Toxicity of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water (Plant-Derived) to Immature Stages of Mosquito Vectors
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water
2.2. Mosquito Rearing
2.3. Laboratory Bioassay
2.4. Effects of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water on Hatch Rate of Mosquito Eggs
2.5. Effect of Functional Mineral Water on Mesocyclops Aspericornis
2.6. Optical Properties of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
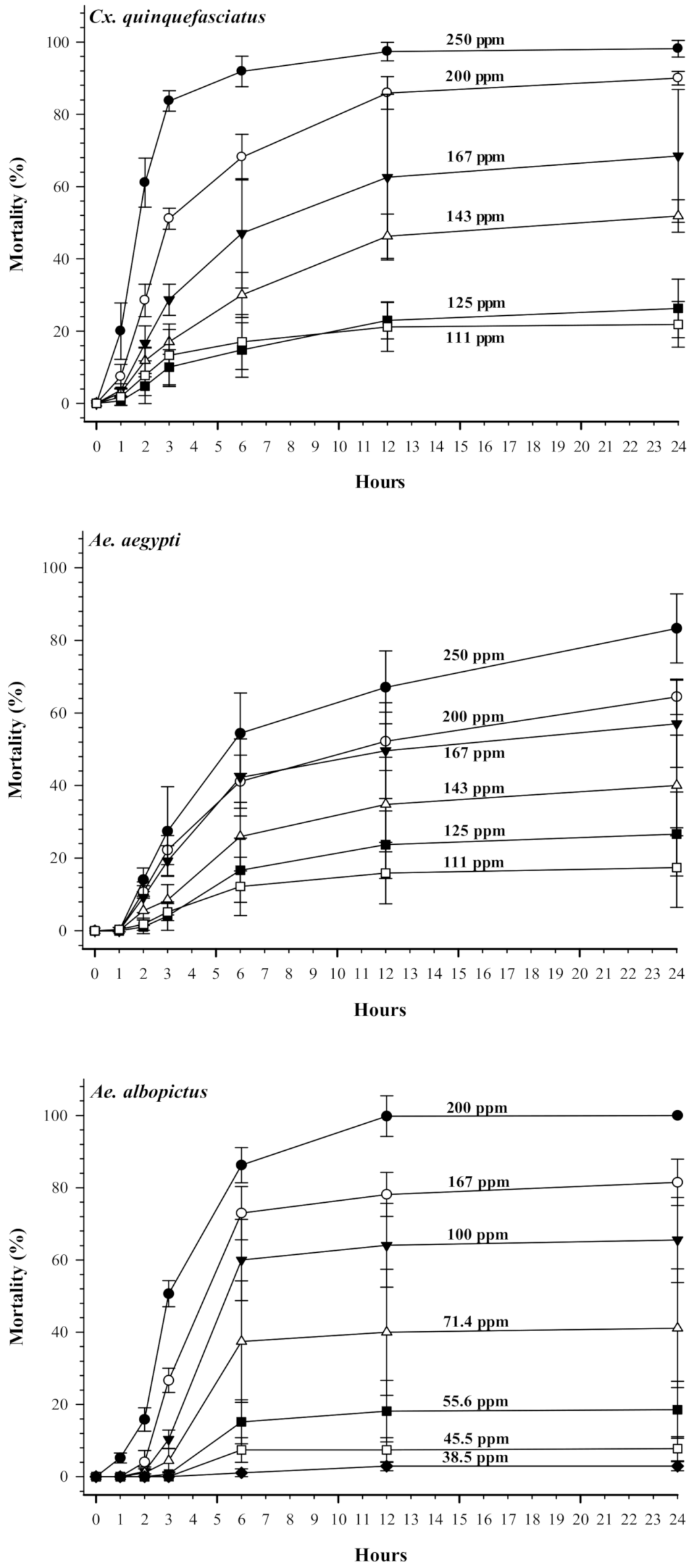
3.1. Larvicidal Activities of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water
3.2. Pupicidal Activities of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water
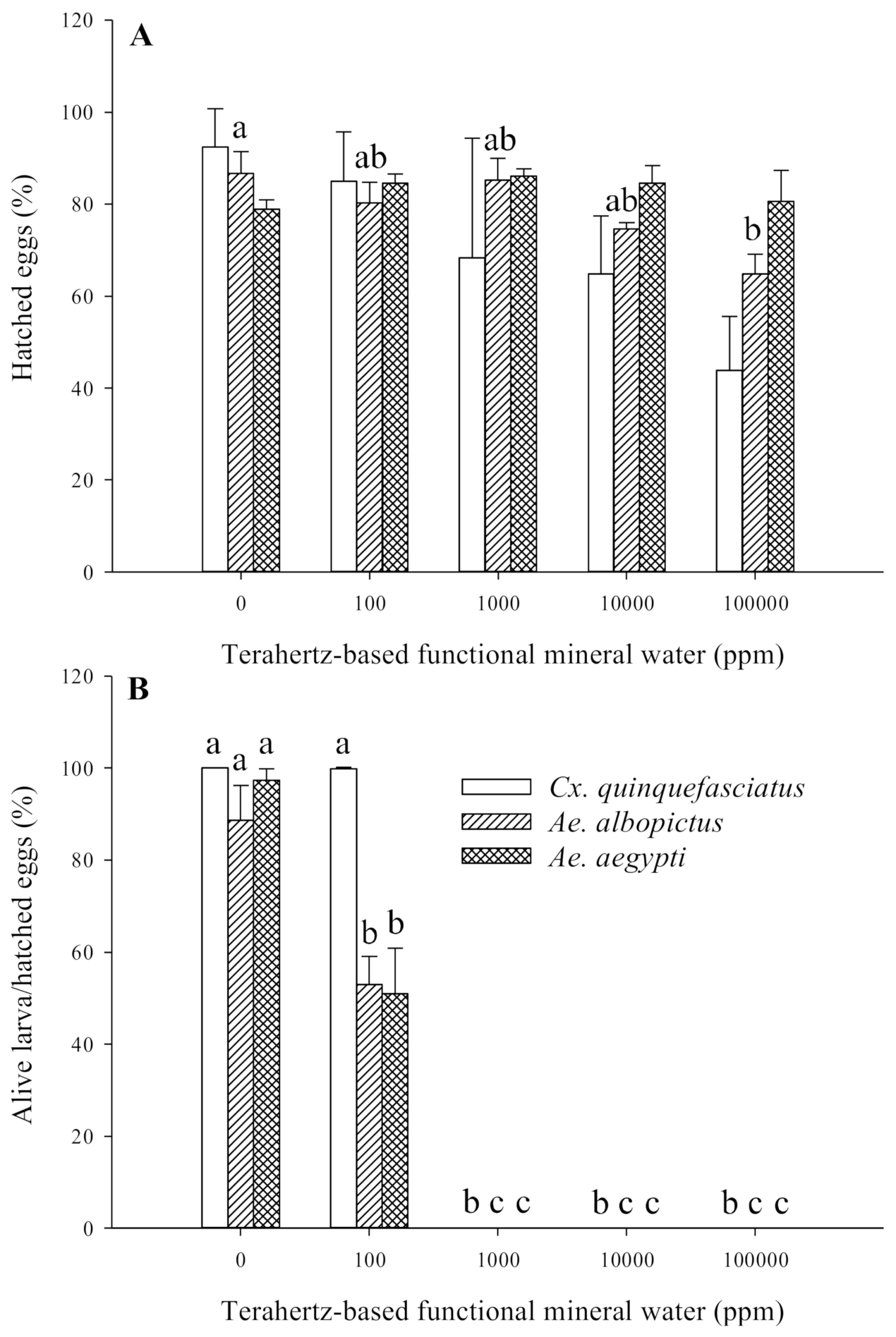
3.3. Effect of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water on Mosquito Eggs
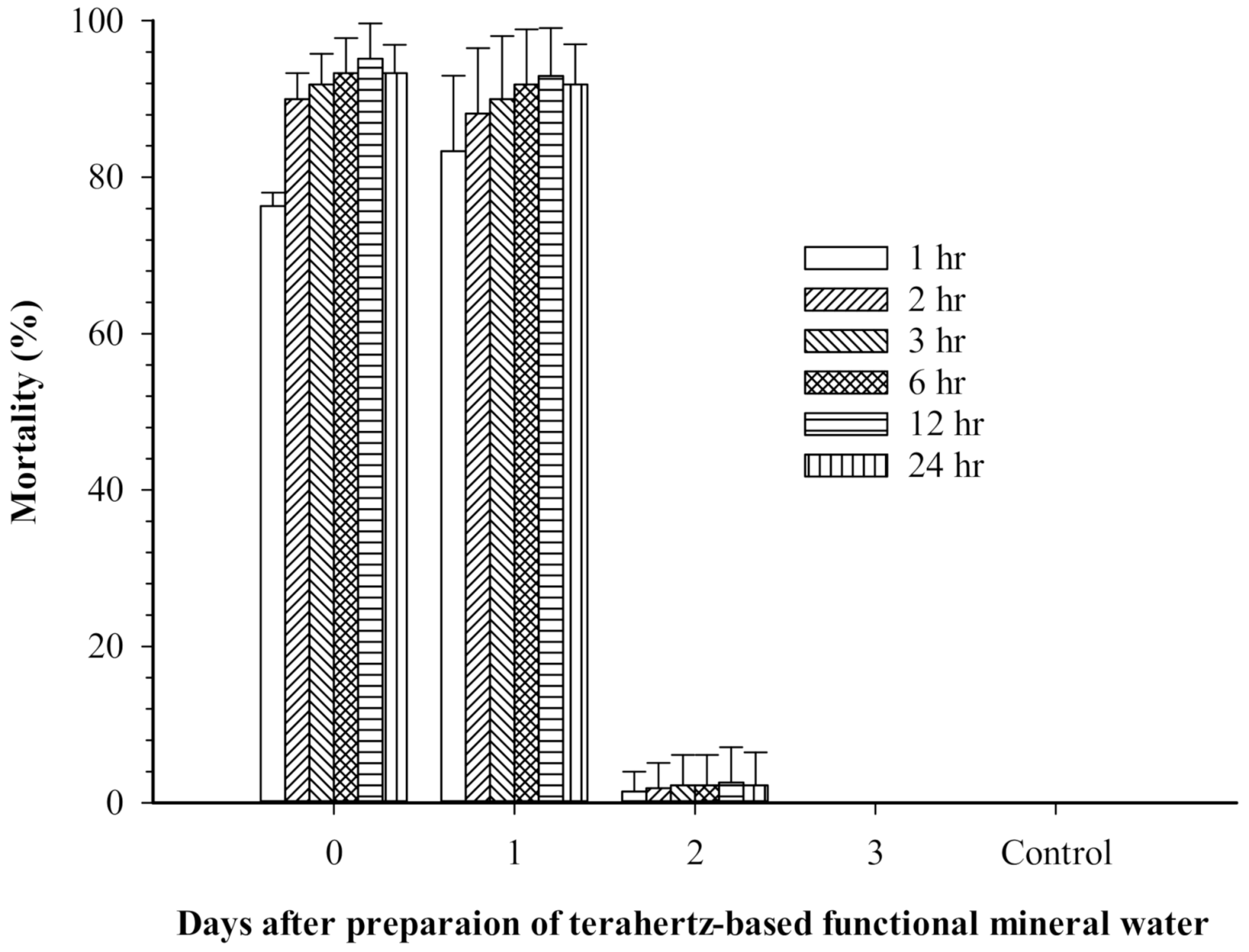
3.4. Toxicity of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water to Mesocyclops Aspericornis
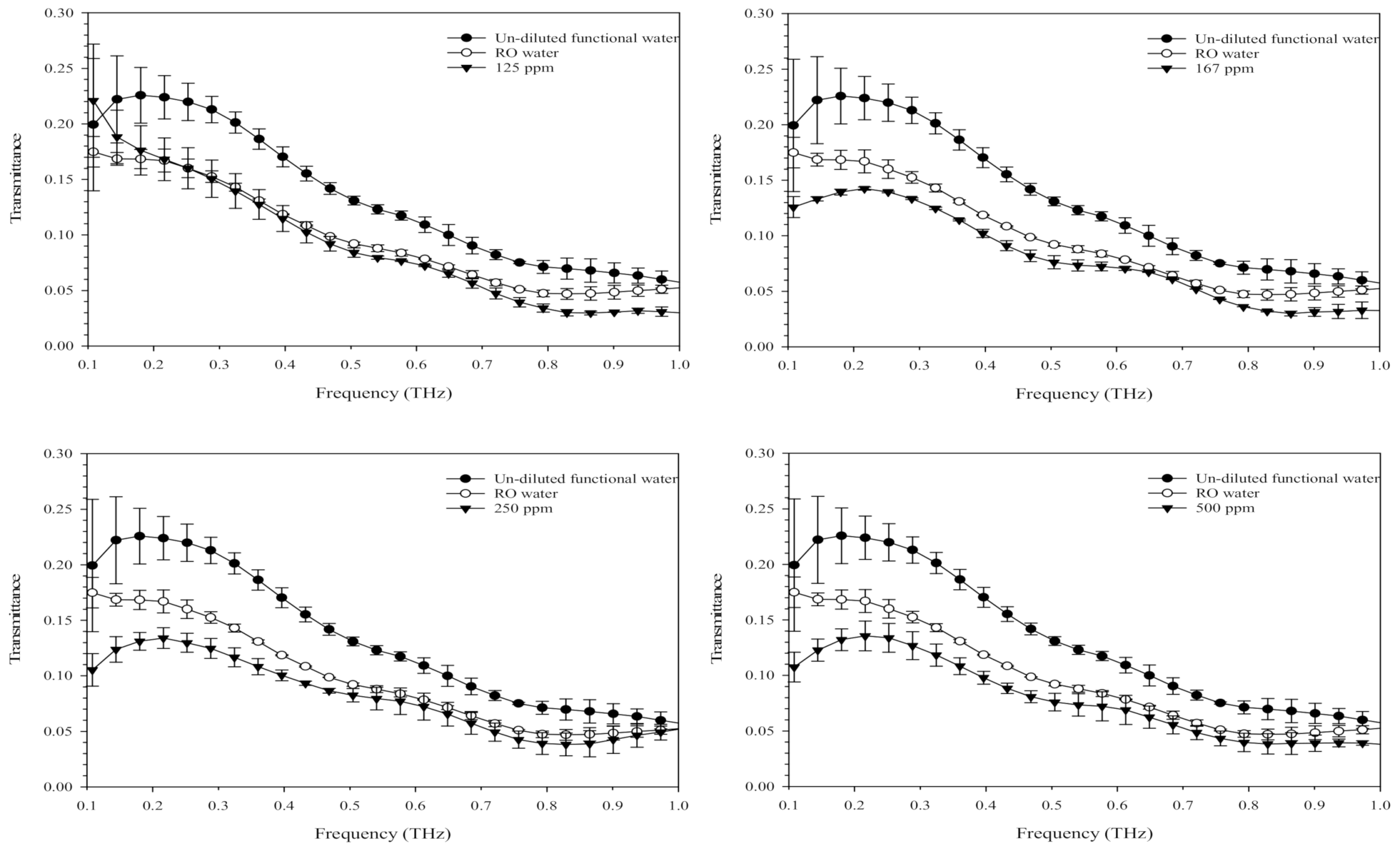
3.5. Optical Properties of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munawar, K.; Alahmed, A.M.; Khalil, S.M.S. Delivery Methods for RNAi in Mosquito Larvae. J. Insect Sci. 2020, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N. Insecticide resistance in mosquitoes: Impact, mechanisms, and research directions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2015, 60, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Dengue and Severe Dengue. In Fact Sheet Number 117; WHO: Genveva, Switzerland, 2014; 39p, Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs117/en/ (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- World Health Organization. W. Malaria. In Fact Sheet Number 94; WHO: Genveva, Switzerland, 2014; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs094/en/ (accessed on 3 January 2021).
- Juliano, S.A.; Westby, K.M.; Ower, G.D. Know Your Enemy: Effects of a Predator on Native and Invasive Container Mosquitoes. J. Med. Entomol. 2019, 56, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benelli, G.; Govindarajan, M.; Rajeswary, M.; Senthilmurugan, S.; Vijayan, P.; Alharbi, N.S.; Kadaikunnan, S.; Khaled, J.M. Larvicidal activity of Blumea eriantha essential oil and its components against six mosquito species, including Zika virus vectors: The promising potential of (4E,6Z)-allo-ocimene, carvotanacetone and dodecyl acetate. Parasitol. Res. 2017, 116, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, H.A.; Khater, E.I. Potency and persistence of the bacterial mosquitocide Bacillus sphaericus against culicine mosquitoes under field conditions. J. Egypt Soc. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warbanski, M.L.; Marques, P.; Frauendorf, T.C.; Phillip, D.A.T.; El-Sabaawi, R.W. Implications of guppy (Poecilia reticulata) life-history phenotype for mosquito control. Ecol Evol. 2017, 7, 3324–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, G.; Jayakody, S.; Wijenayake, W.; Galappaththy, G.N.L.; Yatawara, M.; Harishchandra, J. A comparison of the larvivorous habits of exotic Poecilia reticulata and native Aplocheilus parvus. Bmc Ecol. 2018, 18, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusunoki, M.; Sata, E.; Nishio, K.; Tanaka, T.; Nishida, T.; Sugano, N.; Sato, S.; Asano, M. Acid-electrolyzed functional water induces extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer, a possible novel alarmin, secretion from oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Int. J. Med Sci. 2018, 15, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, T.; Tamura, M.; Suguro, H.; Ohtsu, M.; Omagari, D.; Yoshino, A.; Ogiso, B.; Asano, M. Bactericidal and cytotoxic effects of acid-electrolyzed functional water. J. Oral Sci. 2019, 61, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, M.; Ohshima, T.; Mukumoto, M.; Konishi, H.; Hirashita, A.; Maeda, N.; Nakamura, Y. A study for biofilm removing and antimicrobial effects by microbubbled tap water and other functional water, electrolyzed hypochlorite water and ozonated water. Dent. Mater. J. 2012, 31, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santa Mineral Co., Ltd. 2020. Available online: https://en.santamineral.com/qq-farming (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Kubota, A.; Goda, T.; Tsuru, T.; Yonekura, T.; Yagi, M.; Kawahara, H.; Yoneda, A.; Tazuke, Y.; Tani, G.; Ishii, T.; et al. Efficacy and safety of strong acid electrolyzed water for peritoneal lavage to prevent surgical site infection in patients with perforated appendicitis. Surgury Today 2015, 45, 876–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korenstein-Ilan, A.; Barbul, A.; Hasin, P.; Eliran, A.; Gover, A.; Korenstein, R. Terahertz radiation increases genomic instability in human lymphocytes. Radiat. Res. 