Inducible Expression of Several Drosophila melanogaster Genes Encoding Juvenile Hormone Binding Proteins by a Plant Diterpene Secondary Metabolite, Methyl Lucidone
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Insect Rearing and Feeding
2.3. RNA Extraction, Primers, and qPCR Analysis
2.4. Gene Annotation and Subsequent Data Analyses
3. Results
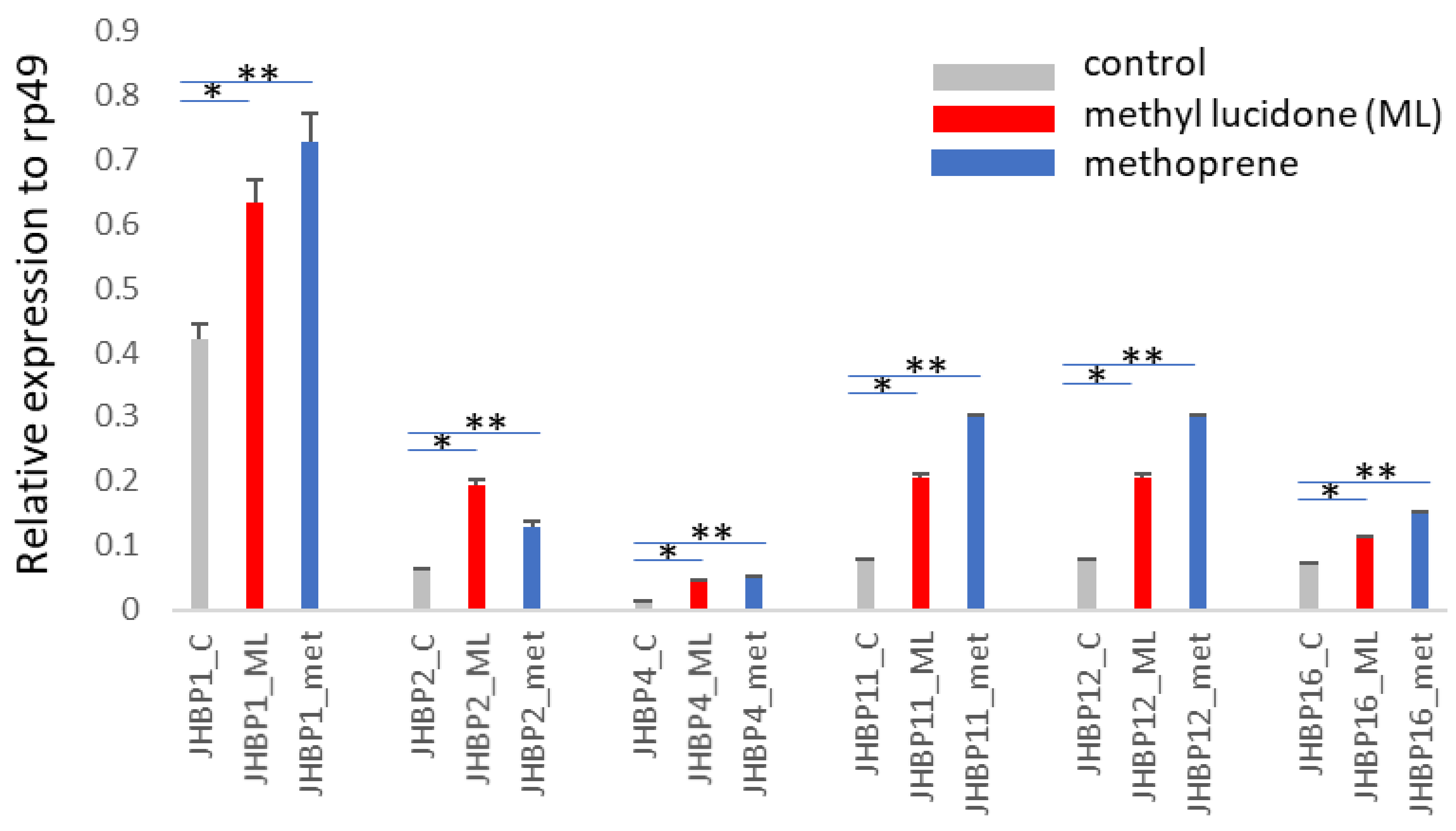
3.1. Six among 16 Genes Harboring a JHBP Domain Are Inducible by ML at the Larval Stage
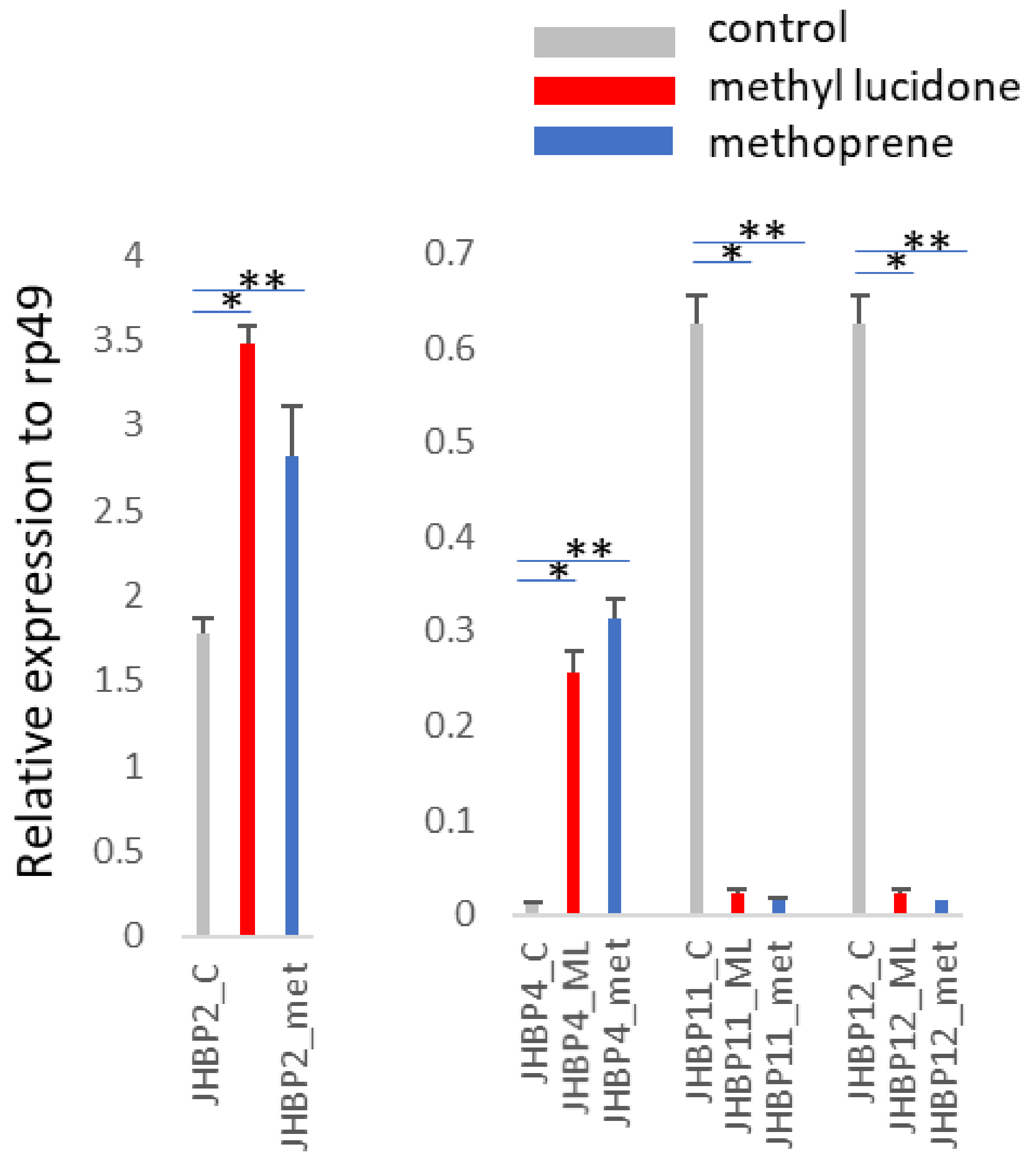
3.2. Regulation of Four Larval-Inducible JHBP Genes at the Pupal Stage by ML and Methoprene
3.3. Stage-Specific Expression of 10 JHBP Genes
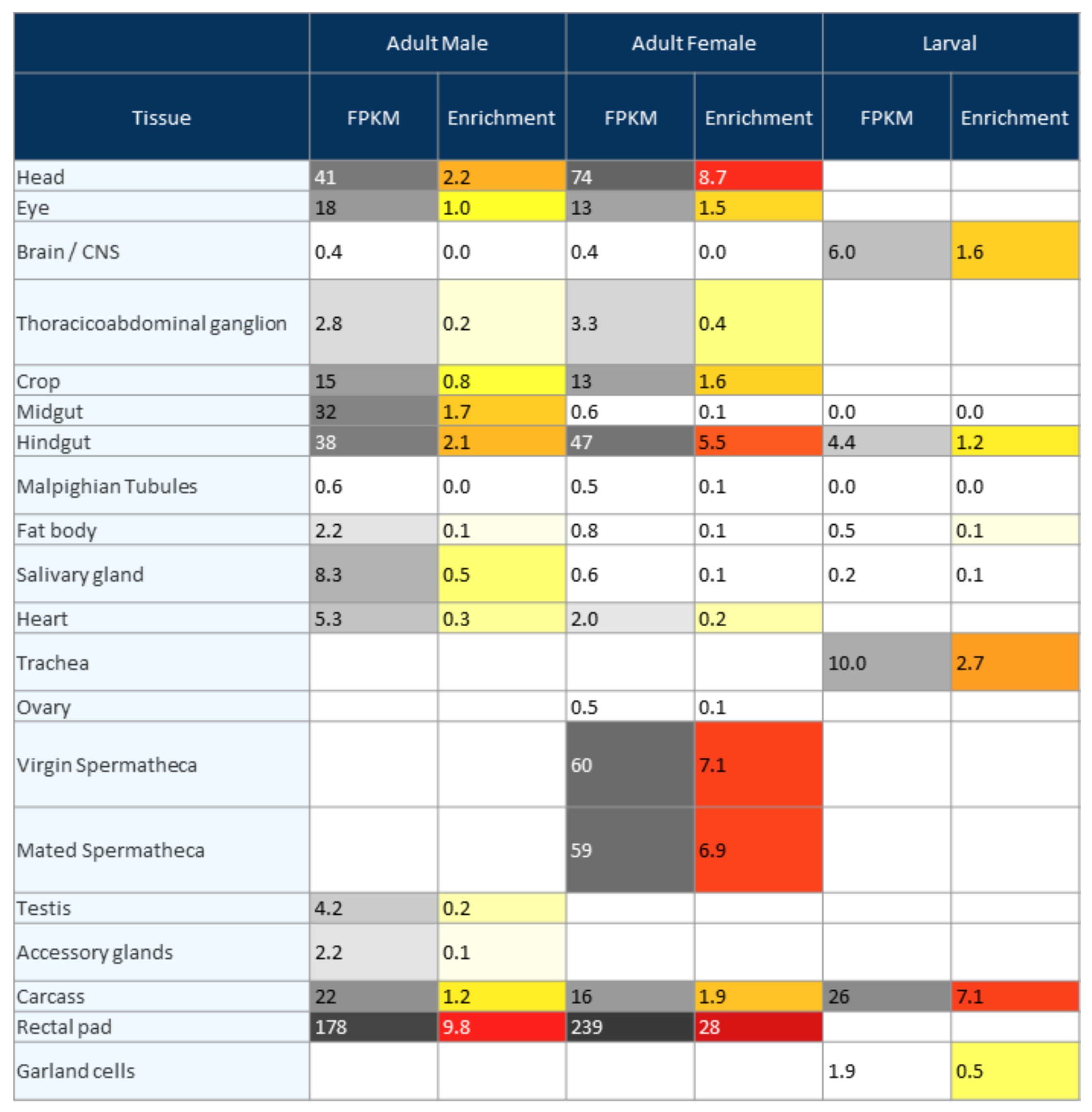
3.4. Tissue Specificity of JHBP Genes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hidayat, P.; Goodman, W.G. Juvenile hormone and hemolymph juvenile hormone binding protein titers and their interaction in the hemolymph of fourth stadium Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1994, 24, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, K.J.; Sanburg, L.L.; Kezdy, F.J.; Law, J.H. The Juvenile Hormone Binding Protein in the Hemolymph of Manduca sexta Johannson (Lepidoptera: Sphingidae). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Touhara, K.; Lerro, K.A.; Bonning, B.C.; Hammock, B.D.; Prestwich, G.D. Ligand binding by a recombinant insect juvenile hormone binding protein. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 2068–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trowell, S.C. High affinity juvenile hormone carrier proteins in the haemolymph of insects. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1992, 103, 795–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touhara, K.; Bonning, B.C.; Hammock, B.D.; Prestwich, G.D. Action of juvenile hormone (JH) esterase on the JH-JH binding protein complex. an in vitro model of JH metabolism in a caterpillar. