A Novel Ethyl Formate Fumigation Strategy for Managing Yellow Tea Thrips (Scirtothrips dorsalis) in Greenhouse Cultivated Mangoes and Post-Harvest Fruits
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fumigants
2.2. Insects
2.3. Efficacy of EF against S. dorsalis during Greenhouse Mango Tree Cultivation and Post-Harvest Mango Fruit Storage
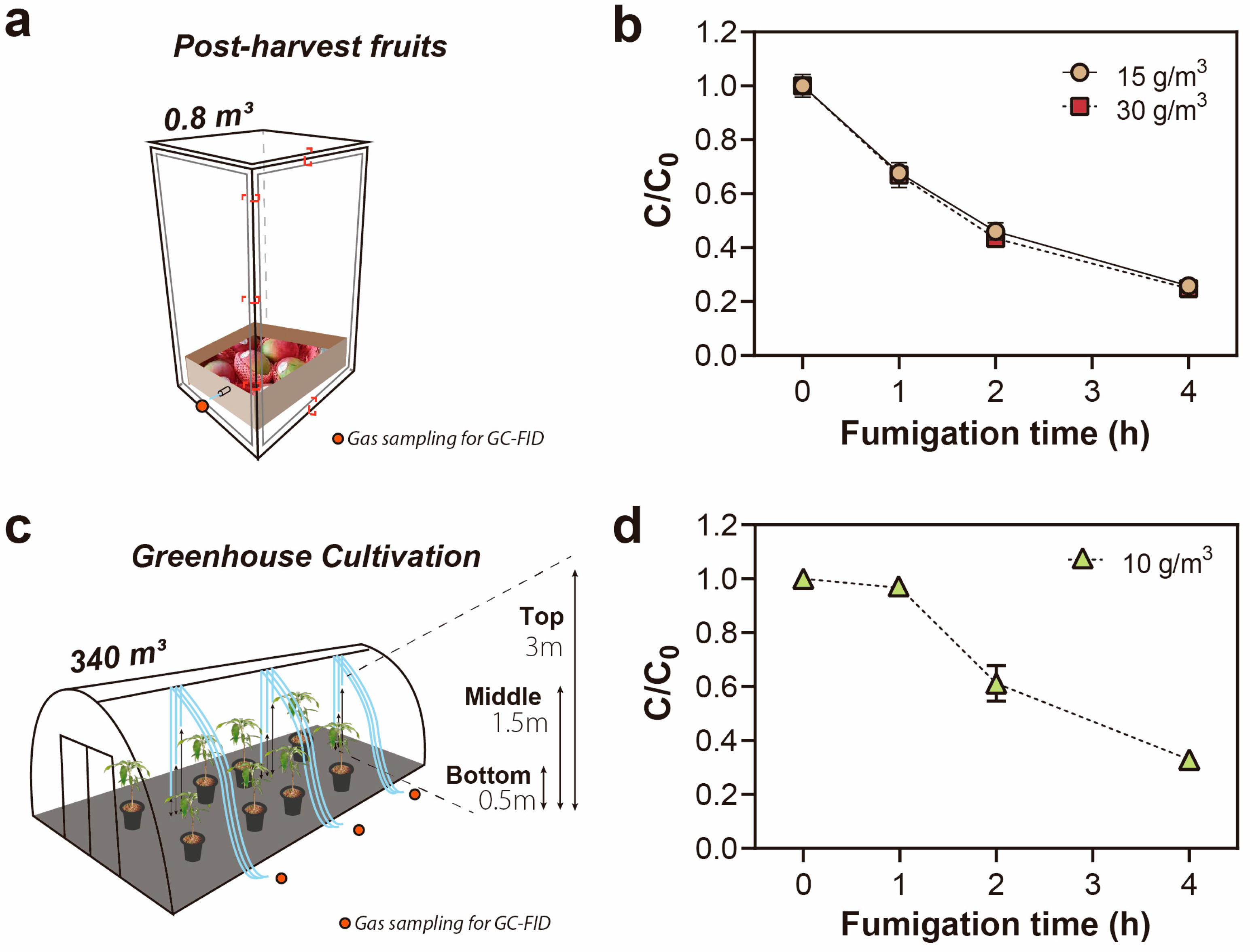
2.4. Post-Harvest Mango Fruit Storage Scenario
2.4.1. Evaluation of EF Sorption in Mango Fruits
2.4.2. Phytotoxic Assessments of Mango Fruits
2.5. Fumigation of the Greenhouse-Cultivated Mango Tree Scenario
2.5.1. Evaluation of EF Sorption in Greenhouse Mango Trees
2.5.2. Phytotoxicity Assessment of Mango Trees
2.5.3. Assessment of Worker Safety in the Greenhouse
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy of 4 h EF Fumigation on S. dorsalis in Two Different Scenarios
3.2. Phytotoxic Assessment of Post-Harvest Mango Fruit Storage
3.3. EF Concentration during/after Fumigation and Its Phytotoxic Effects in Cultivation Mango Trees
4. Discussion
4.1. Efficacy of Various Thrips Using Fumigant and Other Pesticides
4.2. Phytotoxicity of EF towards Cultivated Mango Trees and Post-Harvest Fruits
4.3. Greenhouse Application of EF Fumigation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ji, S.T.; Youm, J.W.; Yoo, J.Y. A feasibility study on the cultivation of tropical fruit in Korea: Focused on mango. J. Korea Acad. Ind. Coop. Soc. 2018, 19, 252–263. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, K.M.; Choi, Y.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Min, S.J.; Choi, D.S.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, D.Y. The classification of climate types and the delineation of their climatic characteristics using new nomals (1991–2020) in the Republic Korea. J. Clim. Res. 2021, 16, 179–195. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.K.; Yun, S.W.; Kim, H.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Yoon, Y.C. Field survey on the maintenance status of greenhouse in Korea. Prot. Hortic. Plant Fact. 2014, 23, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Singh, S.P. Mango: History origin and distribution. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2017, 6, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, S.H.; Ko, H.C. Current situation and prospects on the cultivation program of tropical and subtropical crops in Korea. Korean J. Plant Res. 2019, 32, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency (AQPA). Available online: https://okminwon.pqis.go.kr/minwon/information/statistics.html?statsType=103&frYear=2021&frMonth=01&toYear=2021&toMonth=12&trnType=IN&metType=hwa&itemCd=22150532&itemNm=%EB%A7%9D%EA%B3%A0&x=43&y=16 (accessed on 23 February 2023).
- IPPC. International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures, Publication No. 5: Glossary of Phytosanitary Terms; Secretariat of the International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC), Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hulme, P.E. Trade, transport and trouble: Managing invasive species pathway in an era of globalization. J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 46, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; Pena, J.E. Tropical citrus pests. In Tropical Fruit Pests and Pollinators, Biology, Economic Importance, Natural Enemies and Control; Pena, J.E., Sharp, J.L., Wysoki, M., Eds.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2002; pp. 57–101. [Google Scholar]
