Efficacy of Commercially Available Entomopathogenic Agents against the Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer in South Africa
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rearing of PSHB
2.2. Entomopathogenic Agents and Laboratory Assays
2.3. Beetle Infestation Assay
2.4. Spore Viability Assay
2.5. Observation for Mycosis
2.6. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Pathogenicity in Laboratory Assays
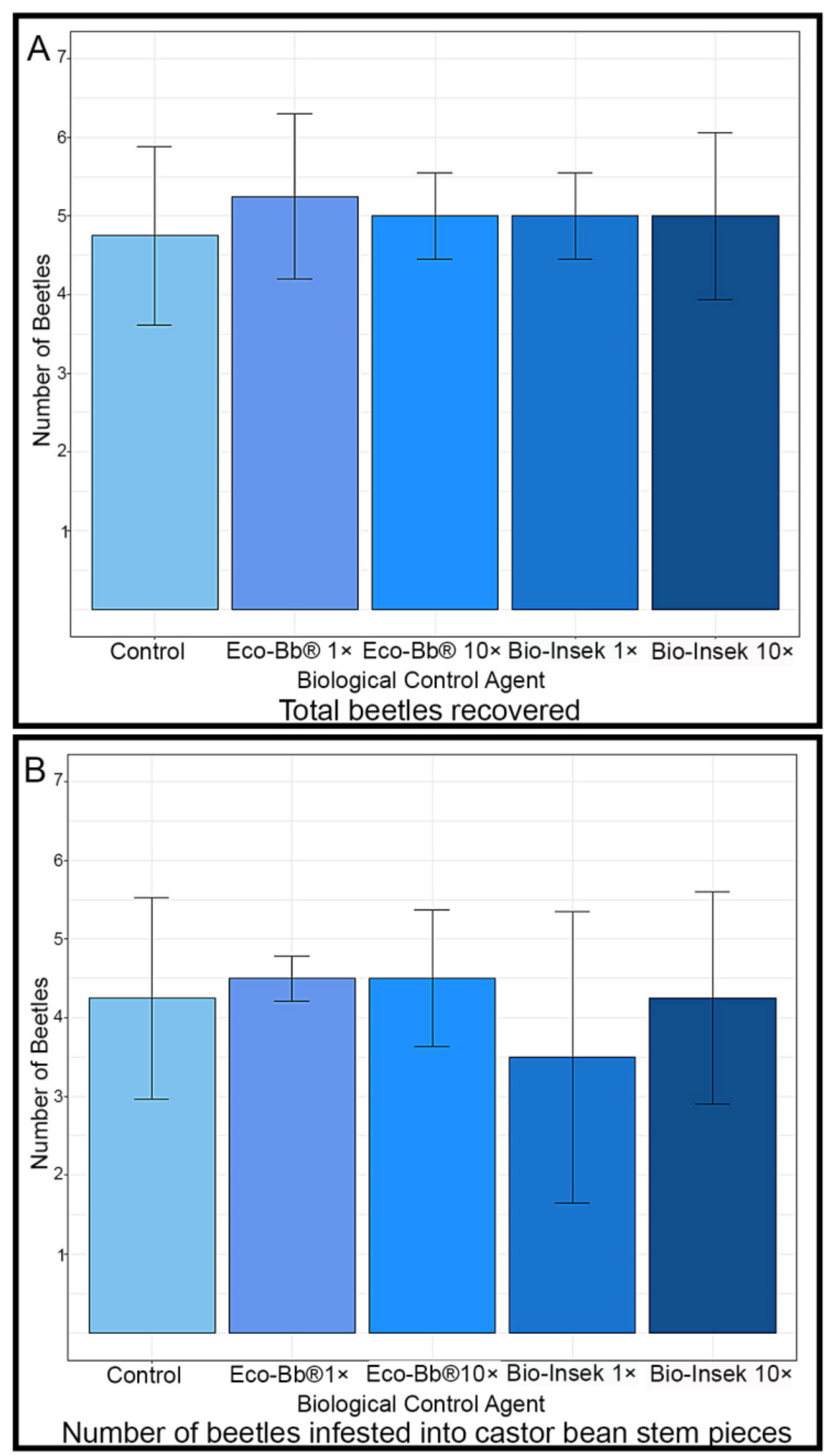
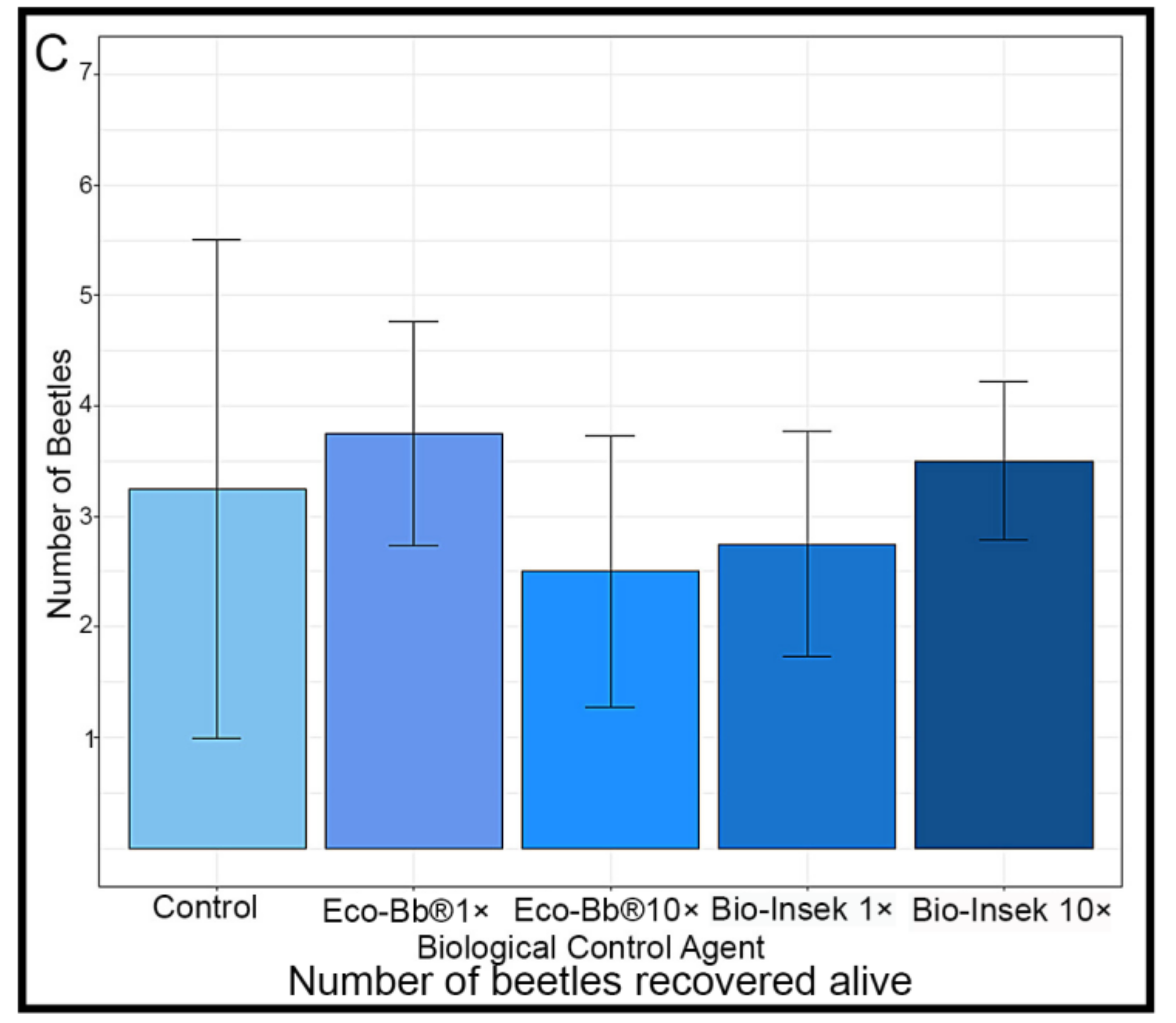
3.2. Pathogenicity in Infestation Assays
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, S.M.; Gomez, D.F.; Beaver, R.A.; Hulcr, J.; Cognato, A. Reassessment of the species in the Euwallacea fornicatus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae) complex after the rediscovery of the “lost” type specimen. Insects 2019, 10, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farrell, B.D.; Sequeira, A.S.; O’Meara, B.C.; Normark, B.B.; Chung, J.H.; Jordal, B.H. The evolution of agriculture in beetles (Curculionidae: Scolytinae and Platypodinae). Evolution 2001, 55, 2011–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, S.; Sharon, M.; Maymon, M.; Mendel, Z.; Protasov, A.; Aoki, T.; Eskalen, A.; O’Donnell, K. Fusarium euwallaceae sp. nov. a symbiotic fungus of Euwallacea sp., an invasive ambrosia beetle in Israel and California. Mycologia 2013, 105, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrillo, D.; Duncan, R.E.; Ploetz, J.N.; Campbell, A.F.; Ploetz, R.C.; Peña, J.E. Lateral transfer of a phytopathogenic symbiont among native and exotic ambrosia beetles. Plant Pathol. 2014, 63, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooyen, E.; Paap, T.; De Beer, Z.W.; Townsend, G.; Fell, S.; Nel, W.J.; Morgan, S.W.; Hill, M.; Roets, F. The polyphagous shot hole borer beetle: Current status of a perfect invader in South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2021, 117, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paap, T.; De Beer, Z.W.; Migliorini, D.; Nel, W.J.; Wingfield, M.J. The Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer (PSHB) and its fungal symbiont Fusarium euwallaceae: A new invasion in South Africa. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2018, 47, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Wit, M.P.; Crookes, D.J.; Blignaut, J.N.; De Beer, Z.W.; Paap, T.; Roets, F.; Van Der Merwe, C.; Van Wilgen, B.W.; Richardson, D.M. An assessment of the potential economic impacts of the invasive Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in South Africa. J. Econ. Entomol. 2022, 115, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, S.; De Beer, Z.W. The impact of the Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer on pecan trees in South Africa. SA Pecan 2019, 82, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Van Den Berg, N.; Du Toit, M.; Morgan, S.W.; Fourie, G.; De Beer, Z.W. First report of Fusarium euwallaceae causing necrotic lesions on Persea americana in South Africa. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twiddy, D.; Fell, S.; De Beer, Z.W.; Fourie, G. Screening for susceptibility of macadamia to Euwallacea fornicatus and its fungal symbiont Fusarium euwallaceae. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jager, M.; Roets, F. Pathogenicity of Fusarium euwallaceae towards apple (Malus domestica) and grapevine (Vitis vinifera). Australas. Plant Dis. Notes 2022, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Griggs, M.H.; Vandenberg, J.D. Competition between biological control fungi and fungal symbionts of ambrosia beetles Xylosandrus crassiusculus and X. germanus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): Mycelial interactions and impact on beetle brood production. Biol. Control 2016, 103, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuncer, C.; Kushiyev, R.; Erper, I.; Ozdemir, I.O.; Saruhan, I. Efficacy of native isolates of Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana against the invasive ambrosia beetle, Xylosandrus germanus Blandford (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2019, 29, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugliuzzo, A.; Biedermann, P.H.W.; Carrillo, D.; Castrillo, L.A.; Egonyu, J.P.; Gallego, D.; Haddi, K.; Hulcr, J.; Jactel, H.; Kajimura, H.; et al. Recent advances toward the sustainable management of invasive Xylosandrus ambrosia beetles. J. Pest Sci. 2021, 94, 615–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, D.; Dunlap, C.A.; Avery, P.B.; Navarrete, J.; Duncan, R.E.; Jackson, M.A.; Behle, R.W.; Cave, R.D.; Crane, J.; Rooney, A.P.; et al. Entomopathogenic fungi as biological control agents for the vector of the laurel wilt disease, the redbay ambrosia beetle, Xyleborus glabratus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Biol. Control 2015, 81, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushiyev, R.; Tuncer, C.; Erper, I.; Ozdemir, I.O.; Saruhan, I. Efficacy of native entomopathogenic fungus, Isaria fumosorosea, against bark and ambrosia beetles, Anisandrus dispar Fabricius and Xylosandrus germanus Blandford (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2018, 28, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toksöz, S.; Oksal, E.; Saruhan, I.; Kepenekci, I. Pathogenicity of the entomopathogenic fungus, Purpureocillium lilacinum TR1 against ambrosia beetles, Xylosandrus germanus (Blandford) and Xyleborus dispar (Fabricius)(Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae). Mun. Ent. Zool. 2018, 13, 471–481. [Google Scholar]
- Reynoso-López, E.; Méndez-Hernández, J.; Ek-Ramos, J.; Montesinos-Matías, R.; Loera, O. Metarhizium robertsii in combination with Trichoderma asperellum reduce the malathion doses used to control ambrosia beetles: The case of Xyleborus affinis. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2021, 31, 1080–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverchon, F.; Contreras-Ramos, S.M.; Eskalen, A.; Guerrero-Analco, J.A.; Quiñones-Aguilar, E.E.; Rios-Velasco, C.; Velázquez-Fernández, J.B. Microbial biocontrol strategies for ambrosia beetles and their associated phytopathogenic fungi. Front. Sustain. Food. Syst. 2021, 5, 737977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooperband, M.F.; Stouthamer, R.; Carrillo, D.; Eskalen, A.; Thibault, T.; Cossé, A.A.; Castrillo, L.A.; Vandenberg, J.D.; Rugman-Jones, P.F. Biology of two members of the Euwallacea fornicatus species complex (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae), recently invasive in the USA, reared on an ambrosia beetle artificial diet. Agric. For. Entomol. 2016, 18, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corallo, B.; Simeto, S.; Martínez, G.; Gómez, D.; Abreo, E.; Altier, N.; Lupo, S. Entomopathogenic fungi naturally infecting the eucalypt bronze bug, Thaumastocoris peregrinus (Heteroptera: Thaumastocoridae), in Uruguay. J. Appl. Entomol. 2019, 143, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E.L.; Meier, P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1958, 53, 457–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.M.; Lumley, T.; Atkinson, E.; Crowson, C. Package ‘survival’. R Topics Documented 2022, 128, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, O.J. Multiple comparisons using rank sums. Technometrics 1964, 6, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.S.; Mann, A.J.; Malesky, D.; Jankowski, E.; Bradley, C. Laboratory and field evaluation of the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) for population management of spruce beetle, Dendroctonus rufipennis (Coleoptera: Scolytinae), in felled trees and factors limiting pathogen success. Environ. Entomol. 2018, 47, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreutz, J.; Vaupel, O.; Zimmermann, G. Efficacy of Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. against the spruce bark beetle, Ips typographus L., in the laboratory under various conditions. J. Appl. Entomol. 2004, 128, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, M.A.; Butt, T.M. Susceptibility of different developmental stages of large pine weevil Hylobius abietis (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) to entomopathogenic fungi and effect of fungal infection to adult weevils by formulation and application methods. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2012, 111, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosana, A.R.R.; Pokorny, S.; Klutsch, J.G.; Ibarra-Romero, C.; Sanichar, R.; Engelhardt, D.; Van Belkum, M.J.; Erbilgin, N.; Bohlmann, J.; Carroll, A.L. Selection of entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) for the biocontrol of Dendroctonus ponderosae (Coleoptera: Curculionidae, Scolytinae) in Western Canada. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 2541–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Griggs, M.H.; Ranger, C.M.; Reding, M.E.; Vandenberg, J.D. Virulence of commercial strains of Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium brunneum (Ascomycota: Hypocreales) against adult Xylosandrus germanus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) and impact on brood. Biol. Control 2011, 58, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrillo, L.A.; Griggs, M.H.; Vandenberg, J.D. Granulate ambrosia beetle, Xylosandrus crassiusculus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae), survival and brood production following exposure to entomopathogenic and mycoparasitic fungi. Biol. Control 2013, 67, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damon, A. A review of the biology and control of the coffee berry borer, Hypothenemus hampei (Coleoptera: Scolytidae). Bull. Entomol. Res. 2000, 90, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grodzki, W.; Kosibowicz, M. An attempt to use the fungus Beauveria bassiana (Bals.) Vuill. in forest protection against the bark beetle Ips typographus (L.) in the field. For. Res. Pap. 2015, 76, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mann, A.J.; Davis, T.S. Entomopathogenic fungi to control bark beetles: A review of ecological recommendations. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3841–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Registration Holder | Product | Active Organism | Concentration Used in Lab Assays | Concentrations Used in Infestation Assays | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recommended Concentration | 10× Recommended Concentration | ||||
| Agro-Organics | Bio-Insek | Beauveria bassiana (Bb) and Metarhizium anisopliae (Ma) | 1.6 × 105 spores/mL Bb 2.8 × 105 spores/mL Ma | 1.6 × 104 spores/mL Bb 2.8 × 104 spores/mL Ma | 1.6 × 105 spores/mL Bb 2.8 × 105 spores/mL Ma |
| Plant Health Products | Eco-Bb® | Beauveria bassiana | 4 × 106 spores/ml | 4 × 106 spores/ml | 4 × 107 spores/ml |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nel, W.J.; Slippers, B.; Wingfield, M.J.; Yilmaz, N.; Hurley, B.P. Efficacy of Commercially Available Entomopathogenic Agents against the Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer in South Africa. Insects 2023, 14, 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14040361
Nel WJ, Slippers B, Wingfield MJ, Yilmaz N, Hurley BP. Efficacy of Commercially Available Entomopathogenic Agents against the Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer in South Africa. Insects. 2023; 14(4):361. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14040361
Chicago/Turabian StyleNel, Wilma J., Bernard Slippers, Michael J. Wingfield, Neriman Yilmaz, and Brett P. Hurley. 2023. "Efficacy of Commercially Available Entomopathogenic Agents against the Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer in South Africa" Insects 14, no. 4: 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14040361
APA StyleNel, W. J., Slippers, B., Wingfield, M. J., Yilmaz, N., & Hurley, B. P. (2023). Efficacy of Commercially Available Entomopathogenic Agents against the Polyphagous Shot Hole Borer in South Africa. Insects, 14(4), 361. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14040361






