Cytochrome P450s Are Essential for Insecticide Tolerance in the Endoparasitoid Wasp Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Identification of P450 Genes in M. pulchricornis
2.3. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. Insecticide Treatment
2.5. qRT-PCR Validation
2.6. dsRNA Synthesis and Injection RNA Interference
3. Results
3.1. Identification of P450s and Phylogenetic Analyses
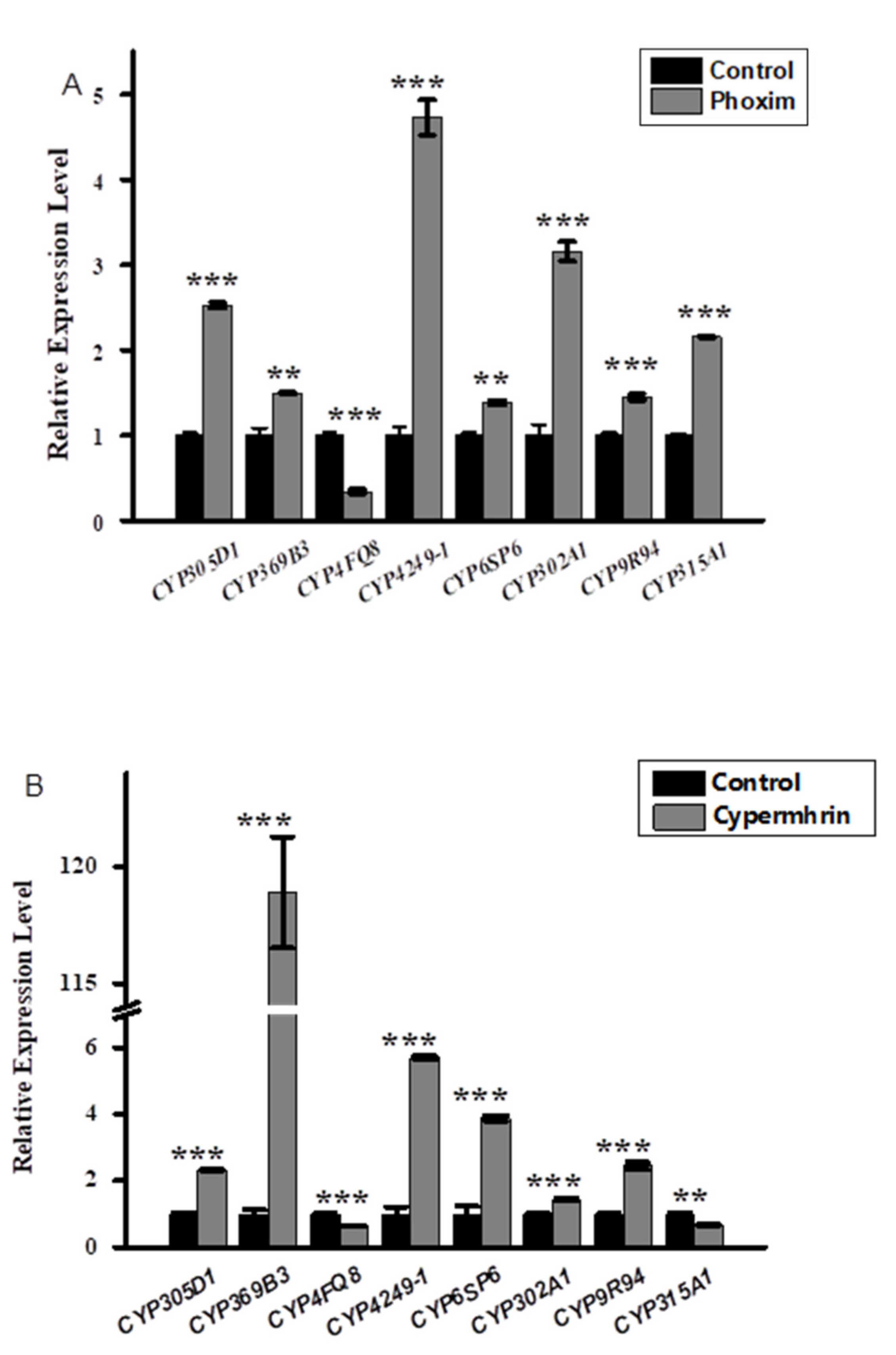
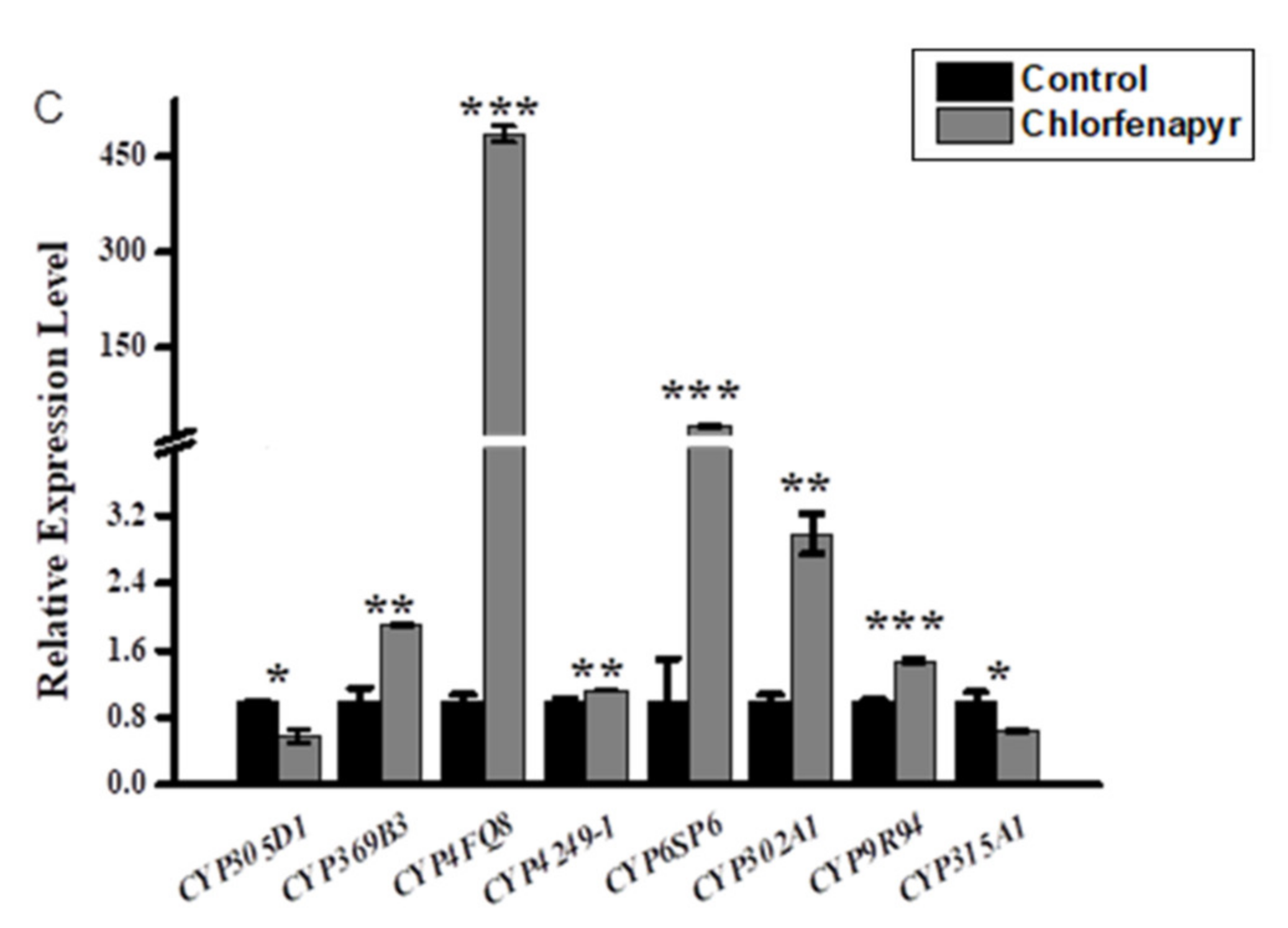
3.2. Relative Expression Profiling of P450s after Phoxim, Cypermethrin and Chlorfenapyr Treatment
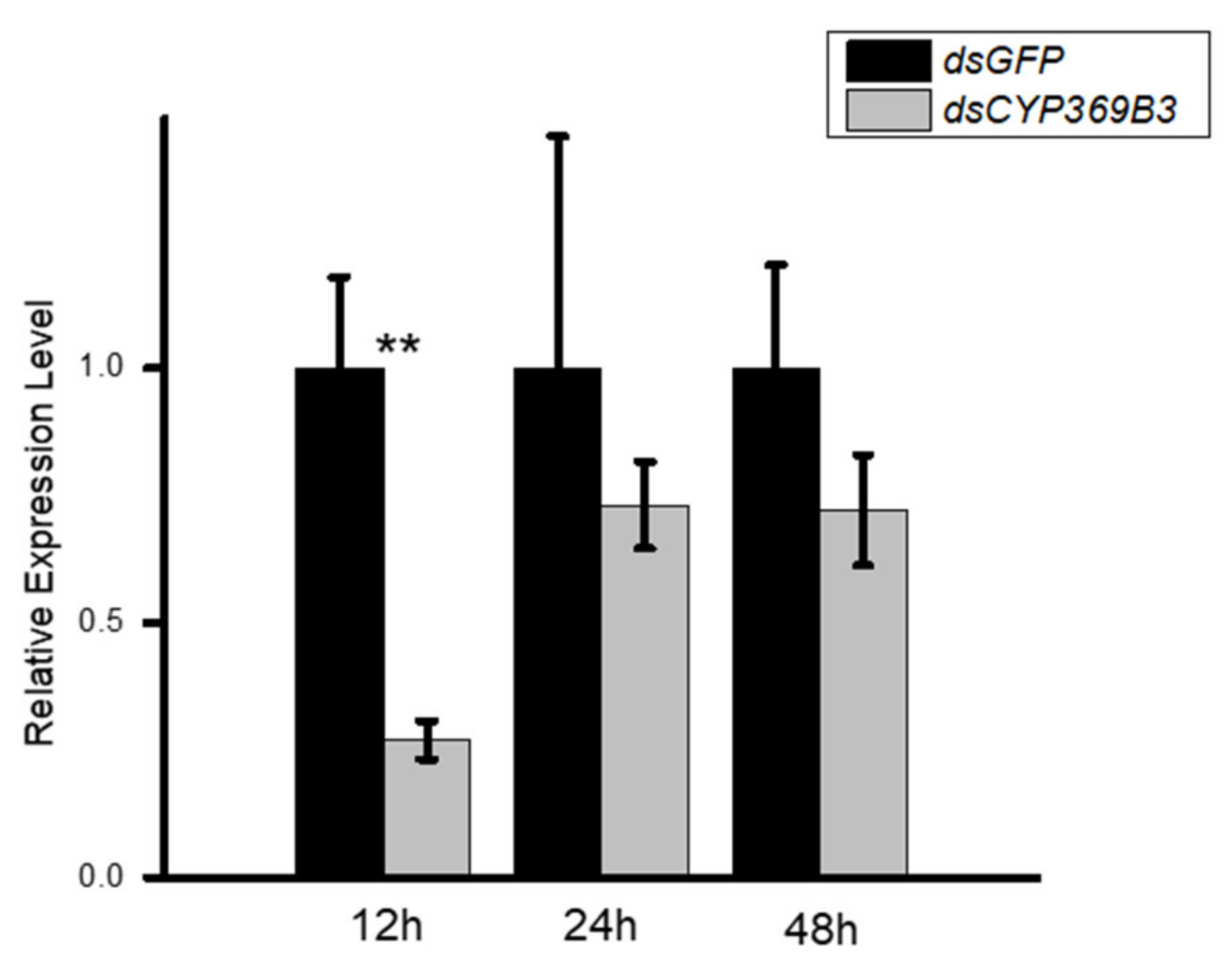
3.3. RNAi for CYP369B3
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feyereisen, R. Insect P450 Enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1999, 44, 507–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, S.; Cohen, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Kumar, D.; Thiel, W. P450 Enzymes: Their Structure, Reactivity, and Selectivity—Modeled by QM/MM Calculations. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 949–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyereisen, R. Insect CYP genes and P450 enzymes. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 8, 236–316. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Schuler, M.A.; Berenbaum, M.R. Molecular Mechanisms of Metabolic Resistance to Synthetic and Natural Xenobiotics. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, C.; Field, L.M. Gene amplification and insecticide resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 886–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, W.L.; Cao, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.X.; Li, S.G. Identification of putative cytochrome P450 monooxygenase genes from the small white butterfly, Pieris rapae (Lepidoptera: Pieridae), and their response to insecticides. Arch. Insect Biochem. 2018, 98, e21455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Cheng, Y.; Li, W.; Li, Y.; Zeng, R.; Song, Y. Activation of CncC pathway by ROS burst regulates cytochrome P450 CYP6AB12 responsible for λ-cyhalothrin tolerance in Spodoptera litura. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 387, 121698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, M.; Jia, Z.; Ahmat, T.; Xie, L.; Jiang, W. Resistance to neonicotinoid insecticides and expression changes of eighteen cytochrome P450 genes in field populations of Bemisia tabaci from Xinjiang, China. Entomol. Res. 2020, 50, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, C.P.C.; Orr, D.B.; Van Duyn, J.W. Effect of insecticides on Trichogramma exiguum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) preimaginal development and adult survival. J. Econ. Entomol. 2000, 93, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.; Feng, S.; Meng, L.; Li, B. Departure mechanisms for host search on high-density patches by the parasitoid, Meteorus pulchricornis. J. Insect Sci. 2014, 14, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Shao, Y.; Xing, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Ofori, A.D.; Tu, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Identification of glutathione-S-transferase genes by transcriptome analysis in Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and their expression patterns under stress of phoxim and cypermethrin. Comp. Biochem. Phys. D 2019, 31, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, B. Developmental interactions between Spodoptera exigua (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera) and its uniparental endoparasitoid, Meteorus pulchricornis (Braconidae: Hymenoptera). Biol. Control. 2006, 38, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.; Liao, C.W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Song, W.M.; He, P.; Zhang, J.; Wu, F.A. Candidate chemosensory genes identified in the endoparasitoid Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) by antennal transcriptome analysis. Comp. Biochem. Phys. D 2017, 22, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.L.; Wu, Y.D. Pesticide Resistance and Management of Helicoverpa Armigera; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1995; pp. 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using Maximum Likelihood, Evolutionary Distance, and Maximum Parsimony Methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheng, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Yan, M.W.; Shao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wu, F.A.; Wang, J. Evaluation of sensitivity to phoxim and cypermethrin in an endoparasitoid, Meteorus pulchricornis (Wesmael) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), and its parasitization Efficiency Under Insecticide Stress. J. Insect Sci. 2021, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.L. Experimental study on the control effect of 24% chlorfenapyr suspending agent on the mulberry pest, Glyphodes pyloalis (Walker). China Seric. 