- Hyun, J.W.; Hwang, R.Y.; Lee, K.S.; Song, J.H.; Lee, P.H.; Kwon, H.M.; Hyun, D.H.; Kim, K.S. Seasonal occurrence of yellow tea thrips, Scirtothrips dorsalis Hood (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in citrus orchards and its damage symptoms on citrus fruits. Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 2012, 51, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masui, S. Estimation of the immigration time of Scirtothrips dorsalis Hood (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) adults in citrus orchards as a function of the total effective temperature. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2008, 43, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.S.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, G.H. Insecticide susceptibilities of rose field-collected populations of western flower thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis in Korea. Korean J. Pest. Sci. 2002, 6, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kyung, Y.J.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, B.S.; Yang, J.O.; Lee, B.H.; Koo, H.N.; Kim, G.H. Efficacy and phytotoxicity of phosphine as fumigants for Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) on asparagus. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 111, 2644–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, C.H. Fumigation in the 21st century. Crop Prot. 2000, 19, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambeau, M.B.; Benitez, D.P.; Dupuis, S.; Ducom, P. Hydrogen cyanide as an immediate alternative to methyl bromide for structural fumigations. In Proceedings of the International Conference Controlled Atmosphere and Fumigation in Stored Products, Fresno, CA, USA, 29 October–3 November 2000; Donahaye, E.J., Navarro, S., Leesch, J.G., Eds.; Executive Printing Services: Clovis, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, J.F.; Toews, M.D.; Arthur, F.H.; Arbogast, R.T. Long-term monitoring of Tribolium castaneum in two flour mills: Seasonal patterns and impact of fumigation. J. Econ. Entomol. 2010, 103, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.G.; Lee, B.H.; Yang, J.O.; Kim, B.S.; Roh, G.H.; Kendra, P.E.; Cha, D.H. Ethyl formate as a methyl bromide alternative for fumigation of citrus: Efficacy, fruit quality, and workplace safety. J. Econ. Entomol. 2021, 114, 2290–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, T.; Bikoba, V.; Tipping, C.; Mitcham, E.J. Ethyl formate as a postharvest fumigant for selected pests of table grapes. J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misumi, T.; Ogawa, N.; Yamada, K.; Shukuya, T. Susceptibilities of five species of scales (Diaspididae and Coccidae) and mealybugs (Pseudococcidae) to fumigation with a gas mixture of ethyl formate and carbon dioxide under normal atmospheric pressure or vacuum. Bull. Plant Prot. Japan. 2013, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, M.J.; Jamieson, L.E.; Chhagan, A.; Page-Weir, N.E.M.; Poulton, J.; Davis, V.A.; Zulhendri, F.; Connolly, P.G. The potential of ethyl formate + carbon dioxide to control a range of horticultural pests. N. Z. Plant Prot. 2013, 66, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, M.; Ren, Y.; Newman, J.; Learmonth, S. Ethyl formate: A potential disinfestation treatment of Eucalyptus weevil (Gonipterus platensis) (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in apples. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 2566–2571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.O.; Park, Y.R.; Hyun, I.H.; Kim, G.H.; Kim, B.S.; Lee, B.H.; Ren, Y.L. A combination treatment using ethyl formate and phosphine to control Planococcus citri (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) on pineapples. J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 2355–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Kim, H.M.; Kim, B.S.; Yang, J.O.; Moon, Y.M.; Ren, Y.L. Evaluation of the synergistic effect between ethyl formate and phosphine for control of Aphis gossypii (Homoptera: Aphididae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.H.; Park, C.G.; Yang, J.O.; Lee, S.E. Concurrent application of ethyl formate and 1-methylcyclopropene to control Tetranychus urticae on exported sweet persimmons (Diospyros Kaki Thunb. ‘Fuyu’). Entomol. Res. 2018, 48, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, H.K.; Kyung, Y.J.; Park, G.H.; Lee, B.H.; Yang, J.O.; Koo, H.N.; Kim, G.H. Fumigation activity of ethyl formate and phosphine against Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) on imported sweet pumpkin. J. Econ. Entomol. 