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 25, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhout, H.F. Insect Hormones; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jindra, M.; Palli, S.R.; Riddiford, L.M. The juvenile hormone signaling pathway in insect development. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 181–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giray, T.; Giovanetti, M.; West-Eberhard, M.J. Juvenile hormone, reproduction, and worker behavior in the neotropical social wasp Polistes canadensis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3330–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hahn, D.A.; Denlinger, D.L. Energetics of insect diapause. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartfelder, K.; Emlen, D.J. 11—Endocrine Control of Insect Polyphenism. In Insect Endocrinology; Gilbert, L.I., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 464–522. [Google Scholar]
- Sliter, T.J.; Sedlak, B.J.; Baker, F.C.; Schooley, D.A. Juvenile hormone in Drosophila melanogaster: Identification and titer determination during development. Insect Biochem. 1987, 17, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Perez, C.; Nouzova, M.; Noriega, F.G. A Quantitative Assay for the Juvenile Hormones and Their Precursors Using Fluorescent Tags. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Edery, I. Daywake, an Anti-siesta Gene Linked to a Splicing-Based Thermostat from an Adjoining Clock Gene. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, 1728–1734.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarov-Blat, L.; So, W.V.; Liu, L.; Rosbash, M. The Drosophila takeout Gene Is a Novel Molecular Link between Circadian Rhythms and Feeding Behavior. Cell 2000, 101, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- So, W.V.; Sarov-Blat, L.; Kotarski, C.K.; McDonald, M.J.; Allada, R.; Rosbash, M. takeout, a novel Drosophila gene under circadian clock transcriptional regulation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 6935–6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dauwalder, B.; Tsujimoto, S.; Moss, J.; Mattox, W. The Drosophila takeout gene is regulated by the somatic sex-determination pathway and affects male courtship behavior. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 2879–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jindra, M.; Uhlirova, M.; Charles, J.P.; Smykal, V.; Hill, R.J. Genetic Evidence for Function of the bHLH-PAS Protein Gce/Met as a Juvenile Hormone Receptor. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, T.G.; Ashok, M. Insecticide resistance resulting from an absence of target-site gene product. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14040–14044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abdou, M.A.; He, Q.; Wen, D.; Zyaan, O.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Baumann, A.A.; Joseph, J.; Wilson, T.G.; Li, S.; et al. Drosophila Met and Gce are partially redundant in transducing juvenile hormone action. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewski, J.; Wang, S.; Wilson, T.G. Interaction of bHLH-PAS proteins involved in juvenile hormone reception in Drosophila. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 342, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Liu, H.; Wen, D.; He, Q.; Wang, S.; Shao, W.; Jiang, R.J.; An, S.; Sun, Y.; et al. Juvenile hormone counteracts the bHLH-PAS transcription factors MET and GCE to prevent caspase-dependent programmed cell death in Drosophila. Development 2009, 136, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Baumann, A.; Wilson, T.G. Drosophila melanogaster Methoprene-tolerant (Met) gene homologs from three mosquito species: Members of PAS transcriptional factor family. J. Insect Physiol. 2007, 53, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Charles, J.P.; Iwema, T.; Epa, V.C.; Takaki, K.; Rynes, J.; Jindra, M. Ligand-binding properties of a juvenile hormone receptor, Methoprene-tolerant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 21128–21133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kayukawa, T.; Minakuchi, C.; Namiki, T.; Togawa, T.; Yoshiyama, M.; Kamimura, M.; Mita, K.; Imanishi, S.; Kiuchi, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of