Frontiers Approaches to the Diagnosis of Thrips (Thysanoptera): How Effective Are the Molecular and Electronic Detection Platforms?
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
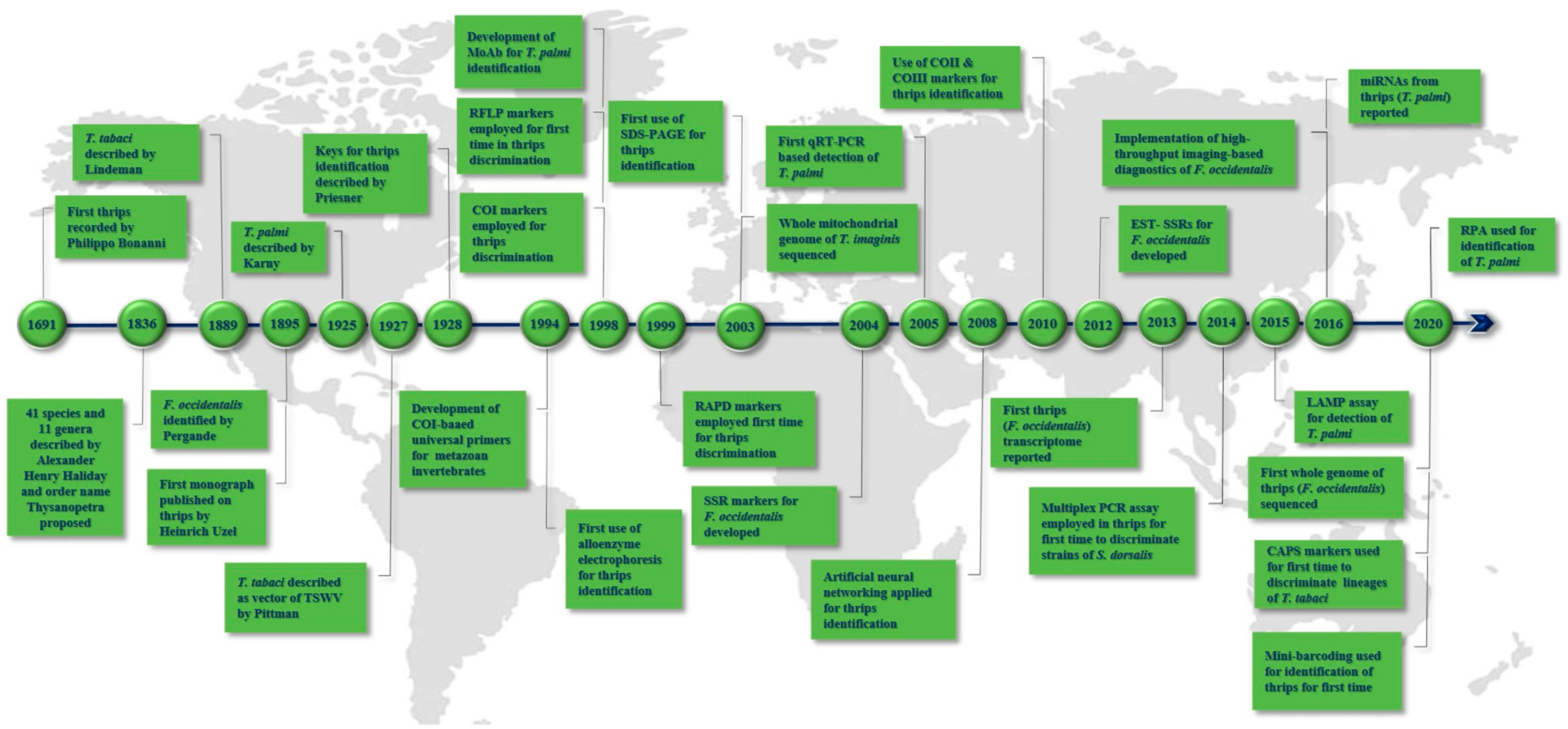
2. Landmarks in Thrips Diagnostics
3. PCR-Based Identification of Thrips Using Molecular Markers
3.1. COI Markers
3.2. Thrips Genetic Diversity Studies Using COI Markers
3.2.1. T. tabaci
3.2.2. T. palmi
3.2.3. Scirtothrips dorsalis Hood
3.2.4. F. schultzei
3.2.5. F. occidentalis
3.3. COII Markers
3.4. COIII Markers
3.5. rRNA-ITS
3.6. Other Marker Genes Used for Thrips Identification
3.7. SSR/Microsatellite Markers
3.8. RFLP Markers
3.9. RAPD Markers
3.10. AFLP Markers
3.11. SCAR Markers
3.12. Cleaved Amplified Polymorphic Sequence (CAPS) Markers
3.13. Multiplex PCR
3.14. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
3.15. Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP)
3.16. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification (RPA)
3.17. Protein-Based Diagnostic Assays
3.18. Mini-Barcode Pyrosequencing
3.19. Microarray/DNA Chip
3.20. Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)
3.21. High-Throughput Imaging-Based Diagnostics
3.22. High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS)
4. Strengths of the Present-Day Molecular and Electronic Platforms and Future Potential
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mound, L.A. Thysanoptera (Thrips) World Checklist. Available online: https://www.ento.csiro.au/thysanoptera/worldthrips.php (accessed on 20 July 2021).
- Mound, L.A.; Morris, D.C. The insect order Thysanoptera: Classification versus systematics. Zootaxa 2007, 1668, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, P.; Peñalver, E.; Azar, D.; Hodebert, G.; Nel, A. Modern thrips families Thripidae and Phlaeothripidae in early Cretaceous amber (Insecta: Thysanoptera). Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 2013, 46, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.; Herbert, A.; Akin, D.S.; Reed, J. Biology, crop injury, and management of thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) infesting cotton seedlings in the United States. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2011, 2, B1–B9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, C.; Kirk, W.D.J. Predatory mites double the economic injury level of Frankliniella occidentalis in strawberry. BioControl 2016, 61, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrella, G.; Gognalons, P.; Gebre-Selassiè, K.; Vovlas, C.; Marchoux, G. An update of the host range of tomato spotted wilt virus. J. Plant Pathol. 2003, 85, 227–264. [Google Scholar]
- Pappu, H.R.; Jones, R.A.C.; Jain, R.K. Global status of tospovirus epidemics in diverse cropping systems: Successes achieved and challenges ahead. Virus Res. 2009, 141, 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.E.; Whitfield, A.E. The genus tospovirus: Emerging Bunyaviruses that threaten food security. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2016, 3, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwood, J.L.; German, T.L.; Moyer, J.W.; Ullman, D.E. Tomato spotted wilt. Plant Health Instr. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, D.G.; Joseph, S.V.; Srinivasan, R.; Diffie, S. Thrips vectors of tospoviruses. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2011, 2, I1–I10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adkins, S. Tomato spotted wilt virus—Positive steps towards negative success. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2000, 1, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.V.R.; Buiel, A.A.M.; Satyanarayana, T.; Dwivedi, S.L.; Reddy, A.S.; Ratna, A.S.; Vijayalakshmi, K.; Ranga Rao, G.V.; Naidu, R.A.; Wightman, J.A. Peanut bud necrosis disease: An overview. In Recent Studies on Peanut Bud Necrosis Disease; ICRISAT Asia Centre: Patancheru, Andhra Pradesh, India, 1995; pp. 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Brunner, P.C.; Chatzivassiliou, E.K.; Katis, N.I.; Frey, J.E. Host-associated genetic differentiation in Thrips tabaci (Insecta; Thysanoptera), as determined from mtDNA sequence data. Heredity 2004, 93, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoddle, M.S.; Heraty, J.M.; Rugman-Jones, P.F.; Mound, L.A.; Stouthamer, R. Relationships among species of Scirtothrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae, Thripinae) using molecular and morphological data. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2008, 101, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.C.; Frey, J.E. Habitat-specific population structure in native western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis (Insecta, Thysanoptera). J. Evol. Biol. 2010, 23, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugman-Jones, P.F.; Hoddle, M.S.; Stouthamer, R. Nuclear-mitochondrial barcoding exposes the global pest western flower thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) as two sympatric cryptic species in its native California. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, A.L.; Booth, W.; Vargo, E.L.; Kennedy, G.G. Thrips tabaci population genetic structure and polyploidy in relation to competency as a vector of tomato spotted wilt virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, G. Pictorial key to the economically important species of Thysanoptera in Central Europe. EPPO Bull. 1994, 24, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mound, L.A.; Kibby, G. Thysanoptera: An Identification Guide; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti, J.S. Yellow dorsally spotted species of thrips (Terebrantia: Thripidae) in India with description of a new species in flowers of Tabernaemontana (Apocynaceae) and Lantana (Verbenaceae). Thrips 1999, 1, 58–65. [Google Scholar]
- Mound, L.A.; Masumoto, M. The genus Thrips (Thysanoptera, Thripidae) in Australia, New Caledonia and New Zealand. Zootaxa 2005, 1020, 1–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.; Verma, R.K. Key for identification of adult female of Scirtothrips dorsalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) based on external morphology. World Appl. Sci. J. 2010, 9, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Moritz, G.; Subramanian, S.; Brandt, S.; Triapitsyn, S.V. Development of a user-friendly identification system for the native and invasive pest thrips and their parasitoids in east Africa. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 59–60. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Li, Z. Identification key to species of Thrips genus from China (Thysanoptera, Thripidae), with seven new records. Zootaxa 2011, 2810, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarlinsky, T.; Funderburk, J. A key to some Frankliniella (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) larvae found in Florida with descriptions of the first instar of select species. Fla. Entomol. 2016, 99, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mound, L.; Nakahara, S.; Tsuda, D.M. Thysanoptera-Terebrantia of the Hawaiian Islands: An identification manual. Zookeys 2016, 549, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cluever, J.D.; Smith, H.A. A photo-based key of thrips (Thysanoptera) associated with horticultural crops in Florida. Fla. Entomol. 2017, 100, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belaam-Kort, I.; Marullo, R.; Attia, S.; Boulahia-Kheder, S. Thrips fauna in citrus orchard in Tunisia: An up-to-date. Bull. Insectology 2020, 73, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, J.N.; Collins, D.W.; Rizvi, R.H.; Northway, B.J.; Danks, C. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against the EU-listed pest Thrips palmi. Food Agric. Immunol. 1998, 10, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Moritz, G.; Delker, C.; Paulsen, M.; Mound, L.A.; Burgermeister, W. Modern methods for identification of Thysanoptera. EPPO Bull. 2000, 30, 591–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayar, K.; Törjék, O.; Kiss, E.; Gyulai, G.; Heszky, L. Intra- and interspecific molecular polymorphism of thrips species. Acta Biol. Hung. 2002, 53, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, P.C.; Fleming, C.; Frey, J.E. A molecular identification key for economically important thrips species (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) using direct sequencing and a PCR-RFLP-based approach. Agric. For. Entomol. 2002, 4, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, S.; Komazaki, S. Identification of thrips species (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) on Japanese fruit trees by polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism of the ribosomal ITS2 region. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2002, 92, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, K.; Boonham, N.; Barker, I.; Collins, D.W. Development of a sequence-specific real-time PCR to the melon thrips Thrips palmi (Thysan., Thripidae). J. Appl. Entomol. 2005, 129, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugman-Jones, P.F.; Hoddle, M.S.; Mound, L.A.; Stouthamer, R. Molecular identification key for pest species of Scirtothrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2006, 99, 1813–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- XiangQin, M.; LiAng, M.; FangHao, W.; ZhongShi, Z.; WenKai, W.; GuiFen, W. SCAR marker for rapid identification of the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2010, 53, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Przybylska, A.; Fiedler, Ż.; Kucharczyk, H.; Obrępalska-Stęplowska, A. Detection of the quarantine species Thrips palmi by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehle, N.; Trdan, S. Traditional and modern methods for the identification of thrips (Thysanoptera) species. J. Pest Sci. 2012, 85, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzel, J. Monografie řádu Thysanoptera; Selbstverlag des Verfassers, Králové: B. E. Tolmana, Hradec Králové, Czech Republic, 1895. [Google Scholar]