2008, 170, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betzalel, N.; Ben Ishai, P.; Feldman, Y. The human skin as a sub-THz receiver—Does 5G pose a danger to it or not? Environ. Res. 2018, 163, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramundo Orlando, A.; Gallerano, G.P. Terahertz radiation effects and biological applications. J. Infrared Milli. Terahz Waves 2009, 30, 1308–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Huang, H.; Hao, S.; Qiu, K.; Gao, H.; Gao, L.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, Z. Insights into the water status in hydrous minerals using terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.P. A novel multiple membrane blood-feeding system for investigating and maintaining Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. J. Vector Ecol. 2014, 39, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerberg, E.J.; Barnard, D.R.; Ward, R.A. Manual for Mosquito Rearing and Experimental Techniques; American Mosquito Control Association Inc.: Lake Charles, LA, USA, 1994; p. 98. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Pesticide Evaluation Scheme. In Guidelines for Laboratozry and Field Testing of Mosquito Larvicides; WHO: Genveva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Su, T.; Mulla, M.S. Ovicidal activity of neem products (azadirachtin) against Culex tarsalis and Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera: Culicidae). J. Am. Mosq. Control Assoc. 1998, 14, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pineda-Cortel, M.R.B.; Cabantog, R.J.R.; Caasi, P.M.; Ching, C.A.D.; Perez, J.B.S.; Godisan, P.G.M.; Latorre, C.M.G.; Lucero, D.R.; Salonga, R.B. Larvicidal and ovicidal activities of Artocarpus blancoi extracts against Aedes aegypti. Pharm. Biol. 2019, 57, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, B.; Ho, C.H.; Zheng, W.J.; Lu, Y.L. Terahertz volatile gas sensing by using polymer microporous membranes. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 2048–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.F.; You, B.; Gao, H.C.; Wang, T.D.; Sun, C.K. Pilot clinical study to investigate the human whole blood spectrum characteristics in the sub-THz region. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 9440–9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.K.; Chen, H.Y.; Tseng, T.F.; You, B.; Wei, M.L.; Lu, J.Y.; Chang, Y.L.; Tseng, W.L.; Wang, T.D. High Sensitivity of T-Ray for Thrombus Sensing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlina, B.L.; Birceanu, O.; Robinson, C.S.; Dhiyebi, H.; Wilkie, M.P. Seasonal variation in the sensitivity of invasive sea lampreys to the lampricide TFM: Importance of energy reserves and temperature. N. Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2008, 28, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar]
- Finney, D. Statistical Method in Biological Assay, 3rd ed.; Mathematics in Medicine Series; Macmillan Publishing Company Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1952; p. 505. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, W.S. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/.2018 (accessed on 14 January 2021).