juvenile hormone-mediated induction of Kruppel homolog 1, a repressor of insect metamorphosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 11729–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miura, K.; Oda, M.; Makita, S.; Chinzei, Y. Characterization of the Drosophila Methoprene-tolerant gene product. Juvenile hormone binding and ligand-dependent gene regulation. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kewley, R.J.; Whitelaw, M.L.; Chapman-Smith, A. The mammalian basic helix-loop-helix/PAS family of transcriptional regulators. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Mead, E.A.; Zhu, J. Heterodimer of two bHLH-PAS proteins mediates juvenile hormone-induced gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Sheng, Z.; Sui, Y.; Palli, S.R. Steroid receptor co-activator is required for juvenile hormone signal transduction through a bHLH-PAS transcription factor, methoprene tolerant. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 8437–8447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.W.; Jeon, J.H.; Jeong, S.A.; Kim, J.A.; Park, D.S.; Shin, Y.; Oh, H.W. A plant diterpene counteracts juvenile hormone-mediated gene regulation during Drosophila melanogaster larval development. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, H.W.; Fang, Y.; An, S.B.; Park, D.S.; Song, H.H.; Oh, S.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, N.; et al. Identification of plant compounds that disrupt the insect juvenile hormone receptor complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1733–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.E.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. 20 years of the SMART protein domain annotation resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leader, D.P.; Krause, S.A.; Pandit, A.; Davies, S.A.; Dow, J.A.T. FlyAtlas 2: A new version of the Drosophila melanogaster expression atlas with RNA-Seq, miRNA-Seq and sex-specific data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D809–D815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Peng, H.