2018, 114, 1625–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyung, Y.J.; Kim, H.K.; Cho, S.W.; Kim, B.S.; Yang, J.O.; Koo, H.N.; Kim, G.H. Comparison of the efficacy and phytotoxicity of phosphine and ethyl formate for controlling Pseudococcus longispinus (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) and Pseudococcus orchidicola in imported foliage nursery plants. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Lim, E.; Park, M.G.; Cha, W. Assessing the Retest Reliability of Prefrontal EEG Markers of Brain Rhythm Slowing in the Eyes-Closed Resting State. Clin. EEG Neurosci. 2020, 51, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.H.; Kim, D.B.; Kim, K.Y.; Park, M.G.; Roh, G.H.; Lee, B.H. Scale-up ethyl formate fumigation to replace methyl bromide on traded mushroom to disinfest mushroom fly (Lycoriella mali). Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.H.; Park, C.G.; Lee, B.H.; Zarders, D.R.; Roh, G.H.; Kendra, P.E.; Cha, D.H. Ethyl formate fumigation and ethyl formate plus cold treatment combination as potential phytosanitary quarantine treatments of Drosophila suzukii in blueberries. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2021, 24, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.B.; Kim, K.W.; Park, M.G.; Roh, G.H.; Cha, D.H.; Lee, B.H. New feasible quarantine disinfestation using ethyl formte for termites and ants on imported lumber. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2021, 24, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.B.; Kwon, T.H.; Park, M.G.; Kim, K.W.; Cha, D.H.; Lee, B.H. Ethyl formate-based quarantine treatment for exotic ants and termites in imported rubber plants and stone products. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.H.; Park, C.G.; Lee, B.H.; Jeong, I.H.; Lee, S.E. A New Approach: Ethyl Formate Fumigation to Control Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in a Yellow Melon Vinyl House. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.S.; Oh, H.K.; Motoyama, N. Insecticide resistance mechanism in the spiraea aphid, Aphis citricola (van der Goot). Korean J. Appl. Entomol. 1995, 34, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.L.; Lee, B.H.; Padovan, B. Penetration of methyl bromide, sulfuryl fluoride, ethanedinitrile and phosphine into timber blocks and the sorption rate of the fumigants. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2011, 47, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Renkema, J.M.; Krey, K.; Devkota, S.; Liburd, O.E.; Funderburk, J. Efficacy of insecticides for season-long control of thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in winter strawberries in Florida. Crop Prot. 2020, 127, 104945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Gong, Y.; Jin, G.; Li, B.; Chen, J.; Kang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Gao, Y.; Reitz, S.; Wei, S. Field-evolved resistance to insecticides in the invasive western flower thrips Frankliniella occidentalis (Pergande) (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in China. Pest Manag. Sci. 2016, 72, 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kakkar, G.; McKenzie, C.L.; Seal, D.R.; Osborne, L.S. An Overview of Chilli Thrips, Scirtothrips dorsalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) Biology, Distribution and Management. In Weed and Pest Control—Conventional and New Challenges, 1st ed.; Sonia Soloneski, S., Marcelo Larramendy, M., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; pp. 53–77. [Google Scholar]
