Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Wing Shape to Identify Populations of Apis mellifera in Camagüey, Cuba
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
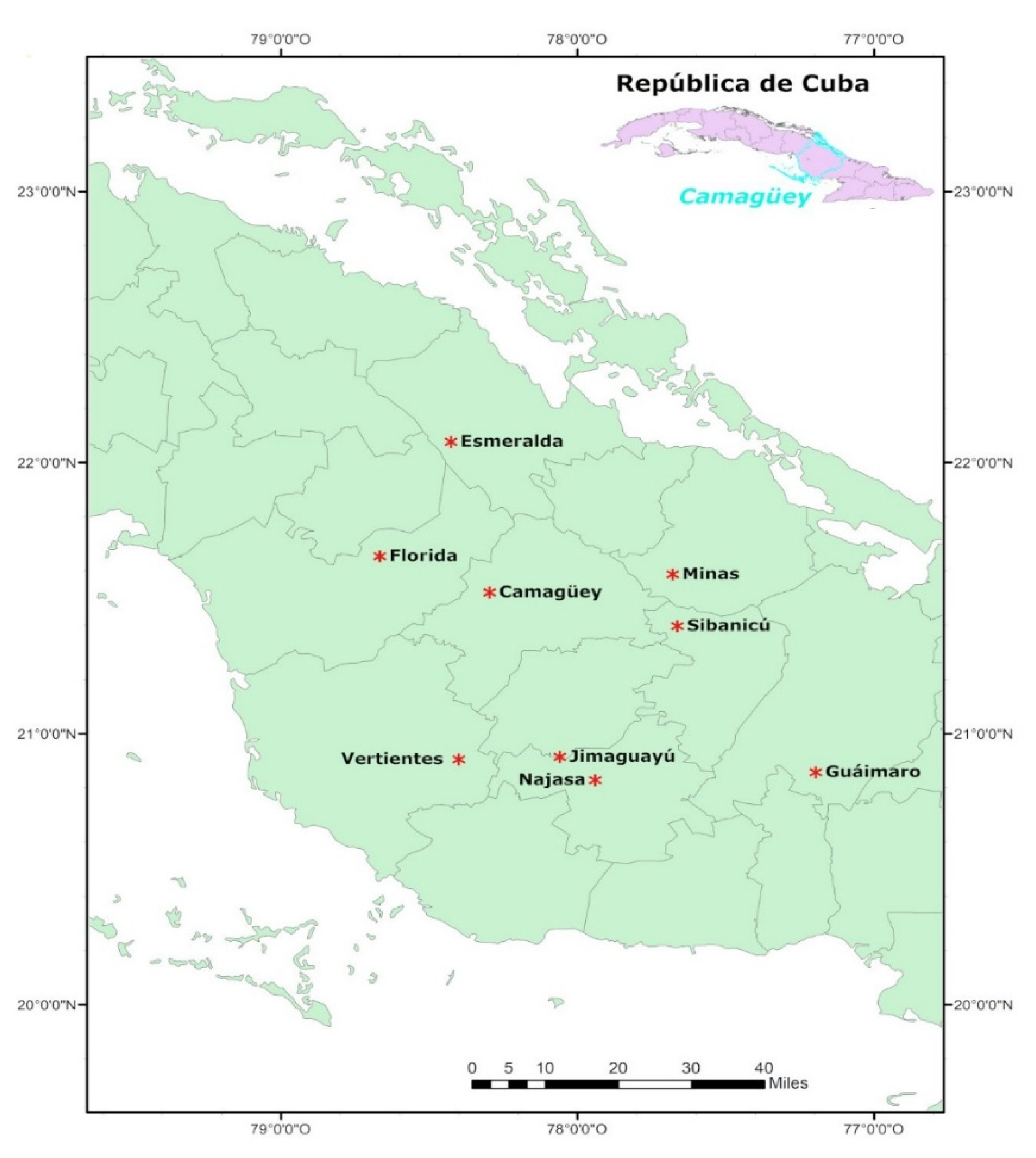
2.1. Geographical Location
2.2. Sampling
