Understanding of Waggle Dance in the Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) from the Perspective of Long Non-Coding RNA
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
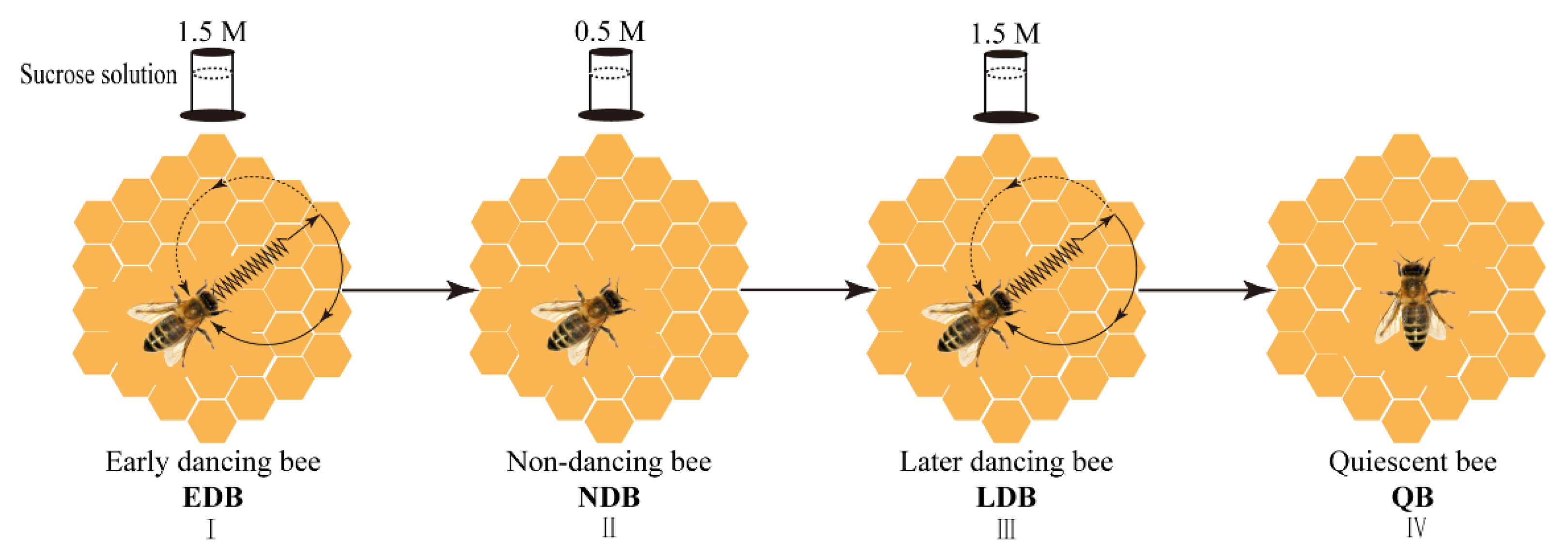
2.1. Bees and Bee Training
2.2. Behavioural Observation and Sampling under Different Concentrations of Sucrose Solution
2.3. Brain Dissection of the Honey bees
2.4. RNA Sequencing Analysis from Four Groups of Honey bee Brains
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis of RNA Sequencing Data
2.6. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) Validation of DElncRNAs
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quality Control and Evaluation of RNA Sequencing Results
3.2. LncRNA-Seq Results from the Four Groups of Honey bee Brains
3.3. GO and KEGG Analysis of the Target Genes of lncRNAs
3.3.1. GO and KEGG Analysis of Target Genes Regulated by DElncRNAs in NDB-vs-EDB and NDB-vs-LDB via the Antisense Regulatory Mechanism
3.3.2. GO and KEGG Analysis of Target Genes Regulated by DElncRNAs in NDB-vs-EDB, NDB-vs-LDB, QB-vs-EDB, QB-vs-LDB via the Cis-Regulatory Mechanism
3.3.3. GO and KEGG Analysis of Target Genes Regulated by DElncRNAs from the Intersection between NDB-vs-EDB and NDB-vs-LDB via the Cis-Regulatory Mechanism
3.3.4. GO and KEGG Analysis of Target Genes Regulated by DElncRNAs from the Intersection between QB-vs-EDB and QB-vs-LDB via the Cis-Regulatory Mechanism
3.3.5. GO and KEGG Analysis of Target Genes Regulated by DElncRNAs in QB-vs-NDB via the Cis-Regulatory Mechanism
3.4. RT-qPCR Validation of Differentially Expressed lncRNAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amdam, G.V.; Page, R.E. The developmental genetics and physiology of honeybee societies. Anim. Behav. 2010, 79, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galizia, C.G.; Eisenhardt, D.; Giurfa, M. Honeybee Neurobiology and Behavior: A Tribute to Randolf Menzel, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Abrol, D.P. Honeybee and Crop Pollination. In Pollination Biology: Biodiversity Conservation and Agricultural Production, 1st ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 5, pp. 85–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ribbands, C.R. Division of labour in the honeybee community. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1952, 140, 32–43. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.Y.; Robinson, G.E. Regulation of honey bee division of labor by colony age demography. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1996, 39, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, C.W. Gene Expression Profiles in the Brain Predict Behavior in Individual Honey Bees. Science 2003, 302, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, J.; Xia, J.; Zhou, X.; Thatcher, S.; Gu, X.; Ament, S.; Newman, T.C.; Green, P.J.; Zhang, W.; Robinson, G.E. Behavioral plasticity in honey bees is associated with differences in brain micrornamicro RNA transcriptome. Genes Brain Behav. 2012, 11, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woodbury, C.B. The learning of stimulus patterns by dogs. J. Comp. Psychol. 1943, 35, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beekmana, M.; Lewa, B.B. Foraging in honeybees--when does it pay to dance? Behav. Ecol. 2008, 19, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marco, R.D.; Farina, W. Changes in food source profitability affect the trophallactic and dance behavior of forager honeybees (Apis mellifera L.). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2001, 50, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Frisch, K. The Dance Language and Orientation of Bees. Anim. Behav. 1969, 17, 394–395. [Google Scholar]
