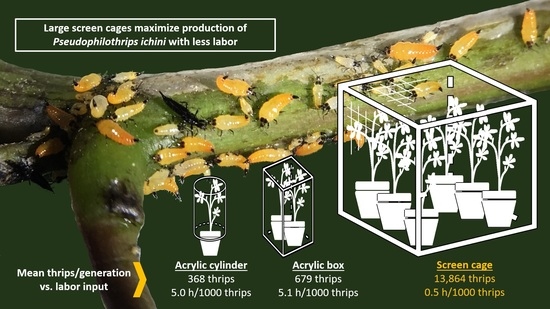
Advances in Mass Rearing Pseudophilothrips ichini (Hood) (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae), a Biological Control Agent for Brazilian Peppertree in Florida
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Production
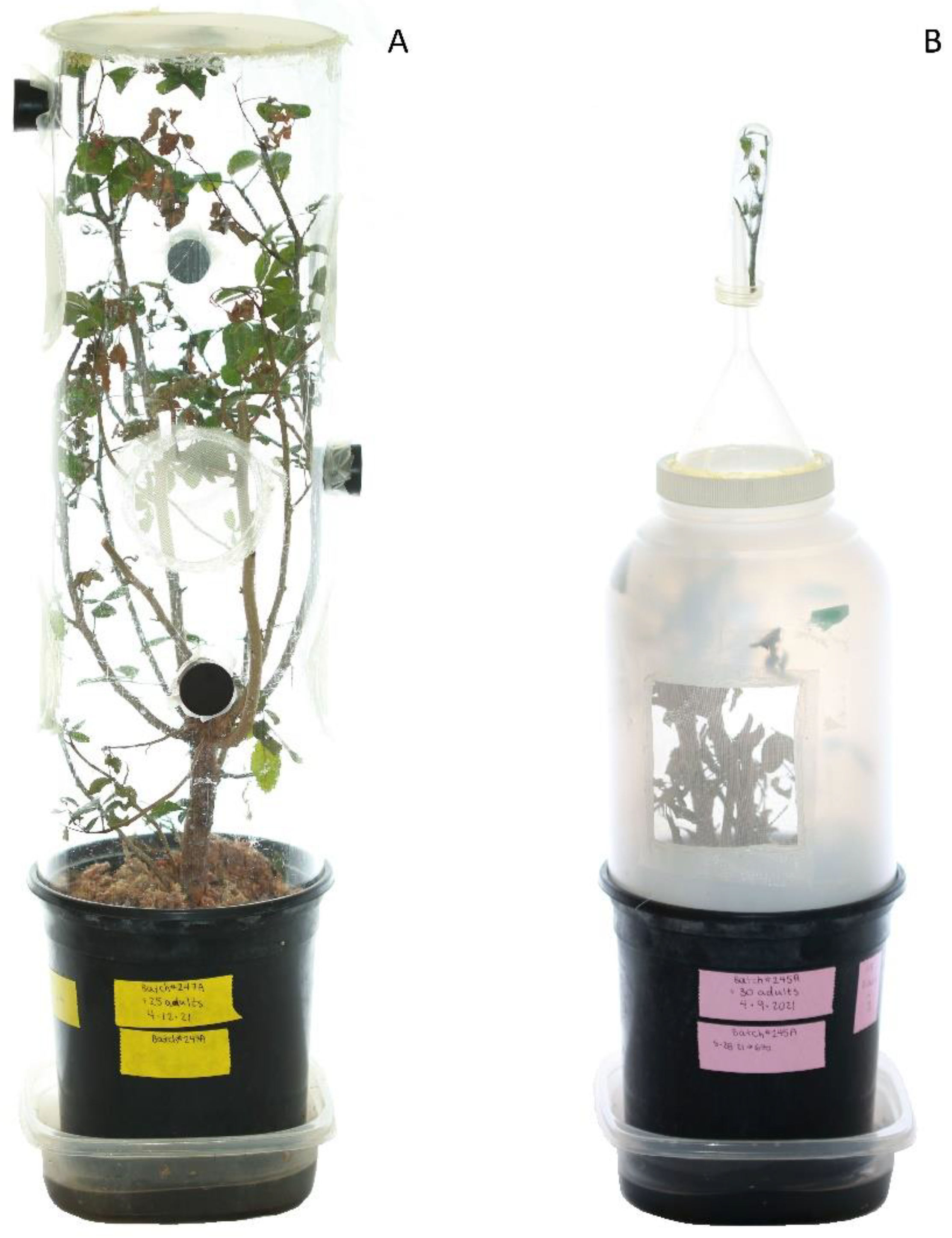
2.2. Thrips Rearing Cages
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Comparisons between Cage Types
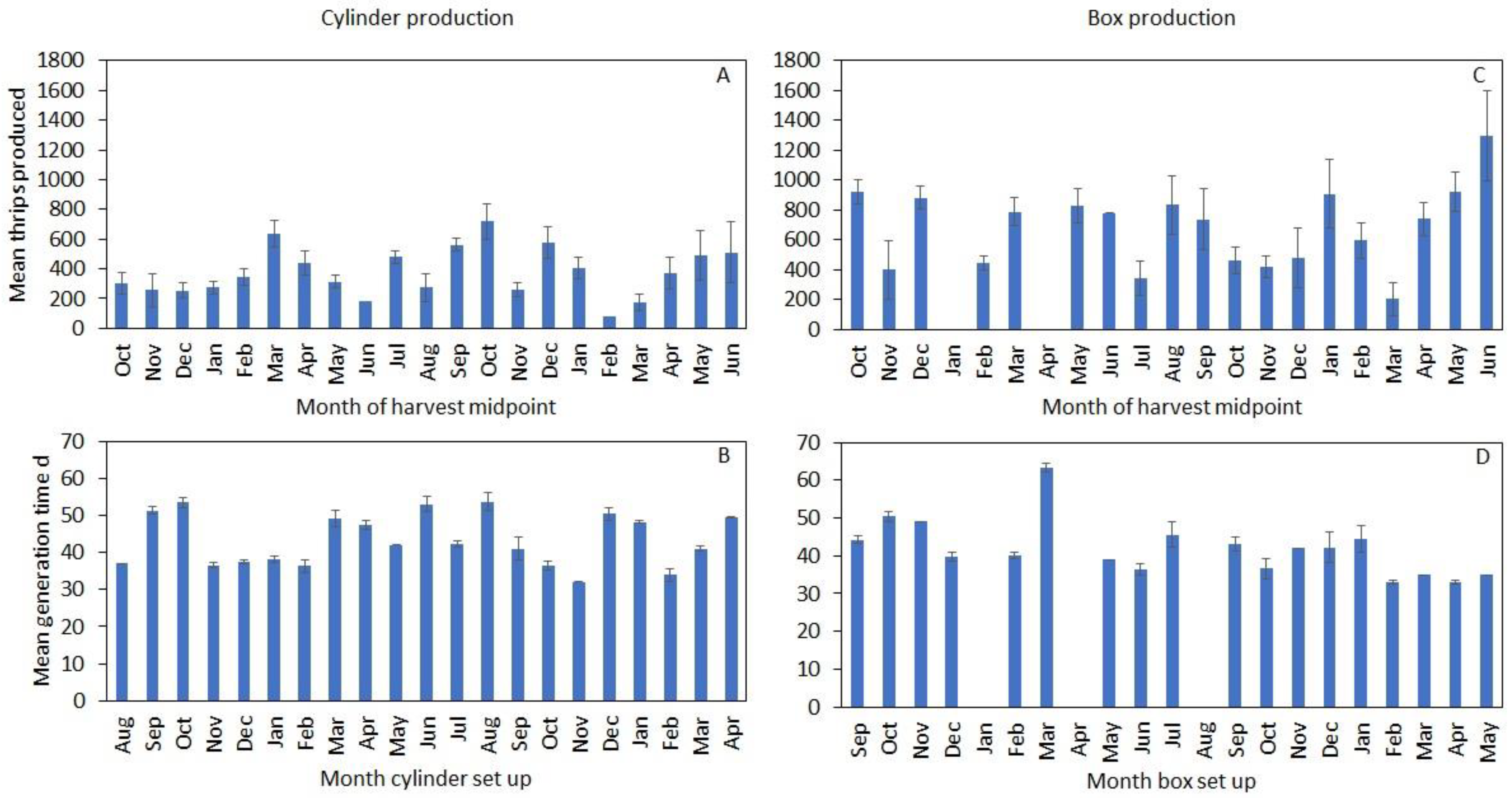
3.2. Temporal Trends in Production
3.3. Temperature and Humidity Variations in Screen Cages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barkley, F.A. Schinus L. Brittonia 1944, 5, 160–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, L.; Pernas, T.; Hill, S.D. Mapping invasive-plant distributions in the Florida Everglades using the digital aerial sketch-mapping technique. Invasive Plant Sci. Manag. 2014, 7, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, D.C.; Simberloff, D.; Hofstetter, R.L.; Haller, W.T.; Sutton, D. The ecological impact of nonindigenous plants. In Strangers in Paradise: Impact and Management of Nonindigenous Species in Florida; Simberloff, D., Schmitz, D.C., Brown, T.C., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; pp. 39–61. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, J.M. Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi. In Invasive Plants of California’s Wildlands; Bossard, C.C., Randall, J.M., Hoshovsky, M.C., Eds.; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2000; Volume 360, pp. 282–287. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshioka, E.R.; Markin, G.P. Efforts of biological control of Christmas berry (Schinus terebinthifolius) in Hawaii. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Exotic Pest Plants, Miami, FL, USA, 2–4 November 1988; Center, T.D., Doren, R.F., Hofstetter, R.L., Myers, R.L., Whiteaker, L.D., Eds.; U.S. Department of the Interior, National Park Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; pp. 377–387. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez, L.; Christoffersen, B. The Quiet Invasion: A Guide to Invasive Plants of the Galveston Bay Area; Galveston Bay Estuary Program: Houston, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Batianoff, G.N.; Franks, A.J. Environmental weed invasions on south-east Queensland foredunes. Proc. R. Soc. Qld. 1998, 107, 15–34. [Google Scholar]
- Presland, G. On the peppertree Schinus L. in Australia. Vic. Nat. 2020, 137, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- McJunkin, D.M. Aspects of Cypress Domes in Southeastern Florida: A Study in Micro-Phytogeography. Master’s Thesis, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 15 December 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, P.M. Exotic plant control and restoration management of a south Florida hammock. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Exotic Pest Plants, Miami, FL, USA, 2–4 November 1988; Center, T.D., Doren, R.F., Hofstetter, R.L., Myers, R.L., Whiteaker, L.D., Eds.; U.S. Department of the Interior, National Park Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1991; pp. 73–85. [Google Scholar]
- Loope, L.L.; Dunevitz, V.L. Impact of Fire Exclusion and Invasion of Schinus Terebinthifolius on Limestone Rockland Pine Forests of Southeastern Florida; Report T-645; U.S. Department of the Interior, Everglades National Park, South Florida Research Center: Homestead, FL, USA, 1981; 30p. [Google Scholar]
