Taxonomic Review of the Genus Caloptilia Hübner, 1825 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) with Descriptions of Three New Species and Seven Newly Recorded Species from Korea
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
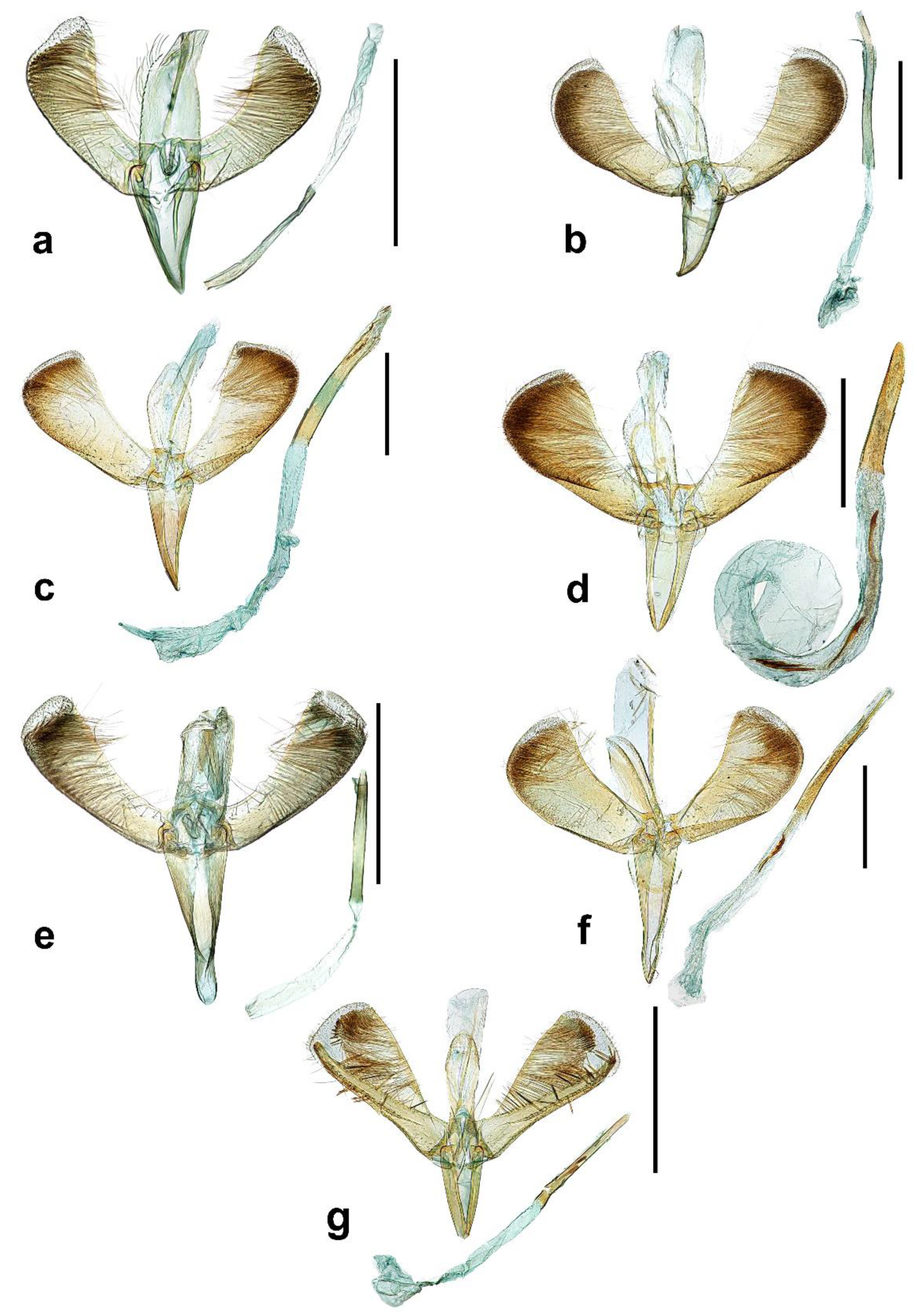
3.1. Description of New Species
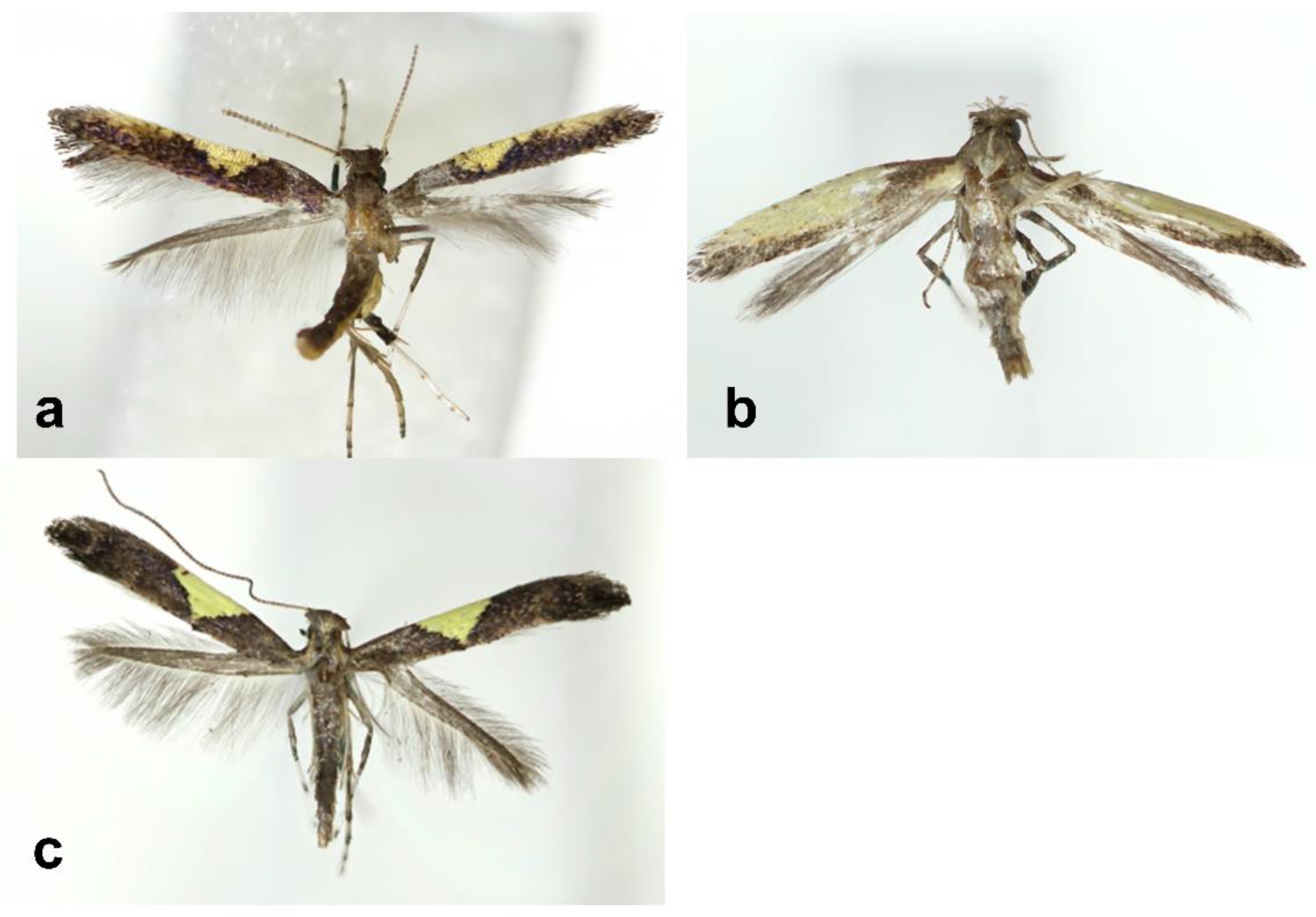
3.1.1. Caloptilia purpureus sp. nov. Kim and Byun, 2022 Bora-ga-neun-na-bang
3.1.2. Caloptilia koreana sp. nov. Kim and Byun, 2022 Han-guk-ga-neun-na-bang
3.1.3. Caloptilia xanthos sp. nov. Kim and Byun, 2022 No-rang-jeom-ga-neun-na-bang
3.2. Redescription of New Records
3.2.1. Caloptilia acericola Kumata, 1966 Gin-no-lang-ga-neun-na-bang
3.2.2. Caloptilia celtidis Kumata, 1982 Huin-mu-nui-ga-neun-na-bang
3.2.3. Caloptilia dentata Liu & Yuan, 1990 Ne-mo-mu-nui-ga-neun-na-bang
3.2.4. Caloptilia kadsurae Kumata, 1966 Nam-o-mi-ja-ga-neun-na-bang
3.2.5. Caloptilia monticola Kumata, 1966 Oe-ban-jeom-ga-neun-na-bang
3.2.6. Caloptilia recitata (Meyrick, 1918) Keun-gal-saeg-mu-nui-ga-neun-na-bang
3.2.7. Caloptilia soyella (van Deventer, 1904) Tob-ni-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3. Checklist of the Genus Caloptilia in Korea
3.3.1. Caloptilia acericola Kumata, 1966 Gin-no-lang-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.2. Caloptilia aceris Kumata, 1966 Dan-pung-ip-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.3. Caloptilia alni Kumata, 1966 O-li-na-mu-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.4. Caloptilia azaleella (Brants, 1913) San-cheol-jjug-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.5. Caloptiliaceltidis Kumata, 1982 Huin-mu-nui-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.6. Caloptilia chrysolampra (Meyrick, 