Impact of Metarhizium robertsii on Adults of the Parasitoid Diachasmimorpha longicaudata and Parasitized Anastrepha ludens Larvae
Abstract
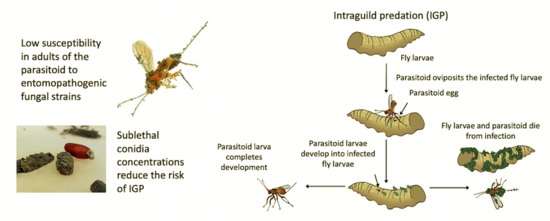
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Test Insects
2.2. Source of Fungi and Preparation of Conidial Suspensions
2.3. Pathogenicity Tests of M. robertsii and M. anisopliae on Adults of D. longicaudata
2.4. IGP on D. longicaudata-parasitized A. ludens Larvae due to Infection by M. robertsii or M. anisopliae
2.5. Medium and Low Lethal Concentration of M. robertsii V3-160
2.6. Effect of Medium and Low Concentrations of M. robertsii on the Longevity of D. longicaudata Reared from Parasitoids Treated as Immatures inside Host Larvae
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Pathogenicity of Fungal Strains on D. longicaudata Adults
3.2. Evaluation of IGP on D. longicaudata-parasitized A. ludens Larvae by M. robertsii and M. anisopliae
3.3. Mean Lethal Concentrations LC50
3.4. Effect of Sub-Lethal Doses (Medium and Low) on D. longicaudata Emergence and Longevity
4. Discussion
Parasitism Affects Fungal Life History
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Willer, H.; Lernoud, J. Organic agriculture worldwide: Current statistics. In The World of Organic Agriculture: Statistics and Emerging Trends 2019; Willer, H., Lernoud, J., Eds.; Research Institute of Organic Agriculture FiBL and IFOAM Organics International: Rheinbreitbach, Germany, 2019; pp. 35–128. ISBN 9781849775991. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, J.; Campos, S.; Flores, S.; Montoya, P. Uso de hongos entomopatógenos en el manejo de moscas de la fruta: Eficacia de adultos estériles vectores y autodiseminadores de conidios. In Moscas de la Fruta: Fundamentos y Procedimientos para su Manejo; Montoya, P., Toledo, J., Hernández, E., Eds.; S y G Editores: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2020; pp. 563–571. ISBN 9786077552338. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez y Ramírez, F.; Hernández-Livera, R.A.; Bello-Rivera, A. El programa nacional de moscas de la fruta en Mexico. In Moscas de la Fruta: Fundamentos y Procedimientos para su Manejo; Montoya, P., Toledo, J., Hernández, E., Eds.; S y G Editores: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2020; pp. 3–20. ISBN 9786077552338. [Google Scholar]
- Montoya, P.; Cancino, J.; Zenil, M.; Santiago, G.; Gutierrez, J.M. The augmentative biological control component in the Mexican National Campaign against Anastrepha spp. Fruit Flies. In Area-Wide Control of Insect Pests: From Research to Field Implementation; Vreysen, M.J.B., Robinson, A.S., Hendrichs, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 661–670. ISBN 9781402060595. [Google Scholar]
- Arredondo-Bernal, H.C.; Rodríguez-Vélez, B. Biological Control in Mexico. In Biological Control in Latin America and the Caribbean: Its Rich History and Bright Future; van Lenteren, J.C., Bueno, V.H.P., Luna, M.G., Colmenarez, Y., Eds.; CABI International: Wallinford, UK, 2019; pp. 308–335. ISBN 9781789242447. [Google Scholar]
- Birke, A.; Guillén, L.; Midgarden, D.; Aluja, M. Fruit flies, Anastrepha ludens (Loew), A. obliqua (Macquart) and A. grandis (Macquart) (Diptera: Tephritidae): Three pestiferous tropical fruit flies that could potentially expand their range to temperate areas. In Potential Invasive Pests; Peña, J.E., Ed.; CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 2013; pp. 192–213. ISBN 978-1-84593-829-1. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J.M. El programa moscas de la fruta en Mexico. In Moscas de la Fruta: Fundamentos y Procedimientos para su Manejo; Montoya, P., Toledo, J., Hernández, E., Eds.; S y G Editores: Ciudad de Mexico, Mexico, 2010; pp. 3–10. ISBN 978-607-7552-06-2. [Google Scholar]
- Montoya, P.; Liedo, P.; Benrey, B.; Cancino, J.; Barrera, J.F.; Sivinski, J.; Aluja, M. Biological control of Anastrepha spp. (Diptera: Tephritidae) in mango orchards through augmentative releases of D. longicaudata (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Biol. Control 2000, 18, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivinski, J.M. The past and potential of biological control of fruit flies. In Fruit Flies Pests. A World Assessment of their Biology and Management; McPheron, B.A., Steck, G.J., Eds.; St. Lucie Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1996; pp. 365–375. ISBN 978-1-57444-014-0. [Google Scholar]
