Long-Tailed Silverfish (Ctenolepisma longicaudata) Control; Bait Choice Based on Primary and Secondary Poisoning
Abstract
:1. Introduction
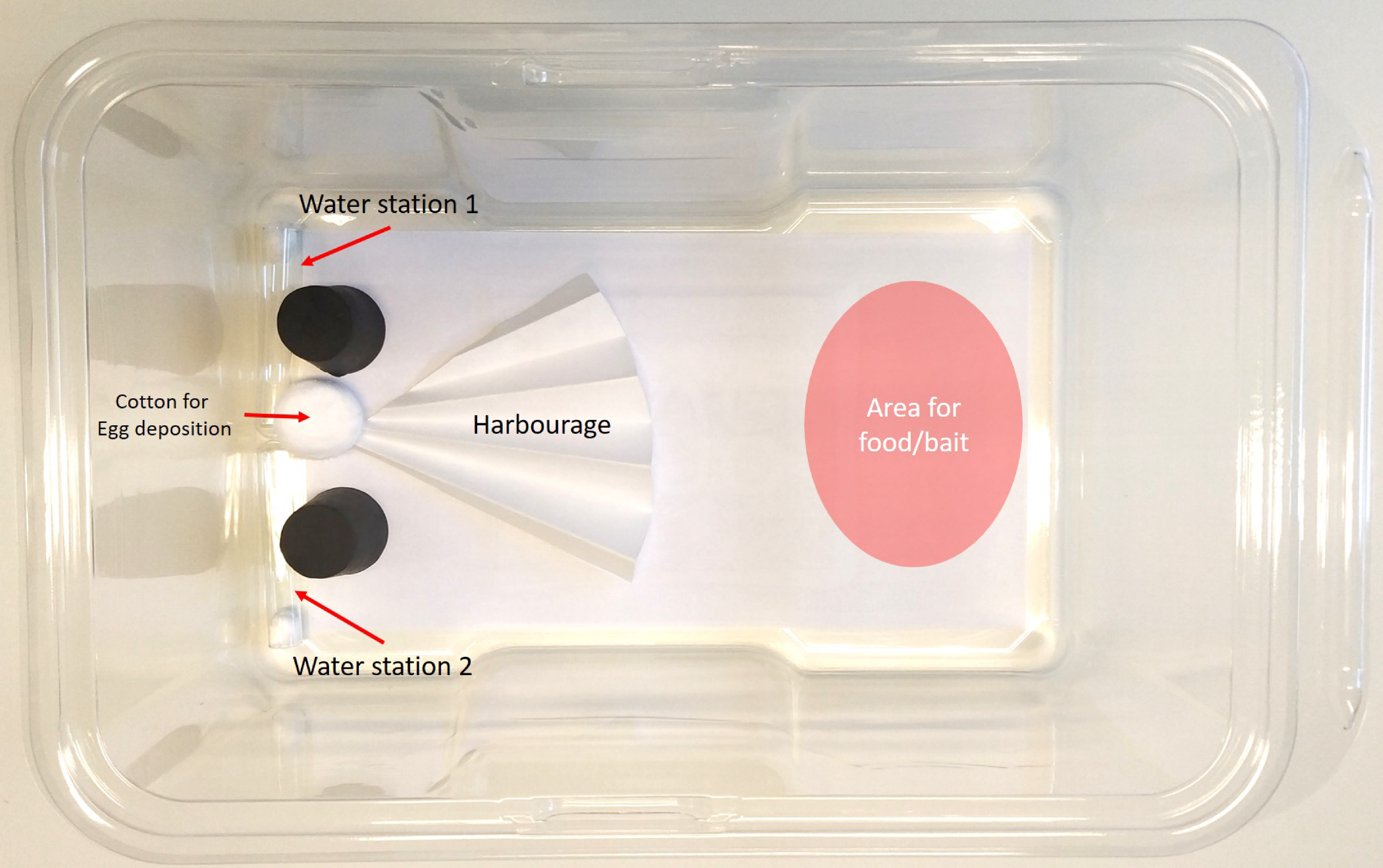
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lock, K. Distribution of the Belgian Zygentoma. Notes Fauniques de Gembloux 2007, 60, 25–27. [Google Scholar]
- Goddard, M.R.; Foster, G.J.; Holloway, G.J. Ctenolepisma longicaudata (Zygentoma: Lepismatidae) new to Britain. Br. J. Ent. Nat. Hist. 2016, 29, 33–35. [Google Scholar]
- Bujis, J. Arthropods that annoy Amsterdam people. Proc. Neth. Entomol. Soc. Meet. 2009, 20, 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Meineke, T.; Menge, K. Ein weiterer fund des Papierfischens Ctenolepisma longicaudata Escherich, 1905 (Zygentoma, Lepismatidae) in Deautchland. Entomol. Nachr. Ber. 2014, 58, 153–154. [Google Scholar]
- Pape, T.; Wahlstedt, U. En silverborstsvans nyinförd till Sverige (Thysanura: Lepismatidae). Ent. Tidskr. 2002, 123, 149–151. [Google Scholar]
- Schoelitsz, B.; Brooks, M. Distribution of Ctenolepisma longicaudata (Zygentoma: Lepismatidae) in the Netherlands. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on Urban Pests; Müller, G., Pospischil, R., Robinson, W.H., Eds.; The Executive Committee of the International Conference on Urban pests: Zurich, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 8, pp. 353–357. [Google Scholar]
- Mattsson, J. En ny børstehale (Lepismatidae) påvist i Norge. Insekt-Nytt 2014, 39, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kulma, M.; Vrabec, V.; Patoka, J.; Rettich, F. The first established population of the invasive silverfish Ctenolepisma longicaudata (Escherich) in the Czech Republic. BioInvasions Rec. 2018, 7, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, E.; Kongsstovu, S.I.; Dahl, H.A.; Mikalsen, S.O. Ctenolepisma longicaudata (Escherich, 1905): A common, but previously unregistered, species of silverfish in the Faroe Islands. Bioinvasions Rec. 2019, 8, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molero-Baltanas, R.; GajuRicart, M.; de Roca, C.B. Anthropophile silverfish: A quantitative study of the Lepismatidae (Insecta: Zygentoma) found in human buildings in Spain. Pedobiologia 1997, 41, 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Aak, A.; Rukke, B.A.; Ottesen, P.S.; Hage, M. Long-tailed silverfish (Ctenolepisma longicaudata)–biology and control. In Norwegian Institute of Public Health Report; Norwegian Institute of Public Health: Oslo, Norway, 2019; pp. 1–43. ISBN 978-82-8082-998-6. Available online: https://www.fhi.no/en/publ/2019/skjeggkre--biologi-og-rad-om-bekjemping/ (accessed on 6 March 2020).
- Mallis, A.; Hedges, S.A.; Moreland, D. Handbook of Pest Control: The Behaviour, Life History, and Control of Household Pests, 10th ed.; Mallis Handbook & Technical Training Company: Valley View, OH, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, G.B.; Owens, J.M.; Corrigan, R.M. Truman’s Scientific Guide to Pest Management Operations, 7th ed.; Advanstar Communications/Purdue University: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gold, R.E.; Jones, S.C. Handbook of Houshold and Structural Insect Pests; Etomological Society of America: Lanham, MD, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Szpryngiel, S. Långsprötad silverfisk i museer, bibliotek och arkiv i Sverige. FoU-anslag, Riksantikvarieämbetet. 2018. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1234711/FULLTEXT01.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2020).
