Knockdown of Vacuolar ATPase Subunit G Gene Affects Larval Survival and Impaired Pupation and Adult Emergence in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect
2.2. Molecular Cloning
2.3. Preparation of DsRNAs
2.4. Dietary Introduction of DsRNA
2.5. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.6. Hematoxylin-Eosin (HE) Staining
2.7. TUNEL Assay
2.8. EdU Labeling
2.9. Determination of Nutrients
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of HvvATPaseG
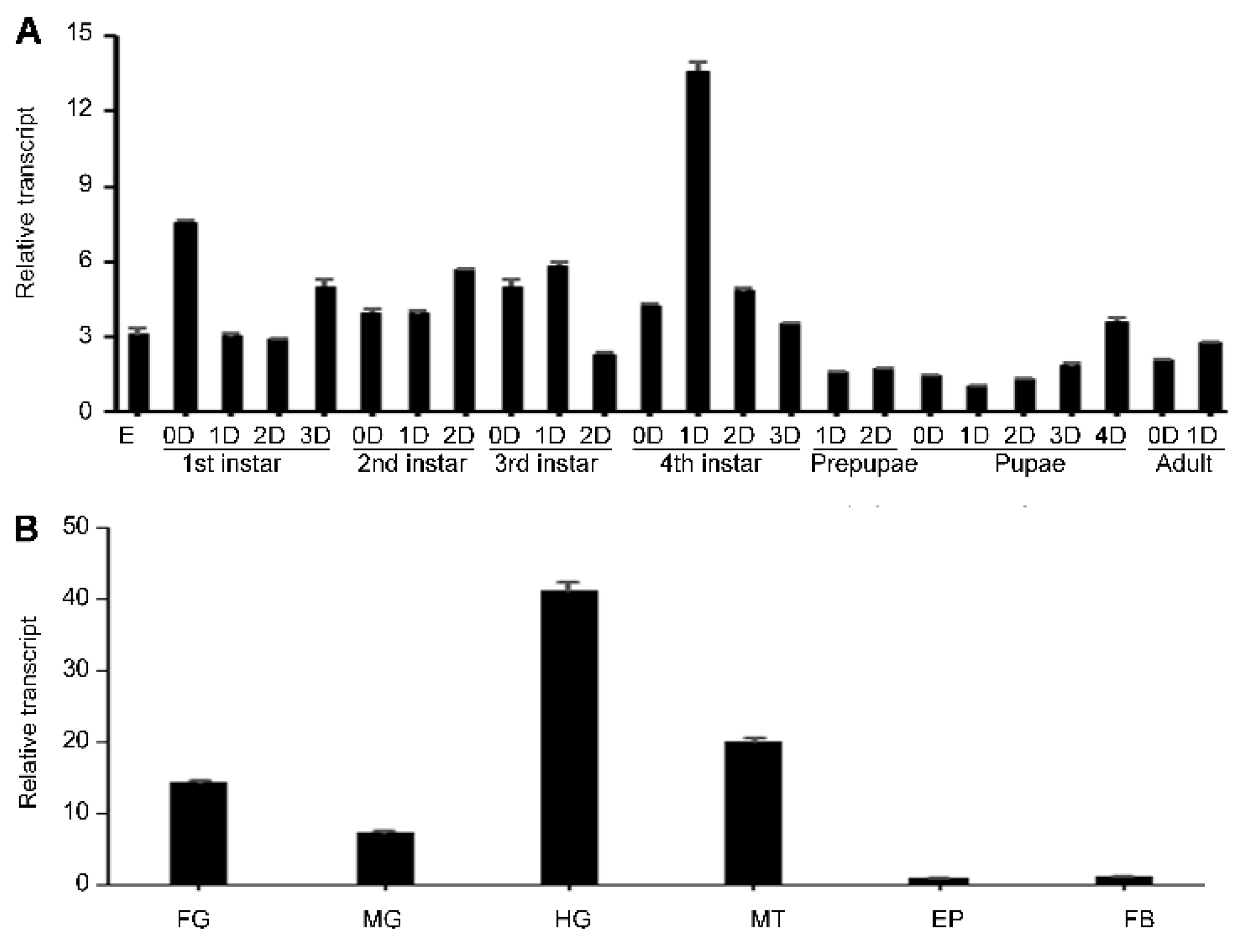
3.2. Expression Profiles of HvvATPaseG
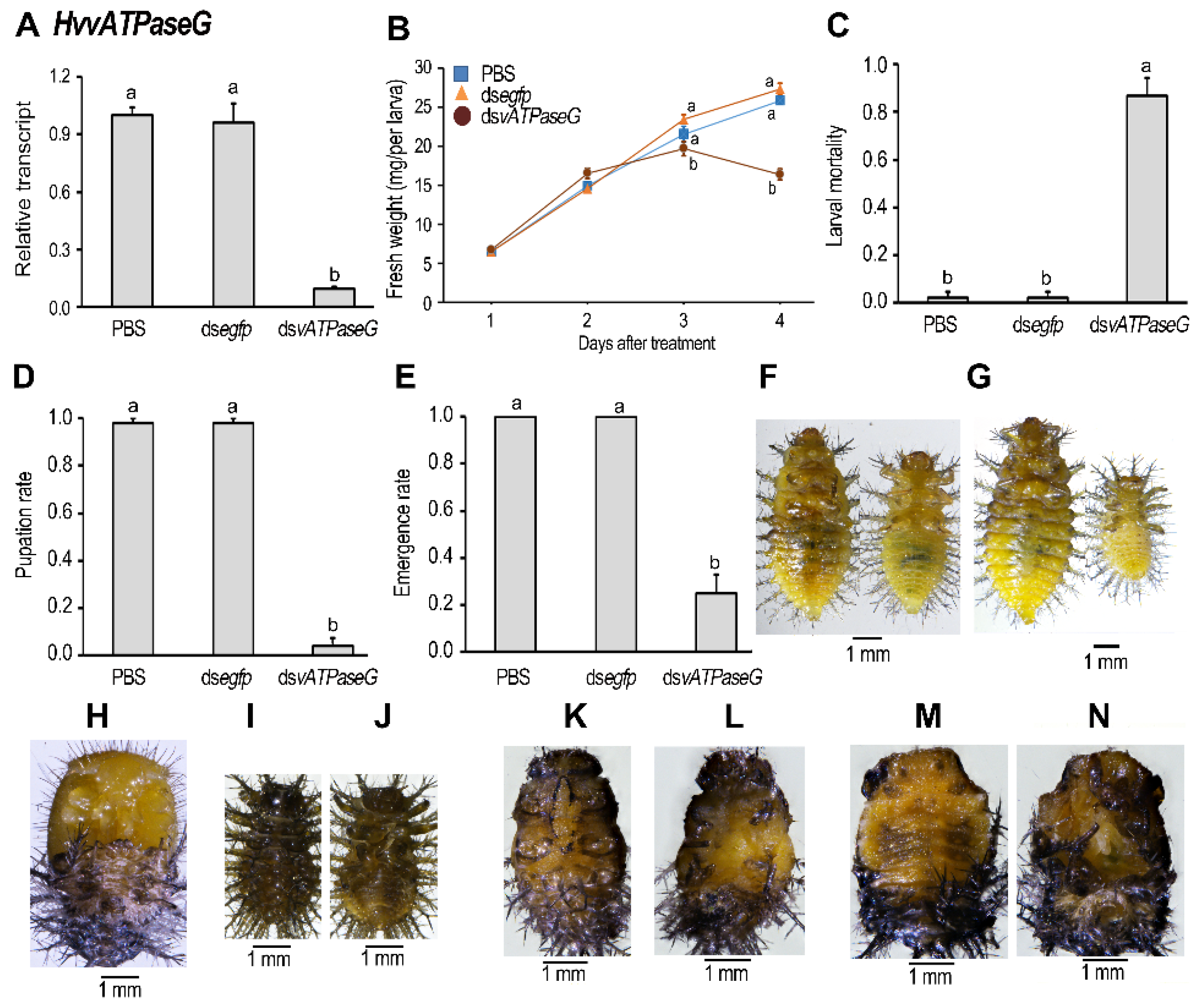
3.3. Ingestion of DsvATPaseG Affects Larval Performance
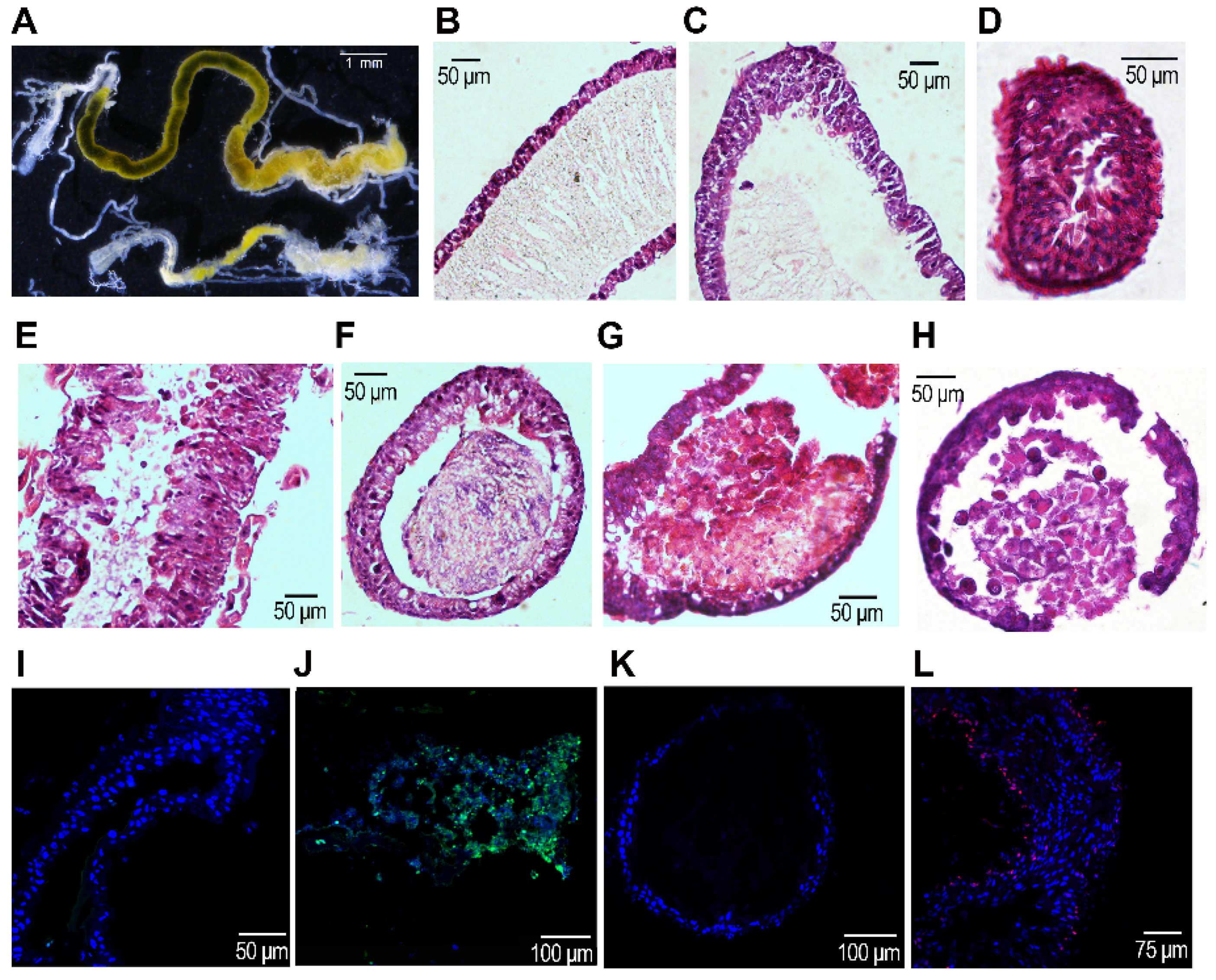
3.4. The Integrity of the Midgut after RNAi
3.5. RNAi of HvvATPaseG on Malpighian Tubules
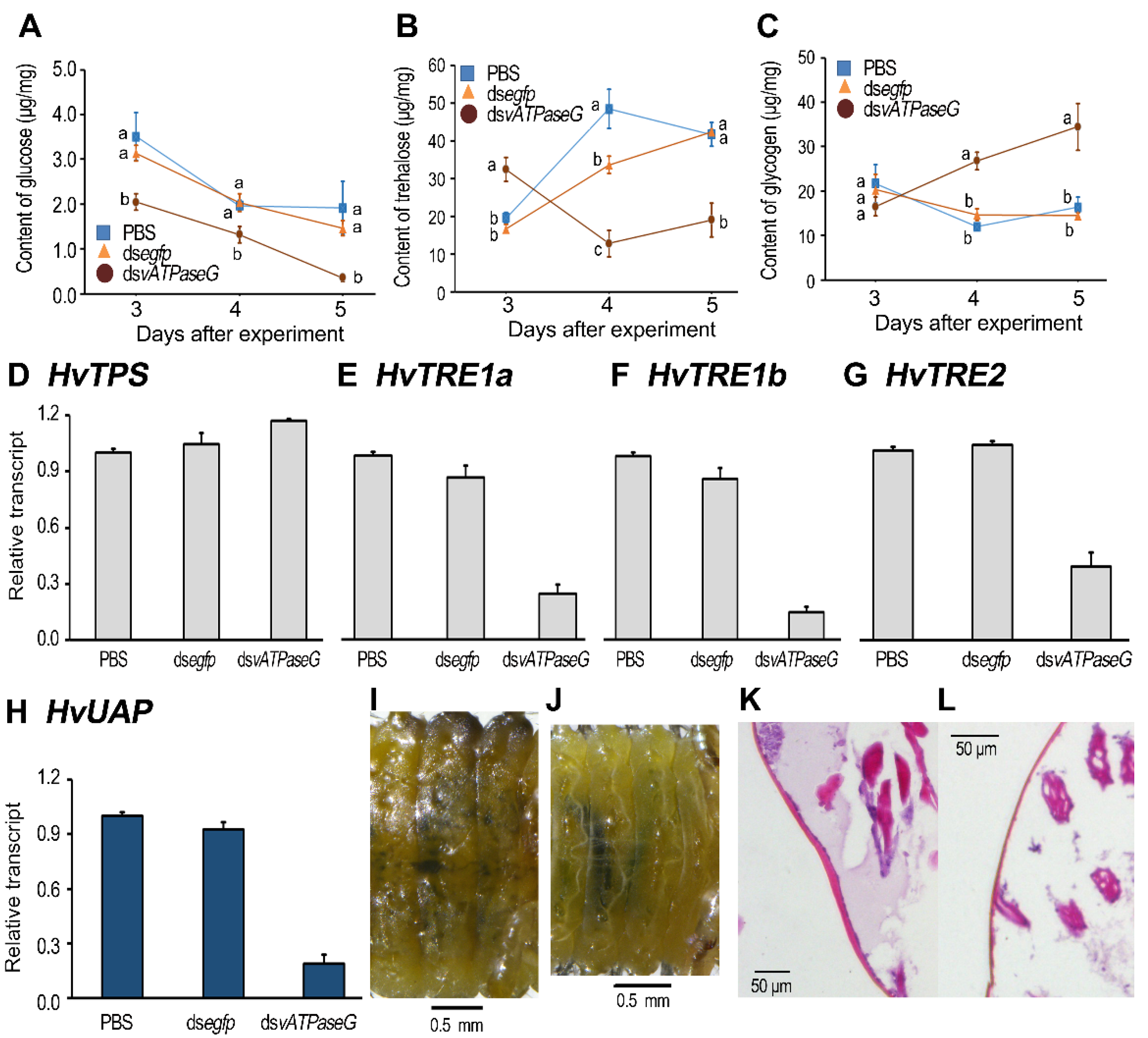
3.6. Silencing HvvATPaseG on the Sugar Contents
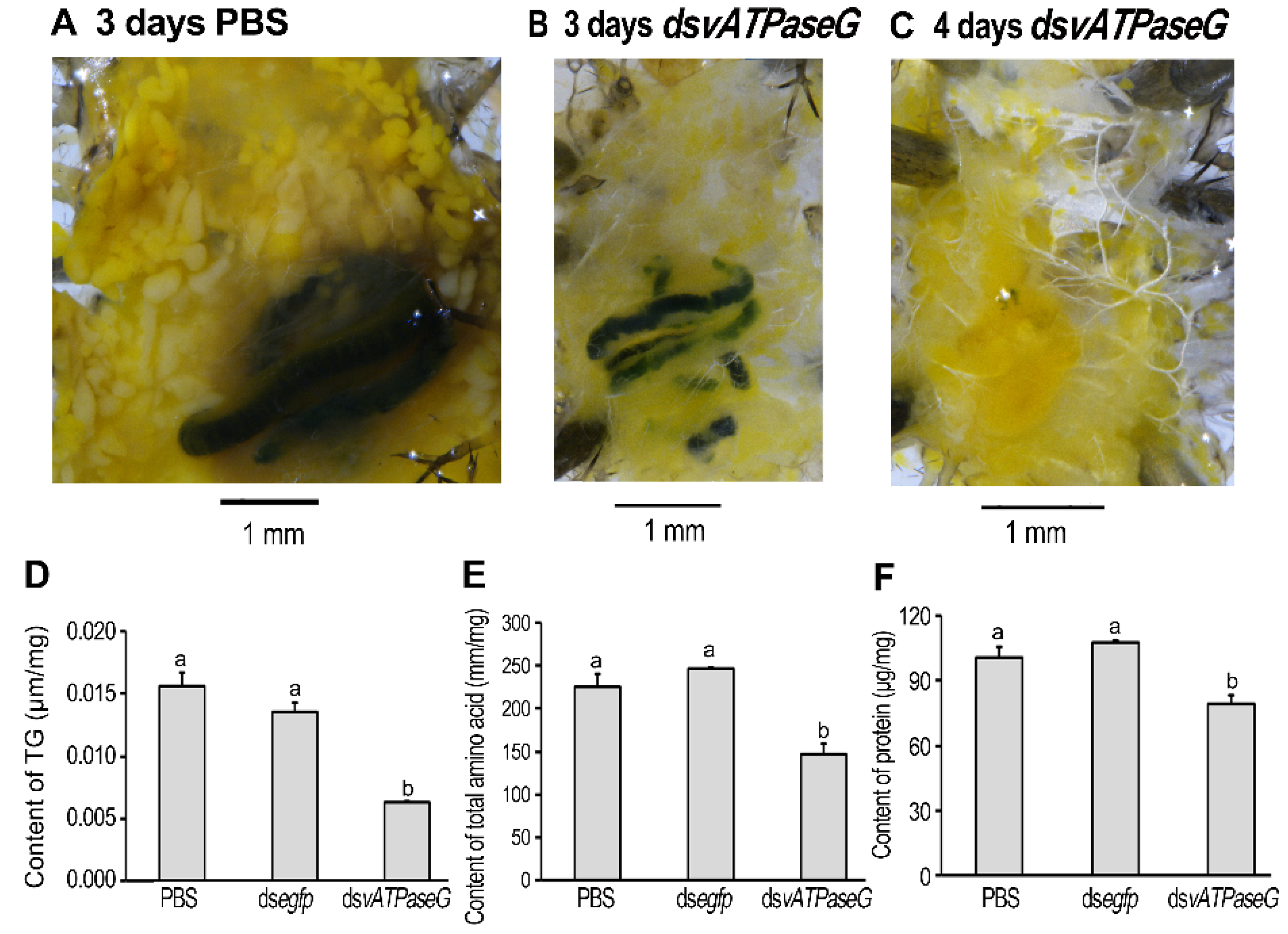
3.7. Shortage of Lipid and Protein in the HvvATPaseG RNAi Larvae
4. Discussion
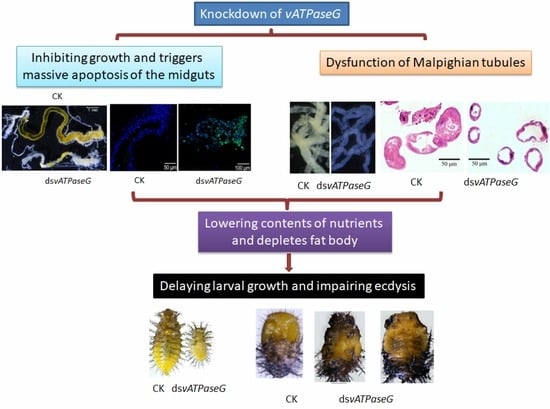
4.1. Knockdown of HvvATPaseG Causes Developmental Arrest
4.2. HvvATPaseG Is Required for Midgut Integrity
4.3. HvvATPaseG Is Essential for Availability of Nutrients
4.4. HvvATPaseG Is Involved in the Formation of Urine in Malpighian Tubules
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbas, Y.M.; Wu, D.; Bueler, S.A.; Robinson, C.V.; Rubinstein, J.L. Structure of V-ATPase from the mammalian brain. Science 2020, 367, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Saito, M.; Tsukahara, A.; Shiokawa, S.; Ueno, K.; Shimamura, H.; Nagano, M.; Toshima, J.Y.; Toshima, J. Functional complementation reveals that 9 of the 13 human V-ATPase subunits can functionally substitute for their yeast orthologs. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 8273–8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, W.R.; Boudko, D.Y.; Rheault, M.; Okech, B.A. NHEVNAT: An H+ V-ATPase electrically coupled to a Na+:nutrient amino acid transporter (NAT) forms an Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE). J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawamura, N.; Sun-Wada, G.