Knockout of Two Cry-Binding Aminopeptidase N Isoforms Does Not Change Susceptibility of Aedes aegypti Larvae to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa Toxins
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mosquito and Bt Strains
2.2. Purification of Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa Protoxins
2.3. sgRNA Design and Synthesis
2.4. Embryo Microinjection and Generation of Ae. aegypti Knockout Strains
2.5. Preparation of Brush Border Membrane Vesicles from Ae. aegypti Larvae
2.6. Proteomic Identification of Midgut BBMVs from Ae. aegypti Larvae
2.7. ELISA Binding Assays
2.8. Bioassay of Bti Cry Toxins
3. Results
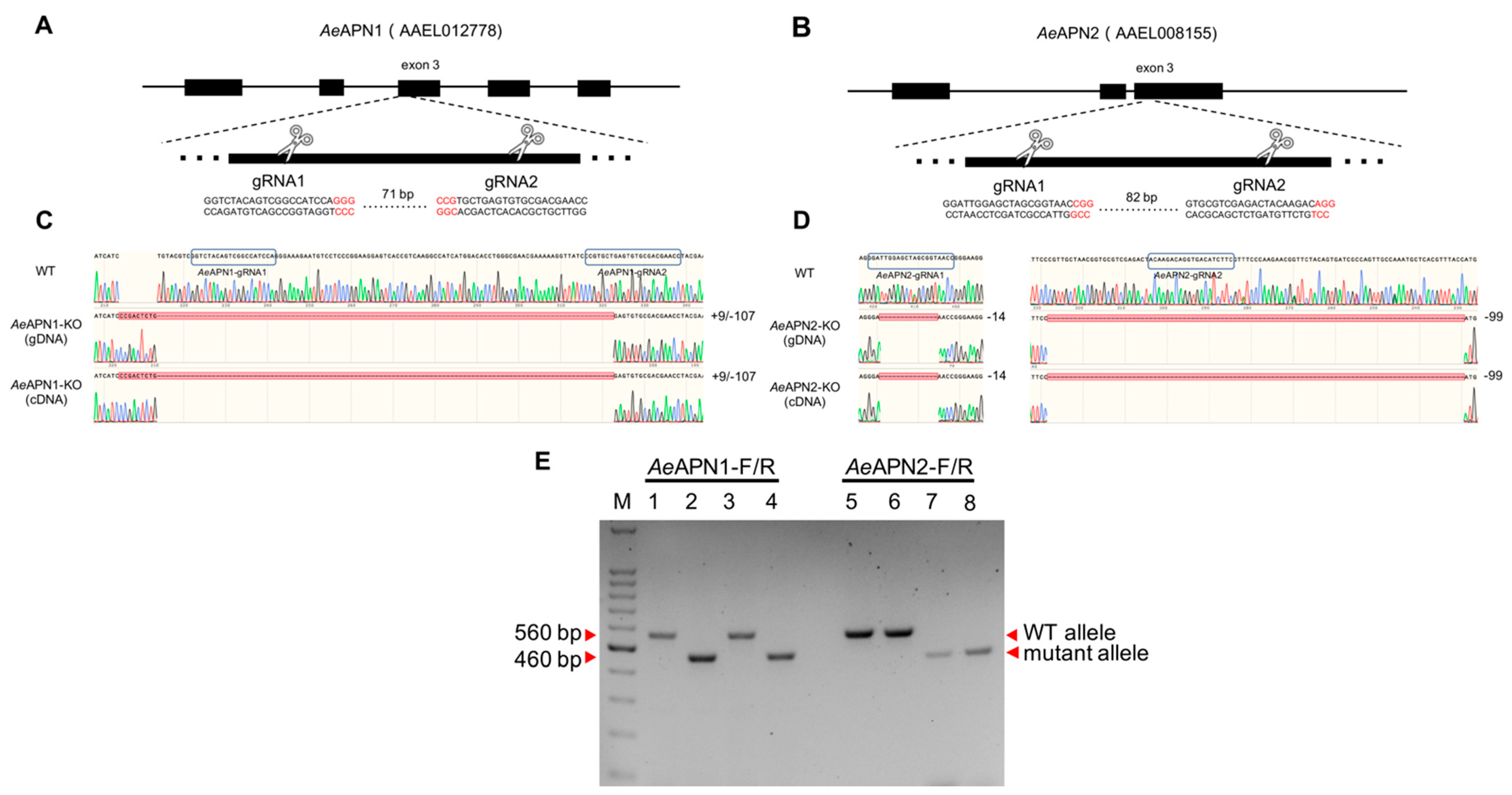
3.1. Generation of Individual AeAPN1 and AeAPN2 Knockout Ae. aegypti Strains by CRISPR/Cas9
3.2. Generation of AeAPN1/AeAPN2 Double-Mutant Ae. aegypti Strain
3.3. Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa Protoxins Binding to BBMVs of the APN Knockouts and the WT Strains
3.4. Response of the Ae. aegypti Larvae to Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa Protoxins
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kyle, J.L.; Harris, E. Global spread and persistence of dengue. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 62, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Global Strategy for Dengue Prevention and Control, 2012–2020. World Health Organization, 2012. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/75303 (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Wilder-Smith, A. Dengue vaccine development: Status and future. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundh. Gesundh. 2020, 63, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotto, P.M.d.A.; Leite, L.C.d.C. The Challenges Imposed by Dengue, Zika, and Chikungunya to Brazil. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crickmore, N.; Zeigler, D.R.; Feitelson, J.; Schnepf, E.; Van Rie, J.; Lereclus, D.; Baum, J.; Dean, D.H. Revision of the nomenclature for the Bacillus thuringiensis pesticidal crystal proteins. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1998, 62, 807–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berry, C.; O’Neil, S.; Ben-Dov, E.; Jones, A.F.; Murphy, L.; Quail, M.A.; Holden, M.T.; Harris, D.; Zaritsky, A.; Parkhill, J. Complete sequence and organization of pBtoxis, the toxin-coding plasmid of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5082–5095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- World Health Organization. Pesticides and Their Application: For the Control of Vectors and Pests of Public Health Importance. World Health Organization, 2006. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/69223 (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Ben-Dov, E. Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis and its dipteran-specific toxins. Toxins (Basel) 2014, 6, 1222–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vachon, V.; Laprade, R.; Schwartz, J.-L. Current models of the mode of action of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal proteins: A critical review. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 111, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.; Gómez, I.; Mendoza Almanza, G.; Gaytán, M.; Soberón, M. Different Models of the Mode of Action of Bt 3d-Cry Toxins; CABI: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 56–68.
- Pardo-López, L.; Soberón, M.; Bravo, A. Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal three-domain Cry toxins: Mode of action, insect resistance and consequences for crop protection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peterson, B.; Bezuidenhout, C.C.; Van den Berg, J. An Overview of Mechanisms of Cry Toxin Resistance in Lepidopteran Insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nocek, B.; Mulligan, R.; Bargassa, M.; Collart, F.; Joachimiak, A. Crystal structure of aminopeptidase N from human pathogen Neisseria meningitidis. Proteins 2008, 70, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pigott, C.R.; Ellar, D.J. Role of receptors in Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxin activity. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 255–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knight, P.J.K.; Knowles, B.H.; Ellar, D.J. Molecular cloning of an insect aminopeptidase N that serves as a receptor for Bacillus thuringiensis CryIA(c) toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 17765–17770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdullah, M.A.; Valaitis, A.P.; Dean, D.H. Identification of a Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11Ba toxin-binding aminopeptidase from the mosquito, Anopheles quadrimaculatus. BMC Biochem. 