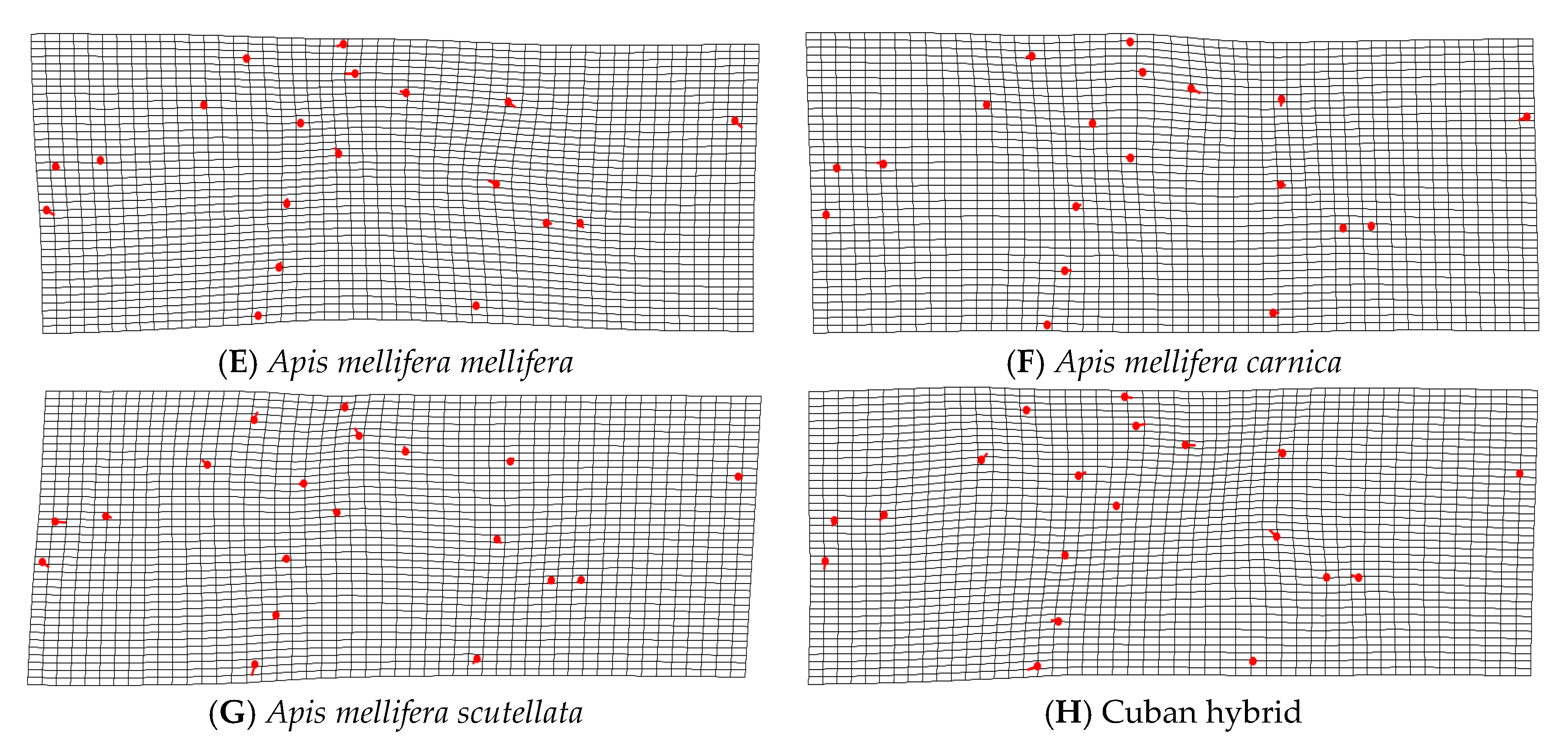
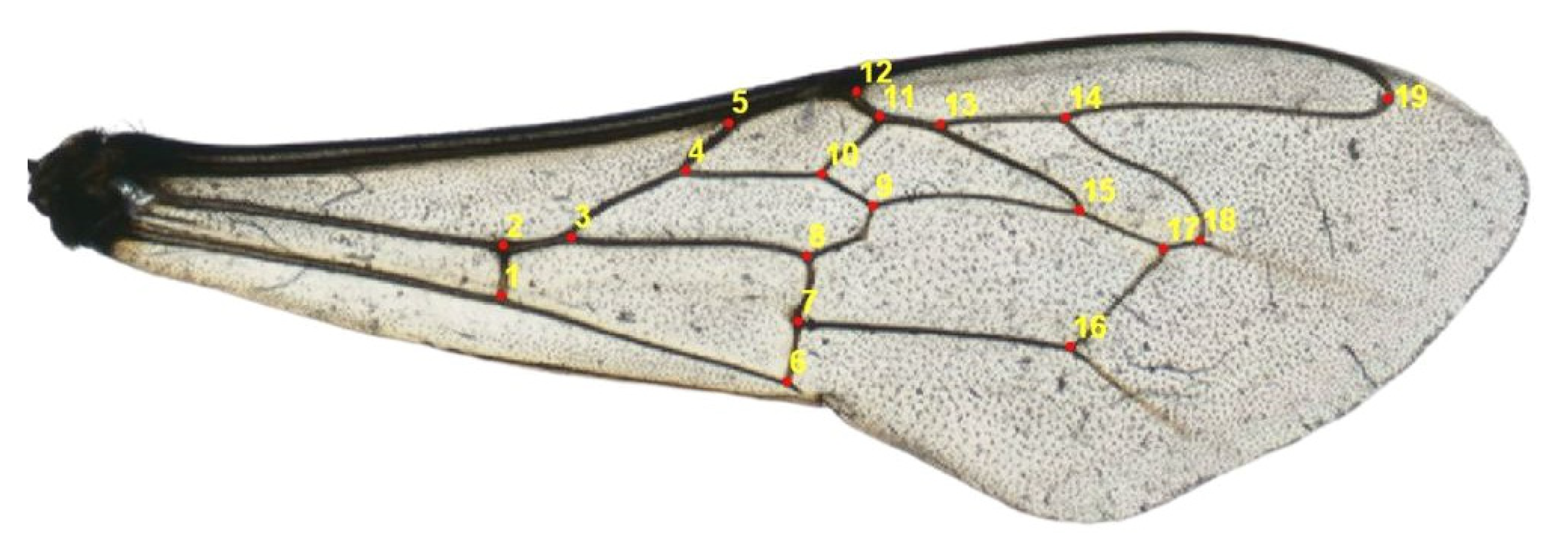
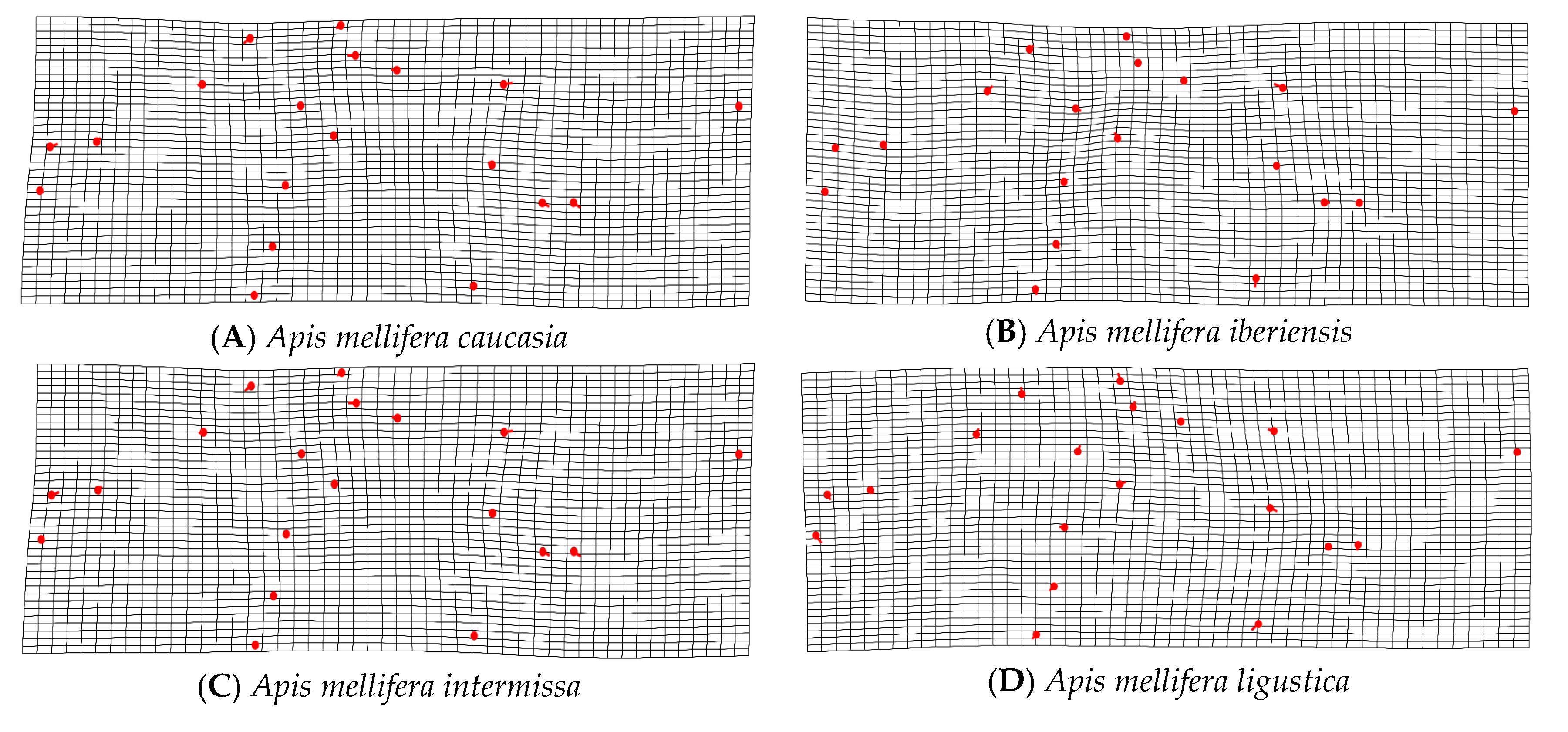
2.3. Geometric Morphometrics
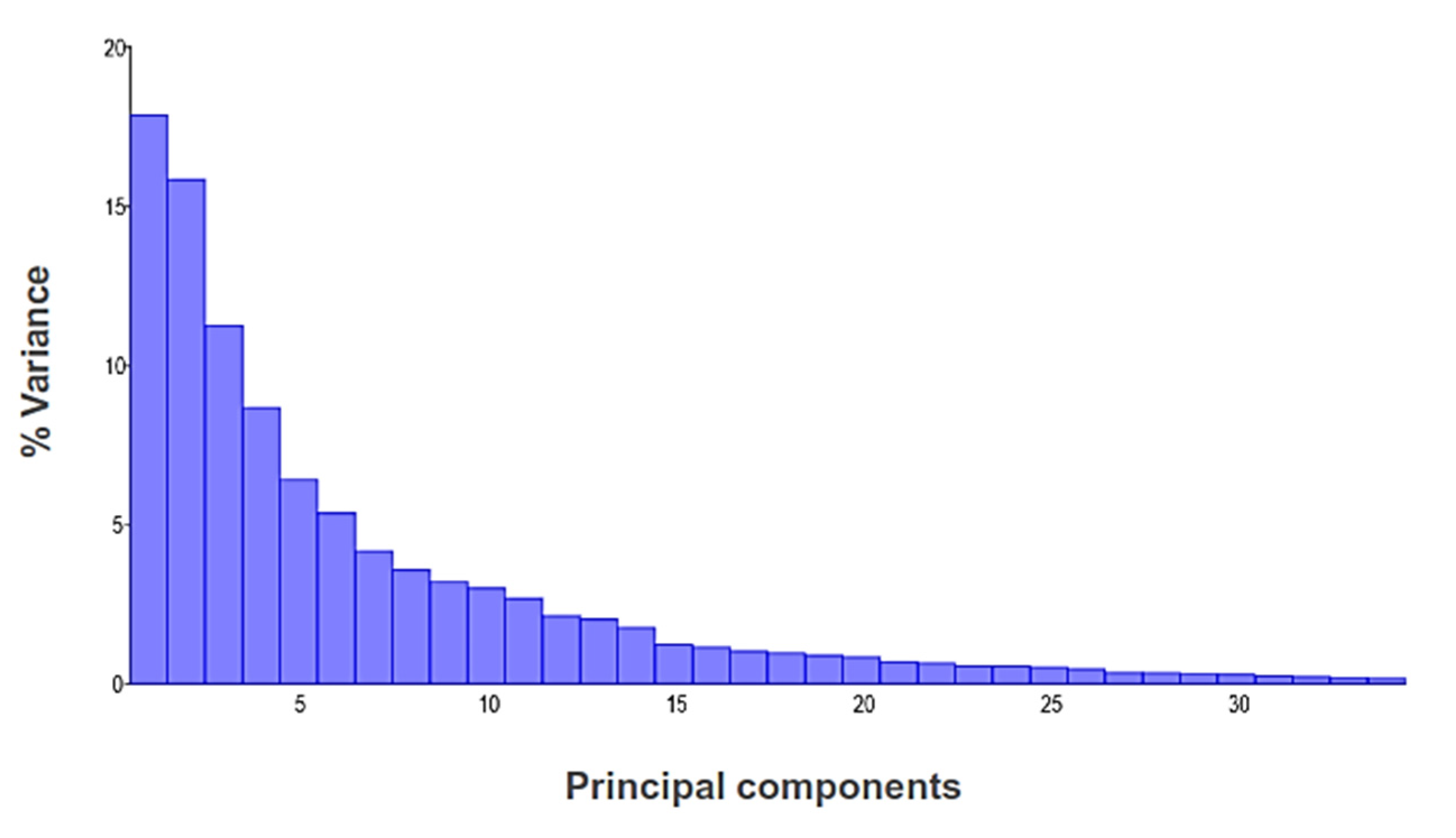
2.4. Statistical Analyses
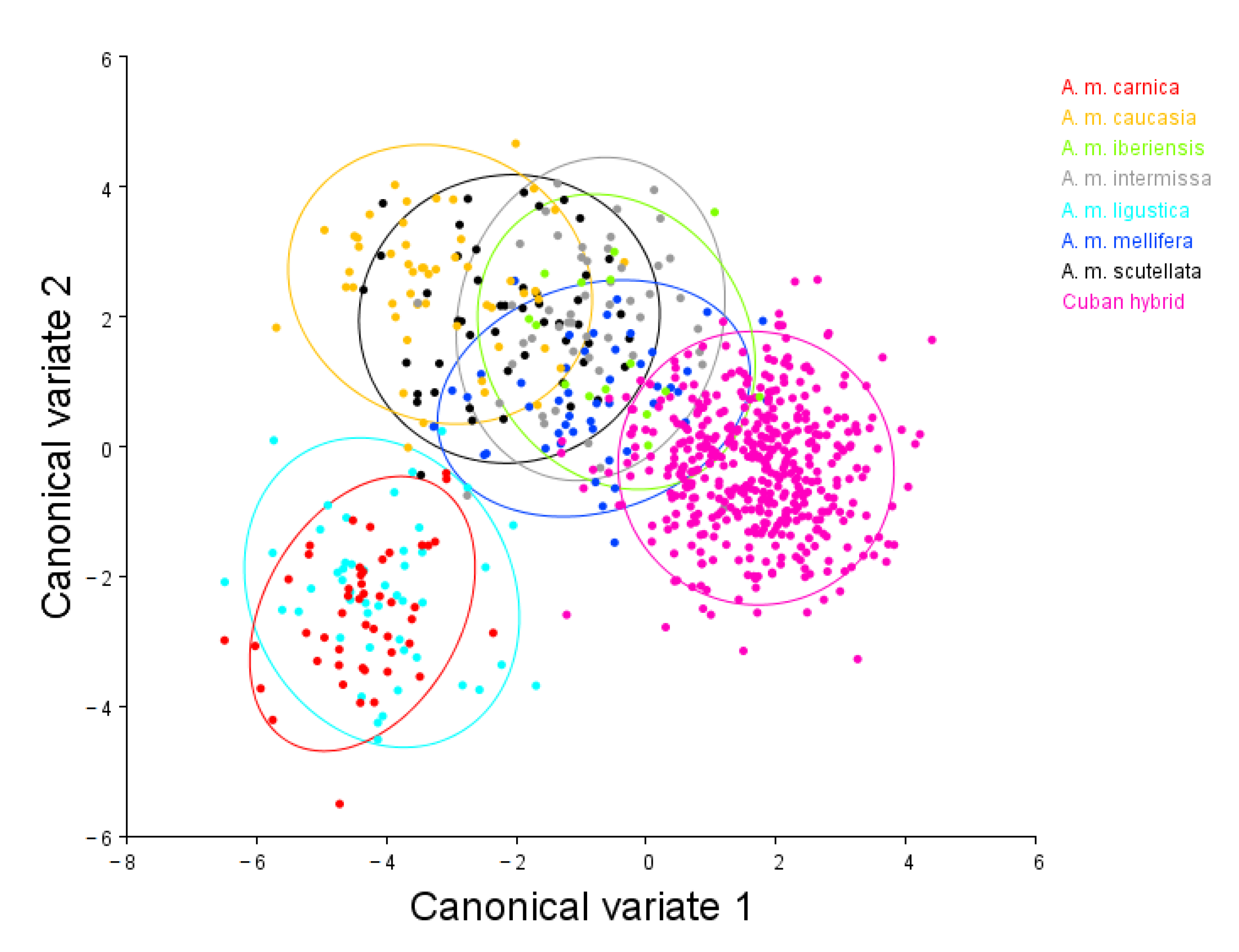