-J.; Zhu, J. Juvenile hormone-activated phospholipase C pathway enhances transcriptional activation by the methoprene-tolerant protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1871–E1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, H.W.; Yun, C.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, J.A.; Park, D.S.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.R.; Song, H.H.; Shin, Y.; Jung, C.S.; et al. Conifer Diterpene Resin Acids Disrupt Juvenile Hormone-Mediated Endocrine Regulation in the Indian Meal Moth Plodia interpunctella. J. Chem. Ecol. 2017, 43, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| JHBPs | GeneID | Gene Expression (Inducibility by Methyl Lucidone) | Flyatlas 2 Enrichments | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JHBP1 | CG1124 | Inducible in larval stage (Figure 1) | Larval carcass and adult rectal pad | |
| JHBP2 | CG2016 | Inducible in larval and pupal stages (Figure 1 and Figure 2) | Larval trachea and adult head | |
| JHBP3 | CG14661 | Mainly expressed in adults, no significant induction (Figure 3) | Female head and carcass | |
| JHBP4 | CG10264 | Inducible in larval and pupal stages (Figure 1 and Figure 2) | None | * |
| JHBP5 | CG10407 | Mainly expressed in male adults (Figure 3), no significant induction | Male testis | |
| JHBP6 | CG14457 | only basal expression in all stages (Figure 3), no significant induction | Larval and adult midgut | |
| JHBP7 | CG11852 | Mainly expressed in pupal stage (Figure 3), no significant induction | Larval trachea and hindgut | |
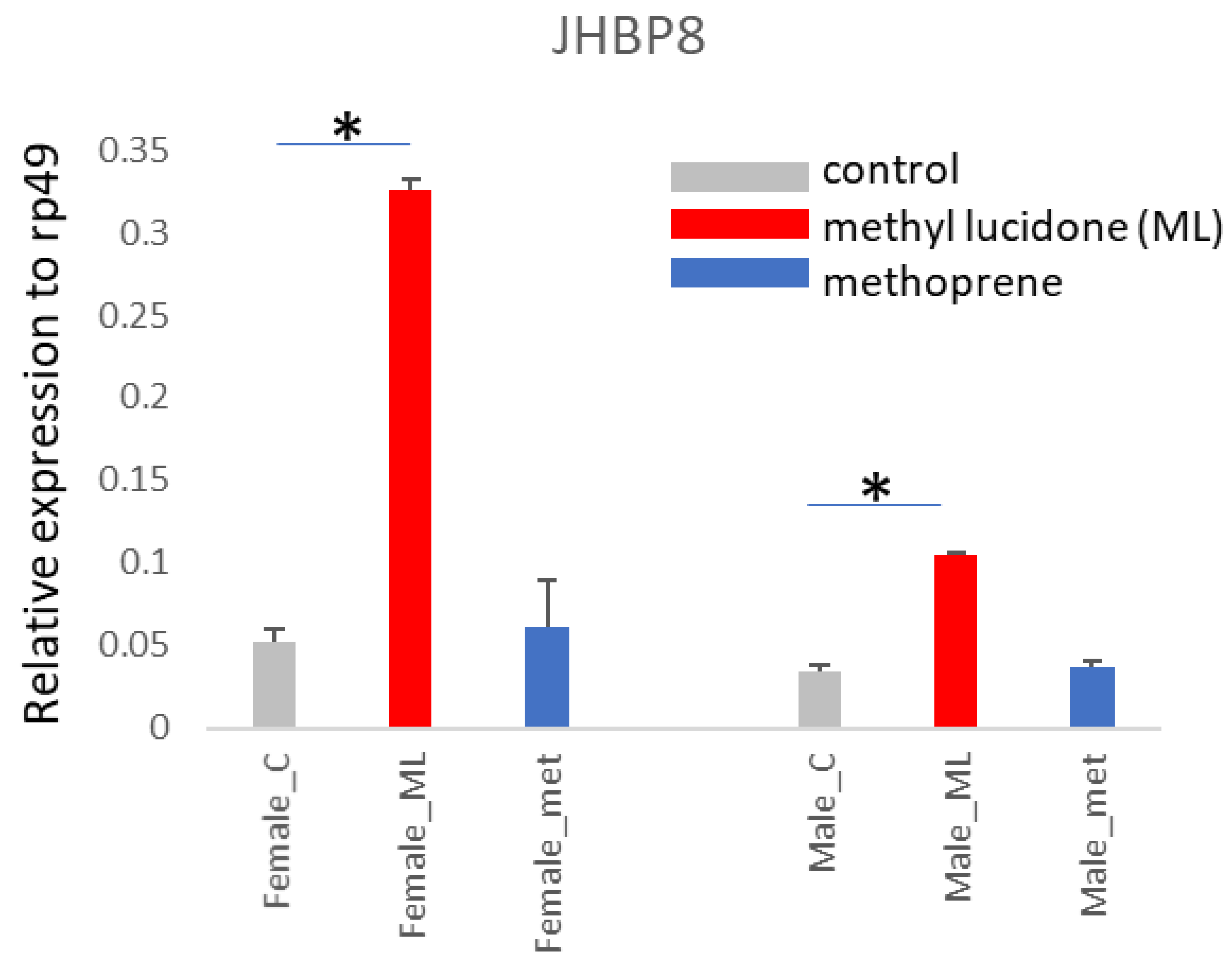
| JHBP8 | CG2650 | Mainly expressed and inducible in adults (Figure 4) | Male rectal pad | Daywake |
| JHBP9 | CG11853 | Mainly expressed in female adults (Figure 3), no significant induction | Ubiquitous | Takeout |
| JHBP10 | CG33680 | Mainly expressed in larvae and female adults (Figure 3), no significant induction | None | *, ** |