1936) Beo-deul-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.7. Caloptilia dentata Liu & Yuan, 1990 Ne-mo-mu-nui-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.8. Caloptilia hidakensis Kumata, 1966 Go-lo-soe-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.9. Caloptilia kadsurae Kumata, 1966 Nam-o-mi-ja-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.10. Caloptilia kisoensis Kumata, 1982 Sin-na-mu-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.11. Caloptilia koreana sp. nov. Kim and Byun, 2022 Han-gug-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.12. Caloptilia leucothoes Kumata, 1982 San-jin-dal-lae-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.13. Caloptilia magnoliae Kumata, 1966 Mog-lyeon-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.14. Caloptilia mandschurica (Christoph, 1882) Bug-bang-min-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.15. Caloptilia monticola Kumata, 1966 Oe-ban-jeom-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.16. Caloptilia pulverea Kumata, 1966 Heug-gal-saeg-jeom-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.17. Caloptilia purpureus sp. nov. Kim and Byun, 2022 Bo-la-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.18. Caloptilia pyrrhaspis (Meyrick, 1931) No-lang-jul-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.19. Caloptilia recitata (Meyrick, 1918) Keun-gal-saeg-mu-nui-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.20. Caloptilia rhois Kumata, 1982 Ot-na-mu-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.21. Caloptilia sapporella (Matsumura, 1931) Jol-cham-na-mu-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.22. Caloptilia schisandrae Kumata, 1966 O-mi-ja-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.23. Caloptilia soyella (van