- Afik, O.; Dag, A.; Shafir, S. Honeybee, Apis mellifera, round dance is influenced by trace components of floral nectar. Anim. Behav. 2008, 75, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, S.R.; Smith, M.L.; Seeley, T.D. Do honeybees use the directional information in round dances to find nearby food sources? Anim. Behav. 2012, 83, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, J.R.; Greggers, U.; Smith, A.D.; Reynolds, D.R.; Menzel, R. The flight paths of honeybees recruited by the waggle dance. Nature 2005, 435, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esch, H.E.; Zhang, S.; Srinivasan, M.V.; Tautz, J. Honeybee dances communicate distances measured by optic flow. Nature 2001, 411, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadagkar, R. The honeybee dance-language controversy. Resonance 1996, 1, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, T.D.; Mikheyev, A.S.; Pagano, G.J. Dancing bees tune both duration and rate of waggle-run production in relation to nectar-source profitability. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2000, 186, 813–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božič, J.; Woodring, J. Variations of brain biogenic amines in mature honeybees and induction of recruitment behavior. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 1998, 120, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, A.R.; Mobbs, P.G.; Davenport, A.P.; Evans, P.D. Biogenic amines in the brain of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Cell Tissue Res. 1983, 234, 655–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagener-Hulme, C.; Kuehn, J.C.; Schulz, D.J.; Robinson, G.E. Biogenic amines and division of labor in honey bee colonies. J. Comp. Physiol. A. 1999, 184, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnick, D.R.; Anton, A.H. Bees and biogenic amines. Physiol. Behav. 1969, 4, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, A.B.; Brockmann, A.; Sarma, M.S.; Robinson, G.E. Neurogenomic and Neurochemical Dissection of Honey Bee Dance Communication. In Honeybee Neurobiology and Behavior: A Tribute to Randolf Menzel; Galizia, C.G., Eisenhardt, D., Giurfa, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 5, pp. 323–339. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, A.B.; Maleszka, R.; Meer, R.; Robinson, G.E. Octopamine modulates honey bee dance behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1703–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barron, A.B.; Maleszka, J.; Meer, R.; Robinson, G.E.; Maleszka, R. Comparing injection, feeding and topical application methods for treatment of honeybees with octopamine. J. Insect Physiol. 2007, 53, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbara, G.S.; Zube, C.; Rybak, J.; Gauthier, M.; Grünewald, B. Acetylcholine, GABA and glutamate induce ionic currents in cultured antennal lobe neurons of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2005, 191, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Long non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, J.T.; Colognori, D.; Lee, J.T. Long noncoding RNAs: Past, present, and future. Genetics 2013, 193, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell. 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome regulation by long noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katayama, S.; Tomaru, Y.; Kasukawa, T.; Waki, K.; Nakanishi, M.; Nakamura, M.; Nishida, H.; Yap, C.C.; Suzuki, M.; Kawai, J.; et al. Antisense transcription in the mammalian transcriptome. Science 2005, 309, 1564–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapusta, A.; Kronenberg, Z.; Lynch, V.J.; Zhuo, X.; Ramsay, L.; Bourque, G.; Yandell, M.; Feschotte, C. Transposable elements are major contributors to the origin, diversification, and regulation of vertebrate long noncoding RNAs. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choudhary, C.; Sharma, S.; Meghwanshi, K.K.; Patel, S.; Shukla, J.N. Long Non-Coding RNAs in Insects. Animals 2021, 11, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Hu, X.; Guo, R.; Xue, R.; Cao, G.; Gong, C. Long Noncoding RNA: Disclosing New Horizon in the Molecular World of Insects. In Trends in Insect Molecular Biology and Biotechnology; Kumar, D., Gong, C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 85–102. [Google Scholar]
