Haplocauda, a New Genus of Fireflies Endemic to the Amazon Rainforest (Coleoptera: Lampyridae) †
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Morphology, Terminology, and Map
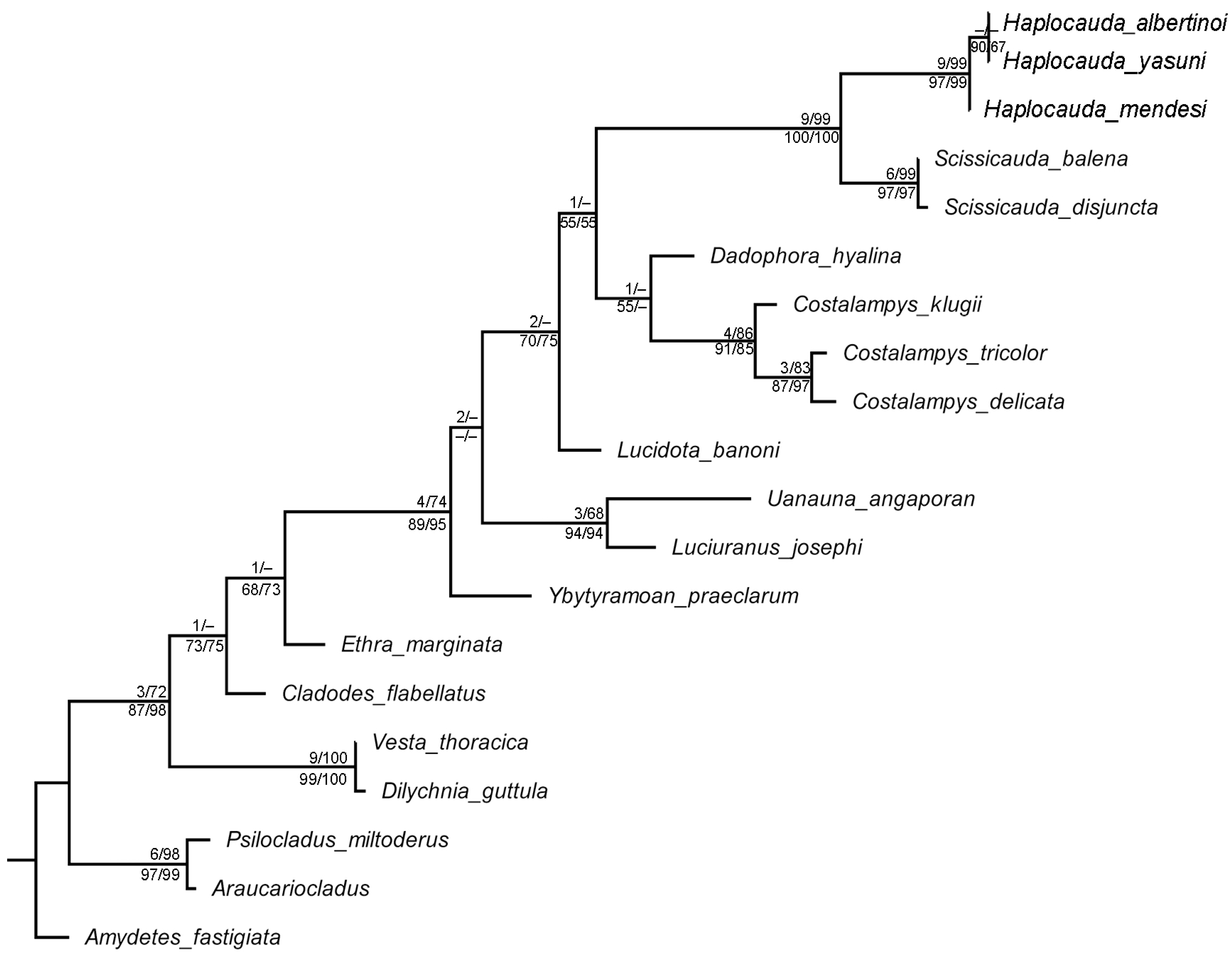
2.2. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Characters
- Antenna, antennomeres III-IX, shape: (0) serrate (Figure 4G), (1) cylindrical.
- Antennal serration, shape: (0) acute (Figure 4G), (1) rounded.
- Antenna, antennomeres III-IX, single lamella: (0) absent, (1) present.
