Impacts of Semiochemical Traps Designed for Bruchus rufimanus Boheman 1833 (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Nontarget Beneficial Entomofauna in Field Bean Crops
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
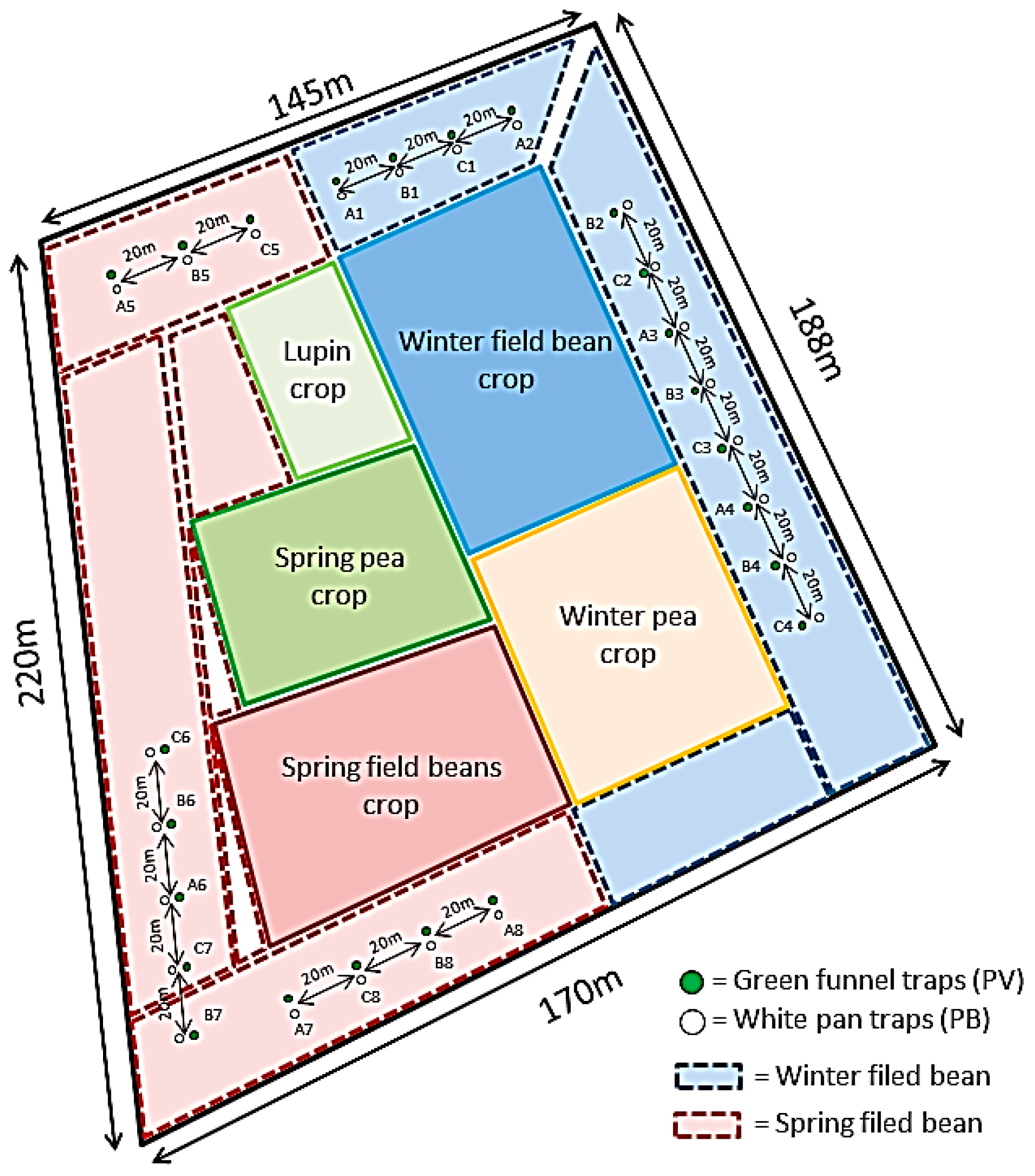
2.2. Traps, Lures and Experimental Design
2.3. Insects Collection, Preparation and Identification
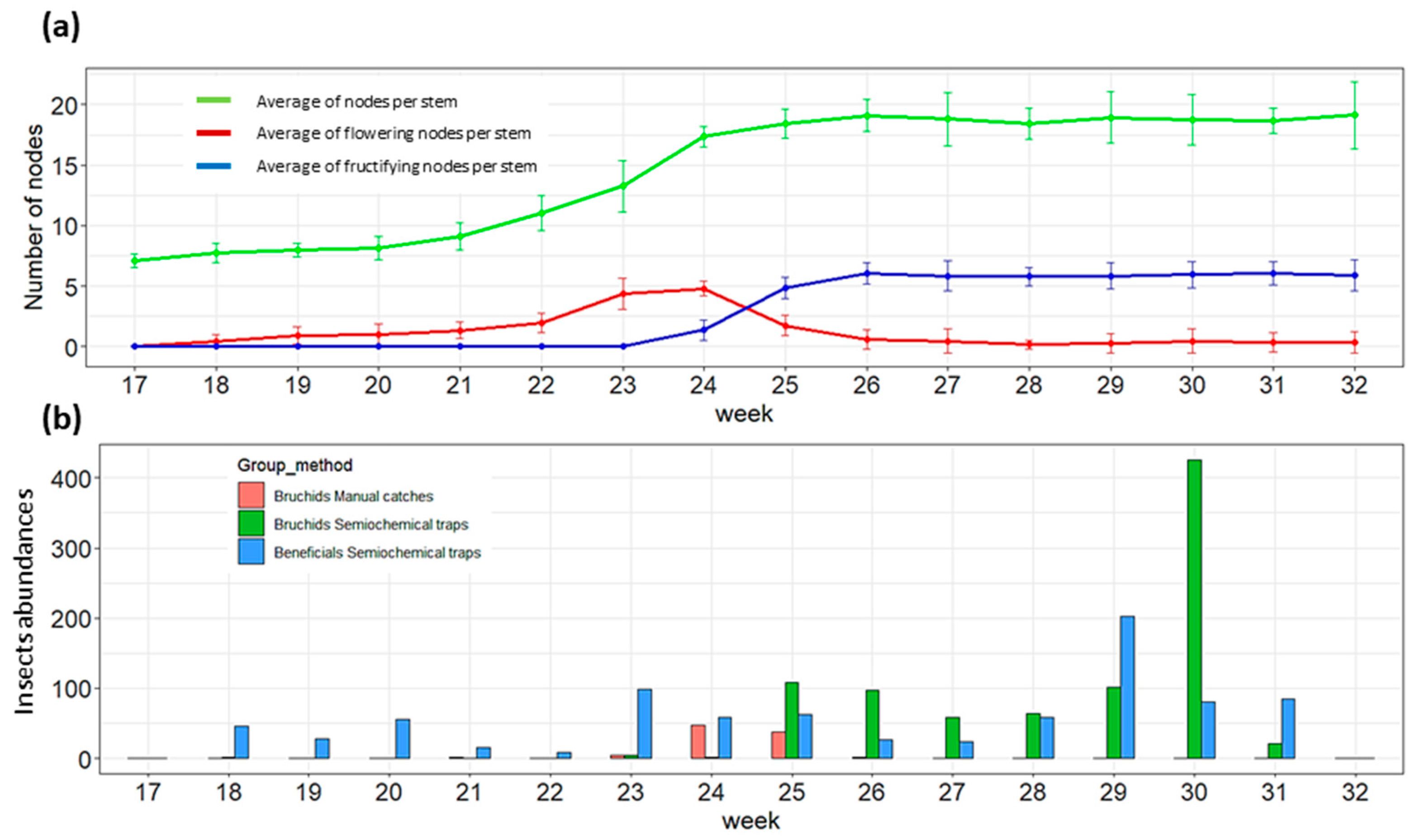
2.4. Monitoring of Field Bean Phenology
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Host Plant Phenology and Population Dynamics of Bbws and Beneficial Insects
3.2. Influence of Trapping Modalities on the Capture of BBWs and Beneficials
3.3. Analyses of Communities
4. Discussion
4.1. Most Efficient Traps for the Capture of Bruchid, Phenological Influences on Catches and Impact on Beneficials
4.2. Analyses of Communities of BBWs and Beneficials: Balanced Impacts According to Functional Groups and Their Ecology
4.3. Maximising B. Rufimanus Trapping and Minimising Beneficial Insect Trapping: A Dilemma
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A



Appendix B
| N° Week | Avg (T) (°C) | Avg (Tmax) (°C) | Avg (Pcum) (mm) | Notes |
| 14 | 9.2 | 15.0 | 0 | |
| 15 | 4.2 | 9.1 | 30.5 | |
| 16 | 4.2 | 9.9 | 2 | |
| 17 | 8.5 | 15.3 | 0 | Trap installation in WFB |
| 18 | 7.9 | 14.5 | 3.9 | |
| 19 | 7.8 | 13.8 | 6.2 | |
| 20 | 13.0 | 18.9 | 5.4 | |
| 21 | 11.2 | 15.4 | 30.2 | |
| 22 | 11.7 | 16.7 | 20.8 | |
| 23 | 17.4 | 23.9 | 11.6 | Trap installation in SFB |
| 24 | 17.9 | 24.2 | 0 | |
| 25 | 21.1 | 28.0 | 25 | |
| 26 | 16.4 | 20.2 | 30 | |
| 27 | 17.3 | 22.0 | 35.5 | |
| 28 | 17.5 | 22.0 | 22 | |
| 29 | 17.1 | 20.3 | 117 | |
| 30 | 19.1 | 25.2 | 6 | |
| 31 | 18.1 | 22.0 | 10.7 | Traps removal in WFB |
| 32 | 17.1 | 21.2 | 56.5 | Traps removal in SFB |
Appendix C
| Taxonomy | Number of Specimens |
| Coleoptera | 291 |
| Coccinellidae | 291 |
| Adalia bipunctata (Linnaeus, 1758) | 2 |
| Coccinella septempunctata Linnaeus, 1758 | 191 |
| Harmonia axyridis (Pallas, 1773) | 71 |
| Hippodamia variegata (Goeze, 1777) | 7 |
| Propylea quatuordecimpunctata (Linnaeus, 1758) | 17 |
| Psyllobora vigintiduopunctata (Linnaeus, 1758) | 3 |
| Diptera | 316 |
| Syrphidae | 316 |
| Epistrophe diaphana (Zetterstedt, 1843) | 1 |
| Epistrophe euchroma (Kowarz, 1885) | 1 |
| Epistrophe nitidicollis (Meigen, 1822) | 1 |
| Episyrphus balteatus De Geer, 1776 | 129 |
| Eristalis tenax (Linnaeus, 1758) | 5 |
| Melanostoma mellina (Linnaeus, 1758) | 45 |
| Metasyrphus corollae (Fabricius, 1794) | 31 |
| Metasyrphus luniger (Meigen, 1822) | 7 |
| Scaeva pyrastri (Linnaeus, 1758) | 3 |
| Sphaerophoria scripta (Linnaeus, 1758) | 84 |
| Syrphus vitripennis Meigen, 1822 | 5 |
| Xylota lenta Meigen, 1822 | 1 |
| Hymenoptera | 817 |
| Andrenidae | 75 |
| Andrena barbilabris (Kirby, 1802) | 1 |
| Andrena bicolor Fabricius, 1775 | 5 |
| Andrena carantonica Pérez, 1902 | 1 |
| Andrena cineraria (Linnaeus, 1758) | 9 |
| Andrena dorsata (Kirby, 1802) | 4 |
| Andrena flavipes Panzer, 1799 | 2 |
| Andrena fulva (Müller, 1776) | 6 |
| Andrena gravida Imhoff, 1832 | 1 |
| Andrena haemorrhoa (Fabricius, 1781) | 3 |
| Andrena minutula (Kirby, 1802) | 13 |
| Andrena nigroaenea (Kirby, 1802) | 12 |
| Andrena nitida (Müller, 1776) | 3 |
| Andrena ovatula (Kirby, 1802) | 6 |
