Genome Assembly and Comparative Analysis of the Egg Parasitoid Wasp Trichogramma dendrolimi Shed Light on the Composition and Evolution of Olfactory Receptors and Venoms
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. PacBio and Illumina Data Generation
2.3. Genome Assembly
2.4. Assessment of the Genome Completeness and Quality
2.5. Genome Annotation
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.7. Gene Family Expansion and Contraction Analysis
2.8. Gene Family Annotation
3. Results
3.1. Genome Sequencing and Assembly
3.2. Genome Annotation
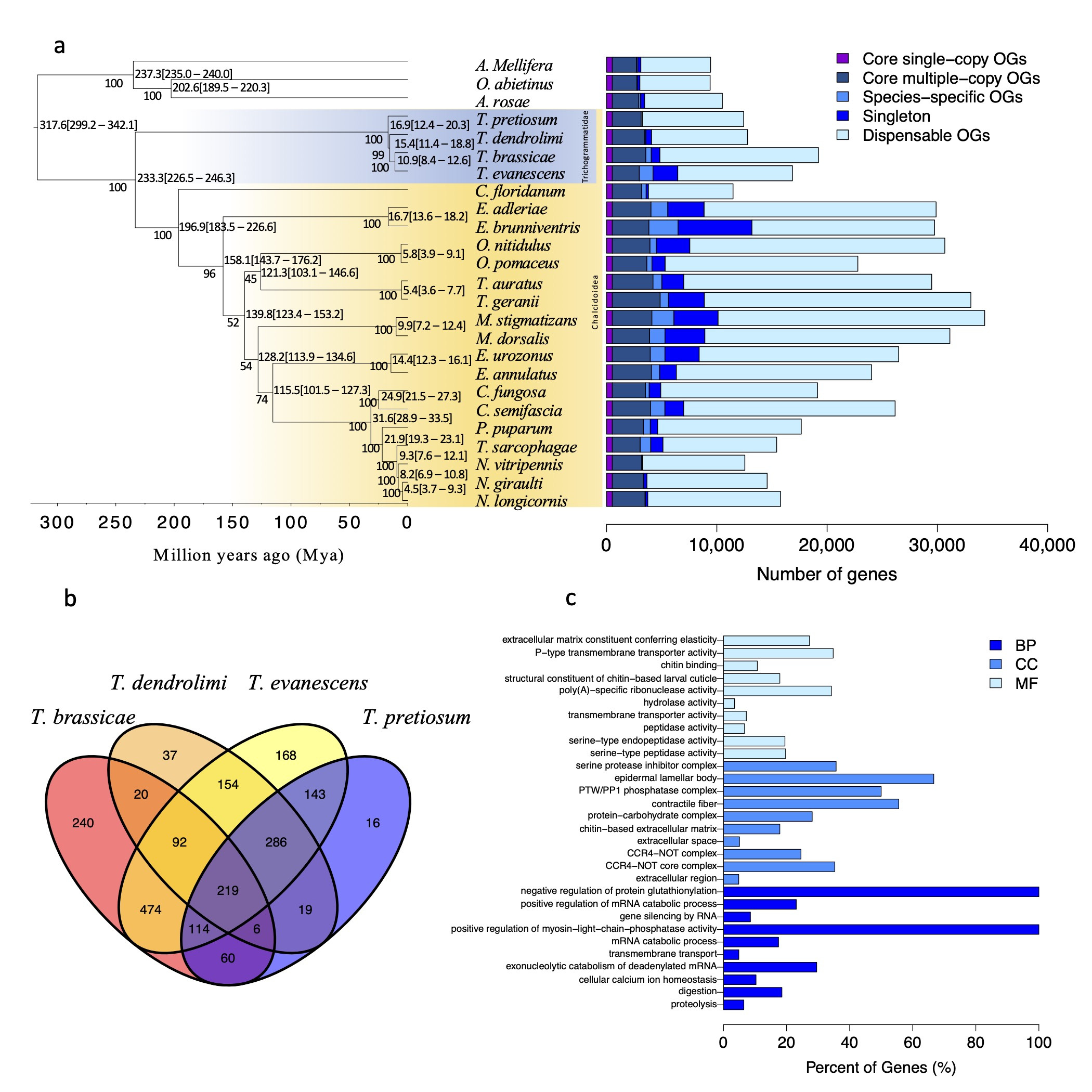
3.3. Orthology and Phylogenetic Analysis
3.4. Gene Family Expansions and Contractions
3.5. Olfactory-Related Genes
3.6. Venom-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, S.M. Biological control with Trichogramma: Advances, successes, and potential of their use. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1996, 41, 375–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurentis, V.L.; Ramalho, D.G.; Santos, N.A.; Carvalho, V.F.P.; Vacari, A.M.; De Bortoli, S.A.; Veneziani, R.C.S.; da Costa Inácio, G.; Dami, B.G. Performance of Trichogramma pretiosum Riley (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) on eggs of Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sousa, T.C.D.S.; Leite, N.A.; Sant’Ana, J. Responses of Trichogramma pretiosum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) to Rice and Corn Plants, Fed and Oviposited by Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Neotrop Entomol. 2021, 50, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, X.; Zang, L.S.; Du, W.M.; Hou, Y.Y.; Ruan, C.C.; Desneux, N. Advantages of diapause in Trichogramma dendrolimi mass production on eggs of the Chinese silkworm, Antheraea pernyi. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.H.; Song, L.W.; Zhang, J.J.; Zang, L.S.; Zhu, L.; Ruan, C.C.; Sun, G.Z. Performance of four Chinese Trichogramma species as biocontrol agents of the rice striped stem borer, Chilo suppressalis, under various temperature and humidity regimes. J. Pest Sci. 2012, 85, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, R. Inoculative releases of Trichogramma dendrolimi for suppressing the oriental fruit moth (Grapholita molesta) in peach orchard in China. Fruits 2016, 71, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Y.-Y.; Yang, X.; Zang, L.-S.; Zhang, C.; Monticelli, L.S.; Desneux, N. Effect of oriental armyworm Mythimna separata egg age on the parasitism and host suitability for five Trichogramma species. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Yue, J.J.; Yang, C.Y. Potential Use of Trichogramma pintoi as a Biocontrol Agent Against Heortia vitessoides (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Desneux, N. Biological Control with Trichogramma in China: History, Present Status and Perspectives. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, G.; Yu, J. External morphology of Trichogramma dendrolimi Matsumura (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) organ and ultrastructure of the sensilla. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2012, 75, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.F.; Kong, X.B.; Wang, H.B.; Zhou, G.; Yu, J.X.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Z. Sensory and immune genes identification and analysis in a widely used parasitoid wasp Trichogramma dendrolimi (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Insect. Sci. 2016, 23, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Du, W.; Zhang, J.; Zou, Z.; Ruan, C. High-throughput profiling of diapause regulated genes from Trichogramma dendrolimi (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.S.; Yan, Z.C.; Zhao, J.J.; Li, Y.X. Transcriptomic analyses of chemosensory genes in Trichogramma japonicum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Comp Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 37, 100755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Qu, Y.L.; Wu, Z.Y.; Lin, Y.; Ruan, C.C.; Desneux, N.; Zang, L.S. Parasitism and Suitability of Fertilized and Nonfertilized Eggs of the Rice Striped Stem Borer, Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae), for Trichogramma Parasitoids. