Acoustic Comparisons of Red Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus) Mortality in Naturally Infested Date Palms after Injection with Entomopathogenic Fungi or Nematodes, Aluminum Phosphide Fumigation, or Insecticidal Spray Treatments
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Tree Selection
2.2. Treatments and Inert Control Injections
2.3. Fungal Isolate Mass Production
2.4. Application of Entomopathogenic Fungi and Inert Control
2.5. Application of Entomopathogenic Nematodes
2.6. Application of Chemical Insecticides
2.6.1. Fipronil (Fiprol)
2.6.2. Phosphine (Aluminum Phosphide)
2.6.3. TreeCare (Emamectin Benzoate)
2.7. Field Evaluation Using Acoustic Sensor: TreeVibes
Acoustic Recordings
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
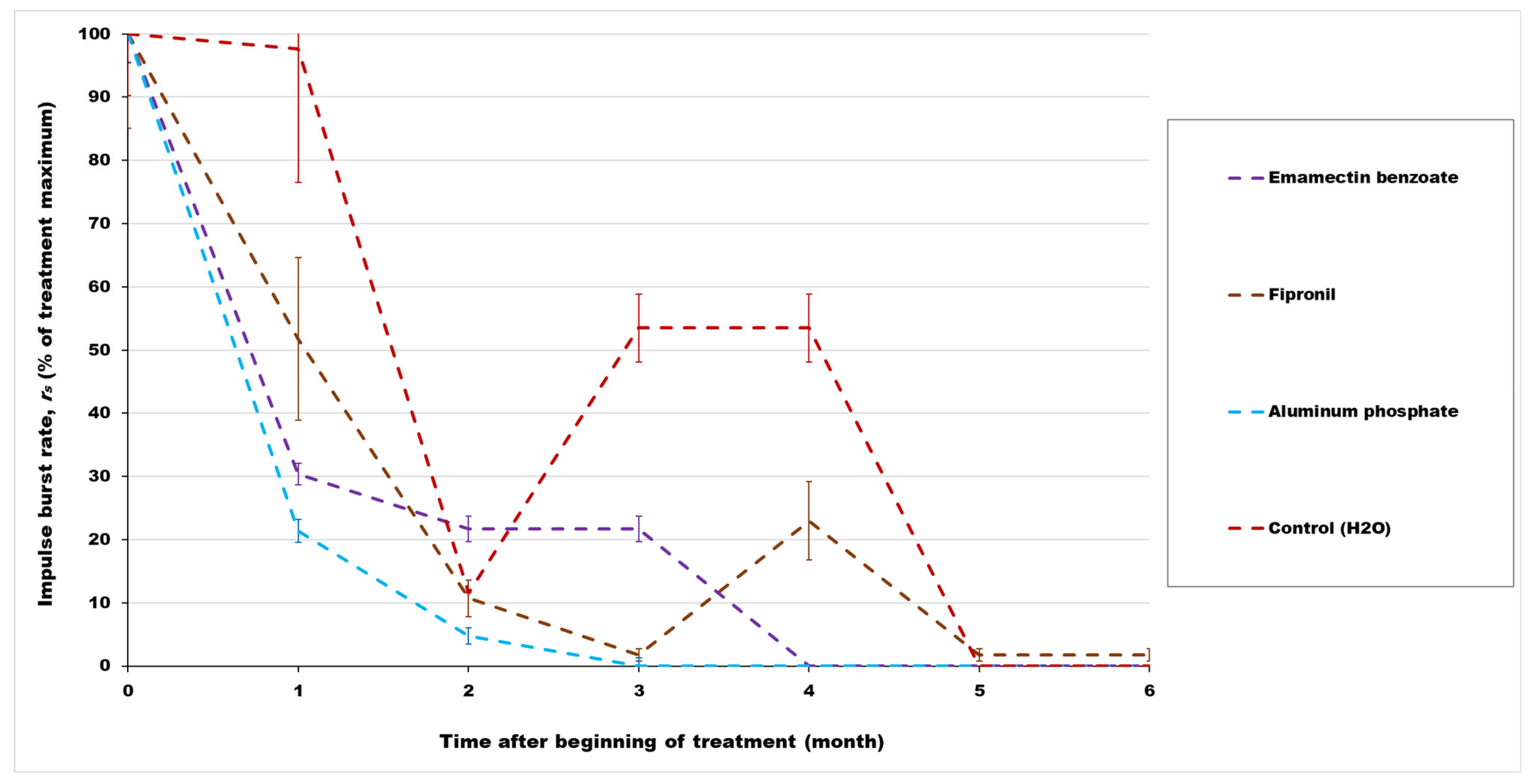
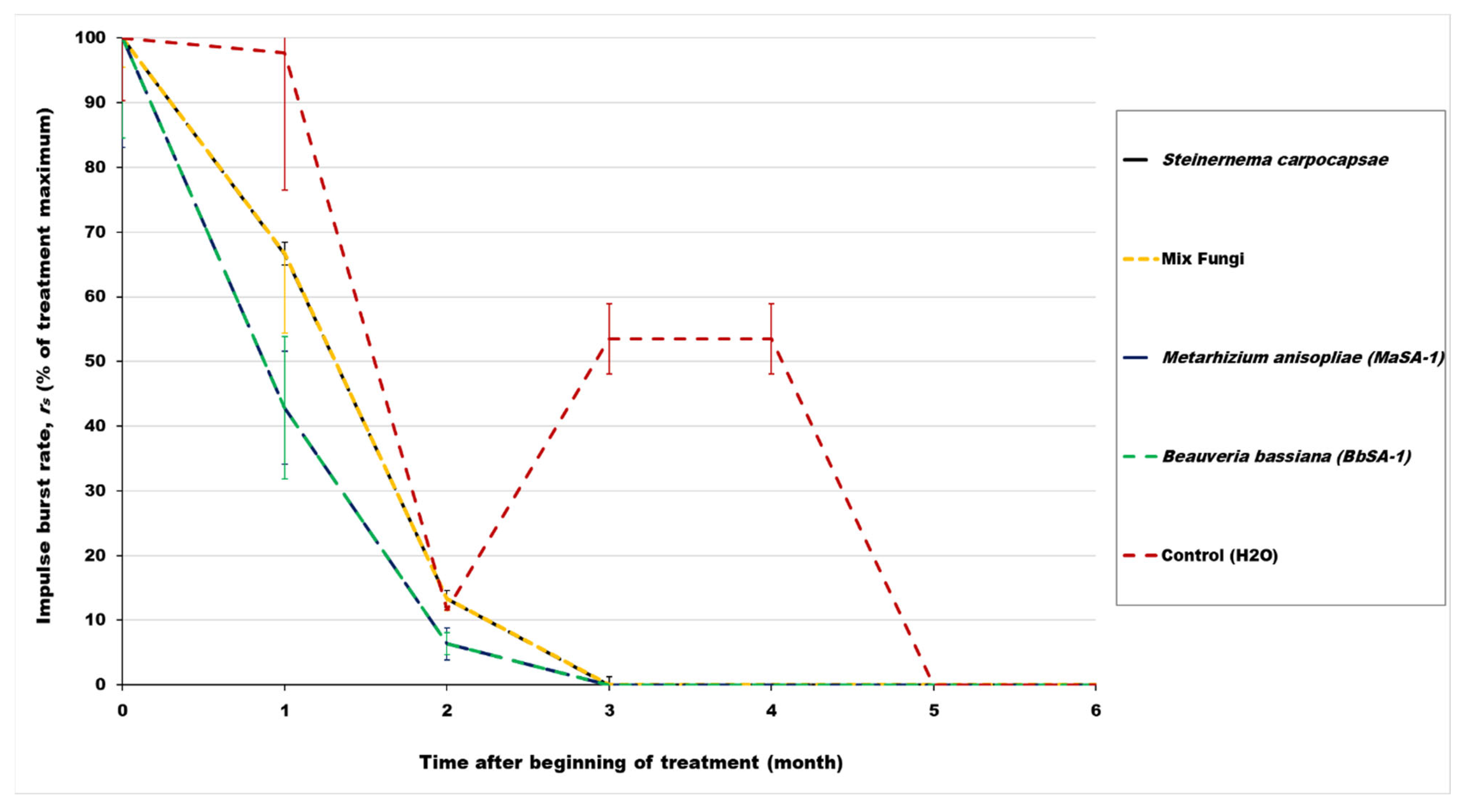
3.1. Monthly Impulse Burst Rates (rs) Monitored from Infested Date Palm Trees after Treatments
3.2. Evaluation of the Rates of Impulse Bursts (rs) Generated from the Infested Date Palm Trees after Treatments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abraham, V.; Shuaibi, M.A.; Faleiro, J.; Abozuhairah, R.; Vidyasagar, P.S. An integrated management approach for red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Oliv. A key pest of date palm in the Middle East. J. Agric. Mar. Sci. 1998, 3, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Rizwan-ul-Haq, M.; Al-Ayedh, H.; AlJabr, A.M. Susceptibility and Immune Defence Mechanisms of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) against Entomopathogenic Fungal Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, M.E.; El-Shafie, H.A.; Alhajhoj, M.R. Recent trends in the early detection of the invasive red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (olivier). In Invasive Species-Introduction Pathways, Economic Impact, and Possible Management Options; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Soud, A.H. Effect of Ethyl Acetate on the Number of Red Palm Weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Olivier (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) Captured in Dark Red and Yellow Aggregation Pheromone Traps. Syr. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 2, 128–140. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, S.A.; Abd El-Salam, A.M.E.; El-Kholy, M.Y. Field Evaluation of Red Palm Weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Oliv. (Coleoptera:Curculionidae) Responses to its Fermenting Date Tree Volatiles. Int. J. Chem. Tech. Res. 2016, 9, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Tapia, G.; Ruiz, M.; Téllez, M. Recommendations for a preventive strategy to control red palm weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus, Olivier) based on the use of insecticides and entomopathogenic nematodes. EPPO Bull. 2011, 41, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldawood, A.S.; Alsagan, F.; Altuwariqi, H.; ALmuteri, A.; Rasool, G.K. Red palm weevil chemical treatments on date palms on date palms in Saudi Arabia: Results of extentive experiment. In Proceedings of the AFPP: Colloque Méditerranéen sur les Ravageurs des Palmiers, Nice, Franch, 16–18 January 2013; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rasool, K.G.; Husain, M.; Salman, S.; Abbas, N.; Mehmood, K.; Sutanto, K.D.; Aldawood, A.S. Toxicity and field efficacy of emamectin benzoate (ARETOR) against red palm weevil, by using Syngenta tree micro-injection technique. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2021, 25, 1120–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakil, W.; Yasin, M.; Qayyum, M.A.; Ghazanfar, M.U.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Bedford, G.O.; Kwon, Y.J. Resistance to commonly used insecticides and phosphine fumigant in red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) in Pakistan. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lla’cer, E.; Martinez de Altube, M.M.; Jacas, J.A. Evaluation of the efficacy of Steinernema carpocapsae in a chitosan formulation against the red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus, in Phoenix canariensis. Biocontrol 2009, 54, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwa, A.; Hegazi, E.M. Comparative Susceptibilities of Different Life Stages of the Red Palm Weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) Treated by Entomopathogenic Nematodes. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesca, N.; Alfonzo, A.; Verde, G.; Settanni, L.; Sinacori, M.; Lucido, P.; Moschetti, G. Biological activity of Bacillus sp. Evaluated on eggs and larvae of red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.c.; Ma, T.l.; Hou, Y.m.; Sun, M. An entomopathogenic bacterium strain, Bacillus thuringiensis, as a biological control agent against the red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Pest. Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopinadhan, P.B.; Mohandas, N.; Vasudevan, K.P. Cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus infecting redpalm weevil of coconut. Curr. Sci. 1990, 59, 577–580. [Google Scholar]
- El-Minshawy, A.M.; Hendi, R.; Gadelhak, G. Viability of stored polyhedrosis virus of the red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (olivier) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Area-Wide Control. Insect Pests 2005, 241–242. [Google Scholar]
- Sutanto, K.D.; Husain, M.; Rasool, K.G.; Al-Qahtani, W.H.; Aldawood, A.S. Pathogenicity of local and exotic entomopathogenic fungi isolates against different life stages of red palm weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qayyum, M.A.; Saleem, M.A.; Saeed, S.; Wakil, W.; Ishtiaq, M.; Ashraf, W.; Ahmed, N.; Ali, M.; Ikram, R.M.; Yasin, M.; et al. Integration of entomopathogenic fungi and eco-friendly insecticides for management of red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 27, 1811–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merghem, A. Susceptibility of the Red Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) to the Green Muscardine Fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae (Metsch.) in the Laboratory and in Palm Trees Orchard. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest. Control. 2011, 21, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Xiang, H.; Hou, Y.; Wen, S.; Ding, Y.; Wu, J.; Yin, X. Identification and virulence evaluation of two entomopathogenic fungal isolates in controlling Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Insect Sci. 2019, 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jalinas, J.; Güerri-Agulló, B.; Dosunmu, O.G.; Lopez Llorca, L.V.; Mankin, R.W. Acoustic activity cycles of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae) early instars after Beauveria bassiana (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) treatments. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2017, 110, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsanea, M.; Habib, S.; Khan, N.F.; Alsharekh, M.F.; Islam, M.; Khan, S. A Deep-Learning Model for Real-Time Red Palm Weevil Detection and Localization. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashry, I.; Mao, Y.; Al-Fehaid, Y.; Al-Shawaf, A.; Al-Bagshi, M.; Al-Brahim, S.; Khee Ng, T.; Ooi, B.S. Early detection of red palm weevil using distributed optical sensor. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, A.; Ruiz, V.; Moltó, E.; Tapia, G.; del Mar Téllez, M. Development of a bioacoustic sensor for the early detection of Red Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Olivier). Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, W.B.; Hussein, M.A.; Becker, T. Detection of the red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus using its bioacoustics features. Bioacoustics 2010, 19, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, A.P.; Purba, S.; Pratomo, Y.B.; Hadi, S.; Suputa, S.; Utami, S.S. Development of cloud-based bioacoustics monitoring system for supporting Integrated Pest Management in Agriculture production. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 449, 012032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalinas, J.; Erri-Agullo, B.G.; Mankin, R.W.; Follana, R.L.; Lopez-Llorca, L.V. Acoustic Assessment of Beauveria bassiana (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) Effects on Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae) Larval Activity and Mortality. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetzroni, A.; Soroker, V.; Cohen, Y. Toward practical acoustic red palm weevil detection. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 124, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudri, N.A.F.R.S.; Mohd Masri, M.M.; Maidin, M.S.T.; Kamarudin, N.; Hussain, M.H.; Abd Ghani, I.; Jalinas, J. Preliminary evaluation of acoustic sensors for early detection of red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus incidence on oil palm and coconut in Malaysia. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2021, 41, 3287–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankin, R.W. Recent Developments in the use of Acoustic Sensors and Signal Processing Tools to Target Early Infestations of Red Palm Weevil in Agricultural Environments 1. Fla. Entomol. 2011, 94, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shawaf, A.M.; Al-Shagag, A.; Al-Bagshi, M.; Al-Saroj, S.; Al-Bather, S.; Al-Dandan, A.M.; Abdallah, A.B.; Faleiro, J.R. A quarantine protocol against red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) (Coleptera: Curculiondae) in date palm. J. Plant. Prot. Res. 2013, 53, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, K.; Razvi, S. Control of red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Oliver, using prophylactic spraying of date palms and trunk injection. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Date Palms; AI-Ain, United Arab Emirates, 25–27 March 2001, pp. 216–222.