- Schmalzer, P.A. Biodiversity of saline and brackish marshes of the Indian River Lagoon: Historic and current patterns. Bull. Mar. Sci. 1995, 57, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers, L.; Bodle, M.J.; Black, D.; Laroche, F. Status of Nonindigenous Species; South Florida Water Management District: West Palm Beach, FL, USA, 2012; 7-1-7-35. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, C.J.; Krauss, N.L. Recent introductions for biological control in Hawaii: VII. Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 1962, 18, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Krauss, N.L. Biological control investigations on Christmas Berry (Schinus terebinthifolius) and Emex (Emex spp.). Proc. Hawaii. Entomol. Soc. 1963, 18, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, G.S.; Mc Kay, F.; Vitorino, M.D.; Manrique, V.; Diaz, R.; Overholt, W.A. Biological control of the invasive weed Schinus terebinthifolia (Brazilian Peppertree): A review of the project with an update on the proposed agents. Southeast. Nat. 2016, 15, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, G.S.; Manrique, V.; Overholt, W.A.; McKay, F.; Dyer, K. Quarantine host range testing of Pseudophilothrips ichini, a potential biological control agent of Brazilian peppertree, Schinus terebinthifolia, in North America and Hawaii. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2017, 162, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winston, R.L.; Schwarzländer, M.; Hinz, H.L.; Day, M.D.; Cock, M.J.W.; Julien, M.H. Biological Control of Weeds: A World Catalogue of Agents and Their Target Weeds; FHTET-2014-04; USDA Forest Service, Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team: Morgantown, WV, USA, 2020; pp. 1–838. Available online: https://www.ibiocontrol.org/catalog/ (accessed on 7 July 2021).