- Antenna, antennomeres III-IX, double lamellae: (0) absent, (1) present.
- Antenna, single flabellar insertion, position: (0) basal, (1) apical, (2) progressively apical.
- Antenna, upright bristles: (0) absent (Figure 4G), (1) present.
- Labrum, connection to frons: (0) connected by membrane (Figure 4C), (1) fused.
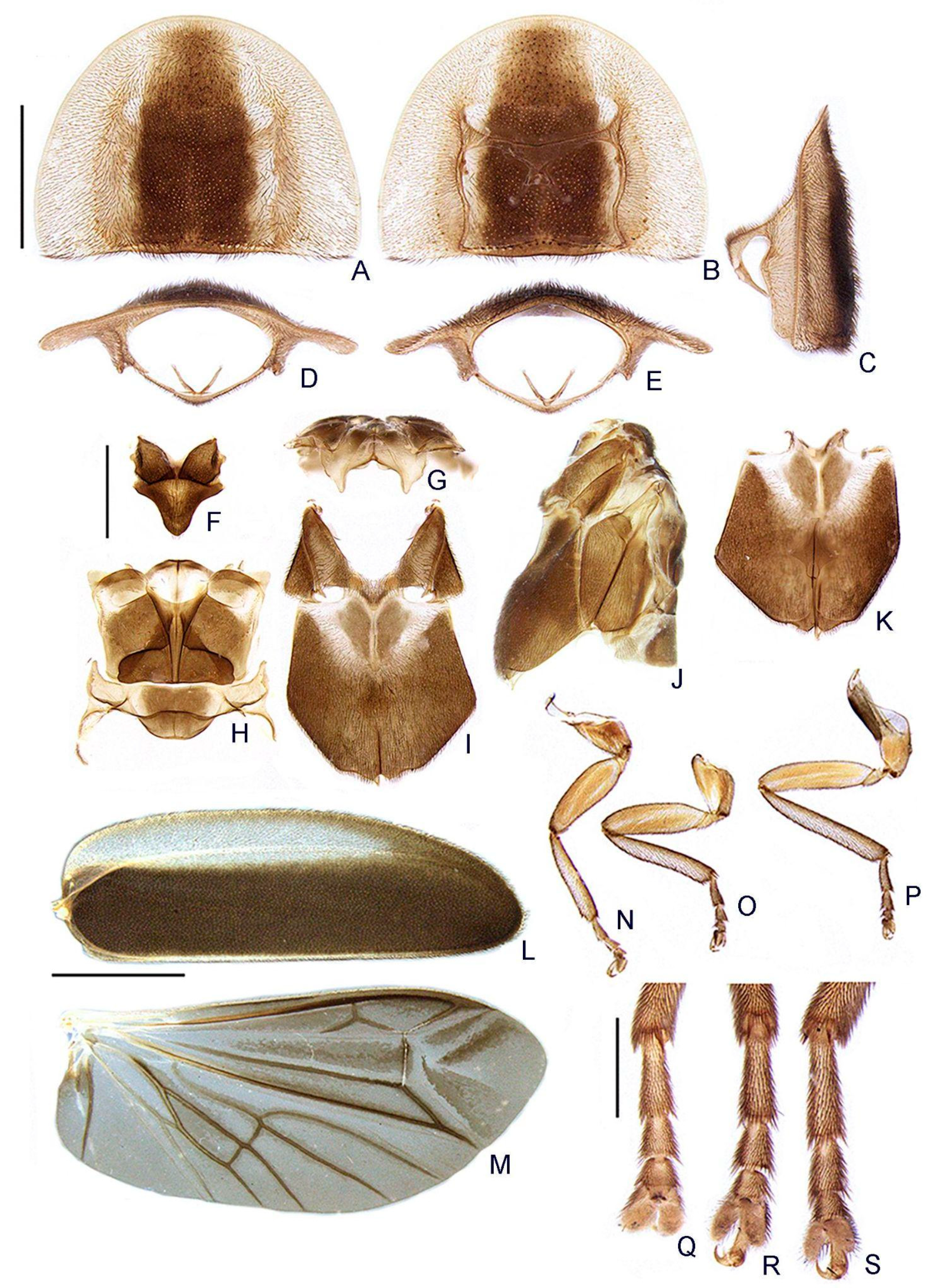
- Frons, shape: (0) concave, (1) flat (Figure 4A,C,D).
