Regional β-Diversity of Stream Insects in Coastal Alabama Is Correlated with Stream Conditions, Not Distance among Sites
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
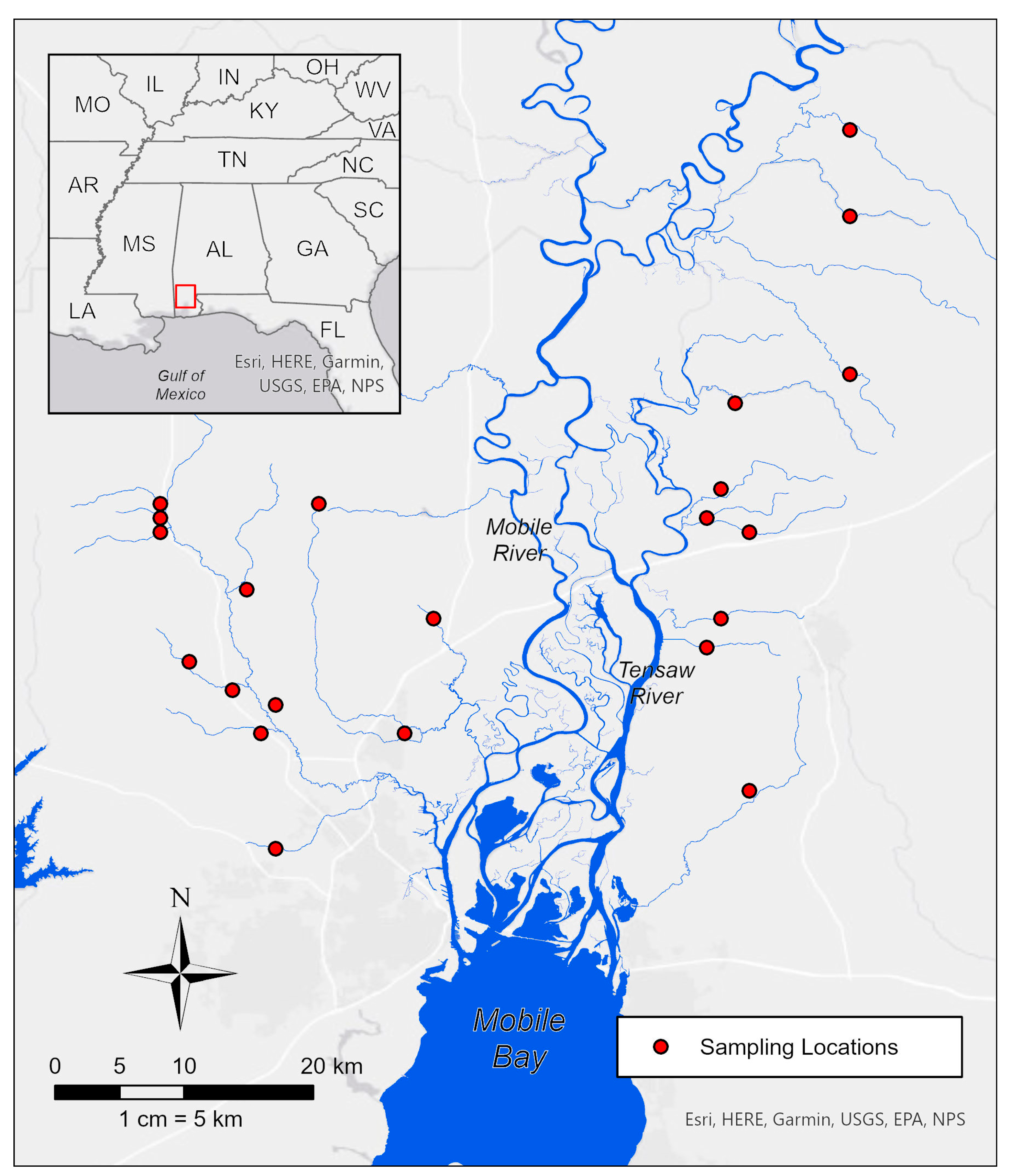
2.1. Study Sites and Sampling Protocols
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Collection and Identification
3.2. Principal Component Analyses of Stream Variables
3.3. Partial Mantel Test Correlations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rosenzweig, M. Species Diversity in Space and Time, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, R.D.; Cox, S.B.; Strauss, R.E.; Willig, M.R. Patterns of functional diversity across an extensive environmental gradient: Vertebrate consumers, hidden treatments and latitudinal trends. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.H. Vegetation of the Siskiyou Mountains, Oregon and California. Ecol. Monogr. 1960, 30, 279–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.H. Evolution and measurement of species diversity. Taxon 1972, 21, 213–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, R.J.; Willis, K.J.; Field, R. Scale and species richness: Towards a general, hierarchical theory of species diversity. J. Biogeogr. 2001, 28, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklefs, R.E. Community diversity: Relative roles of local and regional processes. Science 1987, 235, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouquet, N.; Loreau, M. Community patterns in source-sink metacommunities. Am. Nat. 2003, 162, 544–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, P.; Cáceres, M. Beta diversity as the variance of community data: Dissimilarity coefficients and partitioning. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellend, M. Do commonly used indices of β-diversity measure species turnover? J. Veg. Sci. 2001, 12, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, H.; Ruokolainen, K. Analyzing or explaining beta diversity? Understanding the targets of different methods of analysis. Ecology 2006, 87, 2697–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, H. A diversity of beta diversities: Straightening up a concept gone awry. Part 1. Defining beta diversity as a function of alpha and gamma diversity. Ecography 2010, 33, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Crist, T.O.; Chase, J.M.; Vellend, M.; Inouye, B.D.; Freestone, A.L.; Sanders, N.J.; Cornell, H.V.; Comita, L.S.; Davies, K.F.; et al. Navigating the multiple meanings of β diversity: A roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, D.M.P.; Callisto, M.; Solar, R.R.C.; Macedo, D.R.; Fernandes, G.W. Beta diversity of aquatic invertebrates increases along an altitudinal gradient in a Neotropical mountain. Biotropica 2019, 51, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoner, P.; Marle, P.; Castella, E.; Lehmann, A. Assessment of the stream invertebrate β-diversity along an elevation gradient using a bidimensional null model analysis. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 12, e9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.S.; Melo, A.S. Beta diversity in stream macroinvertebrate assemblages: Among-site and among-microhabitat com-ponents. Hydrobiologia 2008, 598, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hepp, L.U.; Landeiro, V.L.; Melo, A.S. Experimental assessment of the effects of environmental factors and longitudinal position on alpha and beta diversities of aquatic insects in a Neotropical stream. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol. 2012, 97, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, P.V. Ecological and evolutionary drivers of geographic variation in species diversity. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2015, 46, 369–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Wang, X. Global relationships between beta diversity and latitude after accounting for regional diversity. Ecol. Inform. 2015, 25, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J.; Alahuhta, J.; Fattorini, S.; Schmera, D. Predicting beta diversity of terrestrial and aquatic beetles using ecogeographical variables: Insights from the replacement and richness difference components. J. Biogeogr. 2019, 46, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magurran, A.E. Measuring biological diversity. Curr. Biol. 2021, 31, R1174–R1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.J.; Carlson, A.K.; Creed, I.F.; Eliason, E.J.; Gell, P.A.; Johnson, P.T.J.; Kidd, K.A.; MacCormack, T.J.; Olden, J.D.; Ormerod, S.J.; et al. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 849–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pound, K.L.; Larson, C.A.; Passy, S.I. Current distributions and future climate-driven changes in diatoms, insects and fish in US streams. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2021, 30, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benke, A.C.; Wallace, J.B. Trophic basis of production among net-spinning caddisflies in a southern Appalachian stream. Ecology 1980, 61, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benke, A.C.; Henry, R.L.; Gillespie, D.M.; Hunter, R.J. Importance of snag habitat for animal production in southeastern streams. Fisheries 1985, 10, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreadie, J.W.; Bedwell, C.R. Patterns of co-occurrence of stream insects and an examination of a causal mechanism: Ecological checkerboard or habitat checkerboard? Insect Conserv. Divers. 2013, 6, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreadie, J.W.; Bedwell, C. Species composition of local riffle beetle assemblages in small coastal streams of the Gulf of Mexico: The influences of local and regional factors. Aquat. Ecol. 2014, 48, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.E. A Field Guide to Mobile Delta Geomorphology; Geological Survey of Alabama: Tuscaloosa, AL, USA, 1997; Volume 80. [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen, T. A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species content and its application to analyses of the vegetation on Danish commons. Biol. Skr. 1948, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Baselga, A.; Orme, C.D.L. Betapart: An R package for the study of beta diversity. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burr, B.M.; Eisenhour, D.J.; Mettee, M.F.; O’Neil, P.E.; Pierson, J.M. Fishes of Alabama and the Mobile Basin, 1st ed.; Oxmoor House: Birmingham, AL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, R.W.; Cummins, K.W. An Introduction to the Aquatic Insects of North America, 4th ed.; Kendall/Hunt: Dubuque, IA, USA, 2008; pp. 15–37. [Google Scholar]
