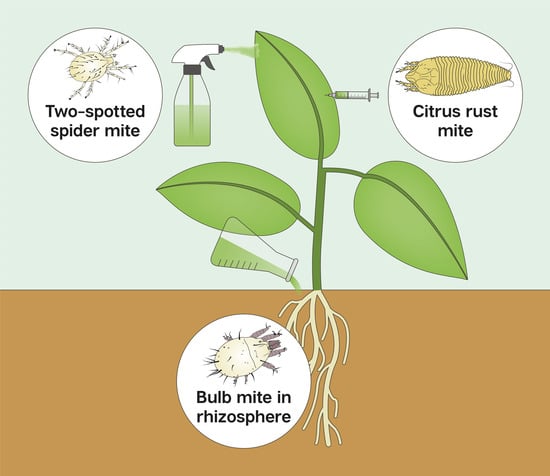
Interactions of Metarhizium brunneum-7 with Phytophagous Mites Following Different Application Strategies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mites
2.2. Fungal Strain
2.3. Plant Material
2.4. Fungal Inoculation of Plant Material
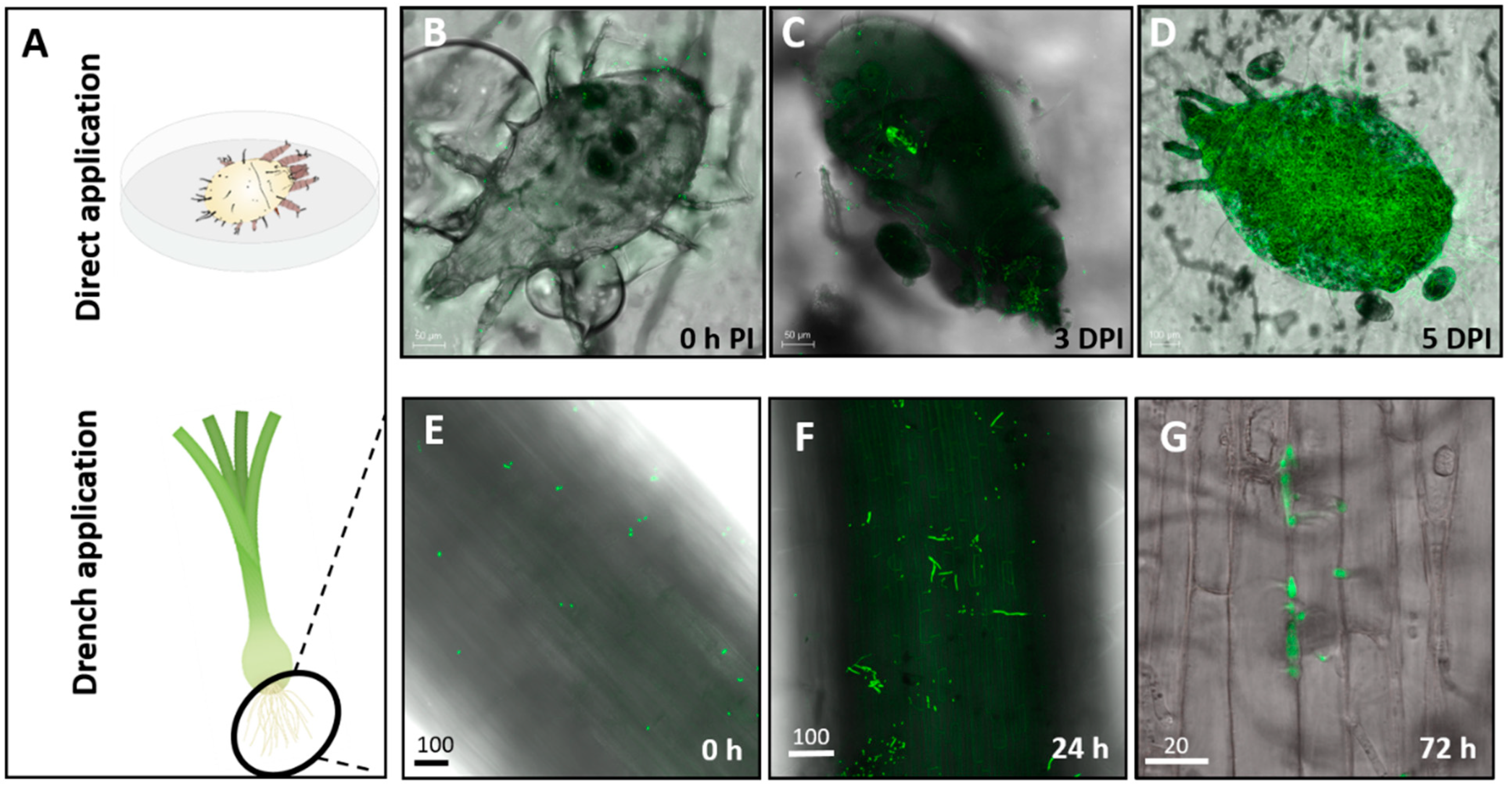
2.5. Plant Sampling for Assessment of Endophytic Colonization and Live Imaging
2.6. Leaf Disc Assay for P. oleivora Susceptibility to Mb7
2.7. In-Vitro Assay for R. robini Susceptibility to Mb7
2.8. In-Planta Bioassay for T. urticae susceptibility to Mb7
2.9. In-Planta Bioassay for R. robini Susceptibility to Mb7
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Assessment of Colonization in Plants Inoculated with Mb7 by Re-Isolation and Live Imaging
3.2. Assessment of the Effect of Directly Applied Mb7 to Mites
3.3. Assessment of the Effect of Mb7, as a Leaf and Root Endophyte, on Mites
3.4. Assessment of the Effect of Mb7, as a Rhizosphere Resident, on Mites
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Leeuwen, T.; Tirry, L.; Yamamoto, A.; Nauen, R.; Dermauw, W. The economic importance of acaricides in the control of phytophagous mites and an update on recent acaricide mode of action research. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2015, 121, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo, D.; De Moraes, G.J.; Peña, J.E. Prospects for Biological Control of Plant Feeding Mites and other Harmful Organisms; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gerson, U.; Smiley, R.L.; Ochoa, R. Mites (Acari) for Pest Control; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Hoy, M.A. Agricultural Acarology: Introduction to Integrated Mite Management; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Marcic, D. Acaricides in modern management of plant-feeding mites. J. Pest. Sci. 2012, 85, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, M.; Palevsky, E.; Rapisarda, C. Insect and Mite Pests. In Integrated Pest and Disease Management in Greenhouse Crops; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 101–146. [Google Scholar]
- Chandler, D.; Davidson, G.; Pell, J.K.; Ball, B.V.; Shaw, K.; Sunderland, K.D. Fungal Biocontrol of Acari. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 357–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ment, D.; Shikano, I.; Glazer, I. Abiotic Factors. In Ecology of Invertebrate Diseases; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 143–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lenteren, J.C.; Bolckmans, K.; Köhl, J.; Ravensberg, W.J.; Urbaneja, A. Biological control using invertebrates and microorganisms: Plenty of new opportunities. BioControl 2018, 63, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaronski, S.T. Ecological factors in the inundative use of fungal entomopathogens. BioControl 2010, 55, 159–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dara, S.K.; Goble, T.A.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I. Leveraging the ecology of invertebrate pathogens in microbial control. In Ecology of Invertebrate Diseases; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 469–493. [Google Scholar]
- Milner, R.J.; Samson, P.; Morton, R. Persistence of conidia of Metarhizium anisopliae in sugarcane fields: Effect of isolate and formulation on persistence over 3.5 years. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2003, 13, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, T.; Mayerhofer, J.; Enkerli, J.; Eilenberg, J.; Meyling, N.V.; de Andrade Moral, R.; Borges Demétrio, C.G.; Delalibera, I. Persistence of Brazilian isolates of the entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae and M. robertsii in strawberry crop soil after soil drench application. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 233, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inglis, G.D.; Goettel, M.S.; Johnson, D.L. Persistence of the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana, on phylloplanes of crested wheatgrass and alfalfa. Biol. Control. 1993, 3, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inglis, G.D.; Goettel, M.S.; Butt, T.M.; Strasser, H. Use of hyphomycetous fungi for managing insect pests. In Fungi Biocontrol Agents; CAB international: Wallingford, UK, 2001; pp. 23–69. [Google Scholar]