2012, 33, 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Liu, N. Genome analysis of cytochrome P450s and their expression profiles in insecticide resistant mosquitoes, Culex quinquefasciatus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Deng, S.; Wei, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Yin, C.; Du, T.; Guo, Z.; Xia, J.; Yang, Z.; et al. MAPK-directed activation of the whitefly transcription factor CREB leads to P450-mediated imidacloprid resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 10246–10253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Liu, N. Identification and characterization of detoxification genes in two cerambycid beetles, Rhaphuma horsfieldi and Xylotrechus quadripes (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae: Clytini). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B 2020, 243, 110431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlogiannitis, S.; Mavridis, K.; Dermauw, W.; Snoeck, S.; Katsavou, E.; Morou, E.; Harizanis, P.; Swevers, L.; Hemingway, J.; Feyereisen, R.; et al. Reduced proinsecticide activation by cytochrome P450 confers coumaphos resistance in the major bee parasite Varroa destructor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2020380118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vatanparast, M.; Ahmed, S.; Lee, D.; Hwang, S.H.; Hammock, B.; Kim, Y. EpOMEs act as immune suppressors in a lepidopteran insect, Spodoptera exigua. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yu, Z.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, E.; Li, S.; Zhu, K.Y.; Feyereisen, R.; Zhang, J. Knockdown of LmCYP303A1 alters cuticular hydrocarbon profiles and increases the susceptibility to desiccation and insecticides in Locusta migratoria. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2020, 168, 104637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudianos, C.; Ranson, H.; Johnson, R.M.; Biswas, S.; Schuler, M.A.; Berenbaum, M.R.; Feyereisen, R.; Oakeshott, J.G. A deficit of detoxification enzymes: Pesticide sensitivity and environmental response in the honeybee. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 615–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarès, S.; Bergé, J.B.; Amichot, M. Cloning and Expression of Cytochrome P450 Genes Belonging to the CYP4 Family and to a Novel Family, CYP48, in Two Hymenopteran Insects, Trichogramma cacœciae and Apis mellifera. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 268, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakeshott, J.G.; Johnson, R.M.; Berenbaum, M.R.; Ranson, H.; Cristino, A.S.; Claudianos, C. Metabolic enzymes associated with xenobiotic and chemosensory responses in Nasonia vitripennis. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, C.; Ye, X. Evolution Analysis of Cytochrome P450 Gene Family in Parasitoid Wasps. Chin. J. Biol. Control. 2019, 35, 335–342. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Pu, X.; Shu, B.; Bin, S.; Lin, J. Transcriptome analysis of putative detoxification genes in the Asian citrus psyllid, Diaphorina citri. Pest Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3857–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, A.; Stegeman, J.J.; Goldstone, J.V.; Nelson, D.R.; Kim, E.Y.; Tanabe, S.; Iwata, H. Cytochrome P450 CYP2 genes in the common cormorant: Evolutionary relationships with 130 diapsid CYP2 clan sequences and chemical effects on their expression. Comp. Biochem. Phys. C 2011, 153, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Z.; Moural, T.W.; Shah, K.; Palli, S.R. Integrated analysis of cytochrome P450 gene superfamily in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Feyereisen, R. Evolution of insect P450. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, T.; Burton, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, W.; Yu, L. Metabolomic analysis of honey bee, Apis mellifera L. response to thiacloprid. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2018, 152, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Ye, C.L.; Zheng, M.H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, L.F.; Lui, H. Research advances in Drosophila drug resistance mediated by cytochrome P450. Genom. Appl. Biology. 2019, 38, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar]
- Hatano, R.; Scott, J.G. Anti-P450lpr Antiserum Inhibits the Activation of Chlorpyrifos to Chlorpyrifos Oxon in House Fly Microsomes. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 1993, 45, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joußen, N.; Schuphan, I.; Schmidt, B. Metabolism of Methoxychlor by the P450-Monooxygenase CYP6G1 Involved in Insecticide Resistance of Drosophila melanogaster after Expression in Cell Cultures of Nicotiana tabacum. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 722–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Wen, Y.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Z.; Han, Z. Biochemical mechanisms of imidacloprid resistance in Nilaparvata lugens: Over-expression of cytochrome P450 CYP6AY1. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Xu, P.F.; Gong, P.P.; Wan, H.; Li, J.H. The current susceptibilities of brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens to triflumezopyrim and other frequently used insecticides in China. Insect Sci. 2021, 28, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.H. Molecular mechanisms of insecticide resistance mediated by cytochrome P450s in insects. Acta. Entomol. Sin. 2014, 57, 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Su, X. Effects of chlorantraniliprole and fipronil on cytochrome P450 genes in oriental armyworm Mythimna separata. J. Plant Prot. 2019, 46, 563–573. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.H.; Yang, B.J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, Z.W. Metabolic resistance in Nilaparvata lugens to etofenprox, a non-ester pyrethroid insecticide. Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2017, 136, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.X.; Li, R.; Zhu, B.; Gao, X.W.; Liang, P. Overexpression of cytochrome P450 CYP6BG1 may contribute to chlorantraniliprole resistance in Plutella xylostella (L.). Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, K. Metabolic Resistance and Regulation Mechanism of Nitenpyram in Nilaparvata Lugens. Ph.D. Thesis, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, X.; Xu, P.; Li, Z.; Ali, E.; Wan, H.; Li, J. Overexpression of CYP6ER1 associated with clothianidin resistance in Nilaparvata lugens (Stal). Pestic. Biochem. Phys. 2019, 154, 39–45. [Google Scholar]



| Gene Name | Acc. No | Encoded Protein Length/aa | Molecular Weight/kD | Isoelectric Point | Blastx Best Hit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Protein Name | E Value | Identity % | Accession | |||||
| MpulCYP4G283 | MZ169337 | 557 | 63.23 | 7.65 | Fopius arisanus | cytochrome P450 4g15 | 0 | 89.61 | XP_011304723.1 |
| MpulCYP4G284 | MZ169336 | 555 | 63.44 | 6.57 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 4g15 | 0 | 80.29 | XP_014300333.1 |