- Godfray, H.C.J. Parasitoids: Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology; Godfray, H.C.J., Ed.; Princeton University Press: Princenton, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 260–306. ISBN 0-691-03325-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ovruski, S.; Aluja, M.; Sivinski, J.; Wharton, R. Hymenopteran parasitoids on fruit-infesting Tephritidae (Diptera) in Latin America and the southern United States: Diversity, distribution, taxonomic status and their use in fruit fly biological control. Integr. Pest Manag. Rev. 2000, 5, 81–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivinski, J.; Vulinec, K.; Aluja, M. Ovipositor length in a guild of parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) attacking Anastrepha spp. fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) in Southern Mexico. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2001, 94, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, P.; Cancino, J. Control biológico por aumento en moscas de la fruta (Diptera: Tephritidae). Fol. Entomol. Mex. 2004, 43, 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, J.; Campos, S.E.; Flores, S.; Liedo, P.; Barrera, J.F.; Villaseñor, A.; Montoya, P. Horizontal transmission of B. bassiana in A. ludens (Diptera: Tephritidae) under laboratory and field cage conditions. J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lezama-Gutiérrez, R.; Trujillo-de la Luz, A.; Molina-Ochoa, J.; Rebolledo-Dominguez, O.; Pescador, A.R.; López-Edwards, M.; Aluja, M. Virulence of M. anisopliae (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) on A. ludens (Diptera: Tephritidae): Laboratory and field trials. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 1080–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Destéfano, R.H.R.; Bechara, I.J.; Messias, C.L.; Piedrabuena, A.E. Effectiveness of M. anisopliae against immature stages of Anastrepha fraterculus fruitfly (Diptera: Tephritidae). Braz. J. Microbiol. 2005, 36, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, W.M.; Ibarra, J.E.; Oropeza, A.; Hernández, M.A.; Toledo-Hernández, R.A.; Toledo, J. Infection of A. ludens (Diptera: Tephritidae) adults during emergence from soil treated with B. bassiana under various texture, humidity, and temperature conditions. Fla. Entomol. 2017, 100, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toledo-Hernández, R.A.; Toledo, J.; Sánchez, D. Effect of Metarhizium anisopliae (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) on food consumption and mortality in the Mexican fruit fly, A. ludens (Diptera: Tephritidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2018, 38, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Llopis, V.; Ayala, I.; Sanchis, J.; Primo, J.; Moya, P. Field efficacy of a Metarhizium anisopliae-based attractant-contaminant device to control Ceratitis capitata (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, S.; Montoya, P.; Toledo, J.; Enkerlin, W.; Liedo, P. Estimation of populations and sterility induction in A. ludens (Diptera: Tephritidae) fruit flies. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 1502–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, C.S.; Finke, D.L.; Snyder, W.E. Are the conservation of natural enemy biodiversity and biological control compatible goals? Biol. Control 2008, 45, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenheim, J.A.; Kaya, H.K.; Ehler, L.E.; Marois, J.J.; Jaffee, B.A. Intraguild predation among biological-control agents theory and evidence. Biol. Control 1995, 5, 303–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.S.T. Interactions between entomopathogenic fungi and entomophagous insects. Adv. Entomol. 2020, 8, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, M.J.; Pell, J.K. Interactions between entomopathogenic fungi and arthropod natural enemies. In Insect-Fungal Associations: Ecology and Evolution; Vega, F.E., Blackwell, M., Eds.; Oxford University Press, Inc: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 51–73. ISBN 0-19-516652-3. [Google Scholar]
- Rännbäck, L.M.; Cotes, B.; Anderson, P.; Rämert, B.; Meyling, N.V. Mortality risk from entomopathogenic fungi affects oviposition behavior in the parasitoid wasp Trybliographa rapae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 124, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De la Rosa, W.; Segura, H.R.; Barrera, J.F.; Williams, T. Laboratory evaluation of the impact of entomopathogenic fungi on Prorops nasuta (Hymenoptera: Bethylidae), a parasitoid of the coffee berry borer. Environ. Entomol. 2000, 29, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlong, M.J.; Pell, J.K. Conflicts between a fungal entomopathogen, Zoophthora radicans, and two larval parasitoids of the diamondback moth. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2000, 76, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, A.L.M.; Lacey, L.A. Interactions among the entomopathogenic fungus, Paecilomyces fumosoroseus (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes), the parasitoid, A. asychis (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae), and their aphid host. Biol. Control 2001, 22, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, M.; Kharazi-pakdel, A.; Allahyari, H.; van Alphen, J.J.M. Interactions among the entomopathogenic fungus, B. bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales), the parasitoid, Aphidius matricariae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), and its host, M. persicae (Homoptera: Aphididae). Biol. Control 2009, 50, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqueel, M.A.; Leather, S.R. Virulence of Verticillium lecanii (Z.) against cereal aphids; does timing of infection affect the performance of parasitoids and predators? Pest Manag. Sci. 2013, 69, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo-Mejía, F.; Tamez-Guerra, P.; Guzmán-Franco, A.W.; Gomez-Flores, R. Can B. bassiana Bals. (Vuill) (Ascomycetes: Hypocreales) and Tamarixia triozae (Burks) (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) be used together for improved biological control of B. cockerelli (Hemiptera: Triozidae)? Biol. Control 2015, 90, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.A.; Hatcher, P.E. Combining entomopathogenic fungi and parasitoids to control the green peach aphid M. persicae. Biol. Control 2017, 110, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gottel, M.S.; Hajek, A.E. Evaluation of non-target effects of pathogens used for management of arthropods. In Evaluating Indirect Ecological Effects of Biological Control; Wajnberg, E., Scott, J., Quimby, P., Eds.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 2001; pp. 81–97. ISBN 0-85199-453-9. [Google Scholar]
- Tamayo-Mejía, F.; Tamez-Guerra, P.; Guzmán-Franco, A.W.; Gomez-Flores, R. Developmental stage affects survival of the ectoparasitoid Tamarixia triozae exposed to the fungus B. bassiana. Biol. Control 2016, 93, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Barrera, O.Y.; Toledo, J.; Liedo, P.; Gómez, J.; Valle-Mora, J.; Cancino, J.; Montoya, P. Does B. bassiana (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) affect the survival and fecundity of the parasitoid C. haywardi (Hymenoptera: Diapriidae)? Environ. Entomol. 2019, 48, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Barrera, O.Y.; Toledo, J.; Cancino, J.; Liedo, P.; Gómez, J.; Valle-Mora, J.; Montoya, P. Interaction between B. bassiana (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae) and C. haywardi (Hymenoptera: Diapriidae) for the management of A. obliqua (Diptera: Tephritidae). J. Insect Sci. 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pell, J.K.; Vandenberg, J.D. Interactions among the aphid Diuraphis noxia, the entomopathogenic fungus P. fumosoroseus and the Coccinellid hippodamia convergens. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2002, 12, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami, F.; Alichi, M.; Minaei, K. Interaction between the entomopathogenic fungus, B. bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) and the parasitoid wasp, Aphidius colemani Viereck (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). J. Entomol. Acarol. Res. 2013, 45, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martins, I.C.; Silva, R.J.; Alencar, J.R.D.C.C.; Silva, K.P.; Cividanes, F.J.; Duarte, R.T.; Agostini, L.T.; Polanczyk, R.A. Interactions between the entomopathogenic fungi B. bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) and the aphid parasitoid D. rapae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) on M. persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Biol. Microb. Control 2014, 107, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, A.; Dunlap, C.A.; Jackson, M.A.; Flores, D.; Patt, J.M.; Sétamou, M. Oviposition behavior and survival of Tamarixia radiata (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), an ectoparasitoid of the asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri (Hemiptera: Liviidae), on hosts exposed to an entomopathogenic fungus, I. fumosorosea (Hypocreales: Cordycipitaceae), under laboratory conditions. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1995–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahi, A.; Safavi, S.A. Sublethal effects of Metarhizium anisopliae on life table parameters of Habrobracon hebetor parasitizing Helicoverpa armigera larvae at different time intervals. BioControl 2016, 61, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, F.R.M.; Brida, A.L.; Martins, L.N.; Abeijon, L.M.; Luntinski, C.J. Biological control of fruit flies of the genus Anastrepha (Diptera: Tephritidae): Current status and perspectives. In Biological Control: Methods, Applications and Challenges; Davenport, L., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 29–71. ISBN 978-1-53612-416-3. [Google Scholar]