- Mandibles, orientation in frontal view: (0) largely overlapping (Figure 4C), (1) crossed.
- Gula, length relative to submentum: (0) at least 1/5 shorter (Figure 7B), (1) as long as, (2) at least 1/5 longer.
- Labium, submentum, shape: (0) subcordiform (Figure 4B), (1) U-shaped, (2) triangular, (3) tongue-shaped.
- Labium, palp, palpomere III, shape: (0) cylindrical and apically rounded; (1) with sides slightly arcuate, apex strongly emarginate; (2) with sides divergent, apex straight to slightly emarginate (Figure 7C,D).
- Pronotum, disc, convexity relative to explanate margins in lateral view: (0) flat (Figure 5C), (1) convex.
- Pronotum, lateral expansions, puncture depth: (0) deep, (1) shallow (Figure 5A).
- Pronotum, anterior margin, shape: (0) acuminate anteriorly, (1) evenly arcuate (Figure 5A).
- Pronotum, ratio between lateral expansion and disc widths: (0) less than 1/3, (1) almost 1/2 (Figure 5A).
- Pronotum, posterolateral angle, minute outwards projection: (0) present, (1) absent (Figure 5A,B).
- Pronotum, disc, sagittal depression: (0) absent (Figure 5A,D,E), (1) present.
- Pronotum, posterior expansion, posterior margin, shape in dorsal view: (0) strongly sinuate, (1) almost straight (Figure 5A,B).
- Hypomeron depth relative to width of the lateral expansion of pronotum: (0) about as long, (1) at least 1/3 shorter (Figure 5E).
- Prosternum, anterior margin, shape: (0) strongly sinuate medially, (1) almost straight (Figure 5B).
- Mesoscutellum, posterior margin, shape: (0) rounded (Figure 5F), (1) truncate.