- Querner, P. Insect pests and integrated pest management in museums, libraries and historic buildings. Insects 2015, 6, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, E. The biology of the silverfish, Ctenolepisma longicaudata, with particular reference to its feeding habits. Proc. Roy. Soc. Victoria 1940, 52, 35–83. [Google Scholar]
- Sahrhage, D. Ökologische untersuchungen am Ofenfischchen, Thermobia domestica (Packard), und Silberfischchen, Lepisma saccharina L. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Entomologie 1954, 35, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, H.L. Physical ecology of the firebrat, Thermobia domestica (Packard). Ecol. Monogr. 1938, 8, 285–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweetman, H.L. Responses of the silverfish, Lepisma saccharina L., to its physical environment. J. Econ. Entomol. 1939, 32, 698–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhang, P. Innovations in insect baiting and its role in reducing insecticide load in urban pest control. Int. Pest Control 2016, 58, 210–212. [Google Scholar]
- Tee, H.S.; Lee, C.Y. Sustainable cockroach managment using insecticidal baits: Formulations, behavioural responses and issues. In Urban Insect Pests—Sustainable Management Strategies; Dhang, P., Ed.; CABI: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 65–85. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, S.R.; Appel, A.G. Efficacy of commercial baits and new active ingredients against firebrats and silverfish (Zygentoma: Lepismatidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapied, B.; Grolleau, F.; Sattelle, D.B. Indoxacarb, an oxadiazine insecticide, blocks insect neuronal sodium channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 132, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narahashi, T. Neurophysiological effects of insecticides. In Hayes’s Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Krieger, R., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2010; pp. 799–817. [Google Scholar]
- Sheets, L. Imidacloprid: A neonicotinoid insecticide. In Hayes’ Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Krieger, R., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2010; pp. 2055–2064. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Eiden, A.; Cooper, R.; Zha, C.; Wang, D.; Reilly, E. Changes in indoor insecticide residue levels after adopting an integrated pest management program to control German cockroach infestations in an apartment building. Insects 2019, 10, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buczkowski, G.; Scherer, C.W.; Bennett, G.W. Horizontal transfer of bait in the German cockroach: Indoxacarb causes secondary and tertiary mortality. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, A.S.; Truong, T.; Goh, K.S.; Spurlock, F.; Tjeerdema, R.S. Environmental fate and toxicology of fipronil. J. Pestic. Sci. 2007, 32, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tingle, C.C.D.; Rother, J.A.; Dewhurst, C.F.; Lauer, S.; King, W.J. Fipronil: Environmental fate, ecotoxicology, and human health concerns. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 176, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Testa, C.; Salis, S.; Rubattu, N.; Roncada, P.; Miniero, R.; Brambilla, G. Occurrence of Fipronil in residential house dust in the presence and absence of pets: A hint for a comprehensive toxicological assessment. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B-Pestic. Contam. Agric. Wastes 2019, 54, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothula, R.; Shirley, D.; Perera, O.P.; Klingeman, W.E.; Oppert, C.; Abdelgaffar, H.M.Y.; Johnson, B.R.; Jurat-Fuentes, J.L. The digestive system in Zygentoma as an insect model for high cellulase activity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0212505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodbury, N.; Gries, G. How Firebrats (Thysanura: Lepismatidae) detect and nutritionally benefit from their microbial symbionts Enterobacter cloacae and Mycotypha microspora. Environ. Entomol. 2013, 42, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woodbury, N.; Moore, M.; Gries, G. Horizontal transmission of the microbial symbionts Enterobacter cloacae and Mycotypha microspora to their firebrat host. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2013, 147, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, N.; Gries, G. Fungal symbiont of firebrats (Thysanura) induces arrestment behaviour of firebrats and giant silverfish but not common silverfish. Can. Entomol. 2013, 145, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, M.N.; Gries, G. Pheromone-based aggregation behaviour of the firebrat, Thermobia domestica (Packard) (Thysanura: Lepismatidae). Chemoecology 2003, 13, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodbury, N.; Gries, G. Pheromone-based arrestment behavior in the common silverfish, Lepisma saccharina, and giant silverfish, Ctenolepisma longicaudata. J. Chem. Ecol. 2007, 33, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVries, Z.C.; Appel, A.G. Effects of temperature on nutrient self-selection in the silverfish Lepisma saccharina. Physiol. Entomol. 2014, 39, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, R.F. The Insects—Structure and Function, 5th ed.; Simpson, S.J., Douglas, A.E., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2013; p. 929. [Google Scholar]