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberson, J.R.; Kring, T.J. Parasitism of developing eggs by Trichogramma pretiosum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae): Host age preference and suitability. Biol. Control 1993, 3, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.Y.; Benelli, G.; Desneux, N.; Ali, A.; Zang, L.S. Trichogramma ostriniae Is More Effective Than Trichogramma dendrolimi As a Biocontrol Agent of the Asian Corn Borer, Ostrinia furnacalis. Insects 2022, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Zhang, Y.F.; Song, Q.T.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y.X. The suitability of Ostrinia furnacalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) eggs for Trichogramma dendrolimi (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) can be changed by T. ostriniae. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 49, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werren, J.H.; Richards, S.; Desjardins, C.A.; Niehuis, O.; Gadau, J.; Colbourne, J.K.; Beukeboom, L.W.; Desplan, C.; Elsik, C.G.; Grimmelikhuijzen, C.J.P.; et al. Functional and Evolutionary Insights from the Genomes of Three Parasitoid Nasonia Species. Science 2010, 327, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branstetter, M.G.; Childers, A.K.; Cox-Foster, D.; Hopper, K.R.; Kapheim, K.M.; Toth, A.L.; Worley, K.C. Genomes of the Hymenoptera. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2018, 25, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, A.R.I.; Kelkar, Y.D.; Wu, X.; Sun, D.; Martinson, E.O.; Yan, Z.; Rugman-Jones, P.F.; Hughes, D.S.T.; Murali, S.C.; Qu, J.; et al. Comparative genomics of the miniature wasp and pest control agent Trichogramma pretiosum. BMC Biol. 2018, 16, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, K.B.; Kursch-Metz, T.; Verhulst, E.C.; Pannebakker, B.A. Hybrid Genome Assembly and Evidence-Based Annotation of the Egg Parasitoid and Biological Control Agent. G3 2020, 10, 3533–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalvingh, K.M.; Chang, P.L.; Nuzhdin, S.V.; Wertheim, B. Genomic changes under rapid evolution: Selection for parasitoid resistance. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20132303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar-Jaramillo, L.; Jalvingh, K.M.; de Haan, A.; Kraaijeveld, K.; Buermans, H.; Wertheim, B. Inter- and intra-species variation in genome-wide gene expression of Drosophila in response to parasitoid wasp attack. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinson, E.O.; Mrinalini; Kelkar, Y.D.; Chang, C.H.; Werren, J.H. The Evolution of Venom by Co-option of Single-Copy Genes. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2007–2013.e2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wajnberg, E. Measuring Genetic Variation in Natural Enemies Used for Biological Control: Why and How? CABI International: Wallingford, UK, 2004; pp. 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Chen, J.; Fang, G.; Pang, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Sheng, Y.; Lu, Y.; et al. Two novel venom proteins underlie divergent parasitic strategies between a generalist and a specialist parasite. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Walenz, B.P.; Berlin, K.; Miller, J.R.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Canu: Scalable and accurate long-read assembly via adaptive k-mer weighting and repeat separation. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biosciences, P. GenomicConsensus: PacBio® Variant and Consensus Caller. Available online: https://github.com/PacificBiosciences/GenomicConsensus (accessed on 12 December 2021).
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K.; et al. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simão, F.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Ioannidis, P.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smit, A.F.A.; Hubley, R.; Green, P. RepeatMasker Open-4.0. 2013–2015. Available online: http://www.repeatmasker.org (accessed on 13 December 2021).