- Elytron, outer margin, shape: (0) straight, (1) rounded (Figure 5L).
- Elytron, distinct black outline: (0) absent, (1) present (Figures 3 and 5L).
- Wing, mp-cu crossvein, position relative to the MP3+4 split: (0) more basal (Figure 5M), (1) more apical.
- Wing, AA3 vein, shape: (0) short (almost as long as wide) and almost perpendicular to AA4 (Figure 5M), (1) elongated and with an acute angle to AA4.
- Wing, r3 crossvein: (0) absent, (1) present (Figure 5M).
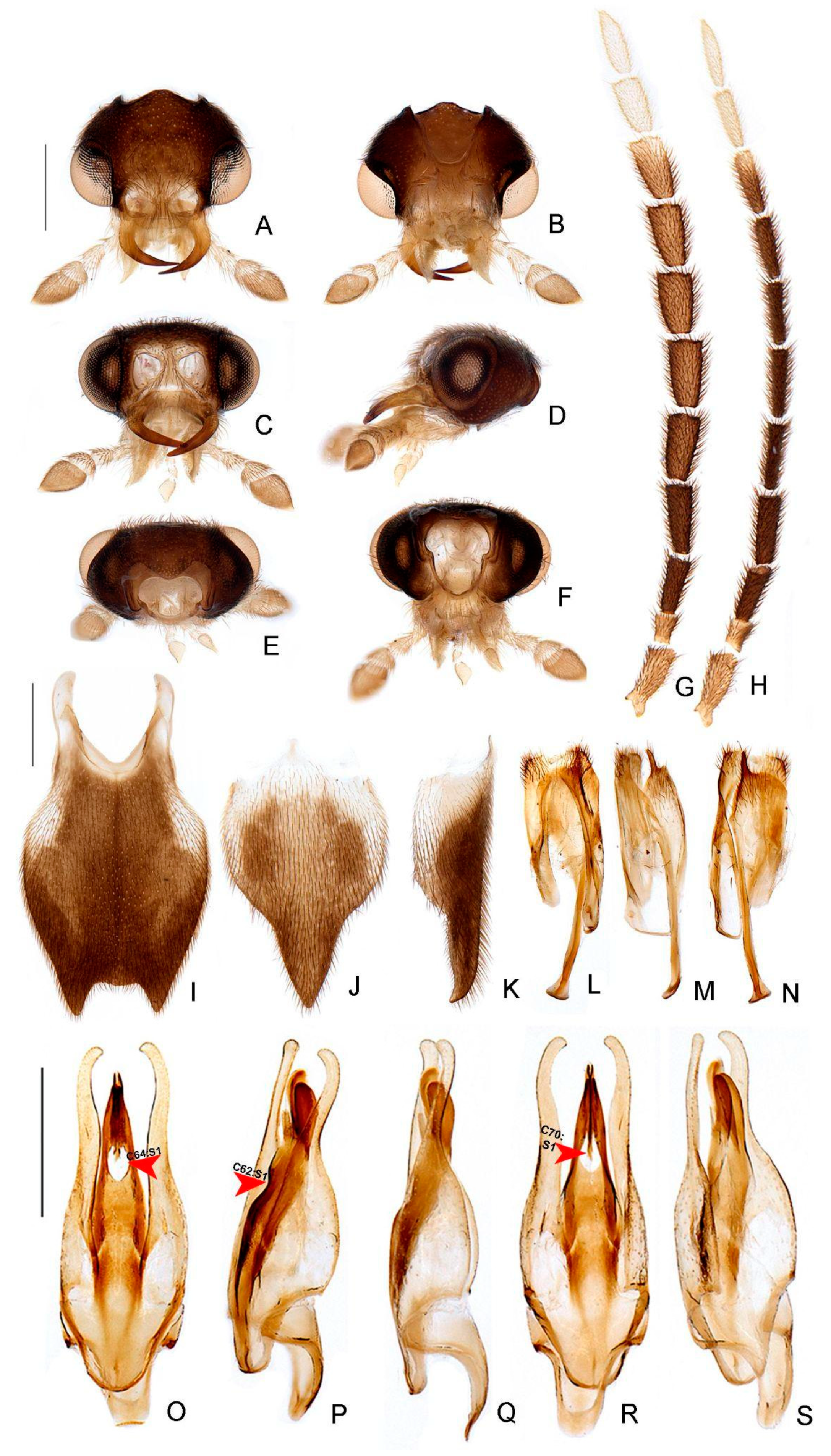
- Terga II-VII, posterior angles, shape: (0) acute (Figure 6A,B), (1) right-angled.
- Sternum VI, lantern: (0) absent (Figures 3 and 6C), (1) present.
- Sternum VI, lantern, length relative to sternum: (0) less than 1/3, (1) more than 1/3.
- Sternum VIII, core length (i.e., excluding the length of median projections) relative to VII: (0) as long as, (1) at least 1/5 longer (Figures 3 and 6C).
- Sternum VIII, posterior margin, tiny mucronate posterior projection: (0) absent (Figure 6C,D), (1) present.
- Sternum VIII, posterior margin, median third, long and wide posterior projection: (0) absent, (1) present (Figure 6C–E).
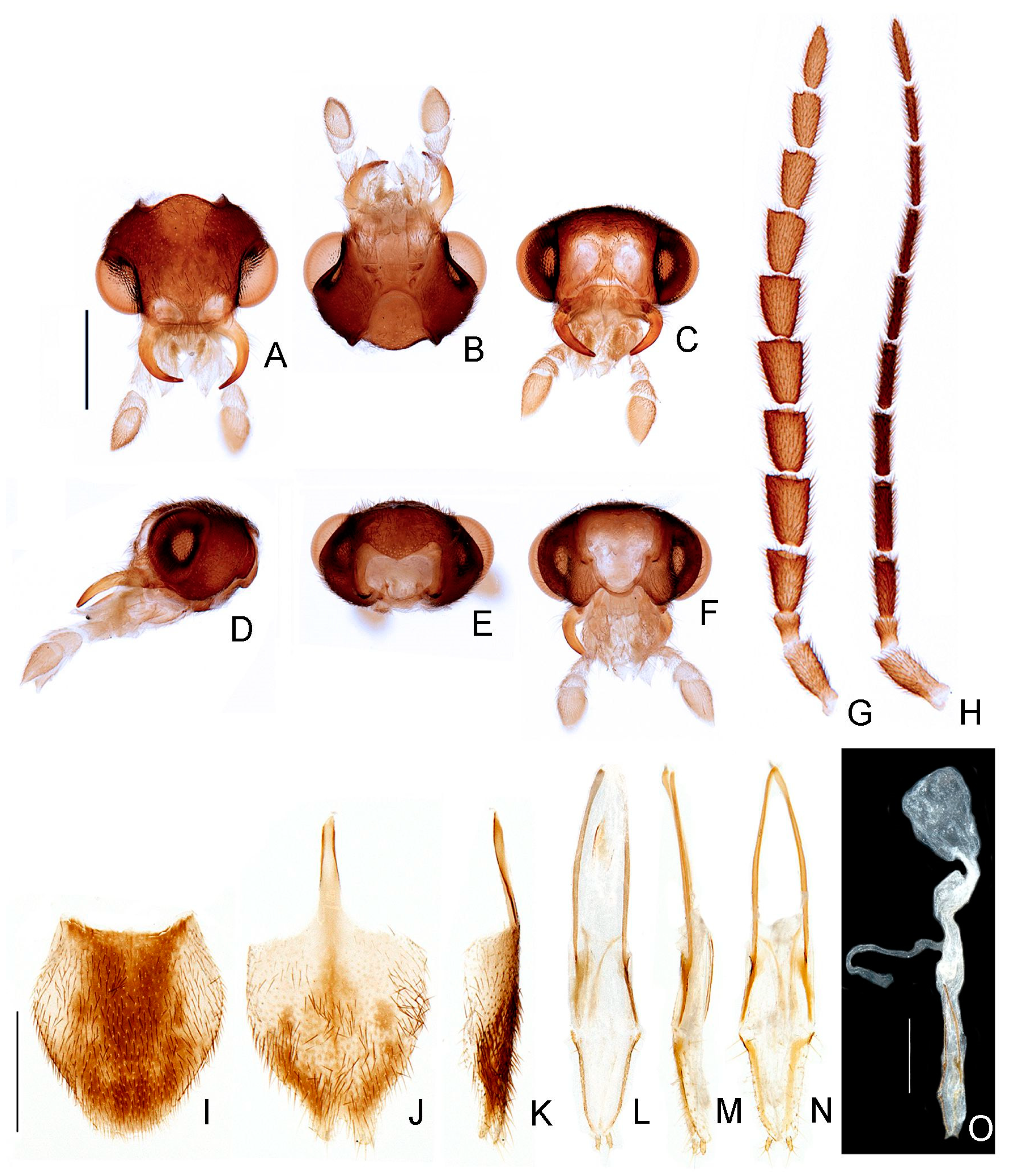
- Sternum VIII, posterior margin, apex of wide posterior projection, shape: (0) rounded (Figure 11J), (1) acute (Figure 6D,E).
- Pygidium, posterior margin, medial indentation: (0) absent (Figure 6F), (1) present.
- Pygidium, length/width ratio: (0) at least 1/5 wider than long, (1) as wide as long, (2) at least 1/5 longer than wide (Figure 6F).