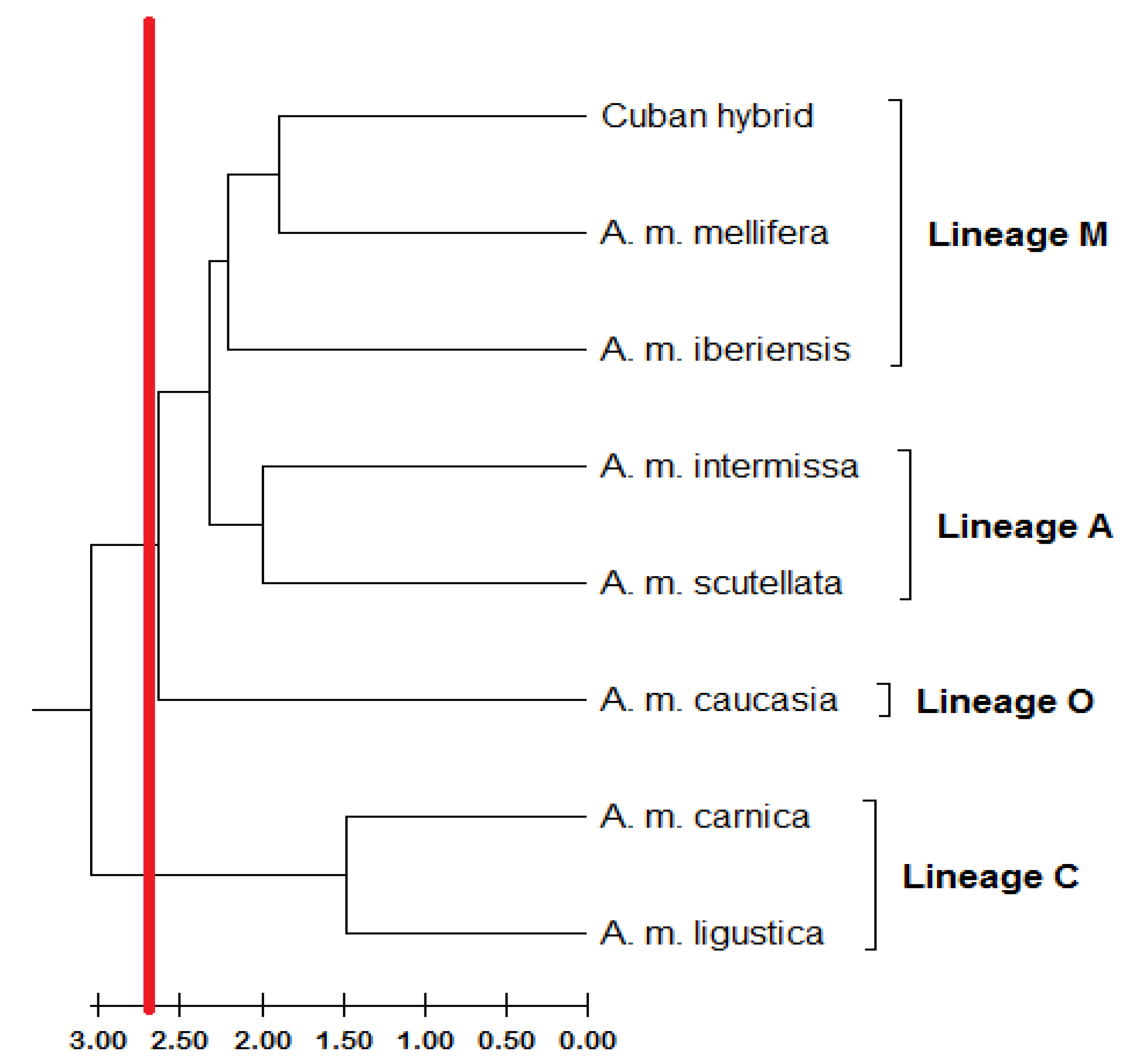
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ilyasov, R.A.; Lee, M.-L.; Takahashi, J.-I.; Kwon, H.W.; Nikolenko, A.G. A revision of subspecies structure of western honey bee Apis mellifera. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 3615–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal, S.; Danforth, B. Bees diversified in the age of eudicots. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20122686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizen, M.A.; Garibaldi, L.A.; Cunningham, S.A.; Klein, A.M. How much does agriculture depend on pollinators? Lessons from long-term trends in crop production. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 1579–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.C. Monitorización de los principales patógenos de las abejas para la detección de alertas y riesgos sanitarios (Doctoral dissertation, Universidad Complutense de Madrid). 2016. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/78501222.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2023).