| MpulCYP4AV17 | MZ169338 | 313 | 35.86 | 6 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 4c3-like | 1.00 × 10−155 | 69.01 | XP_008555432.1 |
| MpulCYP4FQ8 | MZ169339 | 518 | 59.79 | 8.61 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 4C1 | 0 | 69.56 | XP_008550233.1 |
| MpulCYP6AS186 | MZ169329 | 504 | 58.35 | 9.18 | Microplitis demolitor | probable cytochrome P450 6a14 | 0 | 59.84 | XP_008560120.1 |
| MpulCYP6AS187 | MZ169330 | 500 | 57.2 | 9.25 | Microplitis demolitor | probable cytochrome P450 6a14 | 0 | 56.10 | XP_008560120.1 |
| MpulCYP6AS188 | MZ169333 | 500 | 57.59 | 9.15 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 6k1 | 0 | 57.75 | XP_008557726.1 |
| MpulCYP6AS189 | MZ169331 | 499 | 57.42 | 8.28 | Microplitis demolitor | probable cytochrome P450 6a14 | 0 | 67.34 | XP_008560120.1 |
| MpulCYP6AS190 | MZ169332 | 502 | 58.13 | 8.49 | Microplitis demolitor | probable cytochrome P450 6a14 | 0 | 68.76 | XP_008560120.1 |
| MpulCYP6BC12 | MZ169334 | 522 | 60.41 | 8.85 | Polistes dominula | cytochrome P450 6B5-like | 0 | 65.31 | XP_015174482.1 |
| MpulCYP6JT7 | MZ169328 | 498 | 56.83 | 6.26 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 6a2-like | 0 | 61.04 | XP_014299556.1 |
| MpulCYP6SP5 | MZ169326 | 512 | 58.99 | 9.18 | Diachasma alloeum | cytochrome P450 6k1 | 0 | 61.05 | XP_015121128.1 |
| MpulCYP6SP6 | MZ169327 | 502 | 58.3 | 9.31 | Diachasma alloeum | cytochrome P450 6k1 | 0 | 57.49 | XP_015121128.1 |
| MpulCYP6SQ-1 | MZ169325 | 268 | 30.38 | 6.13 | Orussus abietinus | cytochrome P450 6k1-like | 3.00 × 10−139 | 70.63 | XP_012272474.2 |
| MpulCYP9P37 | MZ169322 | 505 | 58.95 | 7.58 | Belonocnema treatae | cytochrome P450 9e2-like | 0 | 58.16 | XP_033219303.1 |
| MpulCYP9R94 | MZ169321 | 508 | 58.7 | 7.97 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 9e2-like | 0 | 61.55 | XP_008557951.2 |
| MpulCYP9R95 | MZ169323 | 507 | 58.28 | 6.9 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 9e2-like | 0 | 58.65 | XP_008557951.2 |
| MpulCYP12-1 | MZ169346 | 224 | 25.57 | 9.16 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 CYP12A2 | 8.00 × 10−96 | 71.14 | XP_008548500.1 |
| MpulCYP301A1 | MZ169345 | 525 | 60.42 | 8.48 | Microplitis demolitor | probable cytochrome P450 301a1, mitochondrial | 0 | 83.69 | XP_008548437.1 |
| MpulCYP301B1 | MZ169342 | 513 | 60 | 8.8 | Microplitis demolitor | probable cytochrome P450 49a1 | 0 | 76.26 | XP_014298339.1 |