- Bikoba, V.N.; Pupin, F.; Biasi, W.V.; Rutaganira, F.U.; Mitcham, E.J. Use of Ethyl formate fumigation to control adult bean thrips in navel oranges. J. Econ. Entomol. 2019, 112, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharoni, Y.; Stewart, J.K.; Guadagni, D.G.; Mon, T.R. Thrips mortality and strawberry quality after vacuum fumigation with acetaldehyde or ethyl formate. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1980, 105, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pupin, F.; Bikoba, V.; Biasi, W.B.; Pedroso, G.M.; Ouyang, Y.; Grafton-Cardwell, E.E.; Mitcham, E.J. Postharvest control of western flower thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) and California red scale (Hemiptera: Diaspididae) with ethyl formate and its impact on citrus fruit quality. J. Econ. Entomol. 2013, 106, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Epenhuijsen, C.W.; Somerfield, K.G.; Hedderley, D.I.; Brash, D.W. Efficacy of ethyl formate and ethyl acetate for the control of onion thrips (Thrips tabaci). N. Z. J. Crop Hort. Sci. 2007, 35, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slot, M.; Nardwattanawong, T.; Hernández, G.G.; Bueno, A.; Riederer, M.; Winter, K. Large differences in leaf cuticle conductance and its temperature response among 24 tropical tree species from across a rainfall gradient. New Phytol. 2021, 232, 1618–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berardini, N.; Fezer, R.; Conrad, J.; Beifuss, U.; Carle, R.; Schieber, A. Screening of mango (Mangifera indica L.) cultivars for their contents of flavonol O- and xanthone C-glycosides, anthocyanins, and pectin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Nam, D.E.; Kim, O.K.; Shim, T.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J. Anti-obesity effects of African mango (Irvingia gabonesis, IGOB 131TM) extract in leptin-deficient obese mice. J. Korean Soc. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2014, 43, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Scenarios | Temp. (°C) | 1 LCt50 (95% CL, g h/m3) | LCt99 (95% CL, g h/m3) | Slope ± SE | df | X2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Post-harvest mango fruits | 11 | 6.89 (6.48–7.33) | 18.18 (15.91–21.62) | 5.52 ± 0.4 | 25 | 27.55 |
| Cultivation in mango tree in greenhouse | 23 | 6.25 (5.86–6.67) | 17.10 (14.83–20.63) | 5.32 ± 0.4 | 8 | 29.42 |
| Applied Dose (g/m3) | Exposure Time (h) | EF Concentration (Mean ± SE, g/m3) | Mortality (Mean ± SE, %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top | Middle | Bottom | |||
| 10 | 0.1 | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 7.9 ± 0.1 | 7.8 ± 0.1 | 100 ± 0.0 |
| 1.0 | 7.9 ± 0.1 | 7.8 ± 0.1 | 7.5 ± 0.1 | ||
| 2.0 | 5.5 ± 0.2 | 4.5 ± 0.1 | 4.7 ± 0.1 | ||
| 4.0 | 2.9 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.0 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | ||
| Ct values (Mean ± SE, g h/m3) | 22.7 ± 0.3 a,† | 20.6 ± 0.3 b | 20.4 ± 0.1 b | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.; Kim, D.; Kwon, S.H.; Roh, G.-H.; Lee, S.; Lee, B.-H.; Lee, S.-E. A Novel Ethyl Formate Fumigation Strategy for Managing Yellow Tea Thrips (Scirtothrips dorsalis) in Greenhouse Cultivated Mangoes and Post-Harvest Fruits. Insects 2023, 14, 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14060568
Kim K, Kim D, Kwon SH, Roh G-H, Lee S, Lee B-H, Lee S-E. A Novel Ethyl Formate Fumigation Strategy for Managing Yellow Tea Thrips (Scirtothrips dorsalis) in Greenhouse Cultivated Mangoes and Post-Harvest Fruits. Insects. 2023; 14(6):568. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14060568
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyeongnam, Dongbin Kim, Soon Hwa Kwon, Gwang-Hyun Roh, Sangman Lee, Byung-Ho Lee, and Sung-Eun Lee. 2023. "A Novel Ethyl Formate Fumigation Strategy for Managing Yellow Tea Thrips (Scirtothrips dorsalis) in Greenhouse Cultivated Mangoes and Post-Harvest Fruits" Insects 14, no. 6: 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14060568
APA StyleKim, K., Kim, D., Kwon, S. H., Roh, G.-H., Lee, S., Lee, B.-H., & Lee, S.-E. (2023). A Novel Ethyl Formate Fumigation Strategy for Managing Yellow Tea Thrips (Scirtothrips dorsalis) in Greenhouse Cultivated Mangoes and Post-Harvest Fruits. Insects, 14(6), 568. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects14060568