Deventer, 1904) Tob-ni-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.24. Caloptilia stigmatella (Fabricius, 1781) Baeg-yang-na-mu-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.25. Caloptilia syrphetias (Meyrick, 1907) Hu-bag-na-mu-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.26. Caloptilia theivora (Walsingham, 1891) Dong-baeg-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.27. Caloptilia xanthos sp. nov. Kim and Byun, 2022 No-rang-jeom-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.28. Caloptilia yasudai Kumata, 1982 No-lan-i-ppal-ga-neun-na-bang
3.3.29. Caloptilia zachrysa (Meyrick, 1907) Sa-gwa-ip-ga-neun-na-bang
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GG | Gyeonggi-do |
| S | Seoul |
| CB | Chungcheongbuk-do |
| DJ | Daejeon |
| SJ | Sejeong |
| GB | Gyeongsangbuk-do |
| GN | Gyeongsangnam-do |
| GW | Gangwon-do |
| JB | Jeollabuk-do |
| JN | Jeollanam-do |
| JJ | Jeju-do |
| TL | Type locality |
| TD | Type depository |
| BMNH | The Natural History Museum, London, U.K. |
| EIHU | Entomological Institute, Hokkaido University, Japan |
| GLAHM | The Hunterian Museum and Art Gallery, United Kingdom |
| HNUSEL | Systematic Entomologu Lab., Hannam University, Korea |
| INU | Department of Life Sciences, Incheon National University, Korea |
| IZAS | Institute of Zoology, Academia Sinica, Beijing, China |
| KNAE | Entomological Collection, Korea National Arboretum, Korea |
| NAAS | National Academy of Agricultural Science, Korea |
| RNHL | Naturalis Biodiversity Center, Leiden, Netherlands |
References
- De Prins, J.; De Prins, W. Global Taxonomic Database of Gracillariidae (Lepidoptera). World Wide Web Electronic Publication. Available online: http://www.gracillariidae.net (accessed on 5 February 2022).
