A Gene-Based Method for Cytogenetic Mapping of Repeat-Rich Mosquito Genomes
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruzzante, L.; Reijnders, M.; Waterhouse, R.M. Of Genes and Genomes: Mosquito Evolution and Diversity. Trends Parasitol. 2019, 35, 32–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lounibos, L.P.; Kramer, L.D. Invasiveness of Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus and Vectorial Capacity for Chikungunya Virus. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, S453–S458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazeille, M.; Madec, Y.; Mousson, L.; Bellone, R.; Barré-Cardi, H.; Sousa, C.A.; Jiolle, D.; Yébakima, A.; de Lamballerie, X.; Failloux, A.B. Zika virus threshold determines transmission by European Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berlin, K.; Koren, S.; Chin, C.S.; Drake, J.P.; Landolin, J.M.; Phillippy, A.M. Assembling large genomes with single-molecule sequencing and locality-sensitive hashing. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, S.; Gurtowski, J.; Ethe-Sayers, S.; Deshpande, P.; Schatz, M.C.; McCombie, W.R. Oxford Nanopore sequencing, hybrid error correction, and de novo assembly of a eukaryotic genome. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.E.; Staber, C.; Zeitlinger, J.; Hawley, R.S. GENOME REPORT: Highly Contiguous Genome Assemblies of 15 Drosophila Species Generated Using Nanopore Sequencing. G3 (Bethesda) 2018, 8, 3131–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, R.A.; Subramanian, G.M.; Halpern, A.; Sutton, G.G.; Charlab, R.; Nusskern, D.R.; Wincker, P.; Clark, A.G.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Wides, R.; et al. The genome sequence of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Science 2002, 298, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharakhova, M.V.; Hammond, M.P.; Lobo, N.F.; Krzywinski, J.; Unger, M.F.; Hillenmeyer, M.E.; Bruggner, R.V.; Birney, E.; Collins, F.H. Update of the Anopheles gambiae PEST genome assembly. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, P.; Sharakhova, M.V.; Sharakhov, I.V. High-resolution cytogenetic map for the African malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemov, G.N.; Peery, A.N.; Jiang, X.; Tu, Z.; Stegniy, V.N.; Sharakhova, M.V.; Sharakhov, I.V. The Physical Genome Mapping of Anopheles albimanus Corrected Scaffold Misassemblies and Identified Interarm Rearrangements in Genus Anopheles. G3 (Bethesda) 2017, 7, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, A.; Liang, J.; Chen, C.; Lukyanchikova, V.; Qi, Y.; Potters, M.; Settlage, R.; Miller, D.; Deschamps, S.; Mao, C.; et al. The beginning of the end: A chromosomal assembly of the New World malaria mosquito ends with a novel telomere. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukyanchikova, V.; Nuriddinov, M.; Belokopytova, P.; Liang, J.; Reijnders, M.; Ruzzante, L.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Tu, Z.; Sharakhov, I.V.; Fishman, V. Anopheles mosquitoes revealed new principles of 3D genome organization in insects. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemov, G.N.; Bondarenko, S.M.; Naumenko, A.N.; Stegniy, V.N.; Sharakhova, M.V.; Sharakhov, I.V. Partial-arm translocations in evolution of malaria mosquitoes revealed by high-coverage physical mapping of the Anopheles atroparvus genome. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, R.M.; Aganezov, S.; Anselmetti, Y.; Lee, J.; Ruzzante, L.; Reijnders, M.; Feron, R.; Berard, S.; George, P.; Hahn, M.W.; et al. Evolutionary superscaffolding and chromosome anchoring to improve Anopheles genome assemblies. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghurye, J.; Koren, S.; Small, S.T.; Redmond, S.; Howell, P.; Phillippy, A.M.; Besansky, N.J. A chromosome-scale assembly of the major African malaria vector Anopheles funestus. Gigascience 2019, 8, giz063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamyatin, A.; Avdeev, P.; Liang, J.; Sharma, A.; Chen, C.; Lukyanchikova, V.; Alexeev, N.; Tu, Z.; Alekseyev, M.A.; Sharakhov, I. Chromosome-level genome assemblies of the malaria vectors Anopheles coluzzii and Anopheles arabiensis. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, B.J.; Dudchenko, O.; Kingan, S.B.; Koren, S.; Antoshechkin, I.; Crawford, J.E.; Glassford, W.J.; Herre, M.; Redmond, S.N.; Rose, N.H.; et al. Improved reference genome of Aedes aegypti informs arbovirus vector control. Nature 2018, 563, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palatini, U.; Masri, R.A.; Cosme, L.V.; Koren, S.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Biedler, J.K.; Krsticevic, F.; Johnston, J.S.; Halbach, R.; Crawford, J.E.; et al. Improved reference genome of the arboviral vector Aedes albopictus. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingan, S.B.; Heaton, H.; Cudini, J.; Lambert, C.C.; Baybayan, P.; Galvin, B.D.; Durbin, R.; Korlach, J.; Lawniczak, M.K.N. A High-Quality De novo Genome Assembly from a Single Mosquito Using PacBio Sequencing. Genes (Basel) 2019, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, R.P.; Reis-Cunha, J.L.; DeBarry, J.D.; Chiari, E.; Kissinger, J.C.; Bartholomeu, D.C.; Macedo, A.M. Assembly of highly repetitive genomes using short reads: The genome of discrete typing unit III Trypanosoma cruzi strain 231. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arensburger, P.; Megy, K.