- Dai, J.; Jin, Q.; Yiwen., E.; Williams, K.; Zhang, X.C. Using liquid water as broadband terahertz wave emitter. Conf. Rec. Soc. Photo-Opt. Instrum. Eng. 2018, 10656, 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.T.; Lin, C.C.; Kuo, T.C.; Chen, S.J.; Huang, R.N. Phytochemical composition and larvicidal activity of essential oils from herbal plants. Planta. 2019, 250, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, K. Laboratory bio-assay of temephos and fenthion against some vector species of public health importance. J. Commun. Dis. 2004, 36, 100–104. [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan, V.; Prabakaran, G.; Paily, K.P.; Balaraman, K. Toxicity of a mosquitocidal metabolite of Pseudomonas fluorescens on larvae & pupae of the house fly, Musca domestica. Indian J. Med. Res. 2005, 121, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, B.L.; Germano, R.N.L.; Braga, K.M.L.; Araújo, E.R.F.; Rocha, D.A.; Obara, M.T. Susceptibility of Aedes aegypti populations to pyriproxyfen in the Federal District of Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2020, 53, e20190489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, I.A.; Mello, C.B.; Peixoto, A.A.; Valle, D. Evaluation of Methoprene effect on Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) development in laboratory conditions. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz. 2005, 100, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnesi, L.C.; Vargas, H.C.M.; Valle, D.; Rezende, G.L. Darker eggs of mosquitoes resist more to dry conditions: Melanin enhances serosal cuticle contribution in egg resistance to desiccation in Aedes, Anopheles and Culex vectors. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrick, M.L.; Gonzalez, R.J.; Bradley, T.J. Sodium and chloride regulation in freshwater and osmoconforming larvae of Culex mosquitoes. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 3345–3354. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, T.M.; Flis, B.J.; Remold, S.K. pH tolerances and regulatory abilities of freshwater and euryhaline Aedine mosquito larvae. J Exp Biol. 2004, 207, 2297–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmink, G.J.; Grundt, J.E. Invited Review Article: Current state of research on biological effects of terahertz radiation. J. Infrared Milli. Terahz Waves 2011, 32, 1074–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Aedes aegypti | Aedes Albopictus | Culex quinquefasciatus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 (ppm) a | 149.8 | 183.4 | 227.9 |
| (LCL-UCL) b | (141.1–159.0) | (165.7–203.0) | (205.0–253.5) |
| LC90 (ppm) a | 198.0 | 268.4 | 345.6 |
| (LCL-UCL) b | (187.2–218.4) | (250.3–298.1) | (318.3–389.4) |
| Regression line | y = −28.41 + 15.11x | y = −20.29 + 10.94x | y = −18.69 + 9.83x |
| Slope | 15.10 ± 2.33 | 10.93 ± 1.54 | 9.85 ± 1.39 |
| Chi-squared value | 1.9215 | 6.2926 | 2.9058 |
| Aedes aegypti | Aedes albopictus | Culex quinquefasciatus | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC50 (ppm) a | 130.6 | 89.6 | 142.4 |
| (LCL-UCL) b | (123.2–138.5) | (57.8–78.2) | (118.4–130.7) |
| LC90 (ppm) a | 286.2 | 179.2 | 204.4 |
| (LCL-UCL)b | (250.1–354.4) | (150.2–232.1) | (193.1–219.6) |
| Regression line | y = −6.75 + 5.30x | y = −3.33 + 4.27x | y = −13.14 + 8.41x |
| Slope | 5.30 ± 0.89 | 4.28 ± 0.57 | 8.41 ± 1.12 |
| Chi-squared value | 0.5717 | 3.0957 | 0.8243 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, T.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Tsai, C.-C.; Chen, S.-J.; Hung, T.-M.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Lu, J.-Y.; Huang, R.-N. Toxicity of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water (Plant-Derived) to Immature Stages of Mosquito Vectors. Insects 2021, 12, 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030211
Kuo T-C, Lin C-C, Tsai C-C, Chen S-J, Hung T-M, Hsieh C-C, Lu J-Y, Huang R-N. Toxicity of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water (Plant-Derived) to Immature Stages of Mosquito Vectors. Insects. 2021; 12(3):211. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030211
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Tai-Chih, Chien-Chung Lin, Ching-Chu Tsai, Shiang-Jiuun Chen, Tso-Min Hung, Che-Chu Hsieh, Ja-Yu Lu, and Rong-Nan Huang. 2021. "Toxicity of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water (Plant-Derived) to Immature Stages of Mosquito Vectors" Insects 12, no. 3: 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030211
APA StyleKuo, T.-C., Lin, C.-C., Tsai, C.-C., Chen, S.-J., Hung, T.-M., Hsieh, C.-C., Lu, J.-Y., & Huang, R.-N. (2021). Toxicity of Terahertz-Based Functional Mineral Water (Plant-Derived) to Immature Stages of Mosquito Vectors. Insects, 12(3), 211. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030211