- Kumata, T. A taxonomic revision of the Gracillaria group occurring in Japan (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae). Ins. Matsum. Ser. 1982, 26, 1–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kumata, T. A new stem-miner of Alder in Japan, with a review of the larval transformation in the Gracillariidae (Lepidoptera). Ins. Matsum. 1978, 13, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, B.K.; Lee, B.W.; Park, K.T.; Bae, Y.S. A Checklist of the Microlepidoptera in Korea (Lepidoptera); Korea National Arboretum: Pocheon, Republic of Korea, 2009; pp. 1–413. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, Y.M.; Lee, B.W.; Byun, B.K. Taxonomic review of the genus Caloptilia Hübner (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) in Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2015, 18, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Choi, C.W.; Lee, S.; Byun, B.K. Taxonomic notes on Phyllocnistis citrella (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) with genital structures and DNA barcode from Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2015, 8, 295–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, D.S.; Byun, B.K. First discovery of winter-emerging leaf-miner: Phyllonorycter styracis (Kumata, 1963) (Lepidoptera, Gracillariidae) from Korea with DNA barcode. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2016, 9, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, D.S.; Byun, B.K. Taxonomic review of the genus Phyllonorycter Hübner (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) in Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2017, 20, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Byun, B.K. An annotated catalogue of the two genera Licrobyla and Spulerina of the family Gracillariidae (Lepidoptera) from Korea with new records. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2019, 12, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Byun, B.K. Genus Eteoryctis Kumata & Kuroko, 1988 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) in Korea with description of a new species. Zootaxa 2022, 5120, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Byun, B.K. Korean species of Gracillaria Haworth, 1828 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae). J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2022, 15, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Ahn, N.H.; Byun, B.K. The Genus Cameraria Chapman, 1902 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae: Lithocolletinae), New to Korea. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2022, 61, 313–318. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Oh, J.I.; Byun, B.K. Five Species of the Subfamily Acrocercopinae (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) New to Korea. Anim. Syst. Evol. Divers. 2022, 38, 113–121. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Oh, J.I.; Byun, B.K. Taxonomic review of the genus Spulerina Vári 1961 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) in Korea. Orient. Insect 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, I.K.; Choi, C.W.; Hwang, R.; Ku, D.S.; Byun, B.K. Indigenous parasitoids as effective natural enemies of Phyllocnistis citrella (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) in Korea. J. For. Res. 2017, 28, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.E.; Jeun, Y.C. Eighteen species of microlepidoptera (Lepidoptera) new to Korea. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2022, 15, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Byun, B.K. Genus Telamoptilia Kumata & Kuroko, 1988 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) new to Korea. Anim. Syst. Evol. Divers. 2022, 38, 162–166. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Byun, B.K. Korean species of Aristaea Meyrick, 1907 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae: Gracillariinae. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2022, 61, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumata, T. Descriptions of twenty new species of the genus Ca1optilia Hübner from Japan including the Ryukyu islands (Lepidotera: Gracillariidae). Ins. Matsum. 1966, 29, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, D. A study of the Chinese Caloptilia Hübner, 1825 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae: Gracillariinae). Sinozoologia 1990, 7, 181–207. [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick, E. Exotic Microlepidoptera 2; Marlborough: Bolton, UK, 1918; Volume 2, pp. 97–224. [Google Scholar]
- van Deventer, W. Microlepidoptera van Java. Tijdschr. Entomol. 1904, 47, 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Holloway, J.D.; Bradley, J.D.; Carger, D.J. CIE Guides to Insects of Importance to Man, 1st ed.; Lepidoptera CAB International: London, UK, 1987; pp. 1–262. [Google Scholar]