- Pilz, C.; Enkerli, J.; Wegensteiner, R.; Keller, S. Establishment and persistence of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae in maize fields. J. Appl. Entomol. 2011, 135, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamisile, B.S.; Dash, C.K.; Akutse, K.S.; Keppanan, R.; Wang, L. Fungal Endophytes: Beyond Herbivore Management. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaber, L.R.; Ownley, B.H. Can we use entomopathogenic fungi as endophytes for dual biological control of insect pests and plant pathogens? Biol. Control. 2018, 116, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.E. The use of fungal entomopathogens as endophytes in biological control: A review. Mycologia 2018, 110, 4–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Leger, R.J. Studies on adaptations of Metarhizium anisopliae to life in the soil. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 98, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; O’Brien, T.R.; Fang, W.; St. Leger, R.J. The plant beneficial effects of Metarhizium species correlate with their association with roots. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7089–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, C.K.; Bamisile, B.S.; Keppanan, R.; Qasim, M.; Lin, Y.; Islam, S.U.; Wang, L. Endophytic entomopathogenic fungi enhance the growth of Phaseolus vulgaris L. (Fabaceae) and negatively affect the development and reproduction of Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae). Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrini, O. Fungal endophytes of tree leaves. In Microbial Ecology of Leaves; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Liarzi, O.; Ezra, D. Endophyte-mediated biocontrol of herbaceous and non-herbaceous plants. In Advances in Endophytic Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 335–369. [Google Scholar]
- Bamisile, B.S.; Dash, C.K.; Akutse, K.S.; Keppanan, R.; Afolabi, O.G.; Hussain, M.; Wang, L. Prospects of endophytic fungal entomopathogens as biocontrol and plant growth promoting agents: An insight on how artificial inoculation methods affect endophytic colonization of host plants. Microbiol. Res. 2018, 217, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dara, S.K. Non-Entomopathogenic Roles of Entomopathogenic Fungi in Promoting Plant Health and Growth. Insects 2019, 10, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gange, A.C.; Koricheva, J.; Currie, A.F.; Jaber, L.R.; Vidal, S. Meta-analysis of the role of entomopathogenic and unspecialized fungal endophytes as plant bodyguards. New Phytol. 2019, 223, 2002–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Canassa, F.; Tall, S.; Moral, R.A.; de Lara, I.A.; Delalibera, I., Jr.; Meyling, N.V. Effects of bean seed treatment by the entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium robertsii and Beauveria bassiana on plant growth, spider mite populations and behavior of predatory mites. Biol. Control. 2019, 132, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ment, D.; Churchill, A.C.; Gindin, G.; Belausov, E.; Glazer, I.; Rehner, S.A.; Samish, M. Resistant ticks inhibit Metarhizium infection prior to haemocoel invasion by reducing fungal viability on the cuticle surface. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1570–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsa, S.; Ortiz, V.; Vega, F.E. Establishing fungal entomopathogens as endophytes. Towards endophytic biological control. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 74, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Behie, S.W.; Jones, S.J.; Bidochka, M.J. Plant tissue localization of the endophytic insect pathogenic fungi Metarhizium and Beauveria. Fungal Ecol. 2015, 13, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humber, R.A. Chapter VI-Identification of entomopathogenic fungi. In Manual of Techniques in Invertebrate Pathology, 2nd ed.; Lacey, L.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 151–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inyang, E.N.; Butt, T.M.; Beckett, A.; Archer, S. The effect of crucifer epicuticular waxes and leaf extracts on the germination and virulence of Metarhizium anisopliae conidia. Mycol. Res. 1999, 103, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łaźniewska, J.; Macioszek, V.K.; Kononowicz, A.K. Plant-fungus interface: The role of surface structures in plant resistance and susceptibility to pathogenic fungi. Physiol. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2012, 78, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonjely, S.; Bidochka, M.J. Generalist and specialist Metarhizium insect pathogens retain ancestral ability to colonize plant roots. Fungal Ecol. 2019, 41, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Geest, L.P.; Bruin, J. Diseases of mites and ticks: From basic pathology to microbial control—An introduction. In Diseases of Mites and Ticks; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, S.D.; Duncan, L.W. Chapter 19-Microbial Control of Insect and Mite Pests of Citrus. In Microbial Control of Insect and Mite, Pests; Lacey, L.A., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 283–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerson, U.; Gafni, A.; Paz, Z.; Sztejnberg, A. A tale of three acaropathogenic fungi in Israel: Hirsutella, Meira and Acaromyces. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2008, 46, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, Z.; Bilkis, I.; Gerson, U.; Kerem, Z.; Sztejnberg, A. Argovin, a novel natural product secreted by the fungus Meira argovae, is antagonistic to mites. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2011, 140, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopická, J.; Zemek, R.; Bohatá, A.; Nermuť, J.; Mráček, Z.; Palevsky, E.; Čurn, V. Možné využití entomopatogenních hub proti roztoči Rhizoglyphus robini (Acari: Acaridae). Aktual. Pozn. V Pěst. Šlecht. Ochraně Rostl. 2017, 12, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Nermuť, J.; Zemek, R.; Mráček, Z.; Palevsky, E.; Půža, V. Entomopathogenic nematodes as natural enemies for control of Rhizoglyphus robini (Acari: Acaridae)? Biol. Control. 2019, 128, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztejnberg, A.; Doron-Shloush, S.; Gerson, U. The biology of the acaropathogenic fungus Hirsutella kirchneri. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 1997, 7, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.V.P.; Tangtrakulwanich, K.; Wu, S.; Miller, J.H.; Ophus, V.L.; Prewett, J.; Jaronski, S.T. Evaluation of the effectiveness of entomopathogens for the management of wireworms (Coleoptera: Elateridae) on spring wheat. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2014, 120, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Resquín-Romero, G.; Garrido-Jurado, I.; Delso, C.; Ríos-Moreno, A.; Quesada-Moraga, E. Transient endophytic colonizations of plants improve the outcome of foliar applications of mycoinsecticides against chewing insects. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2016, 136, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Jurado, I.; Resquín-Romero, G.; Amarilla, S.P.; Ríos-Moreno, A.; Carrasco, L.; Quesada-Moraga, E. Transient endophytic colonization of melon plants by entomopathogenic fungi after foliar application for the control of Bemisia tabaci Gennadius (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae). J. Pest. Sci. 2017, 90, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resquín-Romero, G.; Garrido-Jurado, I.; Quesada-Moraga, E. Combined use of entomopathogenic fungi and their extracts for the control of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisduval) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Biol. Control. 