| Andrena subopaca Nylander, 1848 | 8 |
| Andrena wilkella (Kirby, 1802) | 1 |
| Apidae | 674 |
| Apis mellifera Linnaeus, 1758 | 321 |
| Bombus hortorum Linnaeus, 1761 | 33 |
| Bombus hypnorum (Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 |
| Bombus lapidarius (Linnaeus, 1758) | 20 |
| Bombus pascuorum (Scopoli, 1763) | 15 |
| Bombus pratorum (Linnaeus, 1761) | 5 |
| Bombus terrestris (Linnaeus, 1758) | 275 |
| Bombus vestalis (Geoffroy, 1785) | 1 |
| Nomada flavoguttata (Kirby, 1802) | 1 |
| Nomada fuscicornis Nylander, 1848 | 1 |
| Nomata signata Jurine, 1807 | 1 |
| Colletidae | 3 |
| Hylaeus communis Nylander, 1852 | 2 |
| Hylaeus hyalinatus Smith, 1842 | 1 |
| Halictidae | 56 |
| Halictus scabiosae (Rossi, 1790) | 2 |
| Lasioglossum calceatum (Scopoli, 1763) | 5 |
| Lasioglossum laticeps (Schenck, 1870) | 9 |
| Lasioglossum lativentre (Schenck, 1853) | 8 |
| Lasioglossum leucozonium (Schrank, 1781) | 2 |
| Lasioglossum minutissimum (Kirby, 1802) | 5 |
| Lasioglossum minutulum (Schenck, 1853) | 1 |
| Lasioglossum morio (Fabricius, 1793) | 2 |
| Lasioglossum parvulum (Schenck, 1853) | 1 |
| Lasioglossum pauxillum (Schenck, 1853) | 14 |
| Lasioglossum punctatissimum (Schenck, 1853) | 1 |
| Lasioglossum sp. | 3 |
| Seladonia tumulorum (Linnaeus, 1758) | 4 |
| Sphecodes ephippius (Linnaeus, 1767) | 1 |
| Sphecodes puncticeps Thomson, 1870 | 1 |
| Megachilidae | 8 |
| Chelostoma campanularum (Kirby, 1802) | 1 |
| Megachile ericetorum Lepeletier, 1841 | 2 |
| Osmia bicornis (Linnaeus, 1758) | 3 |
| Osmia caerulescens (Linnaeus, 1758) | 1 |
| Stelis signata (Latreille, 1809) | 1 |
| Melittidae | 1 |
| Melitta leporina (Panzer, 1799) | 1 |
References
- Bedoussac, L.; Journet, E.-P.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Naudin, C.; Corre-Hellou, G.; Jensen, E.S.; Prieur, L.; Justes, E. Ecological Principles Underlying the Increase of Productivity Achieved by Cereal-Grain Legume Intercrops in Organic Farming. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 911–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a Cultivated Planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, D.; Tilman, D. National Food Production Stabilized by Crop Diversity. Nature 2019, 571, 257–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, A.G. Ecosystem Services and Agriculture: Tradeoffs and Synergies. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 2959–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mínguez, M.I.; Rubiales, D. Chapter 15—Faba Bean. In Crop Physiology Case Histories for Major Crops; Sadras, V.O., Calderini, D.F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 452–481. ISBN 978-0-12-819194-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, E.S.; Peoples, M.B.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H. Faba Bean in Cropping Systems. Field Crops Res. 2010, 115, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preissel, S.; Reckling, M.; Schläfke, N.; Zander, P. Magnitude and Farm-Economic Value of Grain Legume Pre-Crop Benefits in Europe: A Review. Field Crops Res. 2015, 175, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, E.S.; Peoples, M.B.; Boddey, R.M.; Gresshoff, P.M.