- Jurka, J. Repbase update: A database and an electronic journal of repetitive elements. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.M.; Hubley, R.; Goubert, C.; Rosen, J.; Clark, A.G.; Feschotte, C.; Smit, A.F. RepeatModeler2 for automated genomic discovery of transposable element families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9451–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birney, E.; Durbin, R. Using GeneWise in the Drosophila annotation experiment. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 547–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanke, M.; Keller, O.; Gunduz, I.; Hayes, A.; Waack, S.; Morgenstern, B. AUGUSTUS: Ab initio prediction of alternative transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W435–W439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korf, I. Gene finding in novel genomes. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haas, B.J.; Delcher, A.L.; Mount, S.M.; Wortman, J.R.; Smith, R.K., Jr.; Hannick, L.I.; Maiti, R.; Ronning, C.M.; Rusch, D.B.; Town, C.D.; et al. Improving the Arabidopsis genome annotation using maximal transcript alignment assemblies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 5654–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, B.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Zhu, W.; Pertea, M.; Allen, J.E.; Orvis, J.; White, O.; Buell, C.R.; Wortman, J.R. Automated eukaryotic gene structure annotation using EVidenceModeler and the Program to Assemble Spliced Alignments. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, A.; Chang, H.Y.; Daugherty, L.; Fraser, M.; Hunter, S.; Lopez, R.; McAnulla, C.; McMenamin, C.; Nuka, G.; Pesseat, S.; et al. The InterPro protein families database: The classification resource after 15 years. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D213–D221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bairoch, A.; Apweiler, R. The SWISS-PROT protein sequence database and its supplement TrEMBL in 2000. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalvari, I.; Argasinska, J.; Quinones-Olvera, N.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Rivas, E.; Eddy, S.R.; Bateman, A.; Finn, R.D.; Petrov, A.I. Rfam 13.0: Shifting to a genome-centric resource for non-coding RNA families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D335–D342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. tRNAscan-SE: A program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rødland, E.A.; Staerfeldt, H.H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNAmmer: Consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Jing, D.; Tang, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, H.; Duanmu, H.; Cong, Y.; Chen, M.; Ye, X.; Zhou, H.; et al. InsectBase 2.0: A comprehensive gene resource for insects. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emms, D.M.; Kelly, S. OrthoFinder: Phylogenetic orthology inference for comparative genomics. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Asimenos, G.; Toh, H. Multiple alignment of DNA sequences with MAFFT. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 537, 39–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. ProtTest 3: Fast selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1164–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML version 8: A tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedges, S.B.; Dudley, J.; Kumar, S. TimeTree: A public knowledge-base of divergence times among organisms. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2971–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hahn, M.W.; Demuth, J.P.; Han, S.G. Accelerated rate of gene gain and loss in primates. Genetics 2007, 177, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, M.V.; Thomas, G.W.; Lugo-Martinez, J.; Hahn, M.W. Estimating gene gain and loss rates in the presence of error in genome assembly and annotation using CAFE 3. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1987–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexa, A.; Rahnenfuhrer, J. topGO: Enrichment analysis for gene ontology. Available online: http://bioconductor.riken.jp/packages/3.0/bioc/vignettes/topGO/inst/doc/topGO.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2021).