| MpulCYP302A1 | MZ169344 | 302 | 34.26 | 8.19 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 302a1, mitochondrial | 1.00 × 10−141 | 66.01 | XP_008552208.1 |
| MpulCYP305D1 | MZ169319 | 492 | 56.32 | 8.58 | Microplitis demolitor | probable cytochrome P450 305a1 | 0 | 69.56 | XP_014295888.1 |
| MpulCYP315A1 | MZ169343 | 222 | 25.09 | 7.71 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 315a1, mitochondrial | 9.00 × 10−92 | 0.5936 | XP_008559430.1 |
| MpulCYP336X1 | MZ169324 | 504 | 58.01 | 8.55 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 9e2 | 0 | 0.5029 | XP_008557820.1 |
| MpulCYP369B3 | MZ169320 | 505 | 116.83 | 6.75 | Microplitis demolitor | probable cytochrome P450 304a1 | 0 | 59.12 | XP_008561134.1 |
| MpulCYP4249-1 | MZ169335 | 258 | 29.53 | 8.64 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 4C1-like | 9.00 × 10−105 | 57.60 | XP_014298773.1 |
| MpulCYP4249-2 | MZ169340 | 209 | 23.92 | 8.91 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 4C1-like | 6.00 × 10−73 | 52.48 | XP_014298773.1 |
| MpulCYP4249-3 | MZ169341 | 301 | 34.15 | 5.77 | Microplitis demolitor | cytochrome P450 4C1-like | 4.00 × 10−92 | 48.44 | XP_014298773.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, X.; Yan, M.; Pang, H.; Wu, F.; Wang, J.; Sheng, S. Cytochrome P450s Are Essential for Insecticide Tolerance in the Endoparasitoid Wasp Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Insects 2021, 12, 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12070651
Xing X, Yan M, Pang H, Wu F, Wang J, Sheng S. Cytochrome P450s Are Essential for Insecticide Tolerance in the Endoparasitoid Wasp Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Insects. 2021; 12(7):651. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12070651
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Xiaorong, Mengwen Yan, Huilin Pang, Fu’an Wu, Jun Wang, and Sheng Sheng. 2021. "Cytochrome P450s Are Essential for Insecticide Tolerance in the Endoparasitoid Wasp Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae)" Insects 12, no. 7: 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12070651
APA StyleXing, X., Yan, M., Pang, H., Wu, F., Wang, J., & Sheng, S. (2021). Cytochrome P450s Are Essential for Insecticide Tolerance in the Endoparasitoid Wasp Meteorus pulchricornis (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Insects, 12(7), 651. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12070651