- Presa-Parra, E.; Hernández-Rosas, F.; Bernal, J.S.; Valenzuela-González, J.E.; Altúzar-Molina, A.; Birke, A. Occurrence, identification, and virulence of native fungal pathogens isolated from Mexican fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) larvae from soils of three cropping Systems. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 1088–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polis, G.A.; Myers, C.A.; Holt, R.D. The ecology and evolution of intraguild predation: Potential competitors that eat each other. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1989, 20, 297–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluja, M.; Sivinski, J.; Ovruski, S.; Guillén, L.; López, M.; Cancino, J.; Torres-Anaya, A.; Gallegos-Chan, G.; Ruíz, L. Colonization and domestication of seven species of native new world hymenopterous larval-prepupal and pupal fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) parasitoids. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2009, 19, 49–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiedy, M.; Saboori, A.; Allahyari, H. Interactions of two natural enemies of Tetranychus urticae, the fungal entomopathogen B. bassiana and the predatory mite, Phytoseiulus persimilis. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2012, 22, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ramírez, G.; Hernández-Rosas, F.; Sánchez-Arroyo, H.; Alatorre-Rosas, R. Infectividad, edad y humedad relativa relacionados con la susceptibilidad de ninfas y adultos de Periplaneta americana a M. anisopliae y B. bassiana (Ascomycota: Hypocreales). Entomotropica 2007, 22, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Barnett, H.; Hunter, B.B. Ilustrated Genera of Imperfect Fungi, 4th ed.; Amer Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1998; ISBN 1560228946. [Google Scholar]
- Montoya, P.; Pérez-Lachaud, G.; Liedo, P. Superparasitism in the fruit fly parasitoid D. longicaudata (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and the implications for mass rearing and augmentative release. Insects 2012, 3, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlanga-Padilla, A.M.; Hernández-Velázquez, V.M. Efecto de la temperatura sobre el crecimiento y la virulencia de Metarhizium aisopliae, M. anisopliae var. acridum y B. bassiana en Schistocerca piceifrons piceifrons. Manejo Integr. Plagas 2002, 63, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; SAGE Publications Inc: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2018; ISBN 978-1-5443-3647-3. [Google Scholar]
- Crawley, M.J. The R Book; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2012; ISBN 9780470973929. [Google Scholar]
- Borges, R.E. Análisis de sobrevivencia utilizando el lenguaje R. In XV Simposio de Estadistica; Universidad Nacional de Colombia: Boyacá, Colombia, 2005; pp. 1–77. [Google Scholar]
- Peto, R.; Peto, J. Asymptotically efficient rank invariant test procedures. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1972, 132, 185–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, A.G.; Rebelo, M. de F. A simple R-based function to estimate lethal concentrations. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 91, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, M.W.; Park, R.M.; Bailer, A.J. Comparing median lethal concentration values using confidence interval overlap or ratio test. Environ. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 1441–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: In Integrated Development for R; RStudio, PBC: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Reyes, I.C.; Bustillo, A.E.; Chaves, B. Efecto de B. bassiana y Metarhizium anisopliae sobre el parasitoide de la broca del café Cephalonomia stephanoderis. Rev. Colomb. Entomol. 1995, 21, 199–204. [Google Scholar]
- Danfa, A.; Van Der Valk, H.C.H.G. Laboratory testing of Metarhizium spp. and B. bassiana on Sahelian non-target arthropods. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 1999, 9, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.M.; Wong, T.T.Y.; Wong, M.A. Influence of parasitoid size and age on male mating success of Opiinae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), larval parasitoids of fruit flies (Diptera: Tephritidae). Biol. Control 1991, 1, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Martínez, L.; Leyva-Vasquez, J.L.; Bravo Mojica, H. Utilización del esperma en hembras de D. longicaudata. Southwest. Entomol. 1993, 18, 293. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, W.M. Host-parasitoid-pathogen interactions. In Parasites and Pathogens of Insects; Beckage, N.E., Thompson, S.N., Federici, B.A., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1993; pp. 231–272. ISBN 978-0-08-091649-1. [Google Scholar]
