High Variability in Pre-Oviposition Time Independent of Diet Available at Eclosion: A key Reproductive Trait in the Ladybird Beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Its Native Range
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Diet at Adult Eclosion
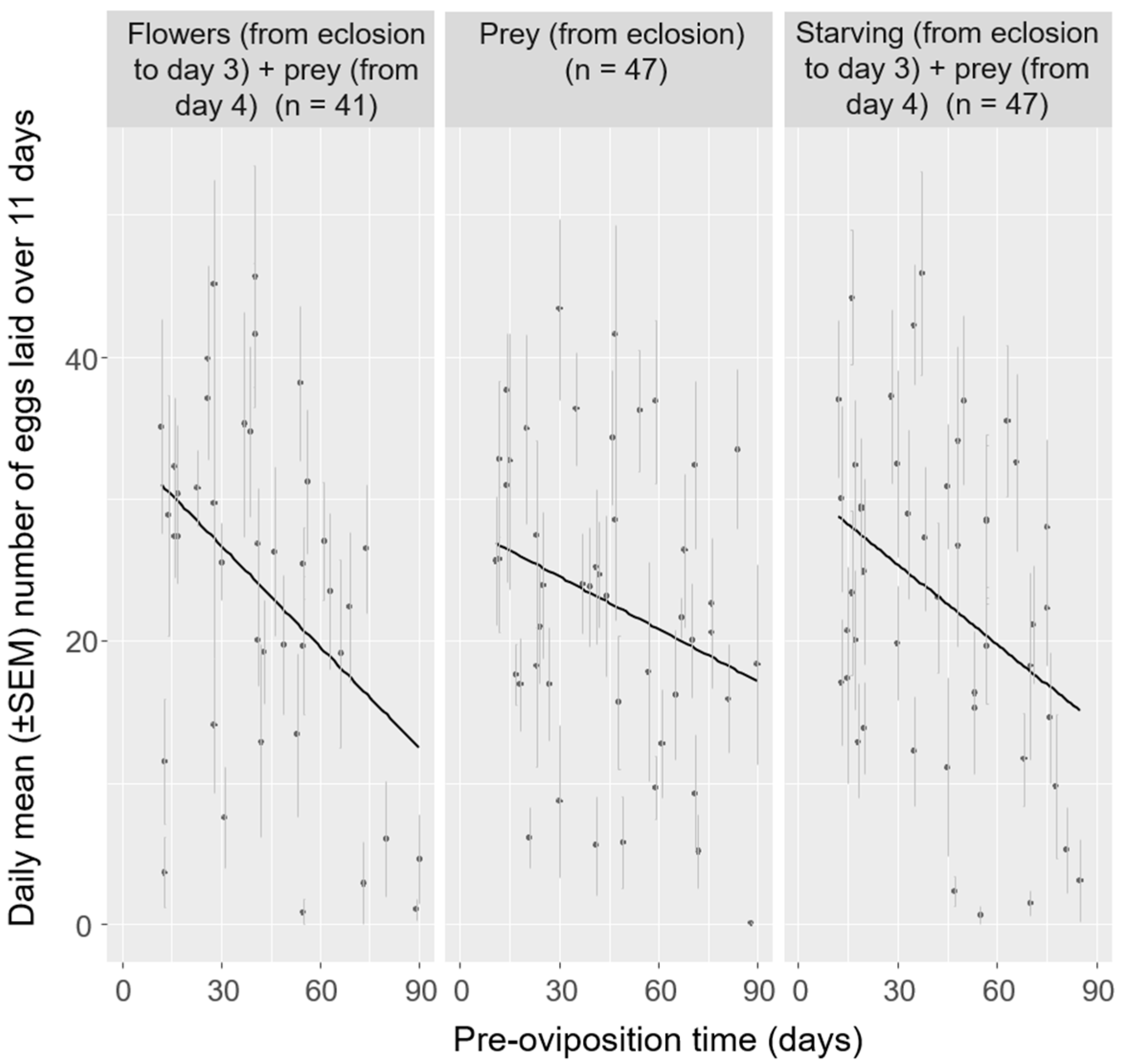
3.2. Effect of Pre-Oviposition Time
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Diet at Adult Eclosion on Pre-Oviposition Time and Fecundity
4.2. Negative Relationships between Pre-Oviposition Time and Fecundity
4.3. Contrasts between Native Populations and Exotic and Long-Term Laboratory Populations of Harmonia axyridis
4.4. Implications for Conservation Biological Control
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, A.D.; Scherber, C.; Brose, U.; Borer, E.T.; Ebeling, A.; Gauzens, B.; Giling, D.P.; Hines, J.; Isbell, F.; Ristok, C.; et al. Biodiversity Enhances the Multitrophic Control of Arthropod Herbivory. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabb6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.F.G. Insect Predator–Prey Dynamics: Ladybird Beetles and Biological Control; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000; pp. 1–257. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, W.E. Give Predators a Complement: Conserving Natural Enemy Biodiversity to Improve Biocontrol. Biol. Control 2019, 135, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M.A.; Nicholls, C.I. Vegetational designs to enhance biological control of insect pests in agroecosystems. In Natural Enemies of Insect Pests in Neotropical Agroecosystems; Souza, B., Vázquez, L., Marucci, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gontijo, L.M. Engineering Natural Enemy Shelters to Enhance Conservation Biological Control in Field Crops. Biol. Control 2019, 130, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassou, A.G.; Tixier, P. Response of Pest Control by Generalist Predators to Local-Scale Plant Diversity: A Meta-Analysis. Ecol. Evol. 2016, 6, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.B.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.L.; Francis, F.; Haubruge, E.; Liu, Y.; Bragard, C.; Cheng, D.F. Adaptation of Wheat-Pea Intercropping Pattern in China to Reduce Sitobion avenae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) Occurrence by Promoting Natural Enemies. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2013, 37, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, S.; Francis, F.; Xu, Q.; Wang, S.; Osawa, N. Perennial flowering strips for conservation biological control of insect pests: From picking and mixing flowers to tailored functional diversity. In Integrative Biological Control; Gao, Y., Hokkanen, H.M.T., Menzler-Hokkanen, I., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 20, pp. 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Gurr, G.M.; Wratten, S.D.; Landis, D.A.; You, M.-S. Habitat Management to Suppress Pest Populations: Progress and Prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatt, S.; Xu, Q.; Francis, F.; Osawa, N. Aromatic Plants of East Asia to Enhance Natural Enemies towards Biological Control of Insect Pests. A Review. Entomol. Gen. 2019, 38, 275–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrycki, J.J.; Harwood, J.D.; Kring, T.J.; O’Neil, R.J. Aphidophagy by Coccinellidae: Application of Biological Control in Agroecosystems. Biol. Control 2009, 51, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodek, I.; Honek, A. Ecology of Coccinellidae; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 1–463. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, E.W. Lady Beetles as Predators of Insects Other than Hemiptera. Biol. Control 2009, 51, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, J.G. Nutritional Aspects of Non-Prey Foods in the Life Histories of Predaceous Coccinellidae. Biol. Control 2009, 51, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, S.; Uyttenbroeck, R.; Lopes, T.; Mouchon, P.; Osawa, N.; Piqueray, J.; Monty, A.; Francis, F. Identification of Flower Functional Traits Affecting Abundance of Generalist Predators in Perennial Multiple Species Wildflower Strips. Arthropod-Plant Interact. 2019, 13, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.W.; Gunther, D.I. The Link between Food and Reproduction in Aphidophagous Predators: A Case Study with Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2005, 102, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodek, I. Food relationships. In Ecology of Coccinellidae; Hodek, I., Honek, A., Eds.; Kluwer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 143–238. [Google Scholar]
- Berkvens, N.; Landyuit, C.; Deforce, K.; Berkvens, D.; Tirry, L.; De Clercq, P. Alternative Foods for the Multicoloured Asian Lady Beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2010, 107, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatt, S.; Osawa, N. The Role of Perilla frutescens Flowers on Fitness Traits of the Ladybird Beetle Harmonia axyridis. BioControl 2019, 64, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, E.W.; Stevenson, A.T.; Richards, D.R. Essential versus Alternative Foods of Insect Predators: Benefits of a Mixed Diet. Oecologia 1999, 121, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawa, N. A Life Table of Ladybird Beetle Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera, Coccinellidae) in Relation to the Aphid Abundance. Jpn. J. Entomol. 1992, 60, 575–579. [Google Scholar]
- Hemptinne, J.-L.; Dixon, A.F.G.; Coffin, J. Attack Strategy of Ladybird Beetles (Coccinellidae): Factors Shaping Their Numerical Response. Oecologia 1992, 90, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osawa, N. Population Field Studies on the Aphidophagous Ladybird Beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): Resource Tracking and Population Characteristics. Popul. Ecol. 2000, 42, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losey, J.E.; Denno, R.F. Positive Predator-Predator Interactions Enhanced Predation Rates and Synergistic Suppression of Aphid Populations. Ecology 1998, 79, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, A.F.G.; Agarwala, B.K. Ladybird-Induced Life–History Changes in Aphids. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 266, 1549–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, B.K.; Yasuda, H.; Sato, S. Life History Response of a Predatory Ladybird, Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), to Food Stress. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2008, 43, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Mishra, G. Omkar Are the Effects of Hunger Stage-Specific? A Case Study in an Aphidophagous Ladybird Beetle. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2021, 111, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, C.; Ponti, L.; Pires, A. Migratory Flight and Pre-Diapause Feeding of Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera) Adults in Agricultural and Mountain Ecosystems of Central Italy. Eur. J. Entomol. 