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Abrudan, J.; Amedeo, P.; Antelo, B.; Bartholomay, L.; Bidwell, S.; Caler, E.; Camara, F.; et al. Sequencing of Culex quinquefasciatus establishes a platform for mosquito comparative genomics. Science 2010, 330, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nene, V.; Wortman, J.R.; Lawson, D.; Haas, B.; Kodira, C.; Tu, Z.J.; Loftus, B.; Xi, Z.; Megy, K.; Grabherr, M.; et al. Genome sequence of Aedes aegypti, a major arbovirus vector. Science 2007, 316, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshevskiy, V.A.; Kinney, N.A.; de Bruyn, B.S.; Mao, C.; Tu, Z.; Severson, D.W.; Sharakhov, I.V.; Sharakhova, M.V. Genomic composition and evolution of Aedes aegypti chromosomes revealed by the analysis of physically mapped supercontigs. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharakhov, I.V.; Sharakhova, M.V. Heterochromatin, histone modifications, and nuclear architecture in disease vectors. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 10, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Deschamps, S.; Zhang, Y.; Llaca, V.; Ye, L.; Sanyal, A.; King, M.; May, G.; Lin, H. A chromosome-scale assembly of the sorghum genome using nanopore sequencing and optical mapping. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudchenko, O.; Batra, S.S.; Omer, A.D.; Nyquist, S.K.; Hoeger, M.; Durand, N.C.; Shamim, M.S.; Machol, I.; Lander, E.S.; Aiden, A.P.; et al. De novo assembly of the Aedes aegypti genome using Hi-C yields chromosome-length scaffolds. Science 2017, 356, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belton, J.M.; McCord, R.P.; Gibcus, J.H.; Naumova, N.; Zhan, Y.; Dekker, J. Hi-C: A comprehensive technique to capture the conformation of genomes. Methods 2012, 58, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharakhova, M.V.; Artemov, G.N.; Timoshevskiy, V.A.; Sharakhov, I.V. Physical Genome Mapping Using Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization with Mosquito Chromosomes. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1858, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.G.; Jiang, X.; Gu, J.; Xu, M.; Wu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bonizzoni, M.; Dermauw, W.; Vontas, J.; et al. Genome sequence of the Asian Tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus, reveals insights into its biology, genetics, and evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5907–E5915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.R.; Koren, S.; Dilley, K.A.; Puri, V.; Brown, D.M.; Harkins, D.M.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Rosen, B.; Chen, X.G.; Tu, Z.; et al. Analysis of the Aedes albopictus C6/36 genome provides insight into cell line utility for viral propagation. Gigascience 2018, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Cutcutache, I.; Koressaar, T.; Ye, J.; Faircloth, B.C.; Remm, M.; Rozen, S.G. Primer3--new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshevskiy, V.A.; Sharma, A.; Sharakhov, I.V.; Sharakhova, M.V. Fluorescent in situ hybridization on mitotic chromosomes of mosquitoes. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 67, e4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessmann, H.; Walter, M.F.; Dimitratos, S.; Woods, D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding putative odourant binding proteins from the antennae of the malaria-transmitting mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Insect Mol. Biol. 2002, 11, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharakhova, M.V.; Timoshevskiy, V.A.; Yang, F.; Demin, S.; Severson, D.W.; Sharakhov, I.V. Imaginal discs: A new source of chromosomes for genome mapping of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, K.S. A Comparative Study of Mosquito Karyotypes1. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1963, 56, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, A.N.; Timoshevskiy, V.A.; Kinney, N.A.; Kokhanenko, A.A.; deBruyn, B.S.; Lovin, D.D.; Stegniy, V.N.; Severson, D.W.; Sharakhov, I.V.; Sharakhova, M.V. Mitotic-chromosome-based physical mapping of the Culex quinquefasciatus genome. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severson, D.W.; Meece, J.K.; Lovin, D.D.; Saha, G.; Morlais, I. Linkage map organization of expressed sequence tags and sequence tagged sites in the mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Insect Mol. Biol. 2002, 11, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickner, P.V.; Mori, A.; Chadee, D.D.; Severson, D.W. Composite linkage map and enhanced genome map for Culex pipiens complex mosquitoes. J. Hered. 2013, 104, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juneja, P.; Osei-Poku, J.; Ho, Y.S.; Ariani, C.V.; Palmer, W.J.; Pain, A.; Jiggins, F.M. Assembly of the Genome of the Disease Vector Aedes aegypti onto a Genetic Linkage Map Allows Mapping of Genes Affecting Disease Transmission. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshevskiy, V.A.; Severson, D.W.; Debruyn, B.S.; Black, W.C.; Sharakhov, I.V.; Sharakhova, M.V. An integrated linkage, chromosome, and genome map for the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

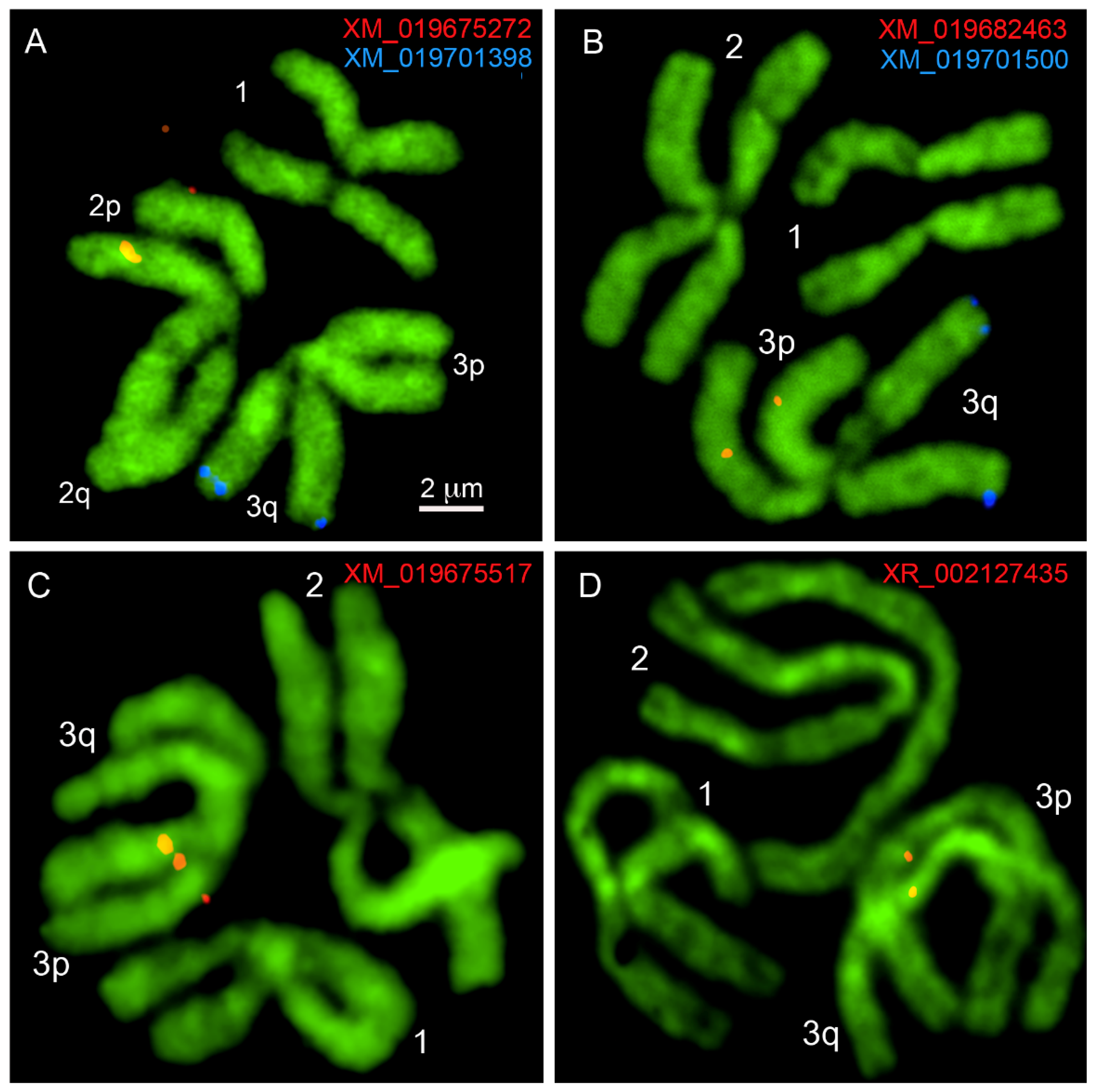
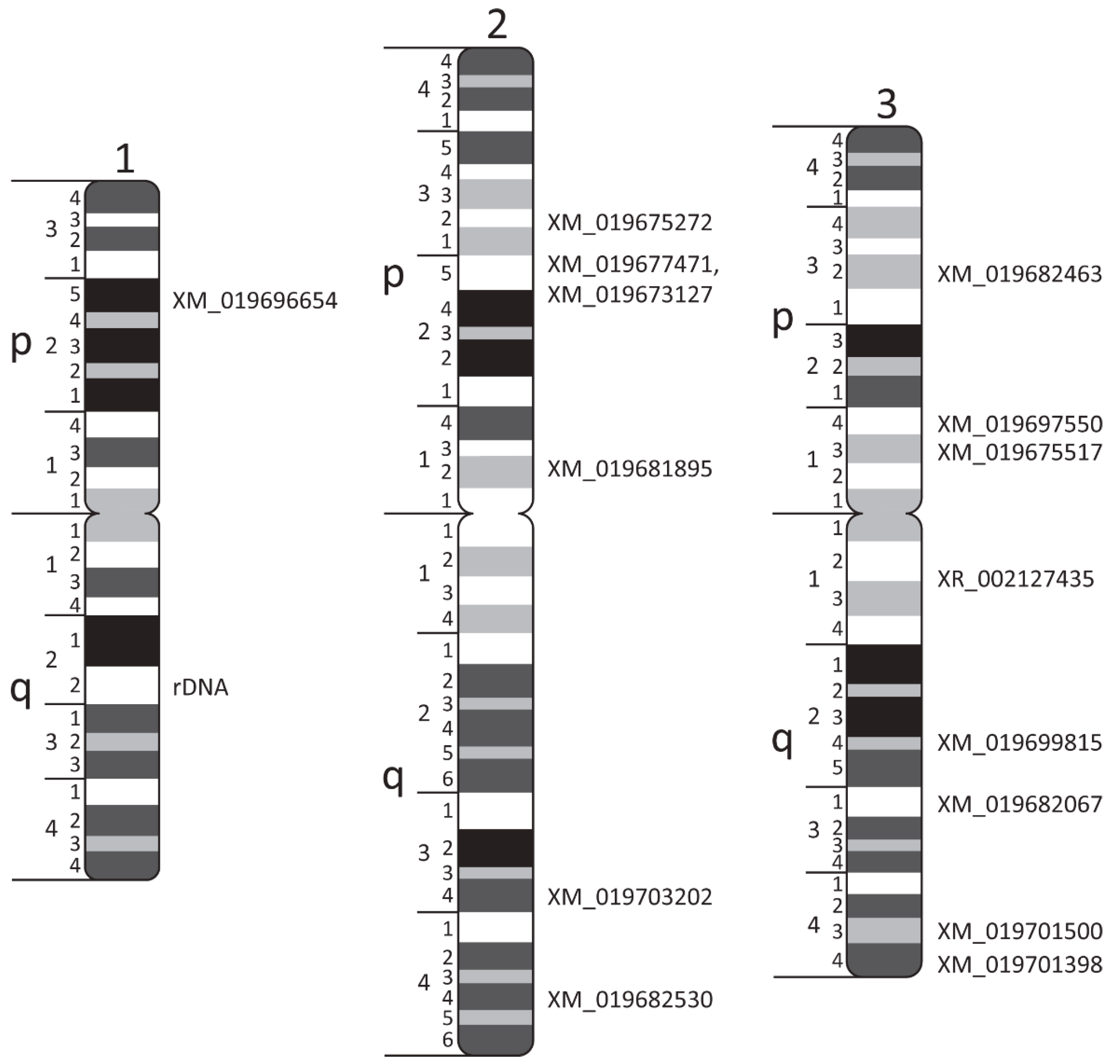
| Transcript ID | Scaffold ID/Number | Chromosome Band | Forward (F) and Reverse (R) Primers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18 S rDNA | 1q22 | F: ATGCAAAATGCAGGAACCTC R: GGTAATAGCAGCTGGGCTTG | |
| XM_019696654 | NW_021838798.1/6 | 1p25 | F: TCGTTCGTGTAGATAAAGTCCAG R: ATGGTTATGAGGTTCCAACAACT |
| XM_019681895 | NW_021838576.1/4 | 2p12 | F: GAAGTAACGGGCTCAGTTCTGGTTTC R: CTTCGAGTAGTTGGACCAGTTCGAGA |