- Rust, M.K.; Su, N.Y. Managing social insects of urban importance. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2012, 57, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desneux, N.; Decourtye, A.; Delpuech, J.M. The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, R.N.C.; Smagghe, G.; Stark, J.D.; Desneux, N. Pesticide-induced stress in arthropod pests for optimized integrated pest management programs. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haynes, K.F. Sublethal effects of neurotoxic insecticides on insect behavior. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1988, 33, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondhalekar, A.D.; Nakayasu, E.S.; Silva, I.; Cooper, B.; Scharf, M.E. Indoxacarb biotransformation in the German cockroach. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 134, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, K.D.; Sacher, M.; Kagaya, Y.; Tsurubuchi, Y.; Mulderig, L.; Connair, M.; Schnee, M. Bioactivation and mode of action of the oxadiazine indoxacarb in insects. Crop. Prot. 2000, 19, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczkowski, G.; Kopanic, R.J., Jr.; Schal, C. Transfer of ingested insecticides among cockroaches: Effects of active ingredient, bait formulation, and assay procedures. J. Econ. Entomol. 2001, 94, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, A.G. Laboratory and field performance of an indoxacarb bait against German cockroaches (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lee, L.C. Influence of sanitary conditions on the field performance of chlorpyrifos-based baits against American cockroaches, Periplaneta americana (L.) (Dictyoptera: Blattidae). J. Vector Ecol. 2000, 25, 218–221. [Google Scholar]
- Rabito, F.A.; Carlson, J.C.; He, H.; Werthmann, D.; Schal, C. A single intervention for cockroach control reduces cockroach exposure and asthma morbidity in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 140, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.L.; Eiden, A.; Cooper, R.; Zha, C.; Wang, D.S. Effectiveness of building-wide integrated pest management programs for German cockroach and Bed bug in a high-rise apartment building. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingha, B.N.; O’Neal, J.; Appel, A.G.; Jackai, L.E.N. Integrated pest management of the German cockroach (Blattodea: Blattellidae) in manufactured homes in rural North Carolina. Fla. Entomol. 2016, 99, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Anikwe, J.C.; Adetoro, F.A.; Anogwih, J.A.; Makanjuola, W.A.; Kemabonta, K.A.; Akinwande, K.L. Laboratory and field evaluation of an indoxacarb gel bait against two cockroach species (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae, Blattidae) in Lagos, Nigeria. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 1639–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snoddy, E.T.; Appel, A.G. Field and laboratory efficacy of three insecticides for population management of the Asian cockroach (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahraki, G.H.; Hafidzi, M.N.; Khadri, M.S.; Rafinejad, J.; Ibrahim, Y.B. Cost-effectiveness of integrated pest management compared with insecticidal spraying against the German cockroach in apartment buildings. Neotrop. Entomol. 2011, 40, 607–612. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, V.K.; Agarwal, A.; Choudhary, V.; Singh, R.; Ahmed, N.; Sharma, M.; Narula, K.; Agrawal, P. Efficacy of imidacloprid and fipronil gels over synthetic pyrethroid and propoxur aerosols in control of German cockroaches (Dictyoptera: Blatellidae). J. Vector Borne Dis. 2010, 47, 39–44. [Google Scholar]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aak, A.; Hage, M.; Rukke, B.A. Long-Tailed Silverfish (Ctenolepisma longicaudata) Control; Bait Choice Based on Primary and Secondary Poisoning. Insects 2020, 11, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030170
Aak A, Hage M, Rukke BA. Long-Tailed Silverfish (Ctenolepisma longicaudata) Control; Bait Choice Based on Primary and Secondary Poisoning. Insects. 2020; 11(3):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030170
Chicago/Turabian StyleAak, Anders, Morten Hage, and Bjørn Arne Rukke. 2020. "Long-Tailed Silverfish (Ctenolepisma longicaudata) Control; Bait Choice Based on Primary and Secondary Poisoning" Insects 11, no. 3: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030170
APA StyleAak, A., Hage, M., & Rukke, B. A. (2020). Long-Tailed Silverfish (Ctenolepisma longicaudata) Control; Bait Choice Based on Primary and Secondary Poisoning. Insects, 11(3), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11030170





