Effect of Acetamiprid, a Neonicotinoid Insecticide, on Locomotor Activity of the American Cockroach
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
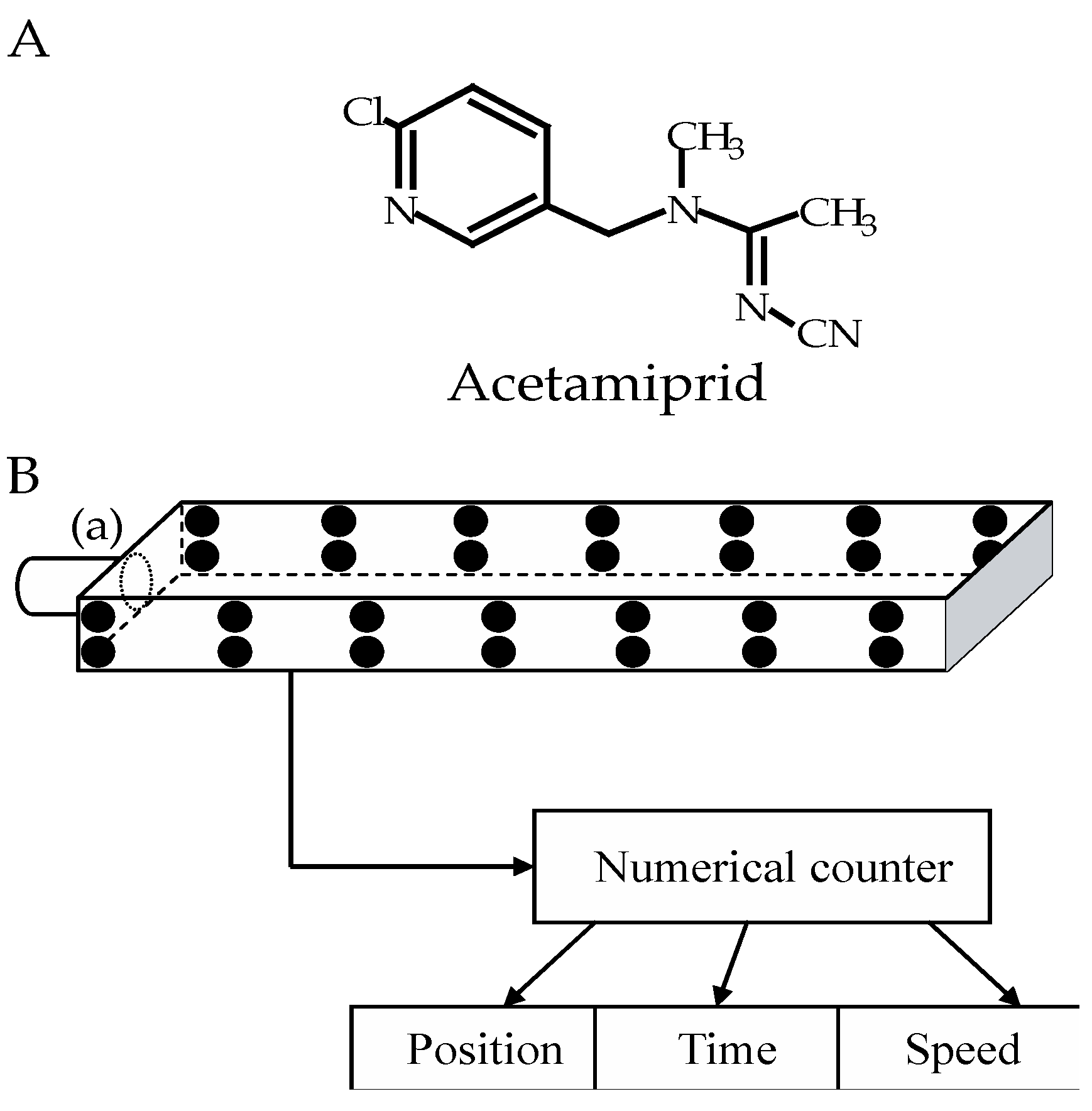
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Exposure Protocol
2.4. Evaluation of Locomotor Activity
2.5. Evaluation of Cockroaches’ Mortality
2.6. Mannitol-Gap Recordings
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Percentage of Cockroaches Displaying Locomotor Activity
3.2. Cockroach Mortality after Acetamiprid Application
3.3. Characterization of Cockroach Locomotor Activity: Immobility and Time of Exploration
3.4. Effect of Acetamiprid on Cockroach Sixth Abdominal Ganglion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, Y.; Long, C.; Bai, X.; Liu, W.; Rong, M.; Lai, R.; An, S. Two new types of allergens from the cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Allergy 2015, 70, 1674–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gore, J.C.; Schal, C. Cockroach allergen biology and mitigation in the indoor environment. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 439–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagabu, S.; Ishihara, R.; Hieda, Y.; Nishimura, K.; Naruse, Y. Insecticidal and neuroblocking potencies of variants of the imidazolidine moiety of imidacloprid-related neonicotinoids and the relationship to partition coefficient and charge density on the pharmacophore. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagabu, S.K.C.; Nishimura, K. Insecticidal and neuroblocking activities toward American cockroach (Periplaneta americana L.) of imidacloprid metabolites, 5-hydroxy-, 4,5-dihydroxy- and 4,5-dehydroimidacloprid. J. Pestic. Sci. 2004, 29, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagabu, S.M.N.; Hibino, R.; Hanzawa, M.; Nishimura, K. Insecticidal and neuroblocking activities of thiamethoxam-type compounds in the American cockroach (Periplaneta americana L.). J. Pestic. Sci. 2005, 30, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriyama, K.; Nishiwaki, H.; Nakagawa, Y.; Nishimura, K. Insecticidal activity and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor binding of dinotefuran and its analogues in the housefly, Musca domestica. Pest Manag. Sci. 2003, 59, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Galligan, J.J.; Hollingworth, R.M. Agonist actions of neonicotinoids on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed by cockroach neurons. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 829–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoid insecticide toxicology: Mechanisms of selective action. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2005, 45, 247–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R. Neonicotinoids-from zero to hero in insecticide chemistry. Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, P.; Nauen, R.; Beck, M.E. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists: A milestone for modern crop protection. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 9464–9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoids and other insect nicotinic receptor competitive modulators: Progress and prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2018, 63, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: Neonicotinoid binding site specificity is usually but not always conserved with varied substituents and species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3365–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Minor structural changes in nicotinoid insecticides