- Pygidium, posterior margin, parasagittal indentations/sinuosities: (0) absent, (1) present (Figure 6F).
- Pygidium, lateral margins, shape: (0) subparallel, (1) rounded (Figure 6F), (2) divergent posteriorly, (3) convergent posteriorly.
- Pygidium, posterior angle length relative to central third: (0) shorter, (1) as long as, (2) longer (Figure 6F).
- Pygidium, postero-lateral angles, degree of development: (0) well-developed (Figure 6F), (1) barely conspicuous.
- Pygidium, anterior angles, blunt anterior projections: (0) absent, (1) present (Figure 6F).
- Pygidium, anterior margin, shape: (0) slightly emarginate, (1) strongly emarginate (Figure 6F).
- Syntergite, anterior margin, indentation: (0) absent, (1) present (Figure 6G).
- Syntergite, anterior margin, degree of indentation: (0) mild, (1) strongly indented, (2) completely separating the syntergite in two elongated sclerotized plates (Figure 6G).
- Syntergite, sagittal membranous suture: (0) absent (Figure 6G), (1) present.
- Syntergite, posterior-apical connection with sternum IX: (0) separated (Figure 6G,H), (1) fused.
- Syntergite, transverse keel, presence: (0) absent, (1) present (Figure 6G).
- Syntergite, transverse keel, position: (0) close to the posterior margin, (1) following contour of anterior margin (Figure 6G).
- Syntergite, length relative to sternum IX: (0) 1/4, (1) 1/2, (2) 2/3 (Figure 6G,H).
- Sternum IX, lateral rods, shape: (0) subparallel-sided, (1) convergent anteriorly (Figure 6H).