- de Figueiró Santos, J.; Coelho, F.C.; Bliman, P.A. Behavioral modulation of the coexistence between Apis mellifera and Varroa destructor: A defense against colony colapse disorder? PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yániz, J.; Ángel, E.; Ramos, P.M.; Sales, E.; Santolaria, P. Caracterización de la abeja melífera en la provincia de Huesca. Lucas Mallada. Rev. Cienc. 2016, 257–271. [Google Scholar]
- Muli, E.; Patch, H.; Frazier, M.; Frazier, J.; Torto, B.; Baumgarten, T.; Kilonzo, J.; Mumoki, F.; Masiga, D.; Tumlinson, J. Evaluation of the distribution and impacts of parasites, pathogens, and pesticides on honey bee (Apis mellifera) populations in East Africa. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genaro, J.A. Origins, composition and distribution of the bees of Cuba (Hymenoptera: Apoidea: Anthophila). Insecta Mundi 2008, 583, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Miguel, I.; Baylac, M.; Iriondo, M.; Manzano, C.; Garnery, L.; Estonba, A. Both geometric morphometric and microsatellite data consistently support the differentiation of the Apis mellifera M evolutionary branch. Apidologie 2011, 42, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, A.; Demedio, J. Racial status and index of hive (Apis mellifera L.) infestation by Varroa destructor (Anderson and Trueman) in Mayabeque, Cuba. Cuba. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 51, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- García, C.A.Y.; Luis, A.R.; Perez Pineiro, A.; Perez Morfi, A.; Invernizzi, C.; Tomasco, I.H. Cuban honey bees: Significant differentiation from European honey bees in incomplete isolation. J. Apic. Res. 2021, 60, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpatov, W. Biometrical studies on variation and races of the honey bee (Apis mellifera L.). Q. Rev. Biol. 1929, 4, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruttner, F. Biogeography and Taxonomy of Honeybees; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Sylvester, H.; Rinderer, T. Fast Africanized Bee Identification System (FABIS). Am. Bee J. 1987, 127, 511–516. [Google Scholar]
- Sanford, M. Africanized honey bee: A biological revolution with human cultural implications. Am. Bee J. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Francoy, T.M.; Wittmann, D.; Drauschke, M.; Müller, S.; Steinhage, V.; Bezerra-Laure, M.A.F.; De Jong, D.; Gonçalves, L.S. Identification of Africanized honey bees through wing morphometrics: Two fast and efficient procedures. Apidologie 2008, 39, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandemir, İ.; Özkan, A.; Fuchs, S. Reevaluation of honeybee (Apis mellifera) microtaxonomy: A geometric morphometric approach. Apidologie 2011, 42, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.A.Y.; Rodrigues, P.J.; Tofilski, A.; Elen, D.; McCormak, G.P.; Oleksa, A.; Henriques, D.; Ilyasov, R.; Kartashev, A.; Bargain, C. Using the Software DeepWings© to Classify Honey Bees across Europe through Wing Geometric Morphometrics. Insects 2022, 13, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, F.; Costa, A.; Truzzi, F.; Silva, F.; Santos, S.; Francoy, T.; Saraiva, A. A reference process for automating bee species identification based on wing images and digital image processing. Ecol. Inform. 2014, 24, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingenberg, C.P. MorphoJ: An integrated software package for geometric morphometrics. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francoy, T.; de Faria Franco, F.; Roubik, D. Integrated landmark and outline-based morphometric methods efficiently distinguish species of Euglossa (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Euglossini). Apidologie 2012, 43, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.A.; De Araújo, E.D.; Marchini, L.C.; Moreti, A.C.D.C.C. Variation morphogeometrics of Africanized honey bees (Apis mellifera) in Brazil. Iheringia. Série Zool. 2012, 102, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksa, A.; Tofilski, A. Wing geometric morphometrics and microsatellite analysis provide similar discrimination of honey bee subspecies. Apidologie 2014, 46, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, F.J. Shape Statistics: Procrustes Superimpositions and Tangent Spaces. J. Classif. 1999, 16, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoshraftar, M.; Nazemi-Rafie, J.; Ghobari, H. Evaluation of the efficacy of mitochondrial ATP 6 and 8, Cyt b and 16S rDNA genes for differentiation of Iranian honeybees (Apis mellifera meda) from commercial subspecies of Apis mellifera L. and comparison with geometric morphometric method. J. Asia-Pacific Èntomol. 