.7 | 15.5 |
| Rapeseed meal | 215 | 88.9 | 38.7 |
| Corn gluten feed | 170 | 89.5 | 22.7 |
| Wheat middlings | 124 | 87.4 | 17.6 |
| Diet | Wheat Middlings | Rice Bran | Rapeseed Meal | Corn Gluten Feed | DDGS | Moisture Source 1 | Trial 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 100 | carrot | VIII | ||||
| B | 100 | carrot | VIII | ||||
| C | 100 | carrot | V | ||||
| D | 100 | carrot | V | ||||
| E | 100 | carrot | V | ||||
| F | 100 | BG | I, II, III, IV, VI, VII | ||||
| G | 100 | BG | IV | ||||
| H | 100 | BG | III | ||||
| I | 100 | BG | I | ||||
| J | 95 | 5 | BG | IV | |||
| K | 90 | 10 | BG | IV | |||
| L | 85 | 15 | BG | IV | |||
| M | 80 | 20 | BG | IV | |||
| N | 95 | 5 | BG | II | |||
| O | 90 | 10 | BG | II | |||
| P | 85 | 15 | BG | II | |||
| Q | 80 | 20 | BG | II | |||
| R | 95 | 5 | BG | VII | |||
| S | 90 | 10 | BG | VII | |||
| T | 85 | 15 | BG | VII | |||
| U | 80 | 20 | BG | VII | |||
| V | 75 | 25 | BG | III | |||
| W | 50 | 50 | BG | III | |||
| X | 95 | 5 | BG | VI | |||
| Y | 90 | 10 | BG | VI | |||
| Z | 85 | 15 | BG | VI | |||
| AA | 80 | 20 | BG | VI | |||
| AB | 75 | 25 | BG | I | |||
| AC | 50 | 50 | BG | I |
| Wheat Middlings | Rice Bran | Rapeseed Meal | Corn Gluten Feed | DDGS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture Source: Brewery Grains * | |||||
| Trial | I, II, III, IV, VI, VII | VI | III | I | |
| Diet | Diet F | Diet I | nd | Diet H | Diet I |
| % Weight of feed | 100.0 ± 0.7 a | 55.0 ± 0.0 b | nd | 100.0 ± 0.0 a | 100.0 ± 0.0 a |
| % Larval yield | 100.0 ± 5.6 a | 38.1 ± 1.8 c | nd | 73.4 ± 2.7 b | 79.7 ± 3.7 b |
| % LM weight after 14 days | 100.0 ± 22.4 a | na | nd | 77.3 ± 7.3 b | 90.5 ± 5.5 a |
| % LM weight after 28 days | 100.0 ± 6.5 a | 43.5 ± 3.0 d | nd | 85.9 ± 2.7 c | 91.3 ± 5.2 b |
| % BE | 100.0 ± 7.1 a | 89.1 ± 4.1 b | nd | 77.6 ± 2.7 c | 78.1 ± 3.6 c |
| Moisture Source: Grated Carrots ** | |||||
| Trial | VIII | VIII | V | V | V |
| Diet | Diet A | Diet B | Diet C | Diet D | Diet E |
| % Weight of feed | 106.6 ± 0.0 a | 23.8 ± 0.0 e | 57.4 ± 0.0 b | 26.2 ± 0.0 d | 35.8 ± 0.0 c |
| % Larval yield | 73.9 ± 1.3 a | 4.1 ± 0.5 d | 39.7 ± 1.4 b | 4.6 ± 0.2 d | 20.0 ± 0.4 c |
| % LM weight after 14 days | 88.3 ± 4.7 a | na | 142.5 ± 21.2 b | na | na |
| % LM weight after 28 days | 82.3 ± 2.7 a | na | 64.6 ± 10.4 b | 11.4 ± 1.1 d | 23.1 ± 1.6 c |
| % BE | 113.0 ± 2.0 a | 32.2 ± 4.0 c | 102.9 ± 3.7 b | 34.9 ± 1.8 c | 102.6 ± 2.1 b |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gianotten, N.; Soetemans, L.; Bastiaens, L. Agri-Food Side-Stream Inclusions in the Diet of Alphitobius diaperinus Part 1: Impact on Larvae Growth Performance Parameters. Insects 2020, 11, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020079
Gianotten N, Soetemans L, Bastiaens L. Agri-Food Side-Stream Inclusions in the Diet of Alphitobius diaperinus Part 1: Impact on Larvae Growth Performance Parameters. Insects. 2020; 11(2):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020079
Chicago/Turabian StyleGianotten, Natasja, Lise Soetemans, and Leen Bastiaens. 2020. "Agri-Food Side-Stream Inclusions in the Diet of Alphitobius diaperinus Part 1: Impact on Larvae Growth Performance Parameters" Insects 11, no. 2: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020079
APA StyleGianotten, N., Soetemans, L., & Bastiaens, L. (2020). Agri-Food Side-Stream Inclusions in the Diet of Alphitobius diaperinus Part 1: Impact on Larvae Growth Performance Parameters. Insects, 11(2), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11020079