Rearing of Black Soldier Fly Larvae with Corn Straw and the Assistance of Gut Microorganisms in Digesting Corn Straw
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Corn Straw Samples
2.2. Rearing of BSFL
2.3. Analysis of Corn Straw
2.4. Gut DNA Extraction and Analysis
2.5. Isolation and Identification of Cellulase-Producing Strains from the Gut
2.6. Effects of Cellulase-Producing Strains on BSFL Digesting Corn Straw
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
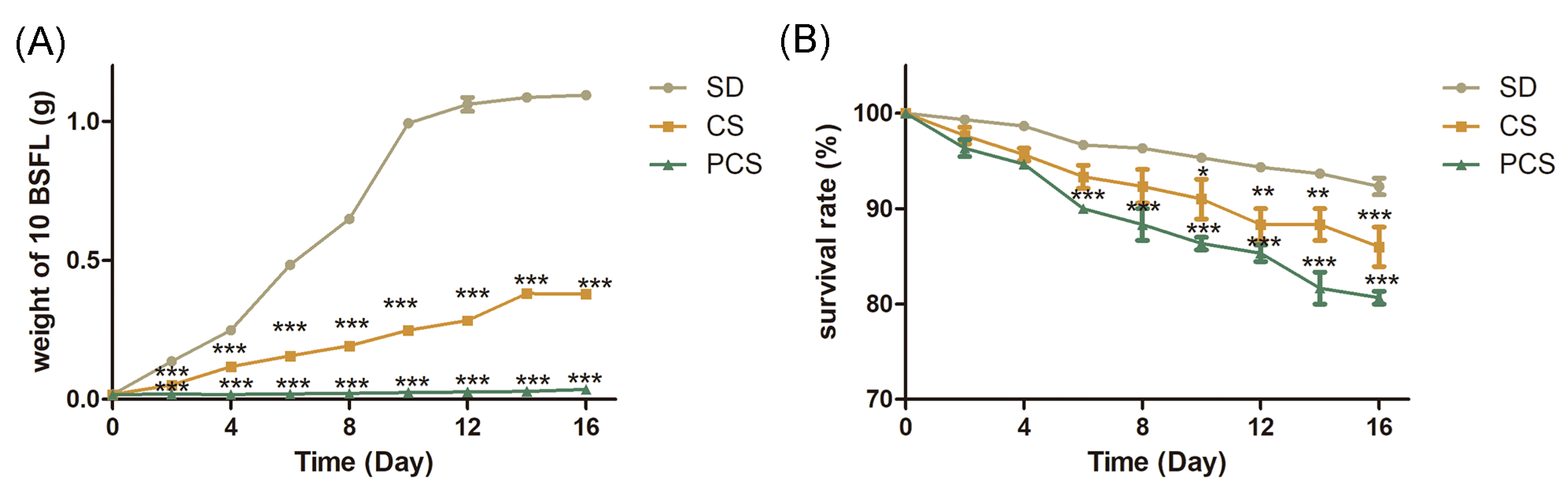
3.1. Growth of BSFL
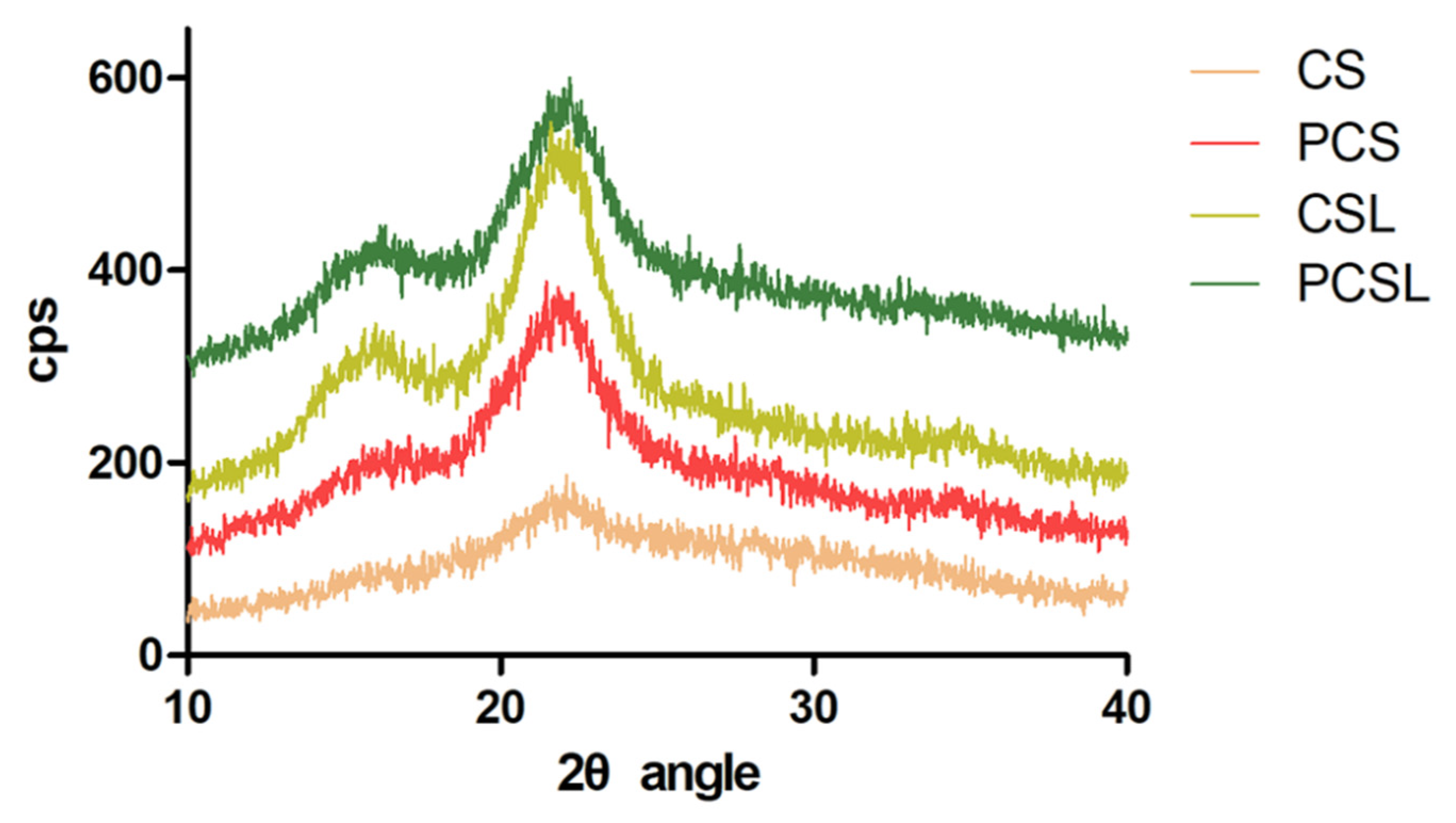
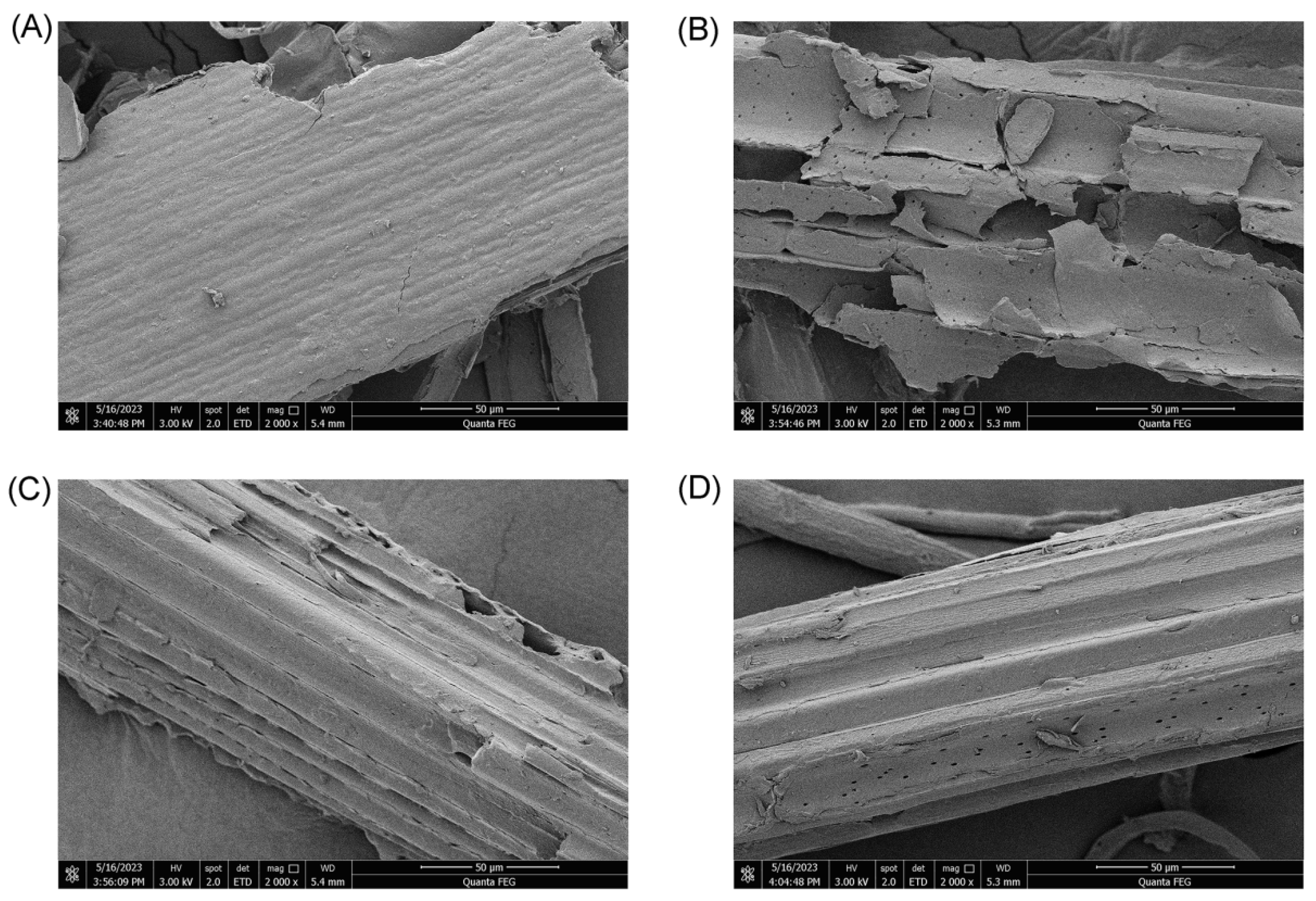
3.2. Digestion of Corn Straw
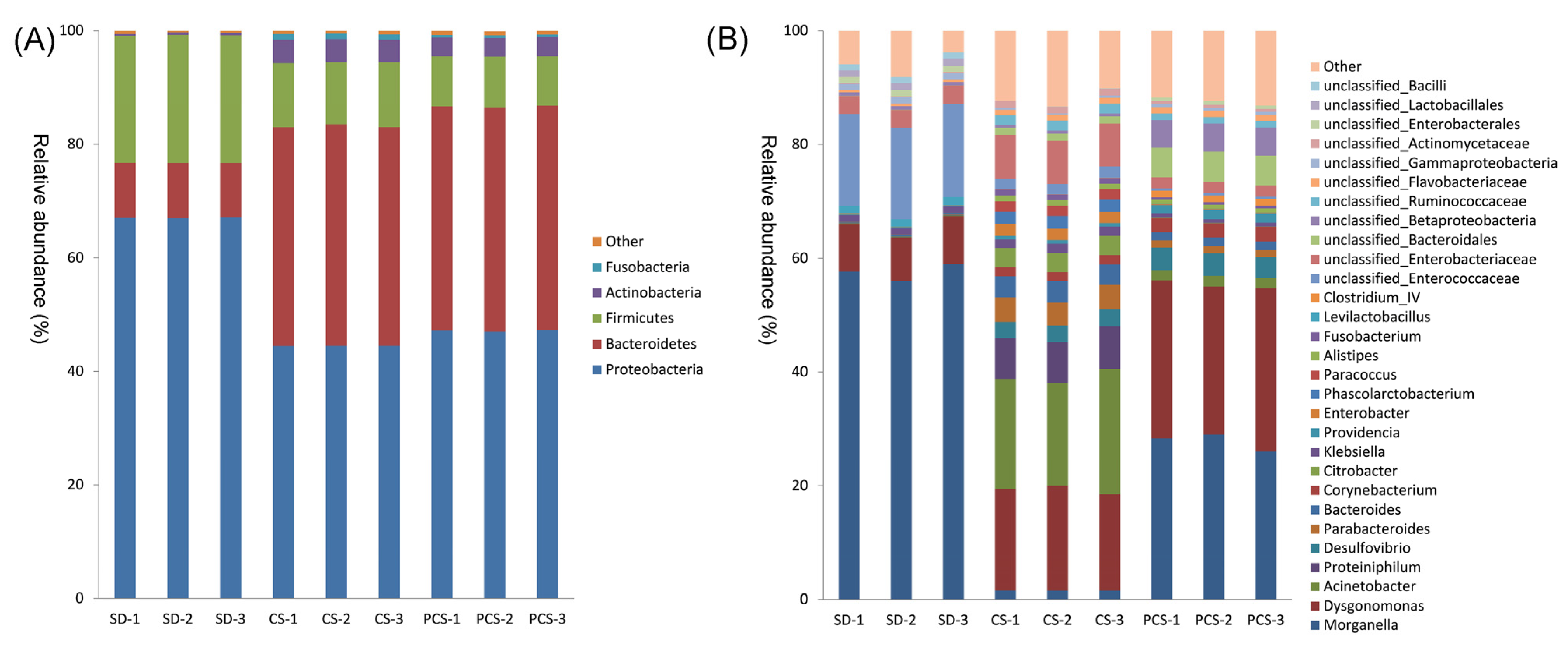
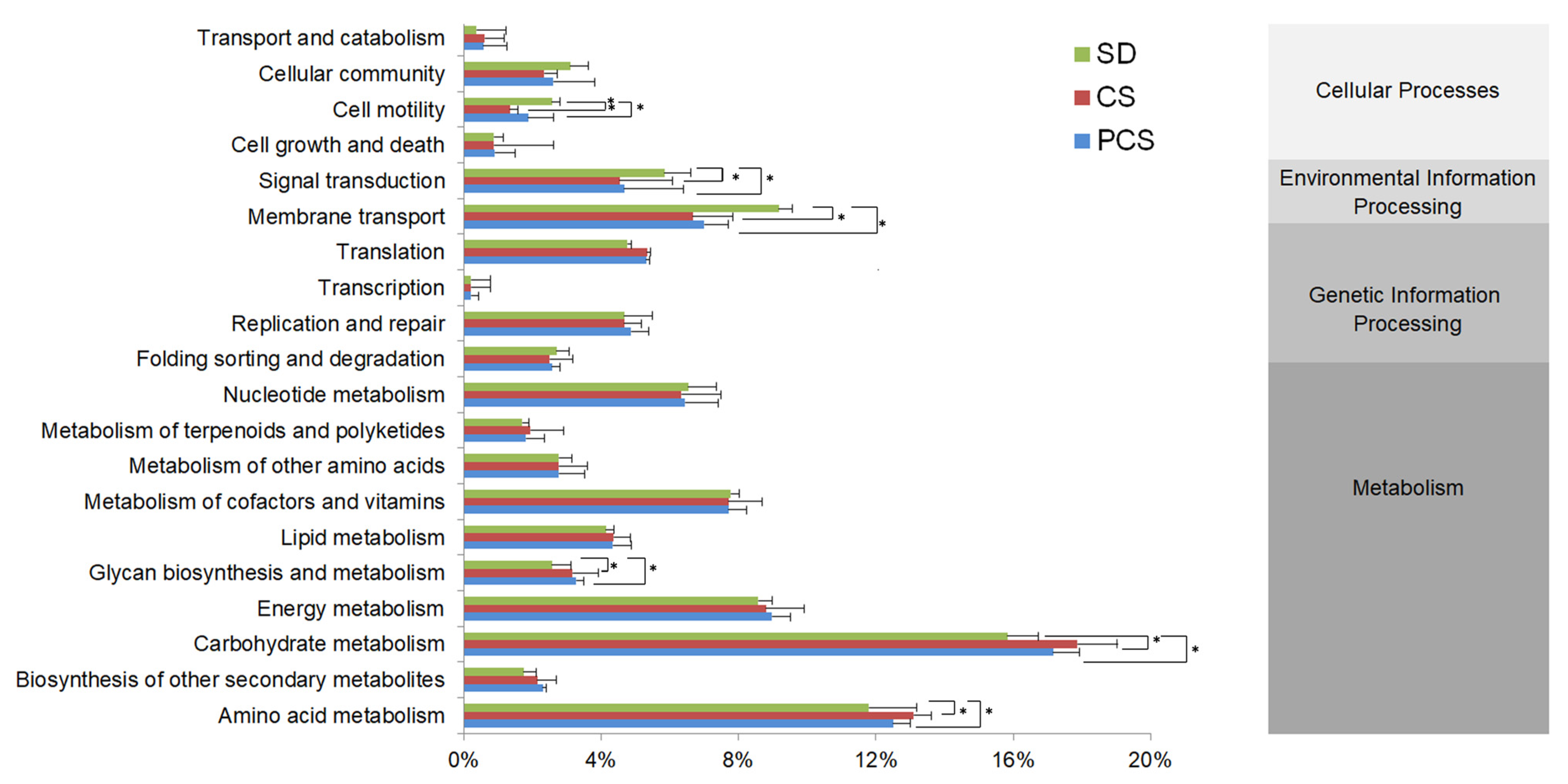
3.3. Larval Gut Microorganisms and the Prediction of Microbial Function
3.4. Cellulase-Producing Bacteria Assisting BSFL in Digesting Corn Straw
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.; Ge, X.; Li, B.; Jin, C. Evaluation on the production of food crop straw in China from 2006 to 2014. Bioenergy Res. 2017, 10, 949–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Ren, L.; Hong, J.; Xu, C. Environmental impact assessment of corn straw utilization in China. J. Clean Prod. 2016, 112, 1700–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewilda, Y.; Fauzi, M.; Aziz, R.; Utami, F.D. Analysis of Food Industry Waste Management based-on the Food Recovery Hierarchy and 3R Concept—A Case Study in Padang City, West Sumatra, Indonesia. J. Ecol. Eng. 2023, 24, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cruz-Morales, P.; Zargar, A.; Belcher, M.S.; Pang, B.; Englund, E.; Dan, Q.; Yin, K.; Keasling, J.D. Biofuels for a sustainable future. Cell 2021, 184, 1636–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, N.; Singh, R.; Singh, P.; Ahmad, I.; Singh, R.P.; Rai, A.K.; Gupta, V.K. Recent advances on lignocellulosic bioresources and their valorization in biofuels production: Challenges and viability assessment. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 29, 103037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.U.; Hollah, C.; Wiesotzki, K.; Rehman, R.U.; Rehman, A.U.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, L.; Nienaber, T.; Heinz, V.; Aganovic, K. Black soldier fly, Hermetia illucens as a potential innovative and environmentally friendly tool for organic waste management: A mini-review. Waste Manag. Res. 2023, 41, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, K.; Sathishkumar, P.; Rajan, D.K.; Rajarajeswaran, J.; Ganesan, A.R. Black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae as potential feedstock for the biodiesel production: Recent advances and challenges. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.S.; Shelomi, M. Review of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) as animal feed and human food. Foods 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Hou, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, S.; Li, Q.; Yu, Z. Biodiesel production from rice straw and restaurant waste employing black soldier fly assisted by microbes. Energy 2012, 47, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manurung, R.; Supriatna, A.; Esyanthi, R.R.; Putra, R.E. Bioconversion of rice straw waste by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.): Optimal feed rate for biomass production. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2016, 4, 1036–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Yao, H.; Chapman, S.J. Pretreatment is an important method for increasing the conversion efficiency of rice straw by black soldier fly larvae based on the function of gut microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 144118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Querejeta, M.; Hervé, V.; Perdereau, E.; Marchal, L.; Herniou, E.A.; Boyer, S.; Giron, D. Changes in bacterial community structure across the different life stages of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens). Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 1254–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eke, M.; Tougeron, K.; Hamidovic, A.; Tinkeu, L.S.N.; Hance, T.; Renoz, F. Deciphering the functional diversity of the gut microbiota of the black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens): Recent advances and future challenges. Anim. Microbiome 2023, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, L.; Ye, K.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, A.; Qiao, R.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; Cai, M.; Yu, C. Characteristics of gut bacterial microbiota of black soldier fly (Diptera: Stratiomyidae) larvae effected by typical antibiotics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 270, 115861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, J.; Liang, T.; Zhang, H.; Liu, K.; Li, X.; Xu, K.; Guo, J.; Luo, Q.; Yang, S. Characteristics of Aflatoxin B(1) degradation by Stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila and it’s combination with black soldier fly larvae. Life 2023, 13, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Deng, X.; Pei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, S. Biochar can improve absorption of nitrogen in chicken manure by black soldier fly. Life 2023, 13, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ma, S.; Li, F.; Zheng, L.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, C.; Fan, M.; Cai, M. Characteristics and mechanisms of ciprofloxacin degradation by black soldier fly larvae combined with associated intestinal microorganisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 811, 151371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, N.; Yu, Y.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, F.; Huang, F.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Rehman, K.U.; et al. Cellulose-degrading bacteria improve conversion efficiency in the co-digestion of dairy and chicken manure by black soldier fly larvae. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorrens, E.; Van Moll, L.; Frooninckx, L.; De Smet, J.; Van Campenhout, L. Isolation and identification of dominant bacteria from black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) envisaging practical applications. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 665546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Ni, H.; Sun, M.; Lin, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; Yang, S. Bacillus velezensis EEAM 10B strengthens nutrient metabolic process in black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) via changing gut microbiome and metabolic pathways. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 880488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.; Lei, A.; Chen, H.; Kang, X.; Ni, H.; Yang, S. Comparative metagenomic and metatranscriptomic analyses reveal the response of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae intestinal microbes and reduction mechanisms to high concentrations of tetracycline. Toxics 2023, 11, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, F.; Roy, N. Isolation and characterization of cellulase-producing bacteria from sugar industry waste. Am. J. Biosci. 2019, 7, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Qu, J. Purification and characterization of an alkali-organic solvent-stable laccase with dye decolorization capacity from newly isolated Lysinibacillus fusiformis W11. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 1935–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannaa, M.; Mansour, A.; Park, I.; Lee, D.W.; Seo, Y.S. Insect-based agri-food waste valorization: Agricultural applications and roles of insect gut microbiota. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2024, 17, 100287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczor, M.; Bulak, P.; Proc-Pietrycha, K.; Kirichenko-Babko, M.; Bieganowski, A. The variety of applications of Hermetia illucens in industrial and agricultural areas—Review. Biology 2022, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, S.A.; Fernando, I.; Nisa, K.; Shah, M.A.; Rahayu, T.; Rasool, A.; Aidoo, O.F. Effects of undesired substances and their bioaccumulation on the black soldier fly larvae, Hermetia illucens (Diptera: Stratiomyidae)—A literature review. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.V.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariuki, E.G.; Kibet, C.; Paredes, J.C.; Mboowa, G.; Mwaura, O.; Njogu, J.; Masiga, D.; Bugg, T.D.H.; Tanga, C.M. Metatranscriptomic analysis of the gut microbiome of black soldier fly larvae reared on lignocellulose-rich fiber diets unveils key lignocellulolytic enzymes. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1120224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnullina, L.; Pudova, D.; Shagimardanova, E.; Shigapova, L.; Sharipova, M.; Mardanova, A. Comparative genome analysis of uropathogenic Morganella morganii strains. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhary, A.; Ale Enriquez, F.; Garrison, R.; Ahring, B.K. Advancing thermophilic anaerobic digestion of corn whole stillage: Lignocellulose decomposition and microbial community characterization. Fermentation 2024, 10, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, A.L.; Kallstrom, G.; Faith, J.J.; Reyes, A.; Moore, A.; Dantas, G.; Gordon, J.I. Extensive personal human gut microbiota culture collections characterized and manipulated in gnotobiotic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6252–6257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Weight of Initial Substrates (g) | Residual Weight of Substrates (g) | Conversion Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SD | 15 | 0.51 ± 0.01 | 96.6 ± 0.06 |