- Landry, B. The Gracillariidae (Lepidoptera, Gracillarioidea) of the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador, with notes on some of their relatives. Rev. Suisse Zool. 2006, 113, 437–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolaev, V.P. New species of gracillariid mining moths (Lepidoptera, Gracillariidae) from the Far East. In Systematics and Zoogeography of the Lepidoptera of the Asiatic Part of the USSR; Trudy Zoologicheskogo Instituta, Akademija Nauk SSSR: Vladivostok, Russia, 1981; Volume 103, pp. 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Ermolaev, V.P. Gracillariid moths of the genus Lithocolletis Hbn. (Lepidoptera, Gracillariidae) trophically associated with elm and maple in the south of the Far East. Entomol. Obozr. Entomol. Rev. 1988, 67, 346–359. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Shen, G. Lepidoptera: Microlepidoptera. In Iconography of Forest Insects in Hunan China; Peng, J., Liu, Y., Eds.; Academia Sinica & Hunan Forestry Institute: Changsha, China, 1992; pp. 666–755. [Google Scholar]
- Ermolaev, V.P. A contribution to the study on the leaf-mining family Gracillariidae of the southern Far East. In Terr. Arhtropoda Far East; Far East Scientific Center: Vladivostok, Russia, 1979; pp. 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ermolaev, V.P. Material on the fauna of Gracillariidae from Sakhalin and the southern Kuril Islands. In Lepidoptera of the Soviet Far East; Ler, P.A., Kirpichnikova, V.A., Kononenko, V.S., Eds.; Far East Scientific Center: Vladivostok, Russia, 1987; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Issiki, S. Icones Heterocerorum Japonicorum in Coloribus Naturalibus; Esaki, T., Issiki, S., Inoue, H., Mutuura, A., Ogata, M., Okagaki, H., Eds.; Hoikusha: Osaka, Japan, 1957; Volume 1, pp. 29–30. [Google Scholar]
- Issiki, S. Iconographia Insectorum Japonicorum, 2nd ed.; Esaki, T., Kuwayama, S., Ishii, T., Shiraki, T., Kawamura, T., Uchida, S., Kinoshita, S., Yuasa, H., Eds.; Hokuryukan: Tokyo, Japan, 1950; pp. 451–454. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, T.B. Life-histories of Indian Insects. Microlepidoptera. VI. Gracillariadae. Mem. Dep. Agric. India. 1921, 1–217. [Google Scholar]
- Hübner, J. (Ed.) Verzeichniss Bekannter Schmettlinge; Verlag: Augsburg, Germany, 1816; pp. 1–431. [Google Scholar]
- Hübner, J. (Ed.) Sammlung Europäischer Schmetterlinge. Achte Horde. Tineae DieSchaben; Nach der Natur Geordnet, Beschrieben und Vorgestellt; Verlag: Augsburg, Germany, 1796; pp. 1–81. [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick, E. On a collection of Lepidoptera from upper Burma. Trans. Entomol. Soc. Lond 1894, 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Agassiz, J.L.R. Nomenclator Zoologicus. Index Universalis Continens Nomina Systematica Generum Animalium Tam Viventium Quam Fassilium, Secundum Ordinem Alphabeticum Disposita, Adjectis Auctoribus, Libris in Quibus Reperiuntor, Anno Editionis, Etymologia, et Familis, ad Quas Pertinent, in Variis Classibus; Part 12; Jent et Glassmann: Soloduri, Indonesia, 1847; pp. 1–1135. [Google Scholar]
- Zeller, P.C. Versuch einer naturgemässen Eintheilung der Schaben. Isis. Oder Enzyklopädische Ztg. Oken 1839, 3, 167–220. [Google Scholar]
- Treitschke, F. Die Schmetterlinge von Europa. Neunter Band. Zweyte Abtheilung. Schaben. Geistchen. G. Hypsolopha-Orneode; Ernst Fleischer: Leipzig, Germany, 1833; pp. 1–294. [Google Scholar]
- Vári, L. South African Lepidoptera. Vol. I. Lithocolletidae; Transvaal Museum: Pretoria, South Africa, 1961; p. 238. [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick, E. Descriptions of Lepidoptera from the South Pacific. Trans. Entomol. Soc. Lond. 1886, 3, 189–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brants, A. Mededeeling te en ven eene, zeer belangrijke waarneming van den Phytopathologischen Dienst. Verslag van de acht- en- zestigste Zomervergadering der Nederlandse entomologische Vereeniging. Tijdschr. Entomol. 1913, 56, 1xx–1xxii. [Google Scholar]
- Busck, A. A new Gracilaria on Azalea (Lepidoptera, Gracillariidae). Insecutor Inscitiae Menstruus 1914, 2, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick, E. Exotic Microlepidoptera 4; Marlborough: Bolton, UK, 1931; Volume 4, pp. 161–192. [Google Scholar]
- Sohn, J.C. Faunistic contribution to the Korea Microlepidoptera and Pyralids (1)-40 Species new to Korea. Tinea 2007, 20, 12–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dugdale, J.S. Lepidoptera—Annotated Catalogue, and Keys of Family-Group Taxa; Entomology Division, DSIR: Auckland, New Zealand, 1988; pp. 1–262. [Google Scholar]
- Kusdas, K.; Reichl, E.R. Die Schmetterlinge Oberösterreichs. Tell 6: Microlepidoptera (Kleinschmetterlinge); Landesmuseum zu Linz: Linz, Austria, 1990; pp. 1–332. [Google Scholar]
- Šumpich, J.; Liška, J.; Sitek, J.; Marek, J.; Skyva, J.; Uricar, J.; Fiala, F.; Jakeš, O.; Dvorák, I.; Maršik, L. Faunistic records from the Czech Republic. Klapalekiana 2011, 47, 281–298. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, C.S. Tillæg til Fortegnelse over Danmark Microlepidoptera. Entomol. Medd. 1927, 17, 7–211. [Google Scholar]