- Sternum IX, length relative to aedeagus (including phallobase): (0) at least slightly shorter, (1) slightly longer, (2) 1/3 longer (Figure 6H,I).
- Sternum IX, anterior/proximal distance between lateral rods: (0) widely separated, (1) gradually close-set, (2) fused (Figure 6H), (3) abruptly close-set.
- Sternum IX, lateral rods, apical margins: (0) acuminate, as thick as core rod, (1) truncate and thickened anteriorly (Figure 6H).
- Sternum IX, posterior margin, median projection: (0) absent, (1) present (Figure 6D).
- Sternum IX, position relative to VIII: (0) completely covered (Figures 3 and 6C), (1) partially exposed.
- Sternum IX, posterior margin, shape: (0) rounded (Figure 6H), (1) acute.
- Phallobase, shape: bilateral symmetry: (0) asymmetrical, (1) symmetrical (Figure 6I).
- Phallobase, length relative to dorsal plate of phallus: (0) at least 1/4 shorter (Figure 6I), (1) as long as.
- Phallus, dorsal plate, connection to parameres: (0) separated, (1) medially fused (Figure 6I).
- Phallus, dorsal plate, median fusion to parameres, extent: (0) up to 1/4 of phallus length (Figure 6I), (1) nearly 1/2 of phallus length.
- Phallus, dorsal plate, apical half, lateral margins, shape: (0) evenly acuminate, (1) abruptly acuminate (Figure 6I), (2) sinuate, (3) subparallel-sided.
- Phallus, dorsal plate, subapical transverse groove: (0) absent, (1) present (Figures 6J and 9P).
- Phallus, dorsal plate, length relative to parameres: (0) at least 1/5 longer, (1) at least 1/5 shorter (Figure 6I–L).
- Phallus, dorsal plate, apical indentation: (0) absent, (1) present (Figure 9O).
- Phallus, dorsal plate, overall shape in lateral view: (0) straight, (1) bent dorsally, (2) bent ventrally (Figure 6I–L), (3) sinuate.
- Phallus, dorsal plate, basal abrupt constriction: (0) absent (Figure 6I–L), (1) present.
- Phallus, dorsal plate, subapical outer keel: (0) absent (Figure 6I–L), (1) present.
- Phallus, dorsal plate, subapical outer teeth: (0) absent (Figure 6I–L), (1) present.
- Phallus, dorsal plate, apical arms (of indented phallus), shape: (0) widely distanced and slightly convergent, (1) close-set and strongly convergent (Figure 6I–L).
- Phallus, ventral plate: (0) absent, (1) present (Figure 9R).
- Phallus, ventral plate, length relative to dorsal plate: (0) half as long, (1) as long as, to slightly longer, (2) 1/3 shorter (Figures 9R and 11Q).
- Paramere, subapical tooth: (0) absent (Figure 6I–L), (1) present.
- Paramere, apex, shape: (0) straight, (1) curved ventrally, (2) curved inwards (Figure 6I–L).
- Paramere, apex, subapical abrupt constriction: (0) absent, (1) present (Figure 6I–L).
- Paramere (lateral view), ventral projection: (0) absent (Figure 6I–L), (1) present.
- Phallus, dorsal plate, subapical transverse groove, depth: (0) shallow (Figure 6I), (1) deep.