- Legeai, F.; Derrien, T. Identification of long non-coding RNAs in insects genomes. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 7, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadano, H.; Yamazaki, Y.; Takeuchi, H.; Kubo, T. Age- and division-of-labour-dependent differential expression of a novel non-coding RNA, Nb-1, in the brain of worker honeybees, Apis mellifera L. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 18, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawata, M.; Yoshino, D.; Takeuchi, H.; Kamikouchi, A.; Ohashi, K.; Kubo, T. Identification and punctate nuclear localization of a novel noncoding RNA, Ks-1, from the honeybee brain. RNA 2002, 8, 772–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawata, M.; Takeuchi, H.; Kubo, T. Identification and analysis of the minimal promoter activity of a novel noncoding nuclear RNA gene, AncR-1, from the honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). RNA 2004, 10, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiya, T.; Ugajin, A.; Kunieda, T.; Kubo, T. Identification of kakusei, a Nuclear Non-Coding RNA, as an Immediate Early Gene from the Honeybee, and Its Application for Neuroethological Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 15496–15509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kiya, T.; Kunieda, T.; Kubo, T. Inducible- and constitutive-type transcript variants of kakusei, a novel non-coding immediate early gene, in the honeybee brain. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaux, C.; Duong, N.; Schneider, S.S.; Southey, B.R.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.; Robinson, G.E. Modulatory Communication Signal Performance Is Associated with a Distinct Neurogenomic State in Honey Bees. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen Sarma, M.; Rodriguez-Zas, S.L.; Hong, F.; Zhong, S.; Robinson, G.E. Transcriptomic profiling of central nervous system regions in three species of honey bee during dance communication behavior. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Liu, F.; Li, W.; Li, Z.; Pan, J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Z.Y.; Su, S. Differences in microRNAs and their expressions between foraging and dancing honey bees, Apis mellifera L. J. Insect Physiol. 2012, 58, 1438–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Shi, T.; Qi, L.; Su, X.; Huang, Z.Y. lncRNA profile of Apis mellifera and its possible role in behavioural transition from nurses to foragers. BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreck, N.L.; Andree, M.; Brent, C.S.; Cox-Foster, D.; Dade, H.A.; Ellis, J.D.; Hatjina, F.; van Englesdorp, D. Standard methods for Apis mellifera anatomy and dissection. J. Apicult. Res. 2013, 52, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, D.; Chen, H.; Du, Y.; Zhou, D.; Geng, S.; Wang, H.; Wan, J.; Xiong, C.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, R. Genome-Wide Identification of Long Non-Coding RNAs and Their Regulatory Networks Involved in Apis mellifera ligustica Response to Nosema ceranae Infection. Insects 2019, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jia, G. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pertea, M.; Kim, D.; Pertea, G.M.; Leek, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1650–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Luo, H.; Bu, D.; Zhao, G.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.Q.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhao, S.Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2007, 35, W345–W349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogata, H.; Goto, S.; Sato, K.; Fujibuchi, W.; Bono, H.; Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketoshi, K.; Takekazu, K.; Takeo, K.; Martin, G. Increased Neural Activity of a Mushroom Body Neuron Subtype in the Brains of Forager Honeybees. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e371. [Google Scholar]
- Fahrbach, S.E. Structure of the mushroom bodies of the insect brain. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2006, 51, 209–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, M.; Zhang, S.; Lehrer, M.; Collett, T. Honeybee navigation en route to the goal: Visual flight control and odometry. J. Exp. Biol. 1996, 199, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taketoshi, K.; Takeo, K.; Martin, G. Analysis of GABAergic and Non-GABAergic Neuron Activity in the Optic Lobes of the Forager and Re-Orienting Worker Honeybee (Apis mellifera L.). PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8833. [Google Scholar]