- Buhl, O.; Falck, P.; Jørgensen, B.; Karsholt, O.; Larsen, K.; Vilhelmsen, F. Fund af småsommerfugle fra Danmark i 1998 (Lepidoptera). Entomol. Medd. 1998, 67, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Réal, P.; Balachowsky, A.S. Famille des Gracillariidae (=Lithocolletidae). In Entomologie Appliquée à L’agriculture. Tome 2; Balachowsky, A.S., Ed.; Masson et Cie éditeurs: Paris, France, 1966; pp. 309–335. [Google Scholar]
- Voigt, G. Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Minen und ihrer Erreger, sowie Beobachtungen über das Vorkommen von Minen im Rheingau und benachbarten rheinischen Gebieten. Jahrb. Nassauer Ver. Nat. 1929, 80, 24–74. [Google Scholar]
- Biesenbaum, W. Die Lepidopterenfauna der Rheinlande und Westfalens. Band 15. Familie Bucculatricidae Fracker, 1915. Familie: Gracillariidae Stainton, 1854. Unterfamilie: Gracillariinae Stainton, 1854; Westfälischer Lepidopterologists Association: Rheinisch, Germany, 2010; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein, K. Die Schmetterlinge Deutschlands mit Besonderer Berücksichtigung Ihrer Biologie und Wirtschaftlichen Bedeutung. 5. Band; Stuttgart, K.G., Ed.; Lutz’ Verlag: Lörrach, Germany, 1933; p. 223. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, K.J.; Koster, J.C.; Muus, T.S.T.; van Nieukerken, E.J. Microlepidoptera in Nederland, vooral in 2007–2010 met een terugblik op 30 jaar faunistisch onderzoek. Entomol. Ber. 2013, 73, 91–117. [Google Scholar]
- Corley, M.F.V.; Rosete, J.; Marabuto, E.; Maravalhas, E.; Pires, P. New and interesting Portuguese Lepidoptera records from 2013 (Insecta: Lepidoptera). SHILAP Rev. Lepidopterol. 2014, 42, 587–613. [Google Scholar]
- Hrubý, K. Prodromus Lepidopter Slovenska; Vydavateľstvo SAV: Bratislava, Slovakia, 1964; pp. 1–962. [Google Scholar]
- Benander, P. Sveriges Lithocolletider (Gracilariidae). Opusc. Entomol. 1944, 9, 79–137. [Google Scholar]
- Whitebread, S.E.; Joos, R. Nachtfalter und Kleinschmetterlinge. In Basler Natur-Atlas I.; Blattner, M., Ritter, M., Ewald, K.C., Eds.; Basler Naturschutz: Basel, Switzerland, 1986; pp. 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick, E. Exotic Microlepidoptera 3; Marlborough: Bolton, UK, 1927; Volume 3, pp. 321–384. [Google Scholar]
- Emmet, A.M. A Field Guide to the Smaller British Lepidoptera, 2nd ed.; British Entomological & Natural History Society: Wokingham, UK, 1988; p. 288. [Google Scholar]
- Heppner, J.B. Arthropods of Florida and Neighbouring Land Areas. Lepidoptera of Florida. Part 1. Introduction and Catalogue. Fla. Dep. Agric. 2003, 17, 1–670. [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick, E. Exotic Microlepidoptera 5(1-2); CABI: Marlborough, UK, 1936; Volume 1–2, pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.T.; Han, S.S. Seven species of Gracillariidae and Lyonetiidae (Lepidoptera) new to Korea and a list of the known host plants for the familes. Korea J. Plant Prot. 1986, 25, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Christoph, H. Neue Lepidoptiera des europaeischen faunengebietes. Horae Asaocietatis Entomol. Ross. 1882, 9, 3–39. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Okabayashi, Y.; Kamijo, K. Structure and function of parasitoid assemblages associated with Phyllonorycter leafminers (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) on deciduous oaks in Japan. Environ. Entomol. 2002, 31, 1052–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.A.; Hattori, K.; Kimura, M.T. Abundance of leafminers and leaf area loss by chewing herbivores in hybrids between Quercus crispula and Quercus dentata. Can. J. For. Res. 2004, 34, 2501–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolaev, V.P. A review of the fauna and ecology of miner-moth (Lep., Gracillariidae) of the Primorye Territory. Pro. Zool. Inst. Acad. Sci. USSR 1977, 70, 98–116. [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura, S. 6000 Illustrated Insects of the Japan-Empire; Tokohshoin: Tokyo, Japan, 1931; pp. 1–1497. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Ermolaev, V.P. New and little known species of leafblotch miners (Lepidoptera, Gracillariidae) from the south of Primorye Territory. Entomol. Obozr. 1986, 65, 741–752. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.M.; Lee, G.S. A new record of Caloptilia schicandrae Kumata (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) from Korea. Insecta Koreana 2001, 18, 91–93. [Google Scholar]
- Fabricius, J.C. Species insectorum exhibentes eorum differentias specificas, synonyma autorum, loca natalia, metamorphosin adiectis observationibus, descriptionibus. Tom II. Impensis Carol. Ernest Bohnii Hambg. Kilonii 1781, 2, 1–517. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, H.; Boll, J. Einige Tineen aus Texas. Entomol. Ztg. 1876, 37, 209–228. [Google Scholar]
- Goeze, J.A.E. Entomologische Beyträge zu des Ritter Linne Zwölften Ausgabe des Natursystems; Bey Weidmanns Erben und Reich: Leipzig, Germany, 1783; pp. 1–178. [Google Scholar]