-H.; Wada, Y. Loss of G2 subunit of vacuolar-type proton transporting ATPase leads to G1 subunit upregulation in the brain. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wieczorek, H.; Brown, D.; Grinstein, S.; Ehrenfeld, J.; Harvey, W.R. Animal plasma membrane energization by proton-motive V-ATPases. BioEssays 1999, 21, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M. The V-ATPase in insect epithelia. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 3201–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forgac, M. Structure and function of vacuolar class of ATP-driven proton pumps. Physiol. Rev. 1989, 69, 765–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W. Physiology of V-ATPases. J. Exp. Biol. 1992, 172, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Benlekbir, S.; Rubinstein, J. Electron cryomicroscopy observation of rotational states in a eukaryotic V-ATPase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 521, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, C.; Stransky, L.; Cotter, K.; Forgac, M. Regulation of V-ATPase activity. Front. Biosci. 2017, 22, 609–622. [Google Scholar]
- Sun-Wada, G.H.; Murata, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Kanazawa, H.; Wada, Y.; Futai, M. Acidic endomembrane organelles are required for mouse postimplantation development. Dev. Biol. 2000, 228, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oka, T.; Murata, Y.; Namba, M.; Yoshimizu, T.; Toyomura, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Sun-Wada, G.-H.; Hamasaki, N.; Wada, Y.; Futai, M. a4, a Unique Kidney-specific Isoform of Mouse Vacuolar H+-ATPase Subunit a. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 40050–40054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toyomura, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Oka, G.H.; Sun-Wada, Y.; Wada, M.; Futai, M. From lysosomes to the plasma membrane: Localization of vacuolar-type H+-ATPase with the a3 isoform during osteoclast differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 22023–22030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wieczorek, H.; Beyenbach, K.W.; Huss, M.; Vitavska, O. Vacuolar-type proton pumps in insect epithelia. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 1611–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muench, S.; Scheres, S.; Huss, M.; Phillips, C.; Vitavska, O.; Wieczorek, H.; Trinick, J.; Harrison, M.A. Subunit Positioning and Stator Filament Stiffness in Regulation and Power Transmission in the V1 Motor of the Manduca sexta V-ATPase. J. Mol. Biol. 2014, 426, 286–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dow, J.A.T. pH gradients in lepidopteran midgut. J. Exp. Biol. 1992, 172, 355–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, M.; Harvey, W.R.; Wieczorek, H. Stoichiometry of K+/H+antiport helps to explain extracellular pH 11 in a model epithelium. FEBS Lett. 1995, 361, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Silva, N.M.; Donini, A.; O’Donnell, M.J. The roles of V-type H + -ATPase and Na + /K + -ATPase in energizing K + and H + transport in larval Drosophila gut epithelia. J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 98, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W.R. Voltage coupling of primary H+ V-ATPases to secondary Na+- or K+-dependent transporters. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Q.; Meng, B.; Xu, H.; Mao, Z. The emerging roles of vacuolar-type ATPase-dependent Lysosomal acidification in neurodegenerative diseases. Transl. Neurodegener. 2020, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzendorfer, H.; Reineke, S.; Zhao, X.-F.; Jacobmeier, B.; Harvey, W.R.; Wieczorek, H. The multigene family of the tobacco hornworm V-ATPase: Novel subunits a, C, D, H, and putative isoforms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2000, 1467, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitagawa, N.; Mazon, H.; Heck, A.; Wilkens, S. Stoichiometry of the peripheral stalk subunits E and G of yeast V1-ATPase determined by mass spectrometry. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 3329–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mazhab-Jafari, M.T.; Rohou, A.; Schmidt, C.; Bueler, S.A.; Benlekbir, S.; Robinson, C.; Rubinstein, J.L. Atomic model for the membrane-embedded VO motor of a eukaryotic V-ATPase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 539, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, S.