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H.; Alves, B., Jr.; Morrison, M.J. Legumes for Mitigation of Climate Change and the Provision of Feedstock for Biofuels and Biorefineries. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 329–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köpke, U.; Nemecek, T. Ecological Services of Faba Bean. Field Crops Res. 2010, 115, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament A European Strategy for the Promotion of Protein Crops Encouraging the Production of Protein and Leguminous Plants in the European Agriculture Sector (2017/2116(INI)) 2018. Available online: https://www.europarl.europa.eu/doceo/document/A-8-2018-0121_EN.html (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Voisin, A.S.; Guéguen, J.; Huyghe, C.; Jeuffroy, M.-H.; Magrini, M.-B.; Meynard, J.M.; Mougel, C.; Pellerin, S.; Pelzer, E. Legumes for Feed, Food, Biomaterials and Bioenergy in Europe: A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2014, 34, 361–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rempel, C.; Geng, X.; Zhang, Y. Industrial Scale Preparation of Pea Flour Fractions with Enhanced Nutritive Composition by Dry Fractionation. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz-Kesting, K.; Thiele, J.; Everwand, G.; Dauber, J. Neighbourhood Effect of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) on Density of Vegetation-Dwelling Natural Biocontrol Agents in Winter Wheat. Biol. Control 2021, 160, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondor, E.B.; Addicott, J.F. Conspicuous Extra-Floral Nectaries Are Inducible in Vicia faba. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuessly, G.S.; Hentz, M.G.; Beiriger, R.; Scully, B.T. Insects Associated with Faba Bean, Vicia faba (FABALES: Fabaceae), in Southern Florida. Fla. Entomol. 2004, 87, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamont, M.; Crépellière, S.; Jaloux, B. Effect of Extrafloral Nectar Provisioning on the Performance of the Adult Parasitoid Diaeretiella rapae. Biol. Control 2013, 65, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everwand, G.; Cass, S.; Dauber, J.; Williams, M.; Stout, J. Legume Crops and Biodiversity. Legum. Crop. Syst. 2017, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abras, M.; Cartrysse, C.; Froidmont, E.; Jamar, D.; Rondia, P.; Wavreille, J. Les Protéagineux, de La Production à La Valorisation—La Féverole, Une Légumineuse à Graines Riche En Protéines et En Énergie; Cellule transversale de Recherchesen Agriculture biologique (CtRAb) du CRA-W: Belgique, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Duc, G. Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.). Field Crops Res. 1997, 53, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, C.; Baldev, B.; Brouwer, J.B.; Erskine, W.; Jermyn, W.A.; Li-Juan, L.; Malik, B.A.; Ahad Miah, A.; Silim, S.N. Biotic and Abiotic Stresses Constraining Productivity of Cool Season Food Legumes in Asia, Africa and Oceania. In Current Plant Science and Biotechnology in Agriculture; Muehlbauer, F.J., Kaiser, W.J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1994; pp. 175–194. ISBN 978-94-011-0798-3. [Google Scholar]