- Al-Ballaa, S.; Faleiro, J. Studies on curative treatment of red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Olivier infested date palms based on an innovative fumigation technique. Arab. J. Plant. Prot. 2019, 37, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ezaby, F.A.A.O.K.; ElAssal, A. Integrated pest management for the control of red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus Oliv in the United Arab Emirates, Eastern region, Al Ain. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Date Palms, Al-Ain, United Arab Emirates, 8–10 March 1998; pp. 269–281. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shafie, H.A.F.; Faleiro, J.R. Red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): Global invasion, current management options, challenges and future prospects. In Invasive Species-Introduction Pathways, Economic Impact, and Possible Management Options; BoD–Books on Demand: Norderstedt, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Francardi, V.; Benvenuti, C.; Barzanti, G.; Roversi, P.F. Autocontamination trap with entomopathogenic fungi: A possible strategy in the control of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) (Coleoptera Curculionidae). Redia 2013, 96, 57–67. [Google Scholar]
- Latifian, M.; Bahar, R.; Amani, M.; Rahkhodaei, E. Mass production of EPF Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) by using agricultural products based on liquid- solid diphasic method for date palm pest control. Int. J. Agric. Crop Sci. 2013, 5, 2338–2341. [Google Scholar]
- Charif, R.; Waack, A.; Strickman, L. Raven Pro 1.4 User’s Manual; Cornell Lab of Ornithology: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2010; p. 25506974. [Google Scholar]
- Jalinas, J.; Güerri-Agulló, B.; Dosunmu, O.G.; Haseeb, M.; Lopez-Llorca, L.V.; Mankin, R.W. Acoustic signal applications in detection and management of Rhynchophorus spp. in fruit-crops and ornamental palms. Fla. Entomol. 2019, 102, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute. SAS. SAS/STAT® 9.1. Users Guide; SAS Institute Inc.: Cary, NC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ballaa, S.R. Fumigant Action of Commonly Used Insecticides as a Curative Treatment of Red Palm Weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier) in Infested Date Palms. Res. Pap. 2020, 38, 333–338. [Google Scholar]
- Mashal, M.M.; Obeidat, B.S. The efficacy assesment of emamectin benzoate using micro injection system to control red palm weevil. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chihaoui-Meridja, S.; Harbi, A.; Abbes, K.; Chaabane, H.; La Pergola, A.; Chermiti, B.; Suma, P. Systematicity, persistence and efficacy of selected insecticides used in endotherapy to control the red palm weevil Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier, 1790) on Phoenix canariensis. Phytoparasitica 2020, 48, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekesi, S. Pathogenicity and antifeedant activity of entomopathogenic hyphomycetes to the cowpea leaf beetle, Ootheca mutabilis Shalberg. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2001, 21, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutanto, K.D.; Al-Shahwan, I.M.; Husain, M.; Rasool, K.G.; Mankin, R.W.; Aldawood, A.S. Field Evaluation of Promising Indigenous Entomopathogenic Fungal Isolates against Red Palm Weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae). J. Fungi 2023, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, M.; Wakil, W.; El-Shafie, H.A.F.; Bedford, G.O.; Miller, T.A. Potential role of microbial pathogens in control of red palm weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus)—A Review. Entomol. Res. 2017, 47, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussenbaum, A.I.; Lecuona, R.E. Selection of Beauveria bassiana sensu lato and Metarhizium anisopliae sensu lato isolates as microbial control agents against the boll weevil (Anthonomus grandis) in Argentina. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 110, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, M.S.T.; Saleh, M.M.E.; Akil, A.M. Laboratory and field evaluation of the pathogenicity of entomopathogenic nematodes to the red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Oliv.) (Col.: Curculionidae). Anz. Für Schädlingskunde 2001, 74, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankin, R.; Mizrach, A.; Hetzroni, A.; Levsky, S.; Nakache, Y.; Soroker, V. Temporal and spectral features of sounds of wood-boring beetle larvae: Identifiable patterns of activity enable improved discrimination from background noise. Fla. Entomol. 2008, 91, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, N.J.; Mankin, R. Acoustical detection of early instar Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Canary Island date palm, Phoenix canariensis (Arecales: Arecaceae). Fla. Entomol. 2012, 95, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rach, M.M.; Gomis, H.M.; Granado, O.L.; Malumbres, M.P.; Campoy, A.M.; Martín, J.J.S. On the Design of a Bioacoustic Sensor for the Early Detection of the Red Palm Weevil. Sensors 2013, 13, 1706–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siriwardena, K.A.P.; Nanayakkara, N.; Fernando, L.C.P.; Nanayakkara, T. Portable acoustic device for detection of coconut palms infested by Rynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Crop Prot. 2010, 29, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potamitis, I.; Rigakis, I.; Tatlas, N.-A.; Potirakis, S. In-vivo vibroacoustic surveillance of trees in the context of the IoT. Sensors 2019, 19, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potamitis, I.; Ganchev, T. On automatic bioacoustic detection of pests: The cases of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus and Sitophilus Oryzae. J. Econ. Entomol. 2009, 102, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njoroge, A.W.; Mankin, R.W.; Smith, B.W.; Baributsa, D. Oxygen consumption and acoustic activity of adult Callosobruchus maculatus (F.) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae) during hermetic storage. Insects 2018, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Fungi | Tree Group | Tree Height (m) | Balloon/Tree | Total Volume, Conidia/mL/Balloon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beauveria bassiana/ Metarhizium anisopliae/ Mixed fungi | 1 | <1 | 1 | 100 mL, 1 × 109 conidia/mL |
| 2 | 1–1.9 | 2 | ||
| 3 | 2–2.9 | 3 | ||
| 4 | 3–3.9 | 4 | ||
| 5 | 4–5 | 4 |