2005, 102, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaji, H. Fauna Japonica, Coccinellidae (Insecta: Coleoptera); Academic Press of Japan: Tokyo, Japan, 1971; pp. 1–345. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, H.E.; Brown, P.M.J.; Adriaens, T.; Berkvens, N.; Borges, I.; Clusella-Trullas, S.; Comont, R.F.; De Clercq, P.; Eschen, R.; Estoup, A.; et al. The Harlequin Ladybird, Harmonia axyridis: Global Perspectives on Invasion History and Ecology. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 997–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandereycken, A.; Durieux, D.; Joie, E.; Sloggett, J.J.; Haubruge, É.; Verheggen, F.J. Is the Multicolored Asian Ladybeetle, Harmonia axyridis, the Most Abundant Natural Enemy to Aphids in Agroecosystems? J. Insect Sci. 2013, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hatt, S.; Xu, Q.; Francis, F.; Chen, J. Intercropping Oilseed Rape with Wheat and Releasing Harmonia axyridis Sex Pheromone in Northern China Failed to Attract and Support Natural Enemies of Aphids. Biotechnol. Agron. Soc. Environ. 2019, 23, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Hatt, S.; Uyttenbroeck, R.; Lopes, T.; Mouchon, P.; Chen, J.; Piqueray, J.; Monty, A.; Francis, F. Do Flower Mixtures with High Functional Diversity Enhance Aphid Predators in Wildflower Strips? Eur. J. Entomol. 2017, 114, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, R.L. The Multicolored Asian Lady Beetle, Harmonia axyridis: A Review of Its Biology, Uses in Biological Control, and Non-Target Impacts. J. Insect Sci. 2003, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mathews, C.R.; Brown, M.W.; Wäckers, F.L. Comparison of Peach Cultivars for Provision of Extrafloral Nectar Resources to Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, S.; Romeis, J.; Collatz, J. Utilization of Plant-Derived Food Sources from Annual Flower Strips by the Invasive Harlequin Ladybird Harmonia axyridis. Biol. Control 2018, 122, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, N. The Effect of Prey Availability on Ovarian Development and Oosorption in the Ladybird Beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2005, 102, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Boufford, D.E.; Ohba, H. Flora of Japan; Kodansha: Tokyo, Japan, 1993; Volume 3a, pp. 1–482. [Google Scholar]
- Specty, O.; Febvay, G.; Grenier, S.; Delobel, B.; Piotte, C.; Pageaux, J.-F.; Ferran, A.; Guillaud, J. Nutritional Plasticity of the Predatory Ladybeetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): Comparison between Natural and Substitution Prey. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2003, 52, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkvens, N.; Bonte, J.; Berkvens, D.; Tirry, L.; De Clercq, P. Influence of Diet and Photoperiod on Development and Reproduction of European Populations of Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Bio. Control 2008, 53, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriyuki, S.; Osawa, N. Intrinsic Prey Suitability in Specialist and Generalist Harmonia Ladybirds: A Test of the Trade-off Hypothesis for Food Specialization. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2012, 144, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 25 August 2020).