confer differential subtype selectivity for mammalian nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 127, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomizawa, M.; Lee, D.L.; Casida, J.E. Neonicotinoid insecticides: Molecular features conferring selectivity for insect versus mammalian nicotinic receptors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 6016–6024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thany, S.H.; Lenaers, G.; Raymond-Delpech, V.; Sattelle, D.B.; Lapied, B. Exploring the pharmacological properties of insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, K.; Ihara, M.; Sattelle, D.B. Neonicotinoid insecticides: Molecular targets, resistance, and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2020, 60, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Takahashi, H.; Hatano, R. A novel insecticide, acetamiprid. In Nicotinoid Insecticides and the Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor; Yamamoto, L., Casida, J.E., Eds.; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 1999; pp. 149–176. [Google Scholar]
- Le Questel, J.Y.; Graton, J.; Ceron-Carrasco, J.P.; Jacquemin, D.; Planchat, A.; Thany, S.H. New insights on the molecular features and electrophysiological properties of dinotefuran, imidacloprid and acetamiprid neonicotinoid insecticides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 7623–7634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodereau-Dubois, B.; List, O.; Calas-List, D.; Marques, O.; Communal, P.Y.; Thany, S.H.; Lapied, B. Transmembrane potential polarization, calcium influx, and receptor conformational state modulate the sensitivity of the imidacloprid-insensitive neuronal insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptor to neonicotinoid insecticides. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 326–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maienfisch, P.; Huerlimann, H.; Rindlisbacher, A.; Gsell, L.; Dettwiler, H.; Haettenschwiler, J.; Sieger, E.; Walti, M. The discovery of thiamethoxam: A second-generation neonicotinoid. Pest Manag. Sci. 2001, 57, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honda, H.; Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Neo-nicotinoid metabolic activation and inactivation established with coupled nicotinic receptor-CYP3A4 and -aldehyde oxidase systems. Toxicol. Lett. 2006, 161, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzidane, Y.; Touinsi, S.; Motte, E.; Jadas-Hecart, A.; Communal, P.Y.; Leduc, L.; Thany, S.H. Effect of thiamethoxam on cockroach locomotor activity is associated with its metabolite clothianidin. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, P.L.; Ritzmann, R.E. Descending influences on escape behavior and motor pattern in the cockroach. J. Neurobiol. 2001, 49, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckingham, S.; Lapied, B.; Corronc, H.; Sattelle, F. Imidacloprid actions on insect neuronal acetylcholine receptors. J. Exp. Biol. 1997, 200, 2685–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, L.A.; Glusman, J.G.; Libersat, F. Octopamine partially restores walking in hypokinetic cockroaches stung by the parasitoid wasp Ampulex compressa. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 4411–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, M.; Armengaud, C.; Raymond, S.; Gauthier, M. Imidacloprid-induced facilitation of the proboscis extension reflex habituation in the honeybee. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2001, 48, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, C.F.; Tilton, E.W. Tests with Acaricides against the Brown Wheat Mite. J. Econ. Entomol. 