- Baugnée, J.-Y.; Drumont, A.; Fagot, J.; Ignace, D. Bruchidius imbricornis (Panzer, 1795), Bruchus occidentalis Lukjanovitch & Ter-Minassian, 1957 et Bruchus brachialis Fåhraeus, 1839 Nouveaux Pour La Faune Belge et Données Récentes de Bruchidius siliquastri Delobel, 2007 (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae, Bruchinae). Bull. Société R. Belge D’EntomologieBulletin Van K. Belg. Ver. Voor Entomol. 2021, 157, 34–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zampetti, M.F.; Ricci, M.S. Guida Ai Coleotteri Bruchidi Della Fauna Italiana: Sistematica e Biologia, Gestione e Controllo; Darwin edizioni, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, A. Coléoptères Bruchides et Anthribides. Faune Fr. 1945, 44, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Boughdad, A.; Lauge, G. Cycle Biologique de Bruchus rufimanus Boh. (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) Sur Vicia faba Var. Minor L.Légumineuse) Au Maroc. Annales de l’ANPP, France Tome III. Ann. ANPP 1997, 3637, 793–801. [Google Scholar]
- Roubinet, E. Management of the Broad Bean Weevil (Bruchus rufimanus Boh.) in Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.). 2016. Available online: https://pub.epsilon.slu.se/13631/1/roubinet_e_160704.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Titouhi, F.; Amri, M.; Messaoud, C.; Haouel, S.; Youssfi, S.; Cherif, A.; Mediouni Ben Jemâa, J. Protective Effects of Three Artemisia Essential Oils against Callosobruchus maculatus and Bruchus rufimanus (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) and the Extended Side-Effects on Their Natural Enemies. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2017, 72, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khelfane-Goucem, K.; Medjdoub-Bensaad, F. Impact of Bruchus rufimanus Infestation upon Broad Bean Seeds Germination. Adv. Environ. Biol 2016, 5, 144–152. [Google Scholar]
- Huignard, J.; Glitho, I.; Monge, J.-P.; Régnault-Roger, C. (Eds.) Insectes Ravageurs des Graines de Légumineuses; Éditions Quae: Versailles, France, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Segers, A.; Caparros Megido, R.; Lognay, G.; Francis, F. Overview of Bruchus rufimanus Boheman 1833 (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae): Biology, Chemical Ecology and Semiochemical Opportunities in Integrated Pest Management Programs. Crop Prot. 2021, 140, 105411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughdad, A.; Lauge, G. Vicia faba Seed Infestation and Losses Due to Bruchus rufimanus Boh. (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in Morocco. FABIS Newsl. 1995, 3637, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Kaniuczak, Z. Seed Damage of Field Bean (Vicia faba L. Var. Minor Harz.) Caused by Bean Weevils (Bruchus rufimanus Boh.) (Coleoptera: Bruchidae). J. Plant Prot. Res. 2004, 44, 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Bruce, T.J.; Martin, J.L.; Smart, L.E.; Pickett, J.A. Development of Semiochemical Attractants for Monitoring Bean Seed Beetle, Bruchus rufimanus. Pest Manag. Sci. 2011, 67, 1303–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrabos, P.; Bouttet, D.; Hemet, A. Contre La Bruche, Intervenir Au Bon Moment. Perspect. Agric. 2007, 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann, M.; Kuhnitzsch, C.; Martens, S.D.; Steinhöfel, O.; Zeyner, A. Control of Bean Seed Beetle Reproduction through Cultivar Selection and Harvesting Time. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 300, 107005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biarnès, V.; Penant, A.; Remurier, B. Guide de Culture Féverole 2018; Terres Inovia: Thiverval-Grignon, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, B.; Huignard, J. Interactions between Photoperiod and Food Affect the Termination of Reproductive Diapause in Bruchus rufimanus (Boh.), (Coleoptera, Bruchidae). J. Insect Physiol. 1992, 38, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pölitz, B.; Reike, H.P. Studies on biology and infestation dynamics of the bean seed beetle (Coleoptera, Bruchidae: Bruchus rufimanus) in Saxony. Gesunde Pflanz. 2019, 71, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medjdoub-Bensaad, F.; Khelil, M.A.; Huignard, J. Bioecology of broad bean bruchid Bruchus rufimanus Boh. (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in a region of Kabylia in Algeria. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2007, 2, 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Gailis, J.; Astašova, N.; Jākobsone, E.; Ozoliņa-Pole, L. Biology of Broadbean Seed Beetle (Bruchus rufimanus; Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) in Latvia. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2022, 72, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, R.W.; Currie, J.E. Some Laboratory Observations on the Rates of Development, Mortality and Oviposition of Several Species of Bruchidae Breeding in Stored Pulses. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1964, 55, 437–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.L. The Biology and Ecology of Bruchus rufimanus (Bean Seed Beetle); Newcastle University—School of Natural and Environmental Sciences: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidi, R.; Taupin, P.; Frérot, B. Physiological Synchrony of the Broad Bean Weevil, Bruchus rufimanus Boh., to the Host Plant Phenology, Vicia faba L. Front. Insect Sci. 2021, 1, 707323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.L.; Smart, L. The Effect of Temperature on the Effectiveness of Spray Applications to Control Bean Seed Beetle (Bruchus rufimanus) in Field Beans (Vicia faba). Asp. Appl. Biol. 2011, 106, 247–254. [Google Scholar]
- Simmen, M. La filière féverole à la loupe: Une culture en mutation. Perspect. Agric. 2020, 481, 12–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lacampagne, J.P. Productions et Marchés Des Pois et Des Féveroles. In Proceedings of the Rencontres Francophones Légumineuses, Angers, France, 24–26 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Frerot, B.; Taupin, P.; Lefranc, M. Bruche de la fève sur féverole: Des messages chimiques décryptés. Perspect. Agric. 2015, 60–63. [Google Scholar]
- Leppik, E.; Pinier, C.; Frérot, B. Communication Chimique Chez Le Principal Ravageur de Féverole: Bruchus rufimanus. Nouvelles Perspectives de Luttes Par Des Médiateurs Chimiques. In Proceedings of the INRA, Halifax, NS, Canada, 13–17 July 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Montagné, N.; Huyghe, C.; Lannou, C.; Bardin, M.; Ris, N. Des odeurs pour lutter contre les ravageurs. Conqu. INRA Pour Biocontrô 2018, 4–9. Available online: https://www.inrae.fr/actualites/conquetes-linra-biocontrole (accessed on 1 February 2022).