- Hoddle, M.S.; Mound, L.A.; Paris, D.L. Thrips of California; CBIT Publishing: Brisbane, QLD, Australia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, G.S.; Silverson, N.; Dyer, K.; Kay, F.M. Brazilian collections and laboratory biology of the thrips Pseudophilothrips ichini (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae): A potential biological control agent of the invasive weed Brazilian peppertree (Sapindales: Anacardiaceae). Fla. Entomol. 2016, 99, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manrique, V.; Diaz, R.; Erazo, L.; Reddi, N.; Wheeler, G.S.; Williams, D.; Overholt, W.A. Comparison of two populations of Pseudophilothrips ichini (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae) as candidates for biological control of the invasive weed Schinus terebinthifolia (Sapindales: Anacardiaceae). Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 24, 518–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T.; Loomans, A.J. Evaluation of an improved method for mass-rearing of thrips and a thrips parasitoid. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2001, 101, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, D.; Farkas, P.; Sojnóczki, A.; Király, K.; Fail, J. Laboratory rearing of Thrips tabaci Lindeman: A review. Bodenkultur 2015, 66, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Pakyari, H.; McNeill, M.R. Effects of photoperiod on development and demographic parameters of the predatory thrips Scolothrips longicornis fed on Tetranychus urticae. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2020, 110, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, G.; Jones, E.; Broggi, E.; Halbritter, D. The impact and production of the Brazilian peppertree biological control agent Pseudophilothrips ichini (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae) is affected by the level of host-plant fertilization. Biol. Control. 2018, 121, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuda, J.P.; Gillmore, J.L.; Medal, J.C.; Pedrosa-Macedo, J.H. Mass rearing of Pseudophilothrips ichini (Thysanoptera: Phlaeo-thripidae), an approved biological control agent for Brazilian peppertree, Schinus terebinthifolius (Sapindales: Anacardiaceae). Fla. Entomol. 2008, 91, 338–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wineriter, S.A.; Buckingham, G.R.; Frank, J.H. Host range of Boreioglycaspis melaleucae Moore (Hemiptera: Psyllidae), a potential biocontrol agent of Melaleuca quinquenervia (Cav.) S.T. Blake (Myrtaceae), under quarantine. Biol. Control. 2003, 27, 273–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, M.; Balciunas, J.K.; Jones, P. Biology and host-range of Boreioglycaspis melaleucae (Hemiptera: Psyllidae), potential biological control agent for Melaleuca quinquenervia (Myrtaceae). Environ. Èntomol. 1997, 26, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppla, N.C.; Ashley, T.R. Quality control in insect mass production: A review and model. Bull. ESA 1989, 35, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbritter, D.A.; Wheeler, G.S. Life history trade-offs of thrips reared on fertilized and unfertilized Brazilian peppertree with respect to changes in plant terpenoid profiles. Biol. Control. 2021, 156, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, G.; Hernandez, K. Control of Pseudophilothrips ichini (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae) with acephate to exclude a biological control agent of Schinus terebinthifolia. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2014, 25, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halbritter, D.A.; Wheeler, G.S. Organic mulch can increase the survival of a weed biological control agent during laboratory mass rearing. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2019, 29, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, C.A. Biologia e Aspectos da Ecologia e do Comportamento Defensiva Comparada de Liothrips ichini Hood 1949 (Thys-anoptera Tubulifera). Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Paraná, Paraná, Brazil, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Chevrier, C.; Nguyen, T.M.; Bressac, C. Heat shock sensitivity of adult male fertility in the parasitoid wasp Anisopteromalus calandrae (Hymenoptera, Pteromalidae). J. Therm. Biol. 2019, 85, 102419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, K.E.; Sinclair, B.J. The relative importance of number, duration and intensity of cold stress events in determining survival and energetics of an overwintering insect. Funct. Ecol. 2014, 29, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Awmack, C.S.; Leather, S. Host plant quality and fecundity in herbivorous insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2002, 47, 817–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.; Zhao, W.; Xing, M.; Zhao, J.; Jiang, Z.; You, J.; Ni, B.; Ni, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; et al. Resource allocation strategies among vegetative growth, sexual reproduction, asexual reproduction and defense during growing season of Aconitum kusnezoffii Reichb. Plant J. 2021, 105, 957–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewel, J.J.; Ojima, D.S.; Karl, D.A.; DeBusk, W.F. Schinus in Successional Ecosystems of Everglades National Park; Report T-676; U.S. Department of the Interior, National Park Service, Everglades National Park, South Florida Research Center: Homestead, FL, USA, 1982; Volume 141, p. 55284. [Google Scholar]







| Cage Type | Number of Batches | Number of F0 Thrips Introduced | Number of F1 Thrips Harvested | Fold Productivity *** | Generation Time (d) *** | Hours of Labor/1000 Thrips | Upfront Cost/Cage (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acrylic cylinder | 189 | 20–50 | 368 ± 20 | 10.4 a ± 0.6 | 42.5 a ± 0.6 | 5.0 | USD 62 (2019) |
| Acrylic box | 91 | 100 | 679 ± 38 | 6.8 b ± 0.4 | 43.3 a ± 0.9 | 5.1 | USD 400 (2014) |
| Lumite® screen | 54 | 1500 | 13,864 ± 1044 | 9.2 a ± 0.7 | 32.9 b ± 0.9 | 0.5 | USD 600 (2020) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Halbritter, D.A.; Rayamajhi, M.B.; Wheeler, G.S.; Leidi, J.G.; Owens, J.R.; Cogan, C.A. Advances in Mass Rearing Pseudophilothrips ichini (Hood) (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae), a Biological Control Agent for Brazilian Peppertree in Florida. Insects 2021, 12, 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12090790
Halbritter DA, Rayamajhi MB, Wheeler GS, Leidi JG, Owens JR, Cogan CA. Advances in Mass Rearing Pseudophilothrips ichini (Hood) (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae), a Biological Control Agent for Brazilian Peppertree in Florida. Insects. 2021; 12(9):790. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12090790
Chicago/Turabian StyleHalbritter, Dale A., Min B. Rayamajhi, Gregory S. Wheeler, Jorge G. Leidi, Jenna R. Owens, and Carly A. Cogan. 2021. "Advances in Mass Rearing Pseudophilothrips ichini (Hood) (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae), a Biological Control Agent for Brazilian Peppertree in Florida" Insects 12, no. 9: 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12090790
APA StyleHalbritter, D. A., Rayamajhi, M. B., Wheeler, G. S., Leidi, J. G., Owens, J. R., & Cogan, C. A. (2021). Advances in Mass Rearing Pseudophilothrips ichini (Hood) (Thysanoptera: Phlaeothripidae), a Biological Control Agent for Brazilian Peppertree in Florida. Insects, 12(9), 790. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects12090790