- Taketoshi, K.; Takeo, K.; Daniel, O. Dance Type and Flight Parameters Are Associated with Different Mushroom Body Neural Activities in Worker Honeybee Brains. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19301. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.B.; Roberts, S.P.; Elekonich, M.M. Age and natural metabolically-intensive behavior affect oxidative stress and antioxidant mechanisms. Exp. Gerontol. 2008, 43, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, K.; Naug, D. Dancers and followers in a honeybee colony differently prioritize individual and colony nutritional needs. Anim. Behav. 2016, 119, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: Novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, B. Brain but not retinal glial cells have carbonic anhydrase activity in the honeybee drone. Neurosci. Lett. 1988, 85, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, A.; Helliwell, P.; Maleszka, R. Effects of NMDA receptor antagonists on olfactory learning and memory in the honeybee (Apis mellifera). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 77, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, S.A.; Fetter, R.D.; Noordermeer, J.N.; Goodman, C.S.; DiAntonio, A. Genetic analysis of glutamate receptors in Drosophila reveals a retrograde signal regulating presynaptic transmitter release. Neuron 1997, 19, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monastirioti, M. Biogenic amine systems in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1999, 45, 106–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.M.; Larsen, J.R. Glutamic acid decarboxylase and the GABA shunt in the supraoesophageal ganglion of the honey-bee, Apis mellifera. J. Insect Physiol. 1972, 18, 439–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L. Glutamic acid as a synaptic transmitter in the nervous system. A review. Brain. Res. 1972, 37, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, I. Octopamine in insects: Neurotransmitter, neurohormone, and neuromodulator. Can. J. Zool. 1982, 60, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Tibbit, C.; Liu, J.L. Effective knockdown of Drosophila long non-coding RNAs by CRISPR interference. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.F.; Zhang, B.; Liao, C.H.; Zeng, Z.J. High-Efficiency CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Gene Editing in Honeybee (Apis mellifera) Embryos. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genet. 2019, 9, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kohno, H.; Suenami, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Sasaki, T.; Kubo, T. Production of Knockout Mutants by CRISPR/Cas9 in the European Honeybee, Apis mellifera L. Zoolog Sci. 2016, 33, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, H.Y.; Liang, L.Q.; Li, Q.F.; Li, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.N.; Guo, Y.K.; Zheng, Q.L.; Lin, Y.; Yang, D.L.; Li, Z.G.; et al. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated knockout of Amyellow-y gene results in melanization defect of the cuticle in adult Apis mellifera. J. Insect Physiol. 2021, 132, 104264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| DElncRNA | NDB-vs-EDB | NDB-vs-LDB | QB-vs-EDB | QB-vs-LDB | QB-vs-NDB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated | 19 | 14 | 19 | 6 | 16 |
| Down-regulated | 18 | 19 | 31 | 23 | 29 |
| Total | 37 | 33 | 50 | 29 | 45 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, W.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Nie, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, Z.; Su, S. Understanding of Waggle Dance in the Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) from the Perspective of Long Non-Coding RNA. Insects 2022, 13, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13020111
Feng W, Huang J, Zhang Z, Nie H, Lin Y, Li Z, Su S. Understanding of Waggle Dance in the Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) from the Perspective of Long Non-Coding RNA. Insects. 2022; 13(2):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13020111
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Wangjiang, Jingnan Huang, Zhaonan Zhang, Hongyi Nie, Yan Lin, Zhiguo Li, and Songkun Su. 2022. "Understanding of Waggle Dance in the Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) from the Perspective of Long Non-Coding RNA" Insects 13, no. 2: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13020111
APA StyleFeng, W., Huang, J., Zhang, Z., Nie, H., Lin, Y., Li, Z., & Su, S. (2022). Understanding of Waggle Dance in the Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) from the Perspective of Long Non-Coding RNA. Insects, 13(2), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13020111