2020, 24, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghonche-Golan, S.; Nazemi-Rafie, J.; Rezapanah, M. The relationship study among Apis spp. using mitochondrial markers, Procrustes coordinates and residuals of geometric morphometric method. Biologia 2022, 77, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, N.C.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Beaman, L.D.; Lim, J.; Harpur, B.A.; Zayed, A.; Allsopp, M.H.; Rinderer, T.E.; Oldroyd, B.P. An abbreviated SNP panel for ancestry assignment of honeybees (Apis mellifera). Apidologie 2017, 48, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofilski, A. Using geometric morphometrics and standard morphometry to discriminate three honeybee subspecies. Apidologie 2008, 39, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, L.; Rodríguez, A.; Morales, A.; Mederos, E.A. Description of forewing venation pattern of the honey bee (Apis mellifera) in Granma, Cuba. Apiciencia 2014, XVI, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield, C.W.; Behura, S.K.; Berlocher, S.H.; Clark, A.G.; Johnston, J.S.; Sheppard, W.S.; Smith, D.R.; Suarez, A.V.; Weaver, D.; Tsutsui, N.D. Thrice out of Africa: Ancient and recent expansions of the honey bee, Apis mellifera. Science 2006, 314, 642–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, I.; Garnery, L.; Iriondo, M.; Baylac, M.; Manzano, C.; Sheppard, W.S.; Estonba, A. Origin, evolution and conservation of the honey bees from La Palma Island (Canary Islands): Molecular and morphological data. J. Apic. Res. 2015, 54, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düttmann, C.; Flores, B.; Sheleby-Elías, J.; Castillo, G.; Rodriguez, D.; Maggi, M.; Demedio, J. Africanized honeybee population (Apis mellifera L.) in Nicaragua: Forewing length and mitotype lineages. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Ayala, R.; Moo-Valle, H.; May-Itzá, W.D.J.; Medina-Peralta, S.; Quezada-Euán, J.J.G. Stock composition of northern neotropical honey bees: Mitotype and morphotype diversity in Mexico (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Apidologie 2016, 47, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francoy, T.; Wittmann, D.; Steinhage, V.; Drauschke, M.; Muller, S.; Cunha, D.; Nascimento, A.; Figueiredo, V.; Simoes, Z.; De Jong, D.; et al. Morphometric and genetic changes in a population of Apis mellifera after 34 years of Africanization. Genet. Mol. Res. 2009, 8, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyerinde, A.; Dike, M.; Banwo, O.; Bamaiyi, L.; Adamu, R. Morphometric and landmark based variations of Apis mellifera L. wings in the savannah agro-ecological zone of Nigeria. Glob. J. Sci. Front. Res. D 2012, 22, 33–41. [Google Scholar]

| Known Classification | N (wings) | A. m. carnica | A. m. ligustica | A. m. mellifera | A. m. scutellata | A. m. caucasia | A. m. iberiensis | A. m. intermissa | Cuban Hybrid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. m. carnica | 50 | 100 | 0 | ||||||
| A. m. ligustica | 50 | 100 | 0 | ||||||
| A. m. mellifera | 50 | 96 | 4 | ||||||
| A. m. scutellata | 50 | 98 | 2 | ||||||
| A. m. caucasia | 50 | 100 | 0 | ||||||
| A. m. iberiensis | 50 | 98 | 2 | ||||||
| A. m. intermissa | 50 | 98 | 2 | ||||||
| Cuban hybrid | 432 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 4.40 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 0.23 | 1.62 | 92.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Masaquiza, D.; Ferrán, M.O.; Guamán, S.; Naranjo, E.; Vaca, M.; Curbelo, L.M.; Arenal, A. Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Wing Shape to Identify Populations of Apis mellifera in Camagüey, Cuba. Insects 2023, 14, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030306
Masaquiza D, Ferrán MO, Guamán S, Naranjo E, Vaca M, Curbelo LM, Arenal A. Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Wing Shape to Identify Populations of Apis mellifera in Camagüey, Cuba. Insects. 2023; 14(3):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030306
Chicago/Turabian StyleMasaquiza, Diego, Mario Octavio Ferrán, Santiago Guamán, Edwin Naranjo, Maritza Vaca, Lino Marcelo Curbelo, and Amilcar Arenal. 2023. "Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Wing Shape to Identify Populations of Apis mellifera in Camagüey, Cuba" Insects 14, no. 3: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030306
APA StyleMasaquiza, D., Ferrán, M. O., Guamán, S., Naranjo, E., Vaca, M., Curbelo, L. M., & Arenal, A. (2023). Geometric Morphometric Analysis of Wing Shape to Identify Populations of Apis mellifera in Camagüey, Cuba. Insects, 14(3), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14030306