- McCreadie, J.W.; Hamada, N.; Grillet, M.E. Spatial-temporal distribution of preimaginal blackflies in Neotropical streams. Hydrobiologia 2004, 513, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, J.; Allan, J.D. Stream Ecology: Structure and Function of Running Waters, 3rd ed.; Springer Nature: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Epler, J.H. Identification Manual for the Water Beetles of Florida: (Coleoptera: Dryopidae, Dytiscidae, Elmidae, Gyrinidae, Haliplidae, Hy-draenidae, Hydrophilidae, Noteridae, Psephenidae, Ptilodactylidae, Scirtidae); State of Florida, Department of Environmental Protection, Division of Water Facilities: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Pescador, M.L.; Rasmussen, A.K.; Richard, B.A.; McCarron, E. A Guide to the Stoneflies (Plecoptera) of Florida; State of Florida, Department of Environmental Protection, Division of Water Resource Management: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, A.K.; Pescador, M.L. A Guide to the Megaloptera and Aquatic Neuroptera of Florida; Department of Environmental Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Daigle, J.J. Florida Dragonflies (Anisoptera): A Species Key to the Aquatic Larval Stages. Fla. Dep. Environ. Regul. Tech. Ser. 1992, 12, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, J.S. Identification Manual for the Dragonfly Larvae (Anisoptera) of Florida; State of Florida, Department of Environmental Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pescador, M.L.; Rasmussen, A.K.; Harris, S.C. Identification Manual for the Caddisfly (Trichoptera) Larvae of Florida; State of Florida, Florida Department of Environmental Protection: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, K.; Gorley, R. Plymouth Routines in Multivariate Ecological Research; Plymouth Marine Laboratory: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Mantel, N. The detection of disease clustering and a generalized regression approach. Cancer Res. 1967, 27 Pt 1, 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, G.P.; Keough, M.J. Experimental Design and Data Analysis for Biologists, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Borcard, D.; Legendre, P. Is the Mantel correlogram powerful enough to be useful in ecological analysis? A simulation study. Ecology 2012, 93, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baselga, A. Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2010, 19, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.; Ricklefs, R.E.; White, P.S. Beta diversity of angiosperms in temperate floras of eastern Asia and eastern North America. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, B.D.; Atmar, W. Nested subsets and the structure of insular mammalian faunas and archipelagos. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 1986, 28, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, W.; Gotelli, N.J. Disentangling community patterns of nestedness and species co-occurrence. Oikos 2007, 116, 2053–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, K.; Gorley, R. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial; PRIMER-E: Plymouth, UK, 2006; p. 192. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.; Ryan, P.D. PAST–Palaeontological Statistics, version 1.90; University of Oslo: Oslo, Norway, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Heino, J.; Melo, A.S.; Bini, L.M.; Altermatt, F.; Al-Shami, S.A.; Angeler, D.G.; Bonada, N.; Brand, C.; Callisto, M.; Cottenie, K.; et al. A comparative analysis reveals weak relationships between ecological factors and beta diversity of stream insect metacommunities at two spatial levels. Ecol. Evol. 2015, 5, 1235–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currie, D.J. Energy and large-scale patterns of animal-and plant-species richness. Am. Nat. 1991, 137, 27–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leibold, M.A.; Holyoak, M.; Mouquet, N.; Amarasekare, P.; Chase, J.M.; Hoopes, M.F.; Holt, R.D.; Shurin, J.B.; Law, R.; Tilman, D.; et al. The metacommunity concept: A framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heino, J. Biodiversity of aquatic insects: Spatial gradients and environmental correlates of assemblage-level measures at large scales. Freshw. Rev. 2009, 2, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCreadie, J.W.; Adler, P.H. The roles of abiotic factors, dispersal, and species interactions in structuring stream assemblages of black flies (Diptera: Simuliidae). Aquat. Biosyst. 2012, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shami, S.A.; Heino, J.; Salmah, M.R.C.; ABU Hassan, A.; Suhaila, A.H.; Madrus, M.R. Drivers of beta diversity of macroinvertebrate communities in tropical forest streams. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1126–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya’cob, Z.; Takaoka, H.; Pramual, P.; Low, V.L.; Sofian-Azirun, M. Distribution pattern of black fly (Diptera: Simuliidae) assemblages along an altitudinal gradient in Peninsular Malaysia. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibold, M.A.; Chase, J.M.; Ernest, S.K.M. Community assembly and the functioning of ecosystems: How metacommunity processes alter ecosystems attributes. Ecology 2017, 98, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, P.L.; Guzman, L.M.; De Meester, L.; Horváth, Z.; Ptacnik, R.; Vanschoenwinkel, B.; Viana, D.S.; Chase, J.M. A process-based metacommunity framework linking local and regional scale community ecology. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1314–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leprieur, F.; Tedesco, P.A.; Hugueny, B.; Beauchard, O.; Dürr, H.H.; Brosse, S.; Oberdorff, T. Partitioning global patterns of freshwater fish beta diversity reveals contrasting signatures of past climate changes. Ecol. Lett. 2011, 14, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maloney, K.O.; Munguia, P.; Mitchell, R.M. Anthropogenic disturbance and landscape patterns affect diversity patterns of aquatic benthic macroin-vertebrates. J. N. Am. Benthol. Soc. 2011, 30, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bie, T.; Meester, L.; Brendonck, L.; Martens, K.; Goddeeris, B.; Ercken, D.; Hampel, H.; Denys, L.; Vanhecke, L.; Gucht, K.; et al. Body size and dispersal mode as key traits determining metacommunity structure of aquatic organisms. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, B.L.; Wahl, C.; Swan, C.M. Experimentally disentangling the influence of dispersal and habitat filtering on benthic invertebrate com-munity structure. Freshw. Biol. 2018, 63, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Summer Collections | Fall Collections | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Family | Genus | % Occurrence | Family | Genus | % Occurrence |
| Elimidae | Ancyronyx | 94.1 | Elmidae | Ancyronyx | 100.0 |
| Aeshnidae | Boyeria | 94.1 | Elmidae | Stenelmis | 95.7 |
| Elimidae | Stenelmis | 94.1 | Coenagrionidae | Argia | 91.3 |
| Elimidae | Dubiraphia | 82.4 | Philopotamidae | Chimarra | 91.3 |
| Leuctridae | Leuctra | 82.4 | Hydropsychidae | Hydropsyche | 91.3 |
| Gomphidae | Gomphus | 76.5 | Gomphidae | Progomphus | 91.3 |
| Hydropsychidae | Chimarra | 70.6 | Hydropsychidae | Cheumatopsyche | 87.0 |
| Elimidae | Gonielmis | 70.6 | Perlidae | Acroneuria | 82.6 |
| Perlidae | Acroneuria | 64.7 | Leuctridae | Leuctra | 82.6 |
| Perlidae | Neoperla | 64.7 | Gomphidae | Gomphus | 78.3 |
| Libellulidae | Neurocordulia | 64.7 | Libellulidae | Neurocordulia | 78.3 |
| Hydropsychidae | Cheumatopsyche | 58.8 | Leptoceridae | Oecetis | 78.3 |
| Macromiidae | Macromia | 58.8 | Calamoceratidae | Anisocentropus | 73.9 |
| Gomphidae | Progomphus | 58.8 | Elmidae | Gonielmis | 73.9 |
| Perlidae | Perlesta | 52.9 | Elmidae | Microcylloepus | 73.9 |
| Elmidae | Dubiraphia | 69.6 | |||
| Perlidae | Perlinella | 69.6 | |||
| Aeshnidae | Boyeria | 65.2 | |||
| Brachycentridae | Brachycentrus | 65.2 | |||
| Perlidae | Paragnetina | 65.2 | |||
| Psephenidae | Ectopria | 56.5 | |||
| Calopterygidae | Calopteryx | 52.2 | |||
| Polycentropodidae | Neuroclipsis | 52.2 | |||
| Data Set | Observed No. of Taxa | Bootstrap Estimator of Taxa |
|---|---|---|
| Fall | ||
| Genus/species | 98 | 107.8 |
| Genus | 75 | 80.9 |
| Species | 44 | 49.2 |
| Summer | ||
| Genus/species | 83 | 93.9 |
| Genus | 62 | 67.8 |
| Species | 50 | 56.5 |
| Principal Components (PC) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | |
| Eigen Analysis | |||||
| Eigenvalue | 3.1060 | 2.7122 | 1.9497 | 1.3903 | 1.1557 |
| % Proportion variance explained | 0.239 | 0.209 | 0.150 | 0.107 | 0.089 |
| % Cumulative variance explained | 0.239 | 0.448 | 0.598 | 0.704 | 0.793 |
| Correlation analysis 1 | |||||
| Depth | 0.363 | −0.650 ** | 0.377 | 0.343 | −0.190 |
| Velocity | 0.622 * | 0.184 | −0.081 | 0.526 * | −0.240 |
| Elevation | −0.449 | −0.567 * | 0.065 | 0.126 | 0.379 |
| Width | 0.511 | 0.215 | 0.276 | −0.548 * | 0.060 |
| Discharge | 0.815 ** | −0.196 | 0.343 | 0.148 | −0.153 |
| Temperature | 0.110 | −0.252 | 0.372 | −0.743 ** | −0.211 |
| pH | 0.359 | 0.314 | 0.649 ** | 0.086 | 0.158 |
| Dissolved O2 | 0.537 * | 0.298 | −0.426 | 0.016 | −0.278 |
| Conductivity | −0.409 | 0.662 ** | 0.500 | 0.133 | 0.134 |
| Hardness | −0.240 | 0.707 ** | 0.541 * | 0.139 | −0.052 |
| Canopy | −0.472 | −0.454 | 0.457 | −0.053 | −0.359 |
| Riparian Veg. | 0.394 | −0.586 * | 0.216 | 0.135 | 0.506 |
| Bed Substrate | 0.558 * | 0.382 | −0.146 | −0.199 | 0.477 |
| Principal Components (PC) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 | |
| Eigen Analysis | |||||
| Eigenvalue | 3.5595 | 2.5328 | 1.9530 | 1.4662 | 1.1505 |
| % Proportion variance explained | 0.274 | 0.195 | 0.150 | 0.113 | 0.089 |
| % Cumulative variance explained | 0.274 | 0.469 | 0.619 | 0.732 | 0.820 |
| Correlation analysis 1 | |||||
| Depth | 0.628 * | 0.188 | −0.535 | 0.026 | 0.175 |
| Velocity | 0.016 | −0.621 * | −0.218 | −0.091 | −0.059 |
| Elevation | 0.551 | 0.318 | −0.156 | 0.058 | 0.373 |
| Width | 0.176 | −0.803 ** | −0.330 | −0.021 | 0.228 |
| Discharge | 0.590 | −0.352 | −0.669 * | 0.050 | 0.043 |
| Temperature | −0.530 | −0.139 | 0.407 | −0.196 | 0.578 |
| pH | −0.323 | −0.166 | −0.071 | −0.789 ** | 0.338 |
| Dissolved O2 | −0.125 | −0.855 ** | 0.183 | 0.157 | 0.011 |
| Conductivity | −0.777 ** | −0.011 | −0.487 | −0.302 | −0.115 |
| Hardness | −0.720 ** | 0.227 | −0.422 | −0.248 | −0.345 |
| Canopy | 0.269 | 0.626 * | −0.233 | −0.224 | 0.289 |
| Riparian Veg. | 0.799 ** | −0.122 | 0.322 | −0.358 | −0.262 |
| Bed Substrate | 0.483 | −0.272 | 0.353 | −0.606 * | −0.426 |
| Data Set | Partial Mantel Correlations 2 | Matrix Fill 3 | βMult | βturn | βnest | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stream Conditions | Distance among Sites | |||||
| Fall | ||||||
| Genus/species | 0.6693 p = 0.0001 | −0.0612 p = 0.7100 | 0.1852 | 0.8471 | 0.7692 | 0.0778 |
| Genus | 0.6333 p = 0.0001 | −0.1071 p = 0.8907 | 0.1417 | 0.8291 | 0.7297 | 0.0994 |
| Species | 0.4464 p = 0.0003 | 0.0684 p = 0.2098 | 0.0831 | 0.8616 | 0.7916 | 0.0697 |
| Summer | ||||||
| Genus/species | 0.6182 p = 0.0013 | 0.1458 p = 0.1216 | 0.2871 | 0.8436 | 0.7525 | 0.0911 |
| Genus | 0.5859 p = 0.0028 | 0.1436 p = 0.1259 | 0.2145 | 0.8210 | 0.7084 | 0.1126 |
| Species | 0.4980 p = 0.0041 | 0.1776 p = 0.0619 | 0.1730 | 0.8479 | 0.7280 | 0.1200 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sankone, C.; Bedwell, C.; McCreadie, J. Regional β-Diversity of Stream Insects in Coastal Alabama Is Correlated with Stream Conditions, Not Distance among Sites. Insects 2023, 14, 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14110847
Sankone C, Bedwell C, McCreadie J. Regional β-Diversity of Stream Insects in Coastal Alabama Is Correlated with Stream Conditions, Not Distance among Sites. Insects. 2023; 14(11):847. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14110847
Chicago/Turabian StyleSankone, Carlos, Chris Bedwell, and John McCreadie. 2023. "Regional β-Diversity of Stream Insects in Coastal Alabama Is Correlated with Stream Conditions, Not Distance among Sites" Insects 14, no. 11: 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14110847
APA StyleSankone, C., Bedwell, C., & McCreadie, J. (2023). Regional β-Diversity of Stream Insects in Coastal Alabama Is Correlated with Stream Conditions, Not Distance among Sites. Insects, 14(11), 847. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14110847