| CS | 15 | 9.45 ± 0.22 *** | 37.4 ± 1.47 *** |
| PCS | 15 | 13.20 ± 0.18 *** | 12.0 ± 1.21 *** |
| Sample | Residual Weight of Substrates (g) | Conversion Rate (%) | Weights of 10 BSFL (g) | Survival Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 9.45 ± 0.22 a | 37.4 ± 1.47 a | 0.372 ± 0.012 a | 85.0 ± 0.5 a |
| L1 | 8.36 ± 0.21 b | 44.3 ± 1.40 b | 0.420 ± 0.023 b | 93.5 ± 1.0 b |
| L2 | 8.74 ± 0.11 c | 41.7 ± 0.73 c | 0.397 ± 0.011 c | 90.5 ± 0.5 cd |
| L3 | 8.48 ± 0.17 b | 43.5 ± 1.13 b | 0.411 ± 0.013 b | 91.0 ± 0.5 c |
| L4 | 8.75 ± 0.21 c | 40.7 ± 0.40 c | 0.357 ± 0.012 d | 89.5 ± 0.5 d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Tian, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Shang, S.; Li, H.; Qu, J.; Chen, P. Rearing of Black Soldier Fly Larvae with Corn Straw and the Assistance of Gut Microorganisms in Digesting Corn Straw. Insects 2024, 15, 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15100734
Wang X, Tian X, Liu Z, Liu Z, Shang S, Li H, Qu J, Chen P. Rearing of Black Soldier Fly Larvae with Corn Straw and the Assistance of Gut Microorganisms in Digesting Corn Straw. Insects. 2024; 15(10):734. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15100734
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xifeng, Xiangru Tian, Zhi Liu, Zhihua Liu, Shuying Shang, Haifeng Li, Jianhang Qu, and Pengxiao Chen. 2024. "