| JHBP11 | CG17189 | Inducible in larval stage, but strongly repressed in pupal stage (Figure 1 and Figure 2) | Female rectal pad | |
| JHBP12 | CG13618 | Inducible in larval stage, but strongly repressed in pupal stage (Figure 1 and Figure 2) | Adult crop and rectal pad | |
| JHBP13 | CG5945 | Mainly expressed in adults, no significant induction (Figure 3) | Adult head | |
| JHBP14 | CG5867 | Mainly expressed in larvae and adults, no significant induction (Figure 3) | Ubiquitous | |
| JHBP15 | CG17279 | only basal expression in all stages (Figure 3), no significant induction | Adult head | |
| JHBP16 | CG15497 | Inducible in larval stage (Figure 1) | None |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shin, S.-W.; Jeon, J.-H.; Kim, J.-A.; Park, D.-S.; Shin, Y.-J.; Oh, H.-W. Inducible Expression of Several Drosophila melanogaster Genes Encoding Juvenile Hormone Binding Proteins by a Plant Diterpene Secondary Metabolite, Methyl Lucidone. Insects 2022, 13, 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050420
Shin S-W, Jeon J-H, Kim J-A, Park D-S, Shin Y-J, Oh H-W. Inducible Expression of Several Drosophila melanogaster Genes Encoding Juvenile Hormone Binding Proteins by a Plant Diterpene Secondary Metabolite, Methyl Lucidone. Insects. 2022; 13(5):420. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050420
Chicago/Turabian StyleShin, Sang-Woon, Jun-Hyoung Jeon, Ji-Ae Kim, Doo-Sang Park, Young-Joo Shin, and Hyun-Woo Oh. 2022. "Inducible Expression of Several Drosophila melanogaster Genes Encoding Juvenile Hormone Binding Proteins by a Plant Diterpene Secondary Metabolite, Methyl Lucidone" Insects 13, no. 5: 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050420
APA StyleShin, S.-W., Jeon, J.-H., Kim, J.-A., Park, D.-S., Shin, Y.-J., & Oh, H.-W. (2022). Inducible Expression of Several Drosophila melanogaster Genes Encoding Juvenile Hormone Binding Proteins by a Plant Diterpene Secondary Metabolite, Methyl Lucidone. Insects, 13(5), 420. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050420