- Fourcroy, A.F. Entomologia Parisiensis; Sive, Catalogus Insectorum Quae in Agro Parisiensi Reperiuntur; Privilegio Academiae: Paris, France, 1785; part 1; pp. 1–544. [Google Scholar]
- Haworth, A.H. Lepidoptera Britannica: Sistens Digestionem Novam Insectorum Lepidopterorum Quae in Magna Britannia Reperiuntur, Larvarum Pabulo, Remporeque Pascendi, Expansione Alarum, Mensibusque Volandi, Synonymis Atque Locis Observationibusque Variis; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1828; pp. 1–609. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, V.T. Micro-Lepidoptera. Can. Entomol. 1872, 4, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzer, G.W.F. Fauna Insectorum Germanicae Initia Oder Deutschlands Insecten. Heft 17; Felsecker: Nürnberg, Germany, 1794; pp. 13–24. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, O.G. Fauna del Regno di Napoli Ossia Enumerazione di Tutti gli Animali che Abitano le Diverse Regioni di Questo Regno e le Acque che le Bagnano Contenente la Descrizione de Nuovi o Poco Esattamente Conosciuti. Lepidotteri; Dai Torchi del Tramater: Azzolino, Napoli, 1836; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kagata, H.; Ohgushi, T. Resource partitioning among three willow leaf miners: Consequence of hostplant phenology. Entomol. Sci. 2001, 4, 257–263. [Google Scholar]
- Kirichenko, N.; Triberti, P.; Akulov, E.; Ponomarenko, M.; Gorokhova, S.; Sheiko, V.; Ohshima, I.; Lopez-Vaamonde, C. Exploring species diversity and host plant associations of leaf-mining micromoths (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) in the Russian Far East using DNA barcoding. Zootaxa 2019, 4652, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynova, E.F. Osobennosti fauny tsheshuekrylykh yuzhnogo Priuralya i ee znatshanie dlya stepnogo lesorasvedeniya. Trudy Zoologicheskogo Instituta. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1952, 11, 66–91. [Google Scholar]
- Akulov, E.N.; Kirichenko, N.I.; Ponomarenko, M.G. Contribution to the Microlepidoptera fauna of the south of the Krasnoyarsk Territory and the Republic of Khakassia. Entomol. Rev. 2018, 97, 110–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitterberger, K. Verzeichnis der im Kronlande Salzburg Bisher Beobachteten Mikrolepidopteren; Ringlschwendtner & Rathmayr: Obersulm, Germany, 1909; p. 358. [Google Scholar]
- Skala, H. Zur Verbreitung einiger Blattminen in Oberösterreich. Entomol. Anz. 1935, 15, 153–155, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kasy, F. Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Schmetterlingsfauna des WWF-Naturreservates Marchauen/Marchegg (mit nani-au) in Niederösterreich. Z. Arb. Osterr. Entomol. 1989, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- de Crombrugghe de Picquendaele, G. Catalogue raisonné des Microlépdoptères de Belgique. Mémoires Société Entomol. Belg. 1906, 13, 1–155. [Google Scholar]
- Buszko, J.; Beshkov, S. A preliminary survey of leafmining moths (Insecta: Lepidopetra: Microlepidoptera) of the Bulgarian part of Eastern Rhodopes. In Biodiversity of Bulgaria. 2. Biodiversity of Eastern Rhodopes; Beron, P., Popov, A., Eds.; Pensoft Publishers: Sofia, Bulgaria, 2004; pp. 723–733. [Google Scholar]
- Skala, H. Minen aus Mittel- und Südeuropa (Fortsetzung und Schluss). Z. Osterr. Entomol.-Ver. 1937, 22, 10–11, 19–20. [Google Scholar]
- Jaroš, J.; Spitzer, K. Food plants of Lepidoptera associated with an alder carr forest in South Bohemia (Central Europe). Acta Musei Bohem. Merid. Ceské Budejovice 2002, 42, 5–60. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, G. Die Schmetterlinge des südwestlichen Deutschlands: Insbesondere der Umgegend von Frankfurt, Nassau und der Hessischen Staaten; Forgotten Books: Bochum, Germany, 1856; pp. 1–498. [Google Scholar]
- Hering, M. Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Oekologie und Systematik blattminierender Insekten. (Minenstudien VIII). Z. Für Angew. Entomol. 1928, 13, 157–198. [Google Scholar]
- Buhr, H. Mecklenburgische Minen. III. Lepidopteren-Minen. Stettin. Entomol. Ztg. 1935, 96, 131–159, 262–292. [Google Scholar]
- Klimesch, J. Contibuto alla fauna Lepidopterologica del Trentino. Studi Trentini Di Sci. Nat. Acta Biol. 1950, 27, 11–68. [Google Scholar]
- Hartig, F. Microlepidotteri della Venezia Tridentina e delle regioni adiacenti. Parte III. (Fam. Gelechiidae—Micropterigidae). Studi Trentini Sci. Nat. Riv. Mus. Stor. Nat. Venezia Tridentina 1964, 41, 1–292. [Google Scholar]
- Hartig, F. Prodromus dei Microlepidotteri della Venezia Tridentina e delle regioni adiacenti. Studi Trentini Sci. Nat. Riv. Mus. Stor. Nat. Venezia Tridentina 1956, 33, 89–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lienig, F. Lepidopterische Fauna von Lievland und Curland. Isis Oder Enzyklopädische Ztg. Von Oken 1846, 3–4, 175–302. [Google Scholar]
- Ivinskis, P.; Pakalniškis, S. Microlepidoptera of Lithuania (Gracillariidae). Liet. TSR Moksl. Akad. Darb. 1984, 1, 26–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ivinskis, P.; Pakalniškis, S.; Puplesis, R. Augalus Minuojantys Vabzdziai; Mokslas: Vilnius, Lithuania, 1985; pp. 1–240. [Google Scholar]