3.2. Phylogenetic Analyses
3.3. Key to Haplocauda Species Based on Males
3.4. Key to Haplocauda Species Based on Females
4. Discussion
4.1. On the Fireflies of the Amazon Rainforest
4.2. On Haplocauda and Scissicauda
4.3. On Firefly Copulation Clamps
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stork, N.E. How Many Species of Insects and Other Terrestrial Arthropods Are There on Earth? Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Douglas, H.B.; Kundrata, R.; Brunke, A.J.; Escalona, H.; Chapados, J.T.; Eyres, J.; Richter, R.; Savard, K.; Ślipiński, A.; McKenna, D.; et al. Anchored Phylogenomics, Evolution and Systematics of Elateridae: Are All Bioluminescent Elateroidea Derived Click Beetles? Biology 2021, 10, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.J.; Stanger-Hall, K.F.; Branham, M.A.; Da Silveira, L.F.L.; Lower, S.E.; Hall, D.W.; Li, X.-Y.; Lemmon, A.R.; Lemmon, E.M.; Bybee, S.M. Higher-Level Phylogeny and Reclassification of Lampyridae (Coleoptera: Elateroidea). Insect Syst. Divers. 2019, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantyne, L.A.; Lambkin, C.L.; Ho, J.-Z.; Jusoh, W.F.A.; Nada, B.; Nak-Eiam, S.; Thancharoen, A.; Wattanachaiyingcharoen, W.; Yiu, V. The Luciolinae of S. E. Asia and the Australopacific region: A revisionary checklist (Coleoptera: Lampyridae) including description of three new genera and 13 new species. Zootaxa 2019, 4687, 1–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silveira, L.F.L.; Mermudes, J.R.M. Systematic review of the firefly genus Amydetes Illiger, 1807 (Coleoptera: Lampyridae), with description of 13 new species. Zootaxa 2014, 3765, 201–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silveira, L.F.L.; Mermudes, J.R.M.; Bocakova, M. Systematic review of the firefly genus Scissicauda (Coleoptera, Lampyridae, Amydetinae) from Brazil. ZooKeys 2016, 558, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Silveira, L.F.L.; Souto, P.M.; Mermudes, J.R.M. Four new species of Luciuranus fireflies from the Brazilian Atlantic Rainforest (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). Zootaxa 2018, 4413, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campello-Gonçalves, L.; Souto, P.M.; Mermudes, J.R.M.; Silveira, L.F.L. Uanauna gen. nov., a new genus of fireflies endemic to the Brazilian Atlantic forest (Coleoptera: Lampyridae), with key to brazilian genera of Lucidotina. Zootaxa 2019, 4585, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silveira, L.F.L.; Khattar, G.; Vaz, S.; Wilson, V.A.; Souto, P.M.; Mermudes, J.R.M.; Stanger-Hall, K.F.; Macedo, M.V.; Monteiro, R.F. Natural history of the fireflies of the Serra dos Órgãos mountain range (Brazil: Rio de Janeiro)—One of the ‘hottest’ firefly spots on Earth, with a key to genera (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). J. Nat. Hist. 2020, 54, 275–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, S.; Mermudes, J.R.M.; Paiva, P.C.; Da Silveira, L.F.L. Systematic review and phylogeny of the firefly genus Dilychnia (Lampyridae: Lampyrinae), with notes on geographical range. Zool. J. Linn. Soc. 2020, 190, 844–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, S.; Guerrazzi, M.C.; Rocha, M.; Faust, L.; Khattar, G.; Mermudes, J.; da Silveira, L.F.L. On the intertidal firefly genus Micronaspis Green, 1948, with a new species and a phylogeny of Cratomorphini based on adult and larval traits (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). Zool. Anz.—A J. Comp. Zool. 2021, 292, 64–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, R.S.T.; Lloyd, M.W.; Brady, S.G. Phylogenomics indicates Amazonia as the major source of Neotropical swarm-founding social wasp diversity. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2020, 287, 20200480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junior, C.H.L.S.; Pessôa, A.C.M.; Carvalho, N.S.; Reis, J.B.C.; Anderson, L.O.; Aragão, L.E.O.C. The Brazilian Amazon deforestation rate in 2020 is the greatest of the decade. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 5, 144–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QGIS.org. QGIS Geographic Information System. QGIS Association. 2021. Available online: http://www.qgis.org (accessed on 2 May 2021).
- da Silveira, L.F.L.; Roza, A.S.; Vaz, S.; Mermudes, J.R.M. Description and phylogenetic analysis of a new firefly genus from the Atlantic Rainforest, with five new species and new combinations (Coleoptera: Lampyridae: Lampyrinae). Arthropod Syst. Phylogeny 2021, 79, 115–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddison, W.P. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis. 2018. Available online: http://www.mesquiteproject.org (accessed on 6 June 2021).