- Fountain, M.T.; Baroffio, C.; Borg-Karlson, A.-K.; Brain, P.; Cross, J.V.; Farman, D.I.; Hall, D.R.; Ralle, B.; Rendina, P.; Richoz, P.; et al. Design and Deployment of Semiochemical Traps for Capturing Anthonomus rubi Herbst (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and Lygus rugulipennis Poppius (Hetereoptera: Miridae) in Soft Fruit Crops. Crop Prot. 2017, 99, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renkema, J.M.; Buitenhuis, R.; Hallett, R.H. Optimizing Trap Design and Trapping Protocols for Drosophila ruzukii (Diptera: Drosophilidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 2107–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segers, A.; Dumoulin, L.; Megido, R.C.; Jacquet, N.; Cartrysse, C.; Kamba, P.M.; Pierreux, J.; Richel, A.; Blecker, C.; Francis, F. Varietal and Environmental Effects on the Production of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) Seeds for the Food Industry by Confrontation of Agricultural and Nutritional Traits with Resistance against Bruchus spp. (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae, Bruchinae). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 327, 107831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroffio, C.A.; Sigsgaard, L.; Ahrenfeldt, E.J.; Borg-Karlson, A.-K.; Bruun, S.A.; Cross, J.V.; Fountain, M.T.; Hall, D.; Mozuraitis, R.; Ralle, B.; et al. Combining Plant Volatiles and Pheromones to Catch Two Insect Pests in the Same Trap: Examples from Two Berry Crops. Crop Prot. 2018, 109, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouret, H.; Carre, G.; Roberts, S.P.M.; Morison, N.; Vaissière, B.E. Mise En Place d’une Collection d’abeille (Hymenoptera, Apoidea) Dans Le Cadre d’une Étude de La Biodiversité. Osmia 2007, 1, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagot, J.; Bortels, J.; Dekoninck, W. La Pratique de l’entomologie Du Terrain Au Conservatoire Ou l’essentiel Est de Bien Transmettre. Faun. Entomol. 2022, 75, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, H.E.; Brown, P.M.J.; Comont, R.F.; Poland, R.L.; Slogett, J.J. Ladybirds; Pelagic Publishing: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Baugnée, J.-Y.; Branquart, E. Clef de Terrain Pour La Reconnaissance Des Principales Coccinelles de Wallonie (Chicolorinae, Coccinellinae et Epilachninae; Jeunes & Nature Association and Faculté Universitaire des Sciences Agronomiques de Gembloux: Gembloux, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Verlinden, L. Faune de Belgique—Syrphides (Syrphidae); Edition de l’Institut Royal des Sciences Naturelles de Belgique, Bruxelles: Brussels, Belgium, 1994; 289p. [Google Scholar]
- Patiny, S.; Terzo, M. Catalogue et Clé Des Sous-Genres et Espèces Du Genre Andrena de Belgique et Du Nord de La France (Hymenoptera, Apoidea); Mons University: Mons, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmont, P.; Terzo, M. Catalogue et Clé Des Sous-Genres et Espèces Du Genre Bombus de Belgique et Du Nord de La France (Hymenoptera, Apoidea). Univ. Mons Lab. Zool. 2010, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Pauly, A. Abeilles de Belgique et Des Régions Limitrophes (Insecta: Hymenoptera: Apoidea); Famille Halictidae; de Belgique, F., Ed.; Institut royal des Sciences naturelles de Belgique: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Falk, S. Field Guide to the Bees of Great Britain and Ireland, 1st ed.; Bloomsbury Publishing: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, F.; Haubruge, É. Le Conservatoire entomologique de Gembloux: Lieu de conservation et de valorisation du patrimoine wallon. Entomol. Faun.-Faun. Entomol. 2012, 65, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo-Perdomo, E.; Raffiot, B.; Ollivier, D.; Deulvot, C.; Magnin-Robert, J.-B.; Tayeh, N.; Marget, P. Identification of Novel Sources of Resistance to Seed Weevils (Bruchus spp.) in a Faba Bean Germplasm Collection. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 9, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Data Analysis. In ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Wickham, H., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 189–201. ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, D.; Mächler, M.; Bolker, B.; Walker, S. Package Lme4: Linear Mixed-Effects Models Using Eigen and S4; 2014; Volume 67. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, X.A.; Donaldson, L.; Correa-Cano, M.E.; Evans, J.; Fisher, D.N.; Goodwin, C.E.D.; Robinson, B.S.; Hodgson, D.J.; Inger, R. A Brief Introduction to Mixed Effects Modelling and Multi-Model Inference in Ecology. PeerJ 2018, 2018, e4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hothorn, T.; Bretz, F.; Westfall, P. Simultaneous Inference in General Parametric Models. Biom. J. 2008, 50, 346–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindt, R.; Coe, R. Tree Diversity Analysis. A Manual and Software for Common Statistical Methods for Ecological and Biodiversity Studies; World Agroforestry Centre ICRAF: Nairobi, Kenya, 2005; ISBN 92-9059-179-X. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.O. Diversity and Evenness: A Unifying Notation and Its Consequences. Ecology 1973, 54, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roswell, M.; Dushoff, J.; Winfree, R. Negative Relationship between Interspecies Spatial Association and Trait Dissimilarity. Oikos 2021, 130, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.C.; Ma, K.H.; Chao, A. INEXT: An R Package for Rarefaction and Extrapolation of Species Diversity (Hill Numbers). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1451–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jost, L. Entropy and Diversity. Oikos 2006, 113, 363–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet Michael, F.G.F.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; et al. Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2019, 2, 321–326. [Google Scholar]
- Cáceres, M.D.; Legendre, P. Associations between Species and Groups of Sites: Indices and Statistical Inference. Ecology 2009, 90, 3566–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufrêne, M.; Legendre, P. Species Assemblages and Indicator Species: The Need for a Flexible Asymmetrical Approach. Ecol. Monogr. 1997, 67, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.L. Monitoring of the bean seed beetle (Bruchus rufimanus) in field beans (Vicia faba). Asp. Appl. Biol. 1999, 56, 145–150. [Google Scholar]
- Nayak, G.K.; Roberts, S.P.M.; Garratt, M.; Breeze, T.D.; Tscheulin, T.; Harrison-Cripps, J.; Vogiatzakis, I.N.; Stirpe, M.T.; Potts, S.G. Interactive Effect of Floral Abundance and Semi-Natural Habitats on Pollinators in Field Beans (Vicia faba). Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 199, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodkinson, I.D.; Webb, N.R.; Bale, J.S.; Block, W.; Coulson, S.J.; Strathdee, A.T. Global Change and Arctic Ecosystems: Conclusions and Predictions from Experiments with Terrestrial Invertebrates on Spitsbergen. Arct. Alp. Res. 1998, 30, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, G.V.P.; Sharma, A.; Gadi, R.L. Biology, Ecology, and Management of the Pea Weevil (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2018, 111, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, T.J.A.; Wadhams, L.J.; Woodcock, C.M. Insect Host Location: A Volatile Situation. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, T.J.A.; Pickett, J.A. Perception of Plant Volatile Blends by Herbivorous Insects—Finding the Right Mix. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzinzig, B.; Brünjes, L.; Biagioni, S.; Behling, H.; Link, W.; Westphal, C. Bee Pollinators of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.) Differ in Their Foraging Behaviour and Pollination Efficiency. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 264, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garratt, M.P.D.; Coston, D.J.; Truslove, C.L.; Lappage, M.G.; Polce, C.; Dean, R.; Biesmeijer, J.C.; Potts, S.G. The Identity of Crop Pollinators Helps Target Conservation for Improved Ecosystem Services. Biol. Conserv. 2014, 169, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nation, J.L. Bumblebees: Behaviour, Ecology, and Conservation. Fla. Entomol. 2010, 93, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbeater, E.; Chittka, L. Social Transmission of Nectar-Robbing Behaviour in Bumble-Bees. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhomme, P.; Hines, H.M. Ecology and Evolution of Cuckoo Bumble Bees. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2019, 112, 122–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drossart, M.; Rasmont, P.; Vanormelingen, P.; Dufrêne, M.; Folschweiller, M.; Pauly, A.; Vereecken, N.; Vray, S.; Zambra, E.; D’Haeseleer, J. Belgian Red List of Bees; 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Westrich, P. Die Wildbienen Deutschlands; Verlag Eugen Ulmer: Stuttgart, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vujić, A.; Gilbert, F.; Flinn, G.; Englefield, E.; Ferreira, C.C.; Varga, Z.; Eggert, F.; Woolcock, S.; Böhm, M.; Mergy, R.; et al. Pollinators on the Edge: Our European Hoverflies. The European Red List of Hoverflies; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2022; ISBN 10.2779/652219. [Google Scholar]
- Speight, M.C.D. Species Accounts of European Syrphidae (Diptera) 2010. Syrph Net Database Eur. Syrphidae 2010, 59, 1–285. [Google Scholar]