-H.; Stam, N.J.; Hryc, C.F.; Couoh-Cardel, S.; Pintilie, G.; Chiu, W.; Wilkens, S. The 3.5-Å CryoEM structure of nanodisc-reconstituted yeast vacuolar ATPase V0 proton channel. Mol. Cell. 2018, 69, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muench, S.; Huss, M.; Song, C.F.; Phillips, C.; Wieczorek, H.; Trinick, J.; Harrison, M.A. Cryo-electron microscopy of the vacuolar ATPase motor reveals its mechanical and regulatory complexity. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 386, 989–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, Y.; Sun-Wada, G.-H.; Yoshimizu, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Wada, Y.; Futai, M. Differential localization of the vacuolar H+ pump with G subunit isoforms (G1 and G2) in mouse neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 36296–36303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun-Wada, G.-H.; Yoshimizu, T.; Imai-Senga, Y.; Wada, Y.; Futai, M. Diversity of mouse proton-translocating ATPase: Presence of multiple isoforms of the C, D and G subunits. Gene 2003, 302, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake-Palmer, K.G.; Su, Y.; Smith, A.N.; Karet, F.E. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel form of the human vacuolar H+-ATPase e-subunit: An essential proton pump component. Gene 2007, 393, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toei, M.; Saum, R.; Forgac, M. Regulation and isoform function of the V-ATPases. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4715–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lepier, A.; Gräf, R.; Azuma, M.; Merzendorfer, H.; Harvey, W.R.; Wieczorek, H. The peripheral complex of the tobacco hornworm V-ATPase contains a novel 13-kDa subunit G. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8502–8508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gräf, R.; Harvey, W.R.; Wieczorek, H. Purification and properties of a cytosolic V1-ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20908–20913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.S. Reconstitution of ATPase activity from individual subunits of the clathrin-coated vesicle proton pump. The requirement and effect of three small subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 30980–30985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, A.K.; Du, J.; Davies, S.A.; Dow, J.A. Genome-wide survey of V-ATPase genes in Drosophila reveals a conserved renal phenotype for lethal alleles. Physiol. Genom. 2005, 22, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Zhou, Q.; Ogmundsdottir, M.H.; Möller, K.; Siddaway, R.; Larue, L.; Hsing, M.; Kong, S.W.; Goding, C.R.; Palsson, A.; et al. Mitf is a master regulator of the v-ATPase, forming a control module for cellular homeostasis with v-ATPase and TORC1. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2938–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.-L.; Wang, F.; Guo, J.; Deng, X.-Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Lin, L.-B. Characterization of ladybird Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata transcriptomes across various life stages. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Mu, L.-L.; Jin, L.; Anjum, A.A.; Li, G.-Q. Evaluation of three vacuolar ATPase genes as potential RNAi target in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. J. Asia-Pacific Èntomol. 2021, 24, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ze, L.-J.; Xu, P.; Kang, W.-N.; Wu, J.-J.; Jin, L.; Anjum, A.A.; Li, G.-Q. Disruption of ommochrome biosynthesis affects eye coloration, phototaxis and climbing in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Amino Acids 2021, 53, 1091–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.-H.; Mu, L.-L.; Jin, L.; Anjum, A.A.; Li, G.-Q. RNAi for chitin synthase 1 rather than 2 causes growth delay and molting defect in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 178, 104934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Ze, L.-J.; Kang, W.-N.; Wu, J.-J.; Jin, L.; Ali, A.A.; Li, G.