- Pittman, H.A. Spotted wilt of tomatoes. J. Aust. Counc. Sci. Ind. Res. 1927, 1, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, T.; Loxdale, H.D.; Brookes, C.P. Studying dispersal and persistence of pear thrips populations using genetic markers (allozymes). Courier Forschungsinstitut Senckenberg 1994, 178, 75–78. [Google Scholar]
- Crespi, B.J.; Carmean, D.A.; Mound, L.A.; Worobey, M.; Morris, D. Phylogenetics of social behavior in Australian gall-forming thrips: Evidence from mitochondrial DNA sequence, adult morphology and behavior, and gall morphology. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 1998, 9, 163–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedor, P.; Malenovský, I.; Vaňhara, J.; Sierka, W.; Havel, J. Thrips (Thysanoptera) identification using artificial neural networks. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2008, 98, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asokan, R.; Krishna Kumar, N.K.; Kumar, V.; Ranganath, H.R. Molecular differences in the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I (mtCOI) gene and development of a species-specific marker for onion thrips, Thrips tabaci Lindeman, and melon thrips, T. palmi Karny (Thysanoptera: Thripidae), vectors of tospoviruses (Bunyaviridae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2007, 97, 461–470. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, T.; Sakurai, T. The phylogeny of thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) based on partial sequences of cytochrome oxidase I, 28S ribosomal DNA and elongation factor-1 α and the association with vector competence of tospoviruses. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2007, 42, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Agamy, E.; El-Husseini, M.; El- Sebaey, I.; Wafy, M. Molecular identification of thripids attacking olive groves at Ismailia, Egypt. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. A Entomol. 2017, 10, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Ratnasingham, S.; DeWaard, J.R. Barcoding animal life: Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 divergences among closely related species. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, S96–S99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Timm, A.E.; Stiller, M.; Frey, J.E. A molecular identification key for economically important thrips species (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in southern Africa. Afr. Entomol. 2008, 16, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Singha, D.; Kumar, V.; Pakrashi, A.; Kundu, S.; Chandra, K.; Patnaik, S.; Tyagi, K. DNA barcoding of selected Scirtothrips species (Thysanoptera) from India. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2019, 4, 2710–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubillos-Salamanca, Y.P.; Rodríguez-Maciel, J.C.; Pineda-Guillermo, S.; Silva-Rojas, H.V.; Berzosa, J.; Tejeda-Reyes, M.A.; Rebollar-Alviter, Á. Identification of thrips species and resistance of Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) to malathion, spinosad, and bifenthrin in blackberry crops. Fla. Entomol. 2019, 102, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo-Pérez, D.; Santillán-Galicia, M.T.; Johansen-Naime, R.M.; González-Hernández, H.; Segura-León, O.L.; Ochoa-Martínez, D.L.; Guzman-Valencia, S. Species diversity of thrips (Thysanoptera) in selected avocado orchards from Mexico based on morphology and molecular data. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 2509–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, J.; Hassani-Kakhki, M.; Modarres Awal, M. Identifying thrips (Insecta: Thysanoptera) using DNA barcodes. J. Cell Mol. Res. 2010, 2, 35–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.F.; Meng, X.Q.; Min, L.; Qiao, W.N.; Wan, F.H. Rapid diagnosis of the invasive species, Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande): A species-specific COI marker. J. Appl. Entomol. 2012, 136, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leão, E.U.; de Almeida Spadotti, D.M.; Rocha, K.C.G.; Lima, E.F.B.; Tavella, L.; Turina, M.; Krause-Sakate, R. Efficient detection of Frankliniella schultzei (Thysanoptera, Thripidae) by cytochrome oxidase I gene (mtCOI) direct sequencing and real-time PCR. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2017, 60, e17160425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Mound, L.A.; Zhang, H. A new species of Heliothrips (Thysanoptera, Panchaetothripinae), based on morphological and molecular data. Zootaxa 2019, 4638, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, K.; Kumar, V.; Singha, D.; Chakraborty, R.; Muehlethaler, R. Morphological and DNA barcoding evidence for invasive pest thrips, Thrips parvispinus (Thripidae: Thysanoptera), newly recorded from India. J. Insect Sci. 2015, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganthy, M.; Rageshwari, S.; Senthilraja, C.; Nakkeeran, S.; Malathi, V.G.; Ramaraju, K.; Renukadevi, P. New record of western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in south India. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2016, 1, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, D.; Tyagi, K.; Kumar, V. First record of Podothrips erami (Thysanoptera: Tubulifera) from India. Halteres 2017, 8, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, K.; Hasegawa, E. Discrimination of reproductive forms of Thrips tabaci (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) by PCR with sequence specific primers. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Seal, D.R.; Osborne, L.S.; McKenzie, C.L. Coupling scanning electron microscopy with DNA bar coding: A novel approach for thrips identification. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 49, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Hewitt, G.M. Nuclear integrations: Challenges for mitochondrial DNA markers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1996, 11, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfait, B.; Rustin, P.; Munnich, A.; Rötig, A. Coamplification of nuclear pseudogenes and assessment of heteroplasmy of mitochondrial DNA mutations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 247, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensasson, D.; Zhang, D.X.; Hartl, D.L.; Hewitt, G.M. Mitochondrial pseudogenes: Evolution’s misplaced witnesses. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, J.E.; Frey, B. Origin of intra-individual variation in PCR-amplified mitochondrial cytochrome oxidade I of Thrips tabaci (Thysanoptera: Thripidae): Mitochondrial heteroplasmy or nuclear integration? Hereditas 2004, 140, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marullo, R.; Mercati, F.; Vono, G. DNA barcoding: A reliable method for the identification of thrips species (Thysanoptera, Thripidae) collected on sticky traps in onion fields. Insects 2020, 11, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenser, G.; Szénási, Á. Review of the biology and vector capability of Thrips tabaci Lindeman (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Acta Phytopathol. Entomol. Hung. 2004, 39, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T. Parthenogenetic reproduction in Thrips tabaci and Frankliniella intonsa (Insecta: Thysanoptera). In Advances in Invertebrate Reproduction 5; Hoshi, M., Yamashita, O., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1990; pp. 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Zawirska, I. Untersuchungen über zwei biologische Typen von Thrips tabaci Lind. (Thysanoptera, Thripidae) in der VR Polen. Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 1976, 12, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzivassiliou, E.K. Thrips tabaci: An ambiguous vector of TSWV in perspective. In Thrips and Tospoviruses: Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Thysanoptera, Reggio Calabria, Italy, 2–7 July 2001; Marullo, R., Mound, L., Eds.; ANIC: Canberra, Australia, 2002; pp. 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, R.; Guo, F.; Riley, D.; Diffie, S.; Gitaitis, R.; Sparks, A.; Jeyaprakash, A. Assessment of variation among Thrips tabaci populations from Georgia and Peru based on polymorphism in mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase I and ribosomal ITS2 sequences. J. Entomol. Sci. 2011, 46, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekrat, L.; Manzari, S.; Shishehbor, P. Morphometric and molecular variation in Thrips tabaci Lindeman (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) populations on onion and tobacco in Iran. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2014, 16, 1505–1516. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Hafeez, M.; Lu, Y. Population genetic diversity and structure of Thrips tabaci (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) on allium hosts in China, inferred from mitochondrial COI gene sequences. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, S.; Murai, T. Phylogenetic analysis based on mitochondrial COI gene sequences in Thrips tabaci Lindeman (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in relation to reproductive forms and geographic distribution. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2007, 42, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogo, K.; Miura, K.; Aizawa, M.; Watanabe, T.; Stouthamer, R. Genetic structure in relation to reproduction mode in Thrips tabaci (Insecta: Thysanoptera). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2015, 50, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westmore, G.C.; Poke, F.S.; Allen, G.R.; Wilson, C.R. Genetic and host-associated differentiation within Thrips tabaci Lindeman (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) and its links to tomato spotted wilt virus-vector competence. Heredity 2013, 111, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nault, B.A.; Kain, W.C.; Wang, P. Seasonal changes in Thrips tabaci population structure in two cultivated hosts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, A.L.; Nault, B.A.; Vargo, E.L.; Kennedy, G.G. Restricted gene flow among lineages of Thrips tabaci supports genetic divergence among cryptic species groups. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazia, A.D.; Marullo, R.; Frey, J.E. Preliminary results of molecular polymorphism in field populations of Thrips tabaci Lindeman (Thysanoptera: Thripidae), occurring on onion crops in South Italy. Bodenkult. J.L. Manag. Food Environ. 2015, 66, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Nault, B.A.; Shelton, A.M.; Gangloff-kaufmann, J.L.; Clark, M.E.; Werren, J.L.; Cabrera-la Rosa, J.C.; Kennedy, G.G. Reproductive modes in onion thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) populations from New York onion fields. Environ. Entomol. 2006, 35, 1264–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, R.H.; Collins, D.W.; Walsh, K.; Boonham, N. Assessment of loci for DNA barcoding in the genus thrips (Thysanoptera:Thripidae). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2010, 10, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadirvel, P.; Srinivasan, R.; Hsu, Y.C.; Su, F.C.; Del La Peña, R. Application of cytochrome oxidase I sequences for phylogenetic analysis and identification of thrips species occurring on vegetable crops. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebijith, K.B.; Asokan, R.; Krishna, V.; Ranjitha, H.H.; Krishna Kumar, N.K.; Ramamurthy, V.V. DNA barcoding and elucidation of cryptic diversity in thrips (Thysanoptera). Fla. Entomol. 2014, 97, 1328–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, R.; Ashfaq, M.; Rasool, A.; Hebert, P.D.N. DNA barcode analysis of thrips (Thysanoptera) diversity in Pakistan reveals cryptic species complexes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Jagdale, S.S.; Basavaraj; Dietzgen, R.G.; Jain, R.K. Genetics of Thrips palmi (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). J. Pest Sci. 2020, 93, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, K.; Kumar, V.; Singha, D.; Chandra, K.; Laskar, B.A.; Kundu, S.; Chakraborty, R.; Chatterjee, S. DNA Barcoding studies on thrips in India: Cryptic species and species complexes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebijith, K.B.; Asokan, R.; Kumar, N.K.K.; Krishna, V.; Ramamurthy, V.V. Development of species-specific markers and molecular differences in mtDNA of Thrips palmi Karny and Scirtothrips dorsalis Hood (Thripidae: Thysanoptera), vectors of Tospoviruses (Bunyaviridae) in India. Entomol. News 2012, 122, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, A.M.; Kumar, V.; Hoddle, M.S.; Funderburk, J.E.; Morgan, J.K.; Jara-Cavieres, A.; Shatters, R.G.; Osborne, L.S.; McKenzie, C.L. The Scirtothrips dorsalis species complex: Endemism and invasion in a global pest. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, S.; Hirose, T.; Kakiuchi, K.; Kodama, H.; Kijima, K.; Mochizuki, M. Occurrence of a novel strain of Scirtothrips dorsalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in Japan and development of its molecular diagnostics. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 49, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott-Brown, A.S.; Hodgetts, J.; Hall, J.; Simmonds, M.J.S.; Collins, D.W. Potential role of botanic garden collections in predicting hosts at risk globally from invasive pests: A case study using Scirtothrips dorsalis. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakimura, K. A comment on the color forms of Frankliniella schultzei (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in relation to transmission of the tomato-spotted wilt virus. Pacafic Insects 1969, 11, 761–762. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, G.; Bald, J.G.; Pittman, H.A. Investigations on “Spotted Wilt” of tomatoes. Bull. Counc. Sci. Ind. Res. Aust. 1930, 44, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Wijkamp, I.; Almarza, N.; Goldback, R.; Peters, D. Distinct levels of specificity in thrips transmission of tospoviruses. Phytopathology 1995, 85, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-L.; Lin, F.-C.; Chiu, Y.-C.; Shih, H.-T. Species of Frankliniella trybom (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) from the Asian-Pacific area. Zool. Stud. 2010, 49, 824–838. [Google Scholar]
- Mound, L.A. A review of R. S. Bagnall’s Thysanoptera collections. Bull. Br. Mus. (Nat. Hist.) (Entomol.) 1968, 11 (Suppl. S11), 1–181. [Google Scholar]
- Gikonyo, M.W.; Niassy, S.; Moritz, G.B.; Khamis, F.M.; Magiri, E.; Subramanian, S. Resolving the taxonomic status of Frankliniella schultzei (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) colour forms in Kenya—A morphological-, biological-, molecular- and ecological-based approach. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2017, 37, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereward, J.; Hutchinson, J.A.; McCulloch, G.A.; Silva, R.; Walter, G.H. Divergence among generalist herbivores: The Frankliniella schultzei species complex in Australia (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Arthropod. Plant. Interact. 2017, 11, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macharia, I.; Backhouse, D.; Skilton, R.; Ateka, E.; Wu, S.-B.; Njahira, M.; Maina, S.; Harvey, J. Diversity of thrips species and vectors of tomato spotted wilt virus in tomato production systems in Kenya. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, D.E.; Smith, R.F. The Frankliniella Occidentalis Pergande Complex in California (Thysanoptera: Thripidae); Steinhaus, E.A., Usinger, R.L., Eds.; University of California Publications in Entomology; Literary Licensing, LLC: Whitefish, MT, USA, 1956; ISBN 9781258267407. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, N.A.; Workman, P.J. Confirmation of a pesticide-resistant strain of Western flower thrips in New Zealand. In Proceedings of the Forty Seventh New Zealand Plant Protection Conference, Waitangi, New Zealand, 9–11 August 1994; New Zealand Plant Protection Society: Auckland, New Zealand, 1994; Volume 47, pp. 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Brødsgaard, H.F. Insecticide resistance in European and African strains of western flower thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) tested in a new residue-on-glass test. J. Econ. Entomol. 1994, 87, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.C.; Frey, J.E. Isolation and characterization of six polymorphic microsatellite loci in the western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis (Insecta, Thysanoptera). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2004, 4, 599–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.J.; Wang, Z.H.; Gong, Y.J.; Zhu, L.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Wei, S.J. Low genetic diversity but strong population structure reflects multiple introductions of western flower thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) into China followed by human-mediated spread. Evol. Appl. 2017, 10, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-M.; Sun, J.-T.; Xue, X.-F.; Zhu, W.-C.; Hong, X.-Y.; Yang, X.-M.; Sun, J.-T.; Xue, X.-F.; Zhu, W.-C.; Hong, X.-Y. Development and characterization of 18 novel EST-SSRs from the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2863–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.M.; Lou, H.; Sun, J.T.; Zhu, Y.M.; Xue, X.F.; Hong, X.Y. Temporal genetic dynamics of an invasive species, Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande), in an early phase of establishment. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.-S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, A.-S.; Guo, D.; Tao, Y.-L.; Chu, D. Genetic diversity and inferences on potential source areas of adventive Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in Shandong, China based on mitochondrial and microsatellite markers. Fla. Entomol. 2013, 96, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.-S.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, A.-S.; Guo, D.; Tao, Y.-L.; Chu, D. Sudden widespread distribution of Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in Shandong province, China. Fla. Entomol. 2013, 96, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirnezhad, M.; Schidlo, N.; Klinkhamer, P.G.L.; Leiss, K.A. Variation in genetics and performance of Dutch western flower thrips populations. J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 1816–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.C.; Mound, L.A. Molecular relationships between populations of South African citrus thrips (Scirtothrips aurantii Faure) in South Africa and Queensland, Australia. Aust. J. Entomol. 2004, 43, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarlinsky, T.L.; Rugman-Jones, P.; Funderburk, J.; Stouthamer, R.; Ujueta, C.S. Adult identity crisis in Leucothrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) associated with the tropical ornamental plant Codiaeum variegatum (Euphorbiaceae). Fla. Entomol. 2017, 100, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamzadeh, S.; Incekara, Ü. Review of molecular taxonomy studies on Coleoptera aquatic insects. Int. J. Entomol. Res. 2016, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zoldos, V.; Papes, D.; Cerbah, M.; Panaud, O.; Besendorfer, V.; Siljak-Yakovlev, S. Molecular-cytogenetic studies of ribosomal genes and heterochromatin reveal conserved genome organization among 11 Quercus species. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1999, 99, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, R.E.; Ruiz-Arce, R.; Ciomperlik, M.; Vasquez, J.D.; DeLeón, R. Development of a ribosomal DNA ITS2 marker for the identification of the thrips, Scirtothrips dorsalis. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenser, G.; Almási, A.; Tóbiás, I. Host range and number of generations of pea thrips (Kakothrips pisivorus westwood, 1880) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in Hungary. Acta Phytopathol. Entomol. Hung. 2012, 47, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seepiban, C.; Charoenvilaisiri, S.; Kumpoosiri, M.; Bhunchoth, A.; Chatchawankanphanich, O.; Gajanandana, O. Development of a protocol for the identification of tospoviruses and thrips species in individual thrips. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 222, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, M.T.; Snow, J.W. Phoresy or an accident? Trafficking of flower-feeding thrips by pollen-foraging bees. Ecology 2019, 100, e02671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Alvarado, A.A.; Jaén-Sanjur, J.N.; Galipienso, L.; Elvira-González, L.; Rubio, L.; Herrera-Vásquez, J.A. Molecular identification, occurrence and distribution of Thrips palmi, Frankliniella intonsa and Frankliniella cephalica (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) on cucurbit crops in Panama. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2020, 60, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, T.J.; Ahn, S.J.; An, T.J.; Cho, M.R.; Jeon, H.Y.; Jung, J.A. Thrips in medicinal crops in Korea: Identification and their damages. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 2012, 20, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, T.; Rong, Z.; Jinliang, Z.; Yusheng, W.; Fanghao, W.; Guifen, Z. Identification of invasive species Frankliniella occidentalis and native species F. intonsa based on double gene markers. Chin. J. Biol. Control 2017, 612–622. [Google Scholar]
- Latha, K.R.; Krishna Kumar, N.K.; Mahadeva Swamy, H.M.; Asokan, R.; Ranganath, H.R.; Mahmood, R. Molecular identification and diversity of chilli thrips, Scirtothrips dorsalis Hood (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) employing ITS2 marker. Pest Manag. Hortic. Ecosyst. 2015, 21, 16–26. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, C.D.R.; Apolinario, J.J.G. Localization of populations of Scirtothrips dorsalis Hood collected from various mango-growing areas in the Philippines. Acta Hort. 2017, 1183, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, L.; Chang, N.; Tseng, M.; Yeh, W. Genetic variation of Thrips tabaci Lindeman (Thysanopetra: Thripidae) in the Pacific Rim. Formos. Entomol. 2010, 30, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
- Almási, A.; Tóbiás, I.; Bujdos, L.; Jenser, G. Molecular characterisation of Thrips tabaci Lindeman, 1889 (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) populations in Hungary based on the ITS2 sequences. Acta Zool. Acad. Sci. Hung. 2016, 62, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogler, A.P.; DeSalle, R. Evolution and phylogenetic information content of the ITS-1 region in the tiger beetle Cicindela dorsalis. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1994, 11, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fenton, B.; Malloch, G.; Germa, F. A study of variation in rDNA ITS regions shows that two haplotypes coexist within a single aphid genome. Genome 1998, 41, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, N.P.; Barker, S.C. Intragenomic variation in ITS2 rDNA in the louse of humans, Pediculus humanus: ITS2 is not a suitable marker for population studies in this species. Insect Mol. Biol. 2002, 11, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dentinger, B.T.M.; Didukh, M.Y.; Moncalvo, J.-M. Comparing COI and ITS as DNA barcode markers for mushrooms and allies (Agaricomycotina). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-W.; Wang, P.; Fail, J.; Shelton, A.M. Detection of gene flow from sexual to asexual lineages in Thrips tabaci (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Van der Kooi, C.J.; Schwander, T. Evolution of asexuality via different mechanisms in grass thrips (Thysanoptera: Aptinothrips). Evolution 2014, 68, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckman, R.S.; Mound, L.A.; Whiting, M.F. Phylogeny of thrips (Insecta: Thysanoptera) based on five molecular loci. Syst. Entomol. 2013, 38, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontcuberta García-Cuenca, A.; Dumas, Z.; Schwander, T. Extreme genetic diversity in asexual grass thrips populations. J. Evol. Biol. 2016, 29, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.K.; Varshney, R.K.; Sharma, P.C.; Ramesh, B. Molecular markers and their applications in wheat breeding. Plant Breed. 1999, 118, 369–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, G.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ismail, M.R.; Puteh, A.B.; Rahim, H.A.; Islam, N.K.; Latif, M.A. A review of microsatellite markers and their applications in rice breeding programs to improve blast disease resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 22499–22528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Z.; Zhi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, Z.; Wen, J. Population genetic structure and migration patterns of Dendrothrips minowai (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in Guizhou, China. Entomol. Sci. 2017, 20, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Gao, Y.; Gong, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Wei, S. Population analysis reveals genetic structure of an invasive agricultural thrips pest related to invasion of greenhouses and suitable climatic space. Evol. Appl. 2019, 12, 1868–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondelmann, P.; Nyasani, J.O.; Subramanian, S.; Meyhöfer, R. Genetic structure and diversity of western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis in a French bean agroecosystem of Kenya. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2017, 37, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisheng, D.; Ansheng, Z.; Chuanzhi, Z.; Yi, Y.; Dong, C. Characterization and molecular marker screening of EST-SSRs and their polymorphism compared with Genomic-SSRs in Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera:Thripidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 2012, 55, 634–640. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.; Huang, H.; Gui, F. Development of polymorphic EST-SSR markers by sequence alignment in Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande). J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2014, 17, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rugman-Jones, P.F.; Weeks, A.R.; Hoodle, M.S.; Stouthamer, R. Isolation and characterization of microsatellite loci in the avocado thrips Scirtothrips perseae (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 644–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, K.; Qiu, H.; Li, F.; Cao, Y. Polymorphic microsatellite markers in Thrips hawaiiensis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 49, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.J.; Li, Z.M.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhu, L.; Gong, Y.J.; Chen, M.; Wei, S.J. Bulk development and stringent selection of microsatellite markers in the western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Gong, Y.; Ma, L.; Cao, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Wei, S.; Gao, Y.; Gong, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Genome-wide developed microsatellite markers for the melon thrips Thrips palmi Karny (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Zool. Syst. 2019, 44, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- De Grazia, A.; Marullo, R.; Moritz, G. Molecular diagnosis of native and quarantine pest thrips of southern European citrus orchards. Bull. Insectology 2016, 69, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Przybylska, A.; Fiedler, Ż.; Obrępalska-Stęplowska, A. PCR-RFLP method to distinguish Frankliniella occidentalis, Frankliniella intonsa, Frankliniella pallida and Frankliniella tenuicornis. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2016, 56, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, C.R.; Jeong, D.H.; Park, H.W.; Kim, H.J.; Jeon, K.S.; Yoon, J.B. Molecular identification of thrips in two medicinal crops, Cnidium officinale Makino and Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 2019, 27, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, G.; Paulsen, M.; Delker, M.; Picl, S.; Kumm, S. Identification of thrips using ITS-RFLP analysis. In Thrips and Tospoviruses: Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Thysanoptera, Reggio Calabria, Italy, 2–7 July 2001; ANIC: Canberra, Australia, 2002; pp. 365–367. [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi, R.; Toda, S. Discrimination of two reproductive forms of Thrips tabaci by PCR-RFLP, and distribution of arrhenotokous T. tabaci in Tottori Prefecture. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2011, 55, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, H.O.; Al-Shuhaib, M.B.S. Exploring the potential and limitations of PCR-RFLP and PCR-SSCP for SNP detection: A review. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 6, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.G.K.; Kubelik, A.R.; Livak, K.J.; Rafalski, J.A.; Tingey, S.V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 6531–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, M.; Gafni, R. Morphological and molecular variations in thrips population collected on onion plants in Israel. Folia Entomol. Hung. 1996, 57, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Jenser, G.; Szénási, À.; Törjék, O.; Gyulai, G.; Kiss, E.; Heszky, L.; Fail, J. Molecular polymorphism between population of Thrips tabaci Lindeman (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) propagating on tobacco and onion. Acta Phytopathol. Entomol. Hung. 2001, 36, 365–368. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishna Rao, A. Population Dynamics and Molecular Characterization of Thrips and Their Management in Groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Acharya, N.G. Ranga Agricultural University, Rajendranagar, Hyderabad, India, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gyulai, G.; Bayar, K.; Törjék, O.; Kiss, J.; Szabó, Z.; Heszky, L. Molecular polymorphism among populations of Frankliniella intonsa. In Thrips and Tospoviruses: Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Thysanopetra, Reggio Calabria, Italy, 2–7 July 2001; Marullo, R., Mound, L.A., Eds.; ANIC: Canberra, Australia, 2002; pp. 373–375. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, R.O.; Artoni, R.F.; Vicari, M.R.; Nogaroto, V.; Silva, J.C.; Matiello, R.R.; Almeida, M.C. Population structure and genetic diversity analysis in Gynaikothrips uzeli (Zimerman, 1909) (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae) by RAPD markers. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2012, 102, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainali, B.P.; Shrestha, S.; Lim, U.T.; Kim, Y. Molecular markers of two sympatric species of the genus Frankliniella (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2008, 11, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, R.L.; Ramasubram, T.; Venkatesan, S.; Mohankumar, S. Molecular characterization of tospovirus transmitting thrips populations from India. Am. J. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2005, 1, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Neekhra, B.; Pandey, D.; Jain, K. RAPD marker system in insect study: A review. Indian J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Vos, P.; Hogers, R.; Bleeker, M.; Reijans, M.; Van De Lee, T.; Hornes, M.; Friters, A.; Pot, J.; Paleman, J.; Kuiper, M.; et al. AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 4407–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Forbes, M.R.; Smith, M.L. Characterization of AFLP markers in damselflies: Prevalence of codominant markers and implications for population genetic applications. Genome 2000, 44, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reineke, A.; Schmidt, O.; Zebitz, C.P.W. Differential gene expression in two strains of the endoparasitic wasp Venturia canescens identified by cDNA-amplified fragment length polymorphism analysis. Mol. Ecol. 2003, 12, 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Kritzman, A.; Yonash, N.; Gera, A.; Pollak, N.; Lavi, U. Genetic variation of thrips populations assessed by amplified fragment length polymorphism (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2005, 98, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Wu, Q.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Lu, Y.B. Genetic differentiation among various populations of Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae.) assessed by mtDNA sequence and AFLP. In Proceedings of the IXth International Symposium on Thysanoptera and Tospoviruses. J. Insect Sci. 2010, 10, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Paran, I.; Michelmore, R.W. Development of reliable PCR-based markers linked to downy mildew resistance genes in lettuce. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1993, 85, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, U.; Khan, S.; Mirza, K.J.; Ram, M.; Abdin, M.Z. SCAR markers: A potential tool for authentication of herbal drugs. Fitoterapia 2010, 81, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Mishra, V.K.; Bhoi, T.K. Insect molecular markers and its utility—A review. Int. J. Agric. Environ. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopyanz, N.; Bukanov, N.O.; Westblom, T.U.; Berg, D.E. PCR-based RFLP analysis of DNA sequence diversity in the gastric pathogen Helicobacter pylori. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 6221–6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczny, A.; Ausubel, F.M. A procedure for mapping Arabidopsis mutations using co-dominant ecotype-specific PCR-based markers. Plant J. 1993, 4, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesawat, M.S.; Das Kumar, B. Molecular markers: It’s application in crop improvement. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 12, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, P.; György, Z.; Tóth, A.; Sojnóczki, A.; Fail, J. A simple molecular identification method of the Thrips tabaci (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) cryptic species complex. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2020, 110, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Portillo, P.; Carmen Thomas, M.; Martínez, E.; Marañón, C.; Valladares, B.; Patarroyo, M.E.; López, M.C. Multiprimer PCR system for differential identification of mycobacteria in clinical samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrdanz, R.L. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction method for differentiating western and northern corn rootworm larvae (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, W.B.; Tseng, M.J.; Chang, N.T.; Wu, S.Y.; Tsai, Y.S. Development of species-specific primers for agronomical thrips and multiplex assay for quarantine identification of western flower thrips. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, S.; Minoura, K. Identification of four thrips species (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Res. Bull. Plant Prot. Serv. Jpn. 2015, 51, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, W.B.; Tseng, M.J.; Chang, N.T.; Wu, S.Y.; Tsai, Y.S. Agronomically important thrips: Development of species-specific primers in multiplex PCR and microarray assay using internal transcribed spacer 1 (ITS1) sequences for identification. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2015, 105, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabahi, S.; Fekrat, L.; Zakiaghl, M. A Simple and rapid molecular method for simultaneous identification of four economically important thrips species. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2017, 19, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Jangra, S.; Mittal, A.; Dhall, H.; Jain, R.K.; Ghosh, A. A multiplex PCR assay for rapid identification of major tospovirus vectors reported in India. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhai, Z.; Huang, K.; Zhang, N.; Yuan, Y.; Shang, Y.; Luo, Y. A novel universal primer-multiplex-PCR method with sequencing gel electrophoresis analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e22900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, P.M.; Abramson, R.D.; Watson, R.; Gelfand, D.H. Detection of specific polymerase chain reaction product by utilizing the 5′ → 3′ exonuclease activity of Thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 7276–7280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, R.; Dollinger, G.; Sean Walsh, P.; Griffith, R. Simultaneous amplification and detection of specific DNA sequences. Nature Biotechnol. 1992, 10, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralik, P.; Ricchi, M. A basic guide to real time PCR in microbial diagnostics: Definitions, parameters, and everything. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kox, L.F.F.; van den Beld, H.E.; Zijlstra, C.; Vierbergen, G. Real-time PCR assay for the identification of Thrips palmi. EPPO Bull. 2005, 35, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.S.; Lee, S.E.; Yeh, Y.; Shen, G.S.; Mei, E.; Chang, C.M. Taqman real-time quantitative PCR for identification of western flower thrip (Frankliniella occidentalis) for plant quarantine. Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybylska, A.; Fiedler, Ż.; Frąckowiak, P.; Obrępalska-Stęplowska, A. Real-time PCR assay for distinguishing Frankliniella occidentalis and Thrips palmi. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2018, 108, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kennedy, G.G.; Reay-Jones, F.P.F.; Reisig, D.D.; Toews, M.D.; Roberts, P.M.; Herbert, D.A.; Taylor, S.; Jacobson, A.L.; Greene, J.K. Molecular identification of thrips species infesting cotton in the southeastern United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Osborn, A.M. Advantages and limitations of quantitative PCR (Q-PCR)-based approaches in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 6–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomi, T.; Okayama, H.; Masubuchi, H.; Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Amino, N.; Hase, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.; Levy, J.; Pierson, E.; Gross, D.C. Development of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification procedure as a sensitive and rapid method for detection of “Candidatus liberibacter solanacearum” in potatoes and psyllids. Phytopathology 2012, 102, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faggion, S.A.; Salvador, A.R.; Jacobino, K.L.; Bortolotto, L.F.B.; Lopes, M.B.; Silva, M.; Santos, E.V.; Fachin, A.L.; França, S.C.; Marins, M. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the detection of Ehrlichia canis DNA in blood samples from dogs. Arch. Med. Vet. 2013, 45, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekrat, L.; Aghl, M.Z.; Tahan, V. Application of the LAMP assay as a diagnostic technique for rapid identification of Thrips tabaci (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, P.R.; Sethy, K.; Mohapatra, S.; Panda, D. Loop mediated isothermal amplification: An innovative gene amplification technique for animal diseases. Vet. World 2016, 9, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoli, L.M.; Spoto, G. Isothermal amplification methods for the detection of nucleic acids in microfluidic devices. Biosensors 2013, 3, 18–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schochetman, G.; Ou, C.-Y.; Jones, W.K. Polymerase chain reaction. J. Infect. Dis. 1988, 158, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, E.; Higgins, O.; Forrest, M.S.; Boo, T.W.; Cormican, M.; Barry, T.; Piepenburg, O.; Smith, T.J. Development of a rapid recombinase polymerase amplification assay for the detection of Streptococcus pneumoniae in whole blood. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, R.K.; Stewart, G.; Boissinot, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Recombinase polymerase amplification for diagnostic applications. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Liu, H.; Ye, F.; Xiang, G.; Shan, W.; Xing, W. Rapid and visual detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex using recombinase polymerase amplification combined with lateral flow strips. Mol. Cell. Probes 2017, 36, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, H.; Hou, P.; He, C.; He, H. Rapid visual detection of Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis by recombinase polymerase amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 19, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strayer-Scherer, A.; Jones, J.B.; Paret, M.L. Recombinase polymerase amplification assay for field detection of tomato bacterial spot pathogens. Phytopathology 2019, 109, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priti; Jangra, S.; Baranwal, V.K.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Ghosh, A. A rapid field-based assay using recombinase polymerase amplification for identification of Thrips palmi, a vector of tospoviruses. J. Pest Sci. 2020, 94, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, H.Y.; Wu, H.; Wee, E.J.H.; Trau, M.; Wang, Y.; Botella, J.R. Specific and sensitive isothermal electrochemical biosensor for plant pathogen DNA detection with colloidal gold nanoparticles as probes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 38896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khater, M.; de la Escosura-Muñiz, A.; Altet, L.; Merkoçi, A. In situ plant virus nucleic acid isothermal amplification detection on gold nanoparticle-modified electrodes. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4790–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murai, T. Electrophoretic discrimination of some thrips species (Insecta: Thysanoptera). Advances in Thysanopterology. J. Pure Appl. Zool. 1993, 4, 297–306. [Google Scholar]
- Murai, T. Availability of esterase isozyme on electrophoretic discrimination of thrips species. Cour Forsch Senckenb. 1994, 178, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Reboredo, M.; Martínez De Morentin, I.; Moriyón, I.; Jordana, R. A methodology for thrips larvae identification using protein profiles obtained by SDS-PAGE. BioControl 2003, 48, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Soler, N.; Cervera, A.; Moores, G.D.; Martínez-Pardo, R.; Garcerá, M.D. Esterase isoenzymes and insecticide resistance in Frankliniella occidentalis populations from the south-east region of Spain. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meusnier, I.; Singer, G.A.C.; Landry, J.F.; Hickey, D.A.; Hebert, P.D.N.; Hajibabaei, M. A universal DNA mini-barcode for biodiversity analysis. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummings, P.J.; Ahmed, R.; Durocher, J.A.; Jessen, A.; Vardi, T.; Obom, K.M. Pyrosequencing for microbial identification and characterization. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, e50405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.H.; Huang, C.G.; Wu, W.J.; Wang, H.Y. A rapid insect species identification system using mini-barcode pyrosequencing. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szemes, M.; Bonants, P.; de Weerdt, M.; Baner, J.; Landegren, U.; Schoen, C.D. Diagnostic application of padlock probes—Multiplex detection of plant pathogens using universal microarrays. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, D.W.; Edwards, J. Applications of microarrays for crop improvement: Here, there, and everywhere. Bioscience 2010, 60, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Ding, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J. Rapid identification of Candida spp. frequently involved in invasive mycoses by using flow-through hybridization and Gene Chip (FHGC) technology. J. Microbiol. Methods 2017, 132, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.S.; Choi, H.; Kang, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.; Hwang, S.Y. Development of a DNA microarray for species identification of quarantine aphids. Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.J.; Pang, A.H.; Feng, S.Q.; Cui, B.Y.; Zhao, Z.H.; Kučerová, Z.; Stejskal, V.; Opit, G.; Aulicky, R.; Cao, Y.; et al. Molecular identification of ten species of stored-product psocids through microarray method based on ITS2 rDNA. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.F.; Wang, J.; Feng, J.N. Molecular identifcation of Frankliniella based on COI sequences by DNA barcoding chip. Biotechnol. Bull. 2009, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod, N. Automated Taxon Identification in Systematics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; ISBN 9781420008074. [Google Scholar]
- Fedor, P.; Vaňhara, J.; Havel, J.; Malenovský, I.; Spellerberg, I. Artificial intelligence in pest insect monitoring. Syst. Entomol. 2009, 34, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedor, P.; Maria Peña-Méndez, E.; Kucharczyk, H.; Vaňhara, J.; Havel, J.; Doričov, M.; Prokop, P. Artificial neural networks in online semiautomated pest discriminability: An applied case with 2 thrips species. Turk. J. Agric. For. 2014, 38, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mound, L.A.; Hoddle, M.; Hastings, A. Thysanoptera Californica—Thrips of California. An identification and information system to thrips in California; Lucidcentral.org, Identic Pty Ltd: Stafford Heights, QLD, Australia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Moritz, G. The biology of thrips is not the biology of their adults: A developmental view. In Thrips and Tospoviruses: Proceedings of the 7TH International Symposium on Thysanopetra, Reggio Calabria, Italy, 2–7 July 2001; Marullo, R., Mound, L., Eds.; ANIC: Canberra, Australlia, 2002; pp. 259–267. [Google Scholar]
- Espinoza, K.; Valera, D.L.; Torres, J.A.; López, A.; Molina-Aiz, F.D. Combination of image processing and artificial neural networks as a novel approach for the identification of Bemisia tabaci and Frankliniella occidentalis on sticky traps in greenhouse agriculture. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 127, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.; Parte, A.; Pokharkar, Y.; Pande, N. Recognition of silverleaf whitefly and western flower thrips via image processing and artificial neural network. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 4, 1773–1776. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.; Choi, J.; Qiao, M.U.; Ji, C.-W.; Kim, H.-Y.; Uhm, K.-B.; Chon, T.-S. Automatic identification of tobacco whiteflies, aphids and thrips in greenhouse using image processing techniques. In Proceedings of the 4th WSEAS International Conference on Mathematical Biology and Ecology, Acapulco, Mexico, 25–27 January 2008; pp. 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi, M.A.; Khoshtaghaza, M.H.; Minaei, S.; Jamshidi, B. Vision-based pest detection based on SVM classification method. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 137, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoen, M.P.M.; Kloth, K.J.; Wiegers, G.L.; Krips, O.E.; Noldus, L.P.J.J.; Dicke, M.; Jongsma, M.A. Automated video tracking of thrips behavior to assess host-plant resistance in multiple parallel two-choice setups. Plant Methods 2016, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visschers, I.G.S.; van Dam, N.M.; Peters, J.L. An objective high-throughput screening method for thrips damage quantitation using Ilastik and ImageJ. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2018, 166, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; Barker, S.C. The highly rearranged mitochondrial genome of the plague thrips, Thrips imaginis (insecta: Thysanoptera): Convergence of two novel gene boundaries and an extraordinary arrangement of rRNA genes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Tang, Y.; Xue, X.; Wang, M.; Liu, F.; Fan, J. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of the western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) contains triplicate putative control regions. Gene 2012, 506, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Tang, Y.; Hu, M.; Liu, F.; Zhang, D.; Fan, J. The mitochondrial genome of Frankliniella intonsa: Insights into the evolution of mitochondrial genomes at lower taxonomic levels in Thysanoptera. Genomics 2014, 104, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, A.M.; Kumar, V.; Morgan, J.K.; Jara-Cavieres, A.; Shatters, R.G.; McKenzie, C.L.; Osborne, L.S. A novel mitochondrial genome architecture in thrips (Insecta: Thysanoptera): Extreme size asymmetry among chromosomes and possible recent control region duplication. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Li, H.; Song, F.; Gu, W.; Feng, J.; Cai, W.; Shao, R. Novel insights into mitochondrial gene rearrangement in thrips (Insecta: Thysanoptera) from the grass thrips, Anaphothrips obscurus. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Tyagi, K.; Kundu, S.; Rahaman, I.; Singha, D.; Chandra, K.; Patnaik, S.; Kumar, V. The complete mitochondrial genome of Melon thrips, Thrips palmi (Thripinae): Comparative analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0199404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Song, X.; Wang, X. The complete mitochondrial genome of Odontothrips loti (Haliday, 1852) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2020, 5, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Tyagi, K.; Kundu, S.; Chakraborty, R.; Singha, D.; Chandra, K. The first complete mitochondrial genome of marigold pest thrips, Neohydatothrips samayunkur (Sericothripinae) and comparative analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; Yang, J.; Bei, Y.; Lu, Y. De novo transcriptome sequencing in Frankliniella occidentalis to identify genes involved in plant virus transmission and insecticide resistance. Genomics 2013, 101, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stafford-Banks, C.A.; Rotenberg, D.; Johnson, B.R.; Whitfield, A.E.; Ullman, D.E. Analysis of the salivary gland transcriptome of Frankliniella occidentalis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneweis, D.J.; Whitfield, A.E.; Rotenberg, D. Thrips developmental stage-specific transcriptome response to tomato spotted wilt virus during the virus infection cycle in Frankliniella occidentalis, the primary vector. Virology 2017, 500, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, I.H.; Clark, J.M.; Lee, S.H. Transcriptomic identification and characterization of genes responding to sublethal doses of three different insecticides in the western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 167, 104596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Champagne, D.E.; Culbreath, A.K.; Rotenberg, D.; Whitfield, A.E.; Srinivasan, R. Transcriptome changes associated with Tomato spotted wilt virus infection in various life stages of its thrips vector, Frankliniella fusca (Hinds). J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2156–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Champagne, D.E.; Culbreath, A.K.; Abney, M.R.; Srinivasan, R. Comparison of transcriptomes of an orthotospovirus vector and non-vector thrips species. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widana Gamage, S.M.K.; Rotenberg, D.; Schneweis, D.J.; Tsai, C.-W.; Dietzgen, R.G. Transcriptome-wide responses of adult melon thrips (Thrips palmi) associated with capsicum chlorosis virus infection. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Gupta, M.; Pandher, S.; Kaur, G.; Goel, N.; Rathore, P.; Palli, S.R. RNA sequencing, selection of reference genes and demonstration of feeding RNAi in Thrips tabaci (Lind.) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). BMC Mol. Biol. 2019, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebijith, K.B.; Asokan, R.; Ranjitha Hande, H.; Krishna Kumar, N.K. The first report of miRNAs from a thysanopteran insect, Thrips palmi Karny using high-throughput sequencing. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balan, R.K.; Ramasamy, A.; Hande, R.H.; Gawande, S.J.; Krishna Kumar, N.K. Genome-wide identification, expression profiling, and target gene analysis of microRNAs in the Onion thrips, Thrips tabaci Lindeman (Thysanoptera: Thripidae), vectors of tospoviruses (Bunyaviridae). Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 6399–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotenberg, D.; Baumann, A.A.; Ben-Mahmoud, S.; Christiaens, O.; Dermauw, W.; Ioannidis, P.; Jacobs, C.G.C.; Vargas Jentzsch, I.M.; Oliver, J.E.; Poelchau, M.F.; et al. Genome-enabled insights into the biology of thrips as crop pests. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.K.; Cao, L.J.; Song, W.; Shi, P.; Gao, Y.F.; Gong, Y.J.; Chen, J.C.; Hoffmann, A.A.; Wei, S.J. Chromosome-level assembly of the melon thrips genome yields insights into evolution of a sap-sucking lifestyle and pesticide resistance. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1110–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakao, S.; Yabu, S. Ethological, chemical discrimination between thelytokous, arrhenotokous Thrips nigropilosus UZEL, with discussion of taxonomy. Jpn. J. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1998, 42, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priesner, H. Die Thysanopteren Europas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1927. [Google Scholar]