| Treatment | Mean monthly Impulse Burst Rates (rs) of Red Palm Weevil (RPW) Sound Activities within Initially Infested Palm Trees | Statistical Analysis Fdf1,df2; p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | ||
| Control (water) | 0.43 ± 0.09 aAB | 0.42 ± 0.21 abA | 0.05 ± 0.01 abA | 0.23 ± 0.05 abA | 0.23 ± 0.05 abA | 0 ± 0 bA | 0 ± 0 bA | F6,35 = 2.99; <0.02 |
| Fipronil (Fiprol) | 0.56 ± 0.14 aA | 0.29 ± 0.12 abAB | 0.06 ± 0.02 bA | 0.01 ± 0.01 bB | 0.13 ± 0.06 bB | 0.01 ± 0.01 bB | 0.01 ± 0.01 bB | F6,35 = 6.77; <0.001 |
| Fungus (B. bassiana) | 0.52 ± 0.15 aAB | 0.22 ± 0.11 abAB | 0.03 ± 0.01 bA | 0 ± 0 bB | 0 ± 0 bC | 0 ± 0 bA | 0 ± 0 bA | F6,42 = 7.66; <0.001 |
| Fungus (M. anisopliae) | 0.55 ± 0.16 aA | 0.11 ± 0.08 bB | 0.03 ± 0.02 bA | 0 ± 0 bB | 0 ± 0 bC | 0 ± 0 bA | 0 ± 0 bA | F6,42 = 7.85; <0.001 |
| Mixed fungal isolates | 0.28 ± 0.04 aAB | 0.18 ± 0.12 abAB | 0.03 ± 0.01 bcA | 0 ± 0 bB | 0 ± 0 bC | 0 ± 0 bA | 0 ± 0 bA | F6,56 = 5.23; <0.001 |
| TreeCare (emamectin benzoate) | 0.23 ± 0.04 aB | 0.07 ± 0.01 bB | 0.05 ± 0.02 bA | 0.05 ± 0.02 bB | 0 ± 0 bC | 0 ± 0 bA | 0 ± 0 bA | F6,70 = 14.61; <0.001 |
| Aluminum phosphide | 0.35 ± 0.09 aAB | 0.07 ± 0.04 bB | 0.01 ± 0.01 bA | 0 ± 0 bB | 0 ± 0 bC | 0 ± 0 bA | 0 ± 0 bA | F6,42 = 10.29; <0.001 |
| Nematode (S. carpocapsae) | 0.24 ± 0.04 aAB | 0.11 ± 0.01 bB | 0.03 ± 0.01 cA | 0.03 ± 0.01 cB | 0 ± 0 cC | 0 ± 0 cA | 0 ± 0 cA | F6,70 = 21.51; <0.001 |
| Statistical analysis (F7,56; p) | F = 2.19; 0.052 | F = 1.51; 0.1878 | F = 0.54; 0.7982 | F = 14.07; <0.0001 | F = 14.70; <0.0001 | F = 27.35; <0.0001 | F = 1.56; 0.1700 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sutanto, K.D.; Husain, M.; Rasool, K.G.; Mankin, R.W.; Omer, A.O.; Aldawood, A.S. Acoustic Comparisons of Red Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus) Mortality in Naturally Infested Date Palms after Injection with Entomopathogenic Fungi or Nematodes, Aluminum Phosphide Fumigation, or Insecticidal Spray Treatments. Insects 2023, 14, 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14040339
Sutanto KD, Husain M, Rasool KG, Mankin RW, Omer AO, Aldawood AS. Acoustic Comparisons of Red Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus) Mortality in Naturally Infested Date Palms after Injection with Entomopathogenic Fungi or Nematodes, Aluminum Phosphide Fumigation, or Insecticidal Spray Treatments. Insects. 2023; 14(4):339. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14040339
Chicago/Turabian StyleSutanto, Koko D., Mureed Husain, Khawaja G. Rasool, Richard W. Mankin, Abdalsalam O. Omer, and Abdulrahman S. Aldawood. 2023. "Acoustic Comparisons of Red Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus) Mortality in Naturally Infested Date Palms after Injection with Entomopathogenic Fungi or Nematodes, Aluminum Phosphide Fumigation, or Insecticidal Spray Treatments" Insects 14, no. 4: 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14040339
APA StyleSutanto, K. D., Husain, M., Rasool, K. G., Mankin, R. W., Omer, A. O., & Aldawood, A. S. (2023). Acoustic Comparisons of Red Palm Weevil (Rhynchophorus ferrugineus) Mortality in Naturally Infested Date Palms after Injection with Entomopathogenic Fungi or Nematodes, Aluminum Phosphide Fumigation, or Insecticidal Spray Treatments. Insects, 14(4), 339. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14040339