1955, 48, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callec, J.J.; Sattelle, D.B. A simple technique for monitoring the synaptic actions of pharmacological agents. J. Exp. Biol. 1973, 59, 725–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callec, J.J.; Sattelle, D.B.; Hue, B.; Pelhate, M. Central synaptic actions of pharmacological agents in insects: Oil-gap and mannitol-gap studies. In Neurotox 79; Sherwood, M., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 93–100. [Google Scholar]
- Thany, S.H. Agonist actions of clothianidin on synaptic and extrasynaptic nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on cockroach sixth abdominal ganglion. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thany, S.H. Thiamethoxam, a poor agonist of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on isolated cell bodies, acts as a full agonist at cockroach cercal afferent/giant interneuron synapses. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihaka, R.G.R. R: A language for data analysis and graphics. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 1996, 5, 299–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Feng, Q.; Lai, K.; Huang, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, Q.X. Toxic effects of indoxacarb enantiomers on the embryonic development and induction of apoptosis in zebrafish larvae (Danio rerio). Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliouane, Y.; El Hassani, A.K.; Gary, V.; Armengaud, C.; Lambin, M.; Gauthier, M. Subchronic exposure of honeybees to sublethal doses of pesticides: Effects on behavior. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2009, 28, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauen, R.; Salgado, V.; Kaussmann, M. Thiamethoxam is a neonicotinoid precursor converted to clothianidin in insects and plants. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2003, 76, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Kanda, Y.; Okazawa, A.; Ueno, T. relationship between insecticidal and neurophysiological activities of imidacloprid and related compounds. Pest Biochel. Physiol. 1994, 50, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, M.; Casida, J.E. Selective toxicity of neonicotinoids attributable to specificity of insect and mammalian nicotinic receptors. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2003, 48, 339–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troczka, B.J.; Homem, R.A.; Reid, R.; Beadle, K.; Kohler, M.; Zaworra, M.; Field, L.M.; Williamson, M.S.; Nauen, R.; Bass, C.; et al. Identification and functional charcterisation of a novel N-cyanoamidine neonicotinoid metabolising cytochrome P450, CYP9Q6, from the buff-tailed bumblebee Bombus terrestris. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 111, 103171–103178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beadle, K.; Singh, K.S.; Troczka, B.J.; Randall, E.; Zaworra, M.; Zimmer, C.T.; Hayward, A.; Reid, R.; Kor, L.; Kohler, M.; et al. Genomic insight into neonicotinoid sensitivity in the solitary bee Osmia bicornis. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjon, C.; Troczka, B.J.; Zaworra, M.; Beadle, K.; Randall, E.; Hertlein, G.; Singh, K.S.; Zimmer, C.T.; Homem, R.A.; Lueke, B.; et al. Unravelling the molecular determinants of bee sensitivity to neonicotinoid insecticides. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 1137–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Salgado, V.L.; Hollingworth, R.M. Neural actions of imidacloprid and their involvement in resistance in the Colorado potato beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata (Say). Pest Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzidane, Y.; Goven, D.; Abd-Ella, A.A.; Deshayes, C.; Lapied, B.; Raymond, V. Subchronic exposure to sublethal dose of imidacloprid changes electrophysiological properties and expression pattern of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes in insect neurosecretory cells. Neurotoxicology 2017, 62, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houchat, J.N.; Taillebois, E.; Thany, S.H. Effects of the DAG analogue 1,2-dioctanoyl-sn-glycerol (DiC8) on nicotine- and clothianidin-evoked currents through alpha-bungarotoxin-insensitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors expressed on cockroach neurosecretory cells. Neurotoxicology 2020, 78, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, V.L. Antagonist pharmacology of desensitizing and non-desensitizing nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in cockroach neurons. Neurotoxicology 2016, 56, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bantz, A.; Goven, D.; Siegwart, M.; Maugin, S.; Raymond, V. Exposure to a sublethal dose of imidacloprid induces cellular and physiological changes in Periplaneta americana: Involvement of α2 nicotinic acetylcholine subunit in imidacloprid sensitivity. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2022, 181, 105014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihara, M.; Matsuda, K.; Shimomura, M.; Sattelle, D.B.; Komai, K. Super agonist actions of clothianidin and related compounds on the SAD β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2004, 68, 761–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, J.A.; Pitman, R.M. The pharmacology of alpha-bungarotoxin-resistant acetylcholine receptors on an identified cockroach motoneurone. J. Comp. Physiol. 1993, 172, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, V.L.; Saar, R. Desensitizing and non-desensitizing subtypes of alpha-bungarotoxin-sensitive nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in cockroach neurons. J. Insect Physiol. 2004, 50, 867–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Exposure Method | Control | Acetamiprid (nmol.g−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.5 | 1 | ||
| Haemolymph injection | 6.2 ± 0.7 s | 6.4 ± 1.7 s | 129.3 ± 25.0 s | 319.0 ± 67.0 s |
| Topical application | 5.9 ± 2.1 s | 6.4 ± 2.5 s | 74.4 ± 2.0 s | 189.0 ± 3.0 s |
| Oral application | 6.1 ± 1.7 s | 6.0 ± 2.0 s | 73.4 ± 17.0 s | 137.7 ± 38.0 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taillebois, E.; Cartereau, A.; Thany, S.H. Effect of Acetamiprid, a Neonicotinoid Insecticide, on Locomotor Activity of the American Cockroach. Insects 2024, 15, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010054
Taillebois E, Cartereau A, Thany SH. Effect of Acetamiprid, a Neonicotinoid Insecticide, on Locomotor Activity of the American Cockroach. Insects. 2024; 15(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaillebois, Emiliane, Alison Cartereau, and Steeve H. Thany. 2024. "Effect of Acetamiprid, a Neonicotinoid Insecticide, on Locomotor Activity of the American Cockroach" Insects 15, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010054
APA StyleTaillebois, E., Cartereau, A., & Thany, S. H. (2024). Effect of Acetamiprid, a Neonicotinoid Insecticide, on Locomotor Activity of the American Cockroach. Insects, 15(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15010054