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 1–350. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, E.L.; Meier, P. Nonparametric Estimation from Incomplete Observations. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1958, 53, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, D.; Maechler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Fitting Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 67, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–213. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, A.F.G.; Agarwala, B.K. Triangular Fecundity Function and Ageing in Ladybird Beetles. Ecol. Entomol. 2002, 27, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, R.H.; Wilson, E.O. The Theory of Island Biogeography; Monographs in Population Biology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1967; pp. 1–203. [Google Scholar]
- Varpe, Ø.; Jørgensen, C.; Tarling, G.A.; Fiksen, Ø. Early Is Better: Seasonal Egg Fitness and Timing of Reproduction in a Zooplankton Life-History Model. Oikos 2007, 116, 1331–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catry, T.; Moreira, F.; Alcazar, R.; Rocha, P.A.; Catry, I. Mechanisms and Fitness Consequences of Laying Decisions in a Migratory Raptor. Behav. Ecol. 2017, 28, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osawa, N. Ecology of Harmonia axyridis in Natural Habitats within Its Native Range. BioControl 2011, 56, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Omkar, O. Ageing Trajectory and Longevity Trade-off in an Aphidophagous Ladybird, Propylea dissecta (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2006, 103, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayward, A.D.; Mar, K.U.; Lahdenperä, M.; Lummaa, V. Early Reproductive Investment, Senescence and Lifetime Reproductive Success in Female Asian Elephants. J. Evol. Biol. 2014, 27, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stearns, S.C. The Evolution of Life History Traits: A Critique of the Theory and a Review of the Data. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1977, 8, 145–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooper, K.R. Risk-Spreading and Bet-Hedging in Insect Population Biology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 535–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, E.W. Searching and Reproductive Behaviour of Female Aphidophagous Ladybirds (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): A Review. Eur. J. Entomol. 2003, 100, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Root, R.B.; Kareiva, P.M. The Search for Resources by Cabbage Butterflies (Pieris rapae): Ecological Consequences and Adaptive Significance of Markovian Movements in a Patchy Environment. Ecology 1984, 65, 147–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, J.T.; Strong, D.R. Substantially Submaximal Oviposition Rates by a Mymarid Egg Parasitoid in the Laboratory and Field. Ecology 1993, 74, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.M.J.; Adriaens, T.; Bathon, H.; Cuppen, J.; Goldarazena, A.; Hägg, T.; Kenis, M.; Klausnitzer, B.E.M.; Kovář, I.; Loomans, A.J.M.; et al. Harmonia axyridis in Europe: Spread and Distribution of a Non-Native Coccinellid. BioControl 2008, 53, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, P.M.J.; Thomas, C.E.; Lombaert, E.; Jeffries, D.L.; Estoup, A.; Lawson Handley, L.-J. The Global Spread of Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae): Distribution, Dispersal and Routes of Invasion. BioControl 2011, 56, 623–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeh, A.; Hufbauer, R.A.; Estoup, A.; Ravigné, V.; Frachon, L.; Facon, B. Biological Invasion and Biological Control Select for Different Life Histories. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burgio, G.; Santi, F.; Maini, S. On Intra-Guild Predation and Cannibalism in Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) and Adalia bipunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol. Control 2002, 24, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, E. Intraguild Predation among Aphidophagous Predators. Eur. J. Entomol. 2005, 102, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lopes, T.; Bodson, B.; Francis, F. Associations of Wheat with Pea Can Reduce Aphid Infestations. Neotrop. Entomol. 2015, 44, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhmedi, A.; Haubruge, E.; Francis, F. Effect of Stinging Nettle Habitats on Aphidophagous Predators and Parasitoids in Wheat and Green Pea Fields with Special Attention to the Invader Harmonia axyridis Pallas (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Entomol. Sci. 2009, 12, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellhorn, N.A.; Gagic, V.; Bommarco, R. Time Will Tell: Resource Continuity Bolsters Ecosystem Services. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomine, E.; Rusch, A.; Supplisson, C.; Monticelli, L.S.; Amiens-Desneux, E.; Lavoir, A.-V.; Desneux, N. Highly Diversified Crop Systems Can Promote the Dispersal and Foraging Activity of the Generalist Predator Harmonia axyridis. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 40, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| No | Yes | Rate (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| At least one batch hatched | 11 | 124 | 91.9 |
| Flower | 4 | 37 | 90.2 |
| Prey | 2 | 45 | 95.7 |
| Starving | 5 | 42 | 89.4 |
| At least two batches hatched | 20 | 115 | 85.2 |
| Flower | 9 | 32 | 78.0 |
| Prey | 4 | 43 | 91.5 |
| Starving | 7 | 40 | 85.1 |
| All three batches hatched | 45 | 90 | 66.7 |
| Flower | 14 | 27 | 65.9 |
| Prey | 18 | 29 | 61.7 |
| Starving | 13 | 34 | 72.3 |
| df | χ2 | p | Estimate 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| At least one batch had hatched eggs | ||||
| Pre-oviposition time | 1 | 12.75 | <0.001 *** | - |
| Diet | 2 | 2.503 | 0.286 | |
| Pre-oviposition time × diet | 2 | 1.884 | 0.39 | |
| At least two batches had hatched eggs | ||||
| Pre-oviposition time | 1 | 16.79 | <0.001 *** | - |
| Diet | 2 | 4.766 | 0.092 | |
| Pre-oviposition time × diet | 2 | 4.503 | 0.105 | |
| All three batches had hatched eggs | ||||
| Pre-oviposition time | 1 | 13.59 | <0.001 *** | - |
| Diet | 2 | 1.117 | 0.572 | |
| Pre-oviposition time × diet | 2 | 0.126 | 0.939 |
| df | F | p | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flowers | 1, 39 | 9.391 | 0.004 ** | 0.19 |
| Prey | 1, 45 | 4.845 | 0.033 * | 0.10 |
| Starving | 1, 45 | 8.022 | 0.007 ** | 0.15 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hatt, S.; Osawa, N. High Variability in Pre-Oviposition Time Independent of Diet Available at Eclosion: A key Reproductive Trait in the Ladybird Beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Its Native Range. Insects 2021, 12, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050382
Hatt S, Osawa N. High Variability in Pre-Oviposition Time Independent of Diet Available at Eclosion: A key Reproductive Trait in the Ladybird Beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Its Native Range. Insects. 2021; 12(5):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050382
Chicago/Turabian StyleHatt, Séverin, and Naoya Osawa. 2021. "High Variability in Pre-Oviposition Time Independent of Diet Available at Eclosion: A key Reproductive Trait in the Ladybird Beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Its Native Range" Insects 12, no. 5: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050382
APA StyleHatt, S., & Osawa, N. (2021). High Variability in Pre-Oviposition Time Independent of Diet Available at Eclosion: A key Reproductive Trait in the Ladybird Beetle Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Its Native Range. Insects, 12(5), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12050382