2006, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Hua, G.; Urbauer, J.L.; Adang, M.J. Synergistic and inhibitory effects of aminopeptidase peptides on Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11Ba toxicity in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 8512–8519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Aimanova, K.G.; Pan, S.; Gill, S.S. Identification and characterization of Aedes aegypti aminopeptidase N as a putative receptor of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry11A toxin. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Likitvivatanavong, S.; Aimanova, K.G.; Gill, S.S. A 104 kDa Aedes aegypti aminopeptidase N is a putative receptor for the Cry11Aa toxin from Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.-s.; Yang, S.-j.; Shu, C.-l.; Song, F.-p.; Zhou, X.-p.; Zhang, J. Comparison and optimization of the method for Cry1Ac protoxin preparation in HD73 strain. J. Integr. Agric. 2015, 14, 1598–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.E.; Ellar, D.J. Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis crystal delta-endotoxin: Effects on insect and mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell Sci. 1983, 60, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kistler, K.E.; Vosshall, L.B.; Matthews, B.J. Genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9 in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolfersberger, M.; Luethy, P.; Maurer, A.; Parenti, P.; Sacchi, F.V.; Giordana, B.; Hanozet, G.M. Preparation and partial characterization of amino acid transporting brush border membrane vesicles from the larval midgut of the cabbage butterfly (Pieris brassicae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Physiol. 1987, 86, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Cardeña, A.; Grande, R.; Sánchez, J.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M.; Gómez, I. The C-terminal protoxin domain of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin has a functional role in binding to GPI-anchored receptors in the insect midgut. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batool, K.; Alam, I.; Zhao, G.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.; Huang, E.; Guan, X.; Zhang, L. C-Type Lectin-20 Interacts with ALP1 Receptor to Reduce Cry Toxicity in Aedes aegypti. Toxins 2018, 10, 390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sangadala, S.; Walters, F.S.; English, L.H.; Adang, M.J. A mixture of Manduca sexta aminopeptidase and phosphatase enhances Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal CryIA(c) toxin binding and 86Rb(+)-K+ efflux in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 10088–10092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.L.; Lu, Y.J.; Söhnlein, P.; Brousseau, R.; Laprade, R.; Masson, L.; Adang, M.J. Ion channels formed in planar lipid bilayers by Bacillus thuringiensis toxins in the presence of Manduca sexta midgut receptors. FEBS Lett. 1997, 412, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, K.; Sangadala, S.; Masson, L.; Mazza, A.; Brousseau, R.; Adang, M.J. The Heliothis virescens 170kDa aminopeptidase functions as “Receptor A” by mediating specific Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A δ-endotoxin binding and pore formation. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1997, 27, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, S.; Rajagopal, R.; Venkatesh, G.R.; Srivastava, A.; Bhatnagar, R.K. Knockdown of Aminopeptidase-N from Helicoverpa armigera Larvae and in Transfected Sf21 Cells by RNA Interference Reveals Its Functional Interaction with Bacillus thuringiensis Insecticidal Protein Cry1Ac. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7312–7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, M.; Liang, G.; Wu, K.; Guo, Y.; Ni, X.; Li, X. APN1 is a functional receptor of Cry1Ac but not Cry2Ab in Helicoverpa zea. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroonkesorn, A.; Pootanakit, K.; Katzenmeier, G.; Angsuthanasombat, C. Two specific membrane-bound aminopeptidase N isoforms from Aedes aegypti larvae serve as functional receptors for the Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin implicating counterpart specificity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 461, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, D.J.; Hua, G.; Adang, M.J. Cloning of a Heliothis virescens 110 kDa aminopeptidase N and expression in Drosophila S2 cells. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2003, 33, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Cui, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, B.; Ma, W.; Wang, X.; Lei, C.; Chen, L. Aminopeptidase N1 is involved in Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxicity in the beet armyworm, Spodoptera exigua. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores-Escobar, B.; Rodríguez-Magadan, H.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M.; Gómez, I. Differential role of Manduca sexta aminopeptidase-N and alkaline phosphatase in the mode of action of Cry1Aa, Cry1Ab, and Cry1Ac toxins from Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4543–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.Y.; Du, L.X.; Liu, C.X.; Gong, L.; Han, L.Z.; Peng, Y.F. RNAi in the striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis, establishes a functional role for aminopeptidase N in Cry1Ab intoxication. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2017, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhu, Y.C.; Ottea, J.; Husseneder, C.; Rogers Leonard, B.; Abel, C.; Huang, F. Molecular characterization and RNA interference of three midgut aminopeptidase N isozymes from Bacillus thuringiensis-susceptible and -resistant strains of sugarcane borer, Diatraea saccharalis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saengwiman, S.; Aroonkesorn, A.; Dedvisitsakul, P.; Sakdee, S.; Leetachewa, S.; Angsuthanasombat, C.; Pootanakit, K. In vivo identification of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry4Ba toxin receptors by RNA interference knockdown of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked aminopeptidase N transcripts in Aedes aegypti larvae. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 407, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiewsiri, K.; Wang, P. Differential alteration of two aminopeptidases N associated with resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry1Ac in cabbage looper. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14037–14042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Cheng, H.; Gao, Y.; Wang, G.; Liang, G.; Wu, K. Mutation of an aminopeptidase N gene is associated with Helicoverpa armigera resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.B.; Aimanova, K.G.; Gill, S.S. Alkaline phosphatases and aminopeptidases are altered in a Cry11Aa resistant strain of Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 54, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Chen, W.; Song, X.; Ma, X.; Cotto-Rivera, R.O.; Kain, W.; Chu, H.; Chen, Y.R.; Fei, Z.; Wang, P. Mutation of ABC transporter ABCA2 confers resistance to Bt toxin Cry2Ab in Trichoplusia ni. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 112, 103209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Tay, W.T.; Walsh, T.K.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated genome editing of Helicoverpa armigera with mutations of an ABC transporter gene HaABCA2 confers resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry2A toxins. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 87, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ma, H.; Zhao, S.; Huang, J.; Yang, Y.; Tabashnik, B.E.; Wu, Y. Functional redundancy of two ABC transporter proteins in mediating toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis to cotton bollworm. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Fu, S.; Ma, X.; Baxter, S.W.; Vasseur, L.; Xiong, L.; Huang, Y.; Yang, G.; You, S.; You, M. Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ac toxin requires mutations in two Plutella xylostella ATP-binding cassette transporter paralogs. PLoS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Kain, W.; Wang, P. Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A toxins exert toxicity by multiple pathways in insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 102, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Jin, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.; Gómez, I.; Bravo, A.; Soberón, M.