-Q. Functional divergence of white genes in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata revealed by RNA interference. Insect Mol. Biol. 2020, 29, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Mu, L.; Kang, W.; Ze, L.; Shen, C.; Jin, L.; Anjum, A.A.; Li, G. RNA interference targeting ecdysone receptor blocks the larval–pupal transition in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lü, J.; Chen, S.; Guo, M.; Ye, C.; Qiu, B.; Wu, J.; Yang, C.; Pan, H. Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of the ladybird beetle Henosepilachna vigintioctomaculata. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye-binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-J.; Xue, J.; Lu, B.; Zhang, X.-C.; Zhuo, J.-C.; He, S.-F.; Ma, X.-F.; Jiang, Y.-Q.; Fan, H.-W.; Xu, J.-Y.; et al. Two insulin receptors determine alternative wing morphs in planthoppers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 519, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gausz, J.; Bencze, G.; Gyurkovics, H.; Ashburner, M.; Ish-Horowicz, D.; Holden, J.J. Genetic characterization of the 87C region of the third chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 1979, 93, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-F.; Xu, Q.-Y.; Sun, Q.-K.; Meng, Q.-W.; Mu, L.-L.; Guo, W.-C.; Li, G.-Q. Physiological roles of trehalose in Leptinotarsa larvae revealed by RNA interference of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalase genes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 77, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-F.; Fu, J.; Mu, L.-L.; Guo, W.-C.; Li, G.-Q. Two Leptinotarsa uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine pyrophosphorylase genes LdUAP1 and LdUAP2 are specialized for synthesis of chitin in larval epidermal cuticle and midgut peritrophic matrix. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Yue, W.; Wang, J.; Han, H.; Wang, C. V-ATPase subunit B plays essential roles in the molting process of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Biol. Open 2020, 9, bio048926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.-F.; Mu, L.-L.; Chen, X.; Guo, W.-C.; Li, G.-Q. RNA interference of chitin synthase genes inhibits chitin biosynthesis and affects larval performance in Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say). Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 12, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petek, M.; Turnšek, N.; Gašparič, M.B.; Novak, M.P.; Gruden, K.; Slapar, N.; Popovič, T.; Štrukelj, B.; Jongsma, M.A. A complex of genes involved in adaptation of Leptinotarsa decemlineata larvae to induced potato defense. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2012, 79, 153–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruden, K.; Kuipers, A.G.; Gunčar, G.; Slapar, N.; Štrukelj, B.; Jongsma, M. Molecular basis of Colorado potato beetle adaptation to potato plant defence at the level of digestive cysteine proteinases. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, F.; Nguyen-Quoc, B.; Cloutier, C.; Michaud, D. Protein hydrolysis by Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata, digestive proteases: The catalytic role of cathepsin D. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1999, 42, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, F.; Girard, C.; Cloutier, C.; Michaud, D. A hybrid, broad-spectrum inhibitor of Colorado potato beetle aspartate and cysteine digestive proteinases. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2005, 60, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabio, A.; Gieselmann, V. Lysosomal disorders: From storage to cellular damage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Bioenerg. 2009, 1793, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dow, J.A.T.; Davies, S.A.; Guo, Y.; Graham, S.; Finbow, M.E.; Kaiser, K. Molecular genetic analysis of V-ATPase function in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 202, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karet, F.; Finberg, K.E.; Nelson, R.D.; Nayir, A.; Mocan, H.; Sanjad, S.A.; Rodriguez-Soriano, J.; Santos, F.; Cremers, C.W.; Di Pietro, A.; et al. Mutations in the gene encoding B1 subunit of H+-ATPase cause renal tubular acidosis with sensorineural deafness. Nat. Genet. 