- Rungs, C.E.E. Catalogue Raisonné des Lepidoptères du Maroc. Inventaire Faunistique et Obsevations Écologiques. Tome 1. Trav. L’institut Sci. Série Zool. 1979, 39, 1–222. [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf, H.W.; Snellen, P.C.T. Microlepidoptera in Nederland waargenomen. In Bouwstoffen voor Eene Fauna van Nederland; Herklots, J.A., Ed.; EJ Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1866; Volume 3, pp. 234–317. [Google Scholar]
- Snellen, P.C.T. De Vlinders van Nederland. Microlepidoptera, Systematisch Beschreven; Nijhoff: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1882; Volume 2, pp. 1–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Opheim, M. Revision of Microlepidoptera in the collections of Zoological Museum, Oslo I. Atalanta Nor. 1977, 3, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Büttner, F.O. Die pommerschen, insbesondere die Stettiner Mikrolepidoptern. Stettin. Entomol. Ztg. 1880, 41, 383–473. [Google Scholar]
- Buszko, J. Studies on the mining Lepidoptera of Poland X. Mining Lepidoptera of Torun and surrounding areas. Acta Zool. Crac. 1990, 33, 367–452. [Google Scholar]
- Buszko, J. Studies of the mining lepidoptera of Poland. XIV. Mining Lepidoptera of the Ojców National Park. Wiad. Entomol. 1993, 12, 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Corley, M.F.V. Lepidoptera of Continental Portugal: A Fully Revised List; Martin Corley: Faringdon, UK, 2015; p. 282. [Google Scholar]
- Hrubik, P.; Juhasova, G. Occurrence of horsechestnut mining moth Cameraria ohridella Deschka et Dimic in Slovakia. Acta Hortic. Regiotect. 1998, 1, 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, H. Die Tineen and Pterophoren der Schweiz; Meyer und Zeller: Zürich, Switzerland; Bayerische Staatsbibliothek: München, Germany, 1856; pp. 1–430. [Google Scholar]
- Chambers, V.T. Art. IV. Tineina and their foodplants. Bull. USA Geol. Geogr. Surv. Territ. 1878, 4, 107–124. [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick, E. Descriptions of Indian Micro-Lepidoptera. IV. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 1907, 17, 976–984. [Google Scholar]
- Walsingham, L. A new species of Tineidae. (Gracilaria theivora Wlsm., sp. nov.). Indian Mus. Notes 1891, 2, 49–50. [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell-Lefroy, H.; Howlett, F.M. Indian Insect Life. A Manual of the Insects of the Plains (Tropical India); Thacker, Spink & Co.: Calcutta, Indian; Simla and W. Thacker & Co.: London, UK, 1909; p. 786. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.T. Microlepidoptera of Korea; Insecta Koreana: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1983; Volume 3, pp. 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick, E. Descriptions of South African Micro-Lepidoptera. Ann. Transvaal Mus. 1918, 6, 7–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korean Society of Applied Entomology; The Entomological Society of Korea. Check List of Insects from Korea; Kon-Kuk University Press: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1994; pp. 323–324. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, D.R. Gracillariidae. In Immature Insects; Stehr, F.W., Ed.; Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company: Dubuque, IA, USA, 1987; Volume I, pp. 372–374. [Google Scholar]
- Brito, R.; De Prins, J.; De Prins, W.; Mielke, O.H.H.; Conçalves, G.L.; Moreira, G.R.P. Extant diversity and estimated number of Gracillariidae (Lepidoptera) species yet to be discovered in the Neotropical region. Rev. Bras. Entomol. 2016, 60, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-S.; Shin, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Byun, B.-K. Taxonomic Review of the Genus Caloptilia Hübner, 1825 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) with Descriptions of Three New Species and Seven Newly Recorded Species from Korea. Insects 2022, 13, 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13121107
Kim D-S, Shin Y-M, Lee J-Y, Byun B-K. Taxonomic Review of the Genus Caloptilia Hübner, 1825 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) with Descriptions of Three New Species and Seven Newly Recorded Species from Korea. Insects. 2022; 13(12):1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13121107
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Da-Som, Young-Min Shin, Ji-Young Lee, and Bong-Kyu Byun. 2022. "Taxonomic Review of the Genus Caloptilia Hübner, 1825 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) with Descriptions of Three New Species and Seven Newly Recorded Species from Korea" Insects 13, no. 12: 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13121107
APA StyleKim, D.-S., Shin, Y.-M., Lee, J.-Y., & Byun, B.-K. (2022). Taxonomic Review of the Genus Caloptilia Hübner, 1825 (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) with Descriptions of Three New Species and Seven Newly Recorded Species from Korea. Insects, 13(12), 1107. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13121107