- Askary, H.; Brodeur, J. Susceptibility of larval stages of the aphid parasitoid Aphidius nigripes to the entomopathogenic fungus V. lecanii. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1999, 73, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avery, P.B.; Faull, J.; Simmonds, M.S.J. Effects of P. fumosoroseus and Encarsia formosa on the control of the greenhouse whitefly: Preliminary assessment of a compatability study. BioControl 2008, 53, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sufty, R.; Führer, E. Wechselbeziehungen zwischen Cydia pomonella L. (Lep., Tortricidae), Ascogaster quadridentatus Wesm. (Hym., Braconidae) und dem Pilz B. bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. Zeitschrift für Angew. Entomol. 1985, 99, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, J.J.; van Lenteren, J.C. Host selection and survival of the parasitoid E. formosa on greenhouse whitefly, Trialeurodes vaporariorum, in the presence of hosts infected with the fungus A. aleyrodis. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1993, 69, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluja, M.; Mangan, R.L. Fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) host status determination: Critical conceptual, methodological, and regulatory considerations. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2008, 53, 473–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, P.; Flores, S.; Campos, S.; Liedo, P.; Toledo, J. Simultaneous use of SIT plus disseminator devices of B. bassiana enhances horizontal transmission in A. ludens. J. Appl. Entomol. 2020, 144, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, H.J.; McInnis, D.; Hendrichs, J. Modeling the area-wide integration of male annihilation and the simultaneous release of methyl eugenol-exposed Bactrocera spp. sterile males. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2014, 107, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Strain | Parasitism Condition | Mortality (%) | Germination (%) | Sporulation (Conidia/Larvae) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. anisopliae MAAP1 | Parasitized | 93 ± 06 a | 79.18 ± 17 a | 8.22 ± 7.4 × 107 a |
| Non-parasitized | 91 ± 01 a | 71.87 ± 24 b | 4.96 ± 5.6 × 107 a | |
| M. robertsii V3-160 | Parasitized | 93 ± 01 a | 45.86 ± 23 c | 9.84 ± 9.4 × 107 a |
| Non-parasitized | 94 ± 05 a | 41.04 ± 26 c | 6.28 ± 4.5 × 107 a |
| Parasitism Condition | LC50/LC10 | IC 95% | χ2 | p-Value | Slope | Intercept |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-parasitized | 4.8 × 10⁵ | 7.4 × 10⁵ to 3.1 × 105 | 37.26 | <0.001 | 0.684 | −3.8905 |
| Parasitized | 1.2 × 10⁵ | 1.8 × 10⁵ to 9.2 × 104 | 125.36 | <0.001 | 0.865 | −4.4207 |
| Non-parasitized | 6.5 × 103 | 1.4 × 104 to 2.3 × 103 | 37.26 | <0.001 | 0.684 | −3.8905 |
| Parasitized | 4.2 × 103 | 7.7 × 103 to 1.8 × 103 | 125.36 | <0.001 | 0.865 | −4.4207 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Presa-Parra, E.; Hernández-Rosas, F.; Bernal, J.S.; Valenzuela-González, J.E.; Martínez-Tlapa, J.; Birke, A. Impact of Metarhizium robertsii on Adults of the Parasitoid Diachasmimorpha longicaudata and Parasitized Anastrepha ludens Larvae. Insects 2021, 12, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12020125
Presa-Parra E, Hernández-Rosas F, Bernal JS, Valenzuela-González JE, Martínez-Tlapa J, Birke A. Impact of Metarhizium robertsii on Adults of the Parasitoid Diachasmimorpha longicaudata and Parasitized Anastrepha ludens Larvae. Insects. 2021; 12(2):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12020125
Chicago/Turabian StylePresa-Parra, Ehdibaldo, Francisco Hernández-Rosas, Julio S. Bernal, Jorge E. Valenzuela-González, Jovita Martínez-Tlapa, and Andrea Birke. 2021. "Impact of Metarhizium robertsii on Adults of the Parasitoid Diachasmimorpha longicaudata and Parasitized Anastrepha ludens Larvae" Insects 12, no. 2: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12020125
APA StylePresa-Parra, E., Hernández-Rosas, F., Bernal, J. S., Valenzuela-González, J. E., Martínez-Tlapa, J., & Birke, A. (2021). Impact of Metarhizium robertsii on Adults of the Parasitoid Diachasmimorpha longicaudata and Parasitized Anastrepha ludens Larvae. Insects, 12(2), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12020125