- Milne, J.R.; Milne, M.; Walter, G.H. A key to larval thrips (Thysanoptera) from Granite Belt stonefruit trees and a first description of Pseudanaphothrips achaetus (Bagnall) larvae. Aust. J. Entomol. 1997, 36, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Iliescu, D.D.; Hines, E.L.; Leeson, M.S. Tomato plant health monitoring: An electronic nose approach. In Intelligent Systems for Machine Olfaction: Tools and Methodologies; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 231–248. [Google Scholar]
- Lampson, B.D.; Khalilian, A.; Greene, J.K.; Han, Y.J.; Degenhardt, D.C. Development of a portable electronic nose for detection of cotton damaged by Nezara viridula (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). J. Insects 2014, 2014, 297219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcanti, A.; Shirinzadeh, B.; Zhang, M.; Kretly, L.C. Nanorobot hardware architecture for medical defense. Sensors 2008, 8, 2932–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yew, Y.T.; Sofer, Z.; Mayorga-Martinez, C.C.; Pumera, M. Black phosphorus nanoparticles as a novel fluorescent sensing platform for nucleic acid detection. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.; Kim, S.; Park, J.; Kim, T.S.; Kharbash, R.; Shin, E.C.; Char, K.; Kim, Y.; Li, S. Reactive polymer targeting dsRNA as universal virus detection platform with enhanced sensitivity. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 2440–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Serial No. | Molecular Marker/Technique | Thrips Species Detected | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Mitochondrial cytochrome C oxidase subunit I (COI) | Aeolothrips distinctus, Anaphothrips obscurus, Echinothrips americanus, Franklinothrips megalops, Frankliniella occidentalis, F. schultzei, F. serrata, Haplothrips clarisetis, Heliothrips longisensibilis, H. haemorrhoidalis, H. sylvanus, Hercinothrips femoralis, Leucothrips furcatus, Mycterothrips nilgiriensis, Pathenothrips dracaenae, Podothrips erami, Scirtothrips aurantii, S. oligochaetus, S. perseae, Synaptorthrips psoraleae, Thrips alatus, T. angusticeps, T. hawaiiensis, T. palmi, T. parvispinus, T. tabaci, T. vulgatissimus, T. picipes | [13,14,15,16,17,32,44,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,66,72,73,74,75,76,78,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,98,99,106,107,108,109,110,111] |
| 2. | COII | T. palmi | [82] |
| 3. | COIII | T. palmi | [82] |
| 4. | Internal transcribed spacers (ITS) | Ceratothripoides claratris, Dendrothrips eremicola, F. cephalica, F. fusca, F. intonsa, F. occidentalis, F. schultzei, F. tritici, H. cahirensis, Hydatothrips kassimanus, Kakothrips pisivorus, Megalurothrips distalis, S. aurantii, S. dorsalis, T. palmi, T. tabaci | [46,72,97,110,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123] |
| 5. | Other molecular markers (H3, EF 1-α, and α-tubulin) | A. karnyi, A. stylifer, A. rufus, Frankliniella spp., Scirtothrips spp., T. flavus, T. nigropilosus, T. palmi, T. tabaci, several species in the Melanthripidae, Merothripidae, Phaleothripidae | [45,82,129,130,144] |
| 6. | Single sequence repeat (SSR) or microsatellite markers | D. minowai, F. occidentalis, S. perseae, T. hawaiiensis, T. palmi | [103,105,106,135,137,138,139,140,141,142,143] |
| 7. | Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) markers | A. obscurus, E. americanus, F. bispinosa, F. intonsa, F. occidentalis, F. pallida, F. schultzei, F. tenuicornis, F. tenuicornis, H. spinosus, H. aino, H. haemorrhoidalis, H. femoralis, H. femoralis, Limothrips denticornis, L. cerealium, Moundothrips apterygus, Pezothrips kellyanus, Pathenothrips dracaenae, Pseudanaphothrips achaetus, Rhipiphorothrips cruentatus, S. aceri, S. astrictus, S. aurantii, S. bounites, S. citri, S. derpanofortis, S. dorsalis, S. frondis, S. inermis, S. kenyensis, S. oligochaetus, S. pan, S. perseae, spp., S. rubrocinctus, S. aotearoana, S. linguis, T. angusticeps, T. coloratus, T. flavus, T. hawaiiensis, T. nigropilosus, T. palmi, T. physapusm, T. setotus, T. tabaci, T. picipes | [32,35,97,144,145,146,147,148] |
| 8. | Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers | A. intermedius, F. intonsa, F. occidentalis, F. schultzei, Gynaikothrips uzeli, K. robustus, Odontothrips confusus,S. dorsalis, T. dilatatus, T. palmi, and T. tabaci | [31,151,152,153,154,155,156,157] |
| 9. | Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) markers | F. occidentalis, T. tabaci | [109,162,163] |
| 10. | Sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) markers | F. occidentalis | [36] |
| 11. | Cleaved amplified polymorphic sequences (CAPS) markers | T. tabaci | [170] |
| 12. | Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | F. intonsa, F. occidentalis, F. schultzei, S. dorsalis, T. hawaiiensis, T. palmi, T. tabaci | [90,173,174,175,176,177] |
| 13. | Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) | F. fusca, F. occidentalis, F. schultzei, F. tritici, Neohydatothrips variabilis, T. palmi, T. tabaci | [34,56,182,183,184,185] |
| 14. | Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) | F. occidentalis, T. palmi | [37,190] |
| 15. | Recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) | T. palmi | [199] |
| 16. | Protein-based diagnostics | F. occidentalis, H. haemorrhoidalis, L. cerealium, Taeniothrips inconsequens,T. palmi, T. tabaci | [29,33,41,204,205] |
| 17. | Mini barcoding | T. palmi, T. tabaci | [208] |
| 18. | Microarray/ DNA chip | Dichromothrips smithi, Microcephalothrips abdominalis, F. williamsi, F. cephalica, F. occidentalis, F. intonsa, T. palmi, T. florum, T. hawaiiensis, T. alliorum, T. tabaci, T. fuscipennis, M. usitatus, Stenchaetothrips biformis, S. dorsalis, | [175,214] |
| 19. | Artificial Neural Networking (ANN) | A. albicinctus, A. astutus, A. ericae, A. fasciatus, A. intermedius, A. versicolor, A. vittatus, Chirothrips aculeatus, C. ambulans, C. hamatus, C. manicatus, C. pallidicornis, D. degeeri, D. ornatus, D. saltatrix, F. occidentalis, L. cerealium, L. consimilis, L. denticornis, T. fuscipennis, T. sambuci | [43,216,217,218,220,221] |
| 20. | High-throughput imaging-based diagnostics | F. occidentalis | [220,221,222,223,224,225] |
| 21. | High throughput sequencing (HTS) (mitogenome andtranscriptomewhole genome) | A. obscurus, F. occidentalis, F. fusca, F. intonsa, F. tritici, N. samayunkur, O. loti, S. dorsalis, T. imaginis, T. palmi, T. tabaci | [226,227,228,229,230,231,232,233,234,235,236,237,238,239,240,241,242,243,244,245] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghosh, A.; Jangra, S.; Dietzgen, R.G.; Yeh, W.-B. Frontiers Approaches to the Diagnosis of Thrips (Thysanoptera): How Effective Are the Molecular and Electronic Detection Platforms? Insects 2021, 12, 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100920
Ghosh A, Jangra S, Dietzgen RG, Yeh W-B. Frontiers Approaches to the Diagnosis of Thrips (Thysanoptera): How Effective Are the Molecular and Electronic Detection Platforms? Insects. 2021; 12(10):920. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100920
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhosh, Amalendu, Sumit Jangra, Ralf G. Dietzgen, and Wen-Bin Yeh. 2021. "Frontiers Approaches to the Diagnosis of Thrips (Thysanoptera): How Effective Are the Molecular and Electronic Detection Platforms?" Insects 12, no. 10: 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100920
APA StyleGhosh, A., Jangra, S., Dietzgen, R. G., & Yeh, W.-B. (2021). Frontiers Approaches to the Diagnosis of Thrips (Thysanoptera): How Effective Are the Molecular and Electronic Detection Platforms? Insects, 12(10), 920. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100920