- Sereno, P.C. Logical basis for morphological characters in phylogenetics. Cladistics 2007, 23, 565–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goloboff, P.A.; Catalano, S.A. TNT version 1.5, including a full implementation of phylogenetic morphometrics. Cladistics 2016, 32, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice Across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. The CIPRES science gateway. Syst. Biol. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang Minh, B.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goloboff, P.A.; Carpenter, J.M.; Arias, J.S.; Miranda-Esquivel, D.R. Weighting against homoplasy improves phylogenetic analysis of morphological data sets. Cladistics 2008, 24, 758–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirande, J.M. Weighted parsimony phylogeny of the family Characidae (Teleostei: Characiformes). Cladistics 2009, 25, 574–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nixon, K.C. WinClada (Software); Published by the author: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 734–745. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, P.O. A Likelihood Approach to Estimating Phylogeny from Discrete Morphological Character Data. Syst. Biol. 2001, 50, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, A.M.; Hillis, D.M. Bayesian Analysis Using a Simple Likelihood Model Outperforms Parsimony for Estimation of Phylogeny from Discrete Morphological Data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree v1.4.4. 2009. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 2 January 2021).
- Harrison, L.B.; Larsson, H.C.E. Among-Character Rate Variation Distributions in Phylogenetic Analysis of Discrete Morphological Characters. Syst. Biol. 2014, 64, 307–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, H.; Hasegawa, M. Letter to the Editor Multiple Comparisons of Log-Likelihoods with Applications to Phylogenetic Inference. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimodaira, H. An Approximately Unbiased Test of Phylogenetic Tree Selection. Syst. Biol. 2002, 51, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McDermott, F.A. The taxonomy of the Lampyridae (Coleoptera). Trans. Am. Entomol. Soc. 1964, 90, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, S.P.; Costa, C.; Kramp, K.; Kundrata, R. Hidden diversity in the Brazilian Atlantic rainforest: The discovery of Jurasaidae, a new beetle family (Coleoptera, Elateroidea) with neotenic females. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biffi, G.; Rosa, S.P.; Kundrata, R. Hide-and-Seek with Tiny Neotenic Beetles in One of the Hottest Biodiversity Hotspots: Towards an Understanding of the Real Diversity of Jurasaidae (Coleoptera: Elateroidea) in the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Biology 2021, 10, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roza, A.S. Jurasai ypauoca sp. nov., the sixth species of Jurasaidae, with a key to species of the genus (Coleoptera: Elateroidea). Stud. Neotropical Fauna Environ. 2021, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanger-Hall, K.F.; Lloyd, J.E.; Hillis, D.M. Phylogeny of North American fireflies (Coleoptera: Lampyridae): Implications for the evolution of light signals. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2007, 45, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wing, S.; Lloyd, J.E.; Hongtrakul, T. Male Competition in Pteroptyx Fireflies: Wing-Cover Clamps, Female Anatomy, and Mating Plugs. Fla. Entomol. 1983, 66, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, L.F.L.; Mermudes, J.R.M. Ybytyramoan, a new genus of fireflies (Coleoptera: Lampyridae, Lampyrinae, Photinini) endemic to the Brazilian Atlantic Rainforest, with description of three new species. Zootaxa 2014, 3835, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ballantyne, L.A.; Lambkin, C. A new firefly, Luciola (Pygoluciola) kinabalua, new species (Coleoptera: Lampyridae), from Malaysia, with observations on a possible copulation clamp. Raffles Bull. Zool. 2001, 49, 363–378. [Google Scholar]
- Silveira, L.; Khattar, G.; Souto, P.M.; Mermudes, J.R.M.; Takiya, D.M.; Monteiro, R.F. Integrative taxonomy of new firefly taxa from the Atlantic Rainforest. Syst. Biodivers. 2016, 14, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silveira, L.F.L.d.; Lima, W.; Fonseca, C.R.V.d.; McHugh, J. Haplocauda, a New Genus of Fireflies Endemic to the Amazon Rainforest (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). Insects 2022, 13, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010058
Silveira LFLd, Lima W, Fonseca CRVd, McHugh J. Haplocauda, a New Genus of Fireflies Endemic to the Amazon Rainforest (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). Insects. 2022; 13(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilveira, Luiz Felipe Lima da, William Lima, Cláudio Ruy Vasconcelos da Fonseca, and Joseph McHugh. 2022. "Haplocauda, a New Genus of Fireflies Endemic to the Amazon Rainforest (Coleoptera: Lampyridae)" Insects 13, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010058
APA StyleSilveira, L. F. L. d., Lima, W., Fonseca, C. R. V. d., & McHugh, J. (2022). Haplocauda, a New Genus of Fireflies Endemic to the Amazon Rainforest (Coleoptera: Lampyridae). Insects, 13(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13010058