1999, 21, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.N.; Skaug, J.; Choate, K.A.; Nayir, A.; Bakkaloglu, A.; Ozen, S.; Hulton, S.A.; Sanjad, S.A.; Al-Sabban, E.A.; Lifton, R.P.; et al. Mutations in ATP6N1B, encoding a new kidney vacuolar proton pump 116-kD subunit, cause recessive distal renal tubular acidosis with preserved hearing. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dow, J.A.T. Insights into the Malpighian tubule from functional genomics. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dow, J.A.T. The multifunctional Drosophila melanogaster V-ATPase is encoded by a multigene family. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1999, 31, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dow, J.A.T.; Davies, S.A. Integrative physiology and functional genomics of epithelial function in a genetic model organism. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 687–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zeng, J.; Kang, W.-N.; Jin, L.; Anjum, A.A.; Li, G.-Q. Knockdown of Vacuolar ATPase Subunit G Gene Affects Larval Survival and Impaired Pupation and Adult Emergence in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Insects 2021, 12, 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100935
Zeng J, Kang W-N, Jin L, Anjum AA, Li G-Q. Knockdown of Vacuolar ATPase Subunit G Gene Affects Larval Survival and Impaired Pupation and Adult Emergence in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Insects. 2021; 12(10):935. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100935
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Jie, Wei-Nan Kang, Lin Jin, Ahmad Ali Anjum, and Guo-Qing Li. 2021. "Knockdown of Vacuolar ATPase Subunit G Gene Affects Larval Survival and Impaired Pupation and Adult Emergence in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata" Insects 12, no. 10: 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100935
APA StyleZeng, J., Kang, W.-N., Jin, L., Anjum, A. A., & Li, G.-Q. (2021). Knockdown of Vacuolar ATPase Subunit G Gene Affects Larval Survival and Impaired Pupation and Adult Emergence in Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata. Insects, 12(10), 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12100935