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, K. The Cadherin Protein Is Not Involved in Susceptibility to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab or Cry1Fa Toxins in Spodoptera frugiperda. Toxins 2020, 12, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, S.; Zuo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y. Functional validation of cadherin as a receptor of Bt toxin Cry1Ac in Helicoverpa armigera utilizing the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 76, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zuo, Y.Y.; Li, L.L.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.D. Knockout of three aminopeptidase N genes does not affect susceptibility of Helicoverpa armigera larvae to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A and Cry2A toxins. Insect Sci. 2020, 27, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Candas, M.; Griko, N.B.; Taussig, R.; Bulla, L.A., Jr. A mechanism of cell death involving an adenylyl cyclase/PKA signaling pathway is induced by the Cry1Ab toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9897–9902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| Primer Name | Sequence 5′–3′ |
|---|---|
| sgRNA-R | ATAACGGACTAGCCTTATTTTAACTTGCTATTTCTAGCTCTAAAAC |
| APN1-sgRNA-1-F | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGTCTACAGTCGGCCATCCAGTT TTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC |
| APN1-sgRNA-2-F | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGTTCGTCGCACACTCAGCAGTT TTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC |
| APN2-sgRNA-1-F | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGGATTGGAGCTAGCGGTAACGTT TTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC |
| APN2-sgRNA-2-F | GAAATTAATACGACTCACTATAGTGCGTCGAGACTACAAGACGTT TTAGAGCTAGAAATAGC |
| AeAPN1-F | GGAATGCCGATACTCCAAGATCAAT |
| AeAPN1-R | TGAAAATAATCCACTCATTGGCCGG |
| AeAPN2-F | AGTGTTCTGAACATGTTCCGTGT |
| AeAPN2-R | TATGCGTCGTTGATCAGCTGAGC |
| Injected Component | Injected G0 Embryos | G0 Survivors | G0 Mutants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cas9 protein, APN1-sgRNA-1 and APN1-sgRNA-2 | 400 | 26 | 4 |
| Cas9 protein, APN2-sgRNA-1 and APN2-sgRNA-2 | 800 | 88 | 36 |
| Ae. aegypti Strain | n | Slope (SE) | LC50 (μg/mL) (95% CI) | RR a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 1125 | 2.947 (0.098) | 1.771 (1.663–1.888) | 1 |
| AeAPN1-KO | 1125 | 3.774 (0.181) | 1.504 (1.421–1.591) | 0.849 |
| AeAPN2-KO | 1125 | 3.664 (0.171) | 1.863 (1.771–1.958) | 1.052 |
| AeAPN1/AeAPN2-KO | 1125 | 3.079 (0.135) | 2.221 (2.092–2.367) | 1.254 |
| Ae. aegypti Strain | n | Slope (SE) | LC50 (μg/mL) (95% CI) | RR a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | 1125 | 1.747 (0.110) | 0.602 (0.526–0.685) | 1 |
| AeAPN1-KO | 1125 | 3.192 (0.224) | 0.556 (0.496–0.619) | 0.924 |
| AeAPN2-KO | 1125 | 1.989 (0.124) | 0.599 (0.546–0.653) | 0.995 |
| AeAPN1/AeAPN2-KO | 1125 | 2.770 (0.163) | 0.826 (0.769–0.897) | 1.372 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Yang, X.; He, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Huang, W.; Ou, L.; Yang, Z.; Guan, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Knockout of Two Cry-Binding Aminopeptidase N Isoforms Does Not Change Susceptibility of Aedes aegypti Larvae to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa Toxins. Insects 2021, 12, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030223
Wang J, Yang X, He H, Chen J, Liu Y, Huang W, Ou L, Yang Z, Guan X, Zhang L, et al. Knockout of Two Cry-Binding Aminopeptidase N Isoforms Does Not Change Susceptibility of Aedes aegypti Larvae to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa Toxins. Insects. 2021; 12(3):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030223
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Junxiang, Xiaozhen Yang, Huan He, Jingru Chen, Yuanyuan Liu, Wanting Huang, Luru Ou, Zhaohui Yang, Xiong Guan, Lingling Zhang, and et al. 2021. "Knockout of Two Cry-Binding Aminopeptidase N Isoforms Does Not Change Susceptibility of Aedes aegypti Larvae to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa Toxins" Insects 12, no. 3: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030223
APA StyleWang, J., Yang, X., He, H., Chen, J., Liu, Y., Huang, W., Ou, L., Yang, Z., Guan, X., Zhang, L., & Wu, S. (2021). Knockout of Two Cry-Binding Aminopeptidase N Isoforms Does Not Change Susceptibility of Aedes aegypti Larvae to Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis Cry4Ba and Cry11Aa Toxins. Insects, 12(3), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12030223