- Eddy, S.R. Accelerated Profile HMM Searches. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, P.J.; Warr, C.G.; Carlson, J.R. Candidate taste receptors in Drosophila. Science 2000, 287, 1830–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundin, C.; Käll, L.; Kreher, S.A.; Kapp, K.; Sonnhammer, E.L.; Carlson, J.R.; Heijne, G.; Nilsson, I. Membrane topology of the Drosophila OR83b odorant receptor. FEBS Lett 2007, 581, 5601–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, T.W.; He, Z.; Gorur-Shandilya, S.; Menuz, K.; Larter, N.K.; Stewart, S.; Carlson, J.R. The Drosophila IR20a clade of ionotropic receptors are candidate taste and pheromone receptors. Neuron 2014, 83, 850–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mrinalini; Werren, J. Parasitoid Wasps and Their Venoms; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 187–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, S.J.; Asgari, S. Venom Proteins from Parasitoid Wasps and Their Biological Functions. Toxins 2015, 7, 2385–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denison, R.; Raymond-Delpech, V. Insights into the molecular basis of social behaviour from studies on the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Invert Neurosci 2008, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Yan, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Xiong, S.; Mei, Y.; Wang, F.; et al. A chromosome-level genome assembly of the parasitoid wasp Pteromalus puparum. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 1384–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Graaf, D.C.; Aerts, M.; Brunain, M.; Desjardins, C.A.; Jacobs, F.J.; Werren, J.H.; Devreese, B. Insights into the venom composition of the ectoparasitoid wasp Nasonia vitripennis from bioinformatic and proteomic studies. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2010, 19 (Suppl. S1), 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vincent, B.; Kaeslin, M.; Roth, T.; Heller, M.; Poulain, J.; Cousserans, F.; Schaller, J.; Poirié, M.; Lanzrein, B.; Drezen, J.M.; et al. The venom composition of the parasitic wasp Chelonus inanitus resolved by combined expressed sequence tags analysis and proteomic approach. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goecks, J.; Mortimer, N.T.; Mobley, J.A.; Bowersock, G.J.; Taylor, J.; Schlenke, T.A. Integrative approach reveals composition of endoparasitoid wasp venoms. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Saona, C. Biological Control: Ecology and Applications. Am. Entomol. 2018, 64, E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; He, B.; Monticelli, L.S.; Du, W.; Ruan, C.; Desneux, N.; Zhang, J. Gradually Increasing the Temperature Reduces the Diapause Termination Time of Trichogramma dendrolimi While Increasing Parasitoid Performance. Insects 2022, 13, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhao, X.; Li, M.; He, K.; Huang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Walters, J.R. Insect genomes: Progress and challenges. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2019, 28, 739–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Lin, K.; Wang, G.; Li, F. Genome Sizes of Nine Insect Species Determined by Flow Cytometry and k-mer Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Standage, D.S.; Berens, A.J.; Glastad, K.M.; Severin, A.J.; Brendel, V.P.; Toth, A.L. Genome, transcriptome and methylome sequencing of a primitively eusocial wasp reveal a greatly reduced DNA methylation system in a social insect. Mol. Ecol. 2016, 25, 1769–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kent, C.F.; Minaei, S.; Harpur, B.A.; Zayed, A. Recombination is associated with the evolution of genome structure and worker behavior in honey bees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 18012–18017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peters, R.S.; Niehuis, O.; Gunkel, S.; Bläser, M.; Mayer, C.; Podsiadlowski, L.; Kozlov, A.; Donath, A.; van Noort, S.; Liu, S.; et al. Transcriptome sequence-based phylogeny of chalcidoid wasps (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea) reveals a history of rapid radiations, convergence, and evolutionary success. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2018, 120, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Huang, T.; Tang, B.