| XM_019677471 | NW_021838576.1/4 | 2p25 | F: AGCTCAACCAAAGGAAGGATTTA R: TGATTGTTCACCTTGTTTTCCAC |
| XM_019673127 | NW_021838576.1/4 | 2p25 | F: AAGTGTGCGGAAAATTGTTTACA R: TAATGGATTGAAGCTGCTTTTCG |
| XM_019675272 | NW_021838153.1/2 | 2p32 | F: TCCCTCTTTTATGAACAGCTGTT R: ACAAAACATTCATGCAGTTGTCA |
| XM_019703202 | NW_021838687.1/5 | 2q34 | F: AAACGACAAGAAATGTTCTGCAA R: TTGTGCCGCATTATCATTCATTT |
| XM_019682530 | NW_021838153.1/2 | 2q44 | F: AACAGAGCGGTATCTACAAAGAG R: GTAGAACACGAAGGCATTAGGTA |
| XM_019675517 | NW_021838832.1/63 | 3p13 | F: ACTTCGGTTATGGGTAAGGTTTT R: CAAAGACATGGGATTTTCTCGTC |
| XM_019697550 | NW_021838154.1/20 | 3p14 | F: GGAAGTTTTGTGTCGAAGGAAAA R: GTCGTCCAGATTGTACAGATCTT |
| XM_019682463 | NW_021837045.1/1 | 3p32 | F: GAGACCAACGCAGAGTACGTCTTCAC R: CGCATAGGCTCTGATGAACTTAGTCG |
| XR_002127435 | NW_017857621.1/18 | 3q12 | F: CCATTAAAAACGCCATCTAGCAA R: TATGAGTGTAGTGTGCTAGCAAG |
| XM_019682067 | NW_021838465.1/3 | 3q23 | F: AGGTACCGTACAAAAGAAGTGAA R: ACGGAACTAAGAAACAAAGTCCT |
| XM_019699815 | NW_021837489.1/14 | 3q23 | F: TTCGGTGGAAAAATCGTTTTGAA R: CGAGTTTCTCTATTGCCACTTTG |
| XM_019701500 | NW_021838465.1/3 | 3q43 | F: CGATGGACTGTTCTTCCAATCTA R: TTTGATTTGTGTTTGTCCCAGAC |
| XM_019701398 | NW_021838465.1/3 | 3q44 | F: TCCCGTTACTTCTACGAAATGAG R: CCATCTTCTGGTTTGCATAACAG |
| Comparison Parameters | BAC-Based Genome Mapping | Gene-Based Genome Mapping |
|---|---|---|
| BAC library development and BAC-end sequencing | Required | Not required |
| Primer design | Not required | Required |
| Blocking of unspecific hybridization with Cot1 DNA | Required | Not required |
| Multiple FISH signals are produced in the chromosomes | Often | Never |
| Additional DNA denaturation step in 70% formamide at 72 °C | Required | Not required |
| Expensive | Yes | No |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masri, R.A.; Karagodin, D.A.; Sharma, A.; Sharakhova, M.V. A Gene-Based Method for Cytogenetic Mapping of Repeat-Rich Mosquito Genomes. Insects 2021, 12, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12020138
Masri RA, Karagodin DA, Sharma A, Sharakhova MV. A Gene-Based Method for Cytogenetic Mapping of Repeat-Rich Mosquito Genomes. Insects. 2021; 12(2):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12020138
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasri, Reem A., Dmitriy A. Karagodin, Atashi Sharma, and Maria V. Sharakhova. 2021. "A Gene-Based Method for Cytogenetic Mapping of Repeat-Rich Mosquito Genomes" Insects 12, no. 2: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12020138
APA StyleMasri, R. A., Karagodin, D. A., Sharma, A., & Sharakhova, M. V. (2021). A Gene-Based Method for Cytogenetic Mapping of Repeat-Rich Mosquito Genomes. Insects, 12(2), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12020138








