Observation of the Antimicrobial Activities of Two Actinomycetes in the Harvester Ant Messor orientalis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Ant Samples and Indicator Fungi
2.2. Isolation of Actinomycetes
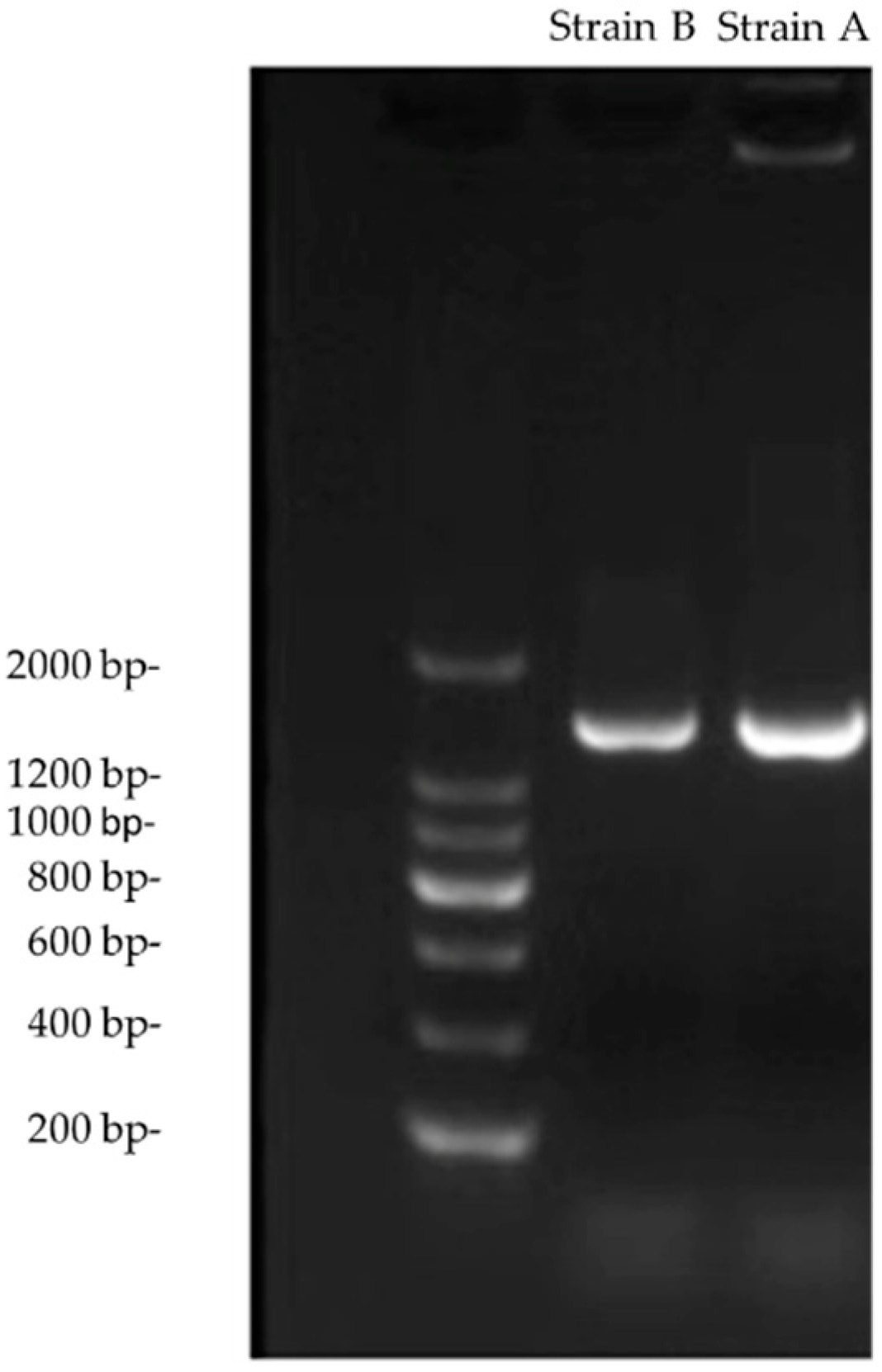
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Biochemical Identification
2.4. Bioassay of the Fungal Inhibition Effect
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Actinomycetes
3.2. Study of Fungal Inhibitory Activity
3.2.1. Fungal Inhibitory Activity of the Fermentation Broth
3.2.2. Inhibitory Activity of Actinomycete Colonies
4. Conclusions
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baumann, P.; Baumann, L.; Lai, C.; Rouhbakhsh, D.; Moran, N.; Clark, M. Genetics, physiology, and evolutionary relationships of the genus Buchnera: Intracellular symbionts of aphids. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 55–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, Y. Endosymbiotic bacteria in insects: Their diversity and culturability. Microbes. Environ. 2009, 24, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schӓfer, A.; Konrad, R.; Kuhnigk, T. Hemicellulose-degrading bacteria and yeasts from the termite gut. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1996, 5, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignell, D.E.; Oskarsson, H.; Anderson, J.M. Association of actinomycete-lik bacteria with soil-feeding termites (Termitidae, Termitinae). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1979, 2, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, C.R.; Scott, J.A.; Summerbell, R.C.; Malloch, D. Fungus-growing ants use antibiotic-producing bacteria to control garden parasites. Nature 2003, 398, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.K.; Zhang, G.F.; Jiao, R.H.; Shen, Y.; Xu, Q.; Tan, R.X.; Ge, H.M. Actinotetraoses A–H: Tetrasaccharide derivatives from a grasshopper-associated Amycolatopsis sp. HCal. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.H.; Li, S.; Zhou, D.X.; Zhang, Y.L. Isolation and identification of termination antagonistic actinomycetes BYC 01 and its active metabolites. Acta Microbiol. Sinica. 2014, 7, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, U.G.; Dash, D.; Rabeling, C.; Rodrigues, A. Coevolution between attine ants and actinomycete bacteria: A reevaluation. Evolution 2008, 62, 2894–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrette, M.G.; Carlson, C.M.; Ortega, H.E.; Thomas, C.; Ananiev, G.E.; Barns, K.J.; Book, A.J.; Cagnazzo, J.; Carlos, C.; Flanigan, W.; et al. The antimicrobial potential of Streptomyces from insect microbiomes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blodgett, J.A.V.; Oh, D.C.; Cao, S.G.; Currie, C.R.; Kolter, R.; Clardy, J. Common biosynthetic origins for polycyclic tetramate macrolactams from phylogenetically diverse bacteria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11692–11697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.J.; Oh, D.C.; Yuceer, M.C.; Klepzig, K.D.; Clardy, J.; Currie, C.R. Bacterial protection of beetle-fungus mutualism. Science 2008, 322, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, M.; Oh, D.C.; Clardy, J.; Currie, C.R. Chemical analyses of wasp-associated Streptomyces bacteria reveal a prolific potential for natural products discovery. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, N.A. Fungus-growing ants: A symbiotic relationship exists between an insect and a plant, involving an effective culturing technique. Science 1966, 3736, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.F. Diversity of Symbiotic Actinomycetes from Camponotus janponicus Mayr and Their Antibacterial Activity. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, X.F.; Xu, Y.J.; Cheng, D.F.; Lu, Y.Y. Identification and culture of Streptomyces sp. DF-5 isolated from Solenopsis invicta and the antifungal activity of its fermentation broth to plant pathogenic fungi. Acta J. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 4, 917–924. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, D.C.; Poulsen, M.; Currie, C.R.; Clardy, J. Dentigerumycin: A bacterial mediator of an ant-fungus symbiosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, A.A.; Chistov, A.A.; Tyurin, A.P.; Prokhorenko, I.A.; Korshun, V.A.; Biryukov, M.V.; Alferova, V.A.; Zakalyukina, Y.V. Chemical ecology of Streptomyces albidoflavus strain A10 associated with carpenter ant Camponotus vagus. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akalyukina, Y.V.; Birykov, M.V.; Lukianov, D.A.; Shiriaev, D.I.; Komarova, E.S.; Skvortsov, D.A.; Kostyukevich, Y.; Tashlitsky, V.N.; Polshakov, V.I.; Nikolaev, E.; et al. Nybomycin-producing Streptomyces isolated from carpenter ant Camponotus vagus. Biochimie 2019, 160, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterman, I.A.; Wieland, M.; Maviza, T.P.; Lashkevich, K.A.; Lukianov, D.A.; Komarova, E.S.; Zakalyukina, Y.V.; Buschauer, R.; Shiriaev, D.I.; Leyn, S.A.; et al. Tetracenomycin X inhibits translation by binding within the ribosomal exit tunnel. Nature Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarsa, C.; McMillan, A.; Warren, R.J. Plant pathogenic fungi decrease in soil inhabited by seed-dispersing ants. Insect. Soc. 2018, 65, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMahon, J.A.; Mull, J.F.; Crist, T.O. Harvester ants (Pogonomyrmex spp.): Their community and ecosystem influences. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2000, 31, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.S. Current status and development strategy for research on plant fungal diseases in China. Plant Prot. 2010, 3, 9–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.D.; Shen, C.R. The fungicide resistance of plant pathogens and solutions. Acta Phytopathol. Sinica 1994, 24, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, M.; Williams, S.T. Ecology of Actinomycetes. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 1984, 1, 189–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solecka, J.; Zajko, J.; Postek, M.; Rajnisz, A. Biologically active secondary metabolites from Actinomycetes. Cent. Euro. J.Bio. 2012, 7, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.M.; Wang, Z.B.; Chen, X.J.; Gu, F.; Zhang, Y.F.; Chen, Z.X.; Pang, X.B. Evaluation of resistance of a novel rice germplasm YSBR1 to sheath blight. Acta Agron. Sin. 2009, 04, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, G.H.; Feng, D.N.; Li, W.; Lian, S.L.; Xi, P.G.; Jiang, Z.D. Research progress in studies on the downy blight disease in litchi. J. Fruit Sci. 2021, 38, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannaa, M.; Kim, K.D. Biocontrol activity of volatile-producing Bacillus megaterium and Pseudomonas protegens against Aspergillus and Penicillium spp. Predominant in stored rice grains: Study II. Mycobiology 2018, 46, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, D.C.; Shaaban, K.A.; Gos, F.M.W.; Thorson, J.S.; Glienke, C.; Rohr, J. Secondary metabolites produced by Microbacterium sp. LGMB471 with antifungal activity against the phytopathogen Phyllosticta citricarpa. Folia Microbiol. 2019, 64, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, S.M.Y.; Pastorino, G.N.; Balatti, P.A. Volatile organic compounds profile synthesized and released by endophytes of tomato (Solanum lycopersici L.) and their antagonistic role. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapidus, A.; Pukall, R.; LaButtii, K.; Copeland, A.; Del Rio, T.G.; Nolan, M.; Chen, F.; Lucas, S.; Tice, H.; Cheng, J.F.; et al. Complete genome sequence of Brachybacterium faecium type strain (Schefferle 6–10(T)). Stand. Genom. Sci. 2009, 1, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, S.; Sevugapperumal, N.; Nallusamy, S.; Shanmugam, H.; Mathiyazhagan, K.; Rangasamy, A.; Subbiah, K.A.; Ganesan, M.V. Differential bacterial endophytome in Foc-resistant banana cultivar displays enhanced antagonistic activity against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense (Foc). Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 2701–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, T.R. In search of ant ancestors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 14028–14029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, G.; Derbyshire, E.R.; Caldera, E.; Currie, C.R.; Clardy, J. Antibiotic and antimalarial quinones from fungus-growing ant-associated Pseudonocardia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldera, E.J.; Poulsen, M.; Suen, G.; Currie, C.R. Insect symbioses: A case study of past, present, and future fungus-growing ant research. Env. Entomol. 2009, 38, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenian, I.; Spiteller, M.; Ghaste, M.; Wirth, R.; Herz, H.; Spiteller, D. Chemical basis of the synergism and antagonism in microbial communities in the nests of leaf-cutting ants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1955–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeder, S.; Wirth, R.; Herz, H.; Spiteller, D. Candicidin-producing Streptomyces support leaf-cutting ants to protect their fungus garden against the pathogenic fungus Escovopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4742–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronque, M.U.V.; Lyra, M.L.; Migliorini, G.H.; Bacci, M., Jr.; Oliveira, P.S. Symbiotic bacterial communities in rainforest fungus-farming ants: Evidence for species and colony specificity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seipke, R.F.; Barke, J.; Brearley, C.; Hill, L.; Yu, D.W.; Goss, R.J.; Hutchings, M.I. A single Streptomyces symbiont makes multiple antifungals to support the fungus farming ant Acromyrmex octospinosus. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zani, R.D.A.; Ferro, M.; Bacci, M. Three phylogenetically distinct and culturable diazotrophs are perennial symbionts of leaf-cutting ants. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 17686–17699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Step | Reaction Temperature (°C) | Reaction Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Initialization | 94 | 15 |
| Denaturing | 94 | 0.5 a |
| Annealing | 55 | 0.5 a |
| Elongation | 72 | 1 a |
| Stop | 72 | 10 |
| Characteristic | Strain A | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2S production | − | − | − | + | + | + | − |
| Acid production from: | |||||||
| D-fructose | + | ND | + | − | + | + | − |
| Maltose | + | + | + | − | + | + | (+) |
| D-mannose | + | ND | (+) | (+) | + | + | − |
| L-rhamnose | + | + | (+) | (+) | + | + | − |
| Sucrose | + | + | − | + | (+) | − | − |
| D-xylose | + | + | − | − | − | + | − |
| Galactose | + | ND | + | + | + | + | + |
| Characteristic | Strain B | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2S production | − | ND | + | + | − | − | + |
| Utilization of: | |||||||
| Maltose | + | ND | + | + | + | + | + |
| D-mannose | − | ND | + | + | + | + | + |
| Acid production from: | |||||||
| L-rhamnose | − | + | − | − | − | + | − |
| Sucrose | + | ND | + | + | + | − | − |
| D-xylose | − | ND | − | − | − | + | − |
| Galactose | − | + | − | + | − | − | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, S. Observation of the Antimicrobial Activities of Two Actinomycetes in the Harvester Ant Messor orientalis. Insects 2022, 13, 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13080691
Wu Y, Liu Y, Yu J, Xu Y, Chen S. Observation of the Antimicrobial Activities of Two Actinomycetes in the Harvester Ant Messor orientalis. Insects. 2022; 13(8):691. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13080691
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yiyang, Yaxuan Liu, Jinyong Yu, Yijuan Xu, and Siqi Chen. 2022. "Observation of the Antimicrobial Activities of Two Actinomycetes in the Harvester Ant Messor orientalis" Insects 13, no. 8: 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13080691
APA StyleWu, Y., Liu, Y., Yu, J., Xu, Y., & Chen, S. (2022). Observation of the Antimicrobial Activities of Two Actinomycetes in the Harvester Ant Messor orientalis. Insects, 13(8), 691. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13080691