2016, 92, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, A.; Okabe, K.; Eckenrode, C.J.; Villani, M.G.; Oconnor, B.M. Biology, ecology, and management of the bulb mites of the genus Rhizoglyphus (Acari: Acaridae). Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2000, 24, 85–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebiush-Mordechai, S.; Erlich, O.; Maymon, M.; Freeman, S.; Ben-David, T.; Ofek, T.; Tsror, L. Bulb and Root Rot in Lily (Lilium longiflorum) and Onion (Allium cepa) in Israel. J. Phytopathol. 2014, 162, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofek, T.; Gal, S.; Inbar, M.; Lebiush-Mordechai, S.; Tsror, L.; Palevsky, E. The role of onion-associated fungi in bulb mite infestation and damage to onion seedlings. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2014, 62, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zindel, R.; Ofek, M.; Minz, D.; Palevsky, E.; Zchori-Fein, E.; Aebi, A. The role of the bacterial community in the nutritional ecology of the bulb mite Rhizoglyphus robini (Acari: Astigmata: Acaridae). FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1488–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flori, P.; Roberti, R. La concia dei bulbi di cipolla con antagonisti fungini per il contenimento di Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cepae. La Difesa Delle Piante 1993, 16, 5–12, (Italian with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Smitley, D.R.; Kennedy, G.G. Photo-oriented aerial-dispersal behavior of Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) enhances escape from the leaf surface. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Plant Host, Cultivar | Target Pest’s Common Name, Latin Name and Taxonomic Family | Target Sites | Inoculation Technique | Endophytic Colonization, % ± SE | Effect on Mite Pest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue Recovery | Live Imaging | |||||
| Citrus volkameriana, Volkamer lemon, ‘Volka’ | Citrus rust mite, Phyllocoptruta oleivora, Eriophyidae | Leaves Leaves | Foliar spray Leaf infiltration | 0 50 ± 12.3% | 0 100% | 62.6 ± 14.1% mortality 4 DPI 0 |
| Phaseolus vulgaris, Common bean, ‘Haricot’ | Two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae, Tetranychidae | Leaves Rhizosphere | Foliar spray Drench | — — | 0 0 | 95.3 ± 1–100% reduction 14 DPI 44 ± 16.7% reduction 14 DPI |
| Allium cepa, Spring onion, ‘Ori’ | Bulb mite, Rhizoglyphus robini, Acaridae | Drench | Rhizosphere | 0 * | 45 ± 7% | 72 ± 10.7% reduction 4 WPI |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ment, D.; Raman, S.; Gal, S.; Ezra, D.; Palevsky, E. Interactions of Metarhizium brunneum-7 with Phytophagous Mites Following Different Application Strategies. Insects 2020, 11, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060330
Ment D, Raman S, Gal S, Ezra D, Palevsky E. Interactions of Metarhizium brunneum-7 with Phytophagous Mites Following Different Application Strategies. Insects. 2020; 11(6):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060330
Chicago/Turabian StyleMent, Dana, Sukirtha Raman, Shira Gal, David Ezra, and Eric Palevsky. 2020. "Interactions of Metarhizium brunneum-7 with Phytophagous Mites Following Different Application Strategies" Insects 11, no. 6: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060330
APA StyleMent, D., Raman, S., Gal, S., Ezra, D., & Palevsky, E. (2020). Interactions of Metarhizium brunneum-7 with Phytophagous Mites Following Different Application Strategies. Insects, 11(6), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects11060330