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Q. The genome of the rice planthopper egg parasitoid wasps Anagrus nilaparvatae casts light on the chemo- and mechanosensation in parasitism. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, S.K.; Mohanraj, P.; Lakshmi, B.L. Chapter 5—Trichogrammatids. In Ecofriendly Pest Management for Food Security; Omkar, I., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 139–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, H.M.; Gadau, J.; Wanner, K.W. The insect chemoreceptor superfamily of the parasitoid jewel wasp Nasonia vitripennis. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2010, 19 (Suppl. S1), 12–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jalely, B.H.; Xu, W. Olfactory Sensilla and Olfactory Genes in the Parasitoid Wasp Trichogramma pretiosum Riley (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Insects 2021, 12, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrinalini; Siebert, A.L.; Wright, J.; Martinson, E.; Wheeler, D.; Werren, J.H. Parasitoid Venom Induces Metabolic Cascades in Fly Hosts. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 350–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, S.; Rivers, D.B. Venom proteins from endoparasitoid wasps and their role in host-parasite interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boivin, G. Reproduction and Immature Development of Egg Parasitoids. In Egg Parasitoids in Agroecosystems with Emphasis on Trichogramma; Consoli, F.L., Parra, J.R.P., Zucchi, R.A., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Colinet, D.; Cazes, D.; Belghazi, M.; Gatti, J.L.; Poirié, M. Extracellular superoxide dismutase in insects: Characterization, function, and interspecific variation in parasitoid wasp venom. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 40110–40121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cusumano, A.; Duvic, B.; Jouan, V.; Ravallec, M.; Legeai, F.; Peri, E.; Colazza, S.; Volkoff, A.N. First extensive characterization of the venom gland from an egg parasitoid: Structure, transcriptome and functional role. J. Insect. Physiol. 2018, 107, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Genomic Feature | Trichogramma dendrolimi |
|---|---|
| Length of the assembly (bp) | 215,209,100 |
| Maximum scaffold length (bp) | 9,241,039 |
| Number of scaffolds | 316 |
| Scaffold N50 (bp) | 1,412,680 |
| Number of genes | 12,785 |
| Average gene length (bp) | 6407.6 |
| Average coding sequence length (bp) | 1389.1 |
| Average exon length (bp) | 268.5 |
| Average intron length (bp) | 1202.3 |
| Average exon number | 5.17 |
| Total size of transposable elements (bp) | 63,402,215 |
| GC content | 39.8% |
| BUSCO scores | C: 93.4% [S: 88.6%, D: 4.8%], F: 1.0%, M: 5.6%, n: 1367 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Jiao, X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hou, Y.; Duan, G.; Du, W.; Ruan, C.; Zhang, J.; et al. Genome Assembly and Comparative Analysis of the Egg Parasitoid Wasp Trichogramma dendrolimi Shed Light on the Composition and Evolution of Olfactory Receptors and Venoms. Insects 2023, 14, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020144
Zhang X, Jiang Z, Jiao X, Yu Y, Wang Z, Hou Y, Duan G, Du W, Ruan C, Zhang J, et al. Genome Assembly and Comparative Analysis of the Egg Parasitoid Wasp Trichogramma dendrolimi Shed Light on the Composition and Evolution of Olfactory Receptors and Venoms. Insects. 2023; 14(2):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020144
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xue, Zhuo Jiang, Xilin Jiao, Yang Yu, Zhenan Wang, Yangyang Hou, Guohua Duan, Wenmei Du, Changchun Ruan, Junjie Zhang, and et al. 2023. "Genome Assembly and Comparative Analysis of the Egg Parasitoid Wasp Trichogramma dendrolimi Shed Light on the Composition and Evolution of Olfactory Receptors and Venoms" Insects 14, no. 2: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020144
APA StyleZhang, X., Jiang, Z., Jiao, X., Yu, Y., Wang, Z., Hou, Y., Duan, G., Du, W., Ruan, C., Zhang, J., & Hu, Y. (2023). Genome Assembly and Comparative Analysis of the Egg Parasitoid Wasp Trichogramma dendrolimi Shed Light on the Composition and Evolution of Olfactory Receptors and Venoms. Insects, 14(2), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020144