- Francis, F.; Colignon, P.; Hastir, P.; Haubruge, E.; Gaspar, C. Evolution of Aphidophagous Ladybird Populations in a Vegetable Crop and Implications as Biological Agents. Meded. Rijksuniv. Te Gent Fak. Van Landbouwkd. En Toegepaste Biol. Wet. 2001, 66, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.R.; Walters, K.F.A.; Port, G.R.; Northing, P. Consumption Rates and Predatory Activity of Adult and Fourth Instar Larvae of the Seven Spot Ladybird, Coccinella septempunctata (L.), Following Contact with Dimethoate Residue and Contaminated Prey in Laboratory Arenas. Biol. Control 2004, 30, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenhumberg, B. Estimating Predatory Efficiency of Episyrphus balteatus (Diptera: Syrphidae) in Cereal Fields. Environ. Entomol. 1995, 24, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Bahlai, C.A.; Frewin, A.; Sears, M.K.; Schaafsma, A.W.; Hallett, R.H. Predation by Coccinella septempunctata and Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on Aphis glycines (Homoptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 2009, 38, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindayana, D.; Meyhöfer, R.; Scholz, D.; Poehling, H.-M. Intraguild Predation among the Hoverfly Episyrphus balteatus de Geer (Diptera: Syrphidae) and Other Aphidophagous Predators. Biol. Control 2001, 20, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATAKAN, E.; PEHLİVAN, S. Attractiveness of Various Colored Sticky Traps to Some Pollinating Insects in Apple. Turk. J. Zool. 2015, 39, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Saona, C.R.; Byers, J.A.; Schiffhauer, D. Effect of Trap Color and Height on Captures of Blunt-Nosed and Sharp-Nosed Leafhoppers (Hemiptera: Cicadellidae) and Non-Target Arthropods in Cranberry Bogs. Crop Prot. 2012, 40, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, E.A.; Cottrell, T.E. Effect of Lures and Colors on Capture of Lady Beetles (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in Tedders Pyramidal Traps. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 1395–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, G.; Reddy Palli, S.; Han, Z. Off-Target Effects of RNAi Correlate with the Mismatch Rate between DsRNA and Non-Target MRNA. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.; Port, G.; Collier, R. Living on the Edge: Using and Improving Trap Crops for Flea Beetle Management in Small-Scale Cropping Systems. Insects 2019, 10, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Trapping Modality | Species Richness | Chao1 Index ± SE | Potential Estimation of Missed Taxa Proportion [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| All the experiment | 67 | 114.88 ± 28.50 | 41.68 |
| PBAGDF | 45 | 74.89 ± 17.44 | 39.91 |
| PBAGDG | 34 | 52.03 ± 12.07 | 34.66 |
| PBIPSF | 37 | 68.62 ± 23.06 | 46.08 |
| PVAGDF | 16 | 28.02 ± 12.92 | 42.90 |
| PVAGDG | 18 | 47.65 ± 28.08 | 62.22 |
| PVIPSF | 24 | 38.88 ± 12.28 | 38.28 |
| Trapping Modality | Taxa | Indicator Statistic | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| PBAGDF | Lasioglossum minutissimum | 0.48 | 0.07 |
| Andrena subopaca | 0.44 | 0.05 * | |
| PBIPSF | Apis mellifera | 0.76 | >0.01 * |
| Melanostoma mellinum | 0.54 | >0.01 * | |
| Lasioglossum laticeps | 0.44 | 0.08 | |
| PVAGDF + PVAGDG | Harmonia axyridis | 0.44 | 0.02 * |
| Coccinella septempunctata | 0.43 | 0.04 * | |
| PBAGDF + PBIPSF | Episyrphus balteatus | 0.59 | >0.01 * |
| Spaerophoria scripta | 0.53 | >0.01 * | |
| PBIPSF + PVIPSF | Bombus hortorum | 0.60 | >0.01 * |
| PBAGDF + PBIPSF + PVIPSF | Bombus pascuorum | 0.48 | >0.01 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Segers, A.; Noël, G.; Delanglez, L.; Caparros Megido, R.; Francis, F. Impacts of Semiochemical Traps Designed for Bruchus rufimanus Boheman 1833 (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Nontarget Beneficial Entomofauna in Field Bean Crops. Insects 2023, 14, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020153
Segers A, Noël G, Delanglez L, Caparros Megido R, Francis F. Impacts of Semiochemical Traps Designed for Bruchus rufimanus Boheman 1833 (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Nontarget Beneficial Entomofauna in Field Bean Crops. Insects. 2023; 14(2):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020153
Chicago/Turabian StyleSegers, Arnaud, Grégoire Noël, Louise Delanglez, Rudy Caparros Megido, and Frédéric Francis. 2023. "Impacts of Semiochemical Traps Designed for Bruchus rufimanus Boheman 1833 (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Nontarget Beneficial Entomofauna in Field Bean Crops" Insects 14, no. 2: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020153
APA StyleSegers, A., Noël, G., Delanglez, L., Caparros Megido, R., & Francis, F. (2023). Impacts of Semiochemical Traps Designed for Bruchus rufimanus Boheman 1833 (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) on Nontarget Beneficial Entomofauna in Field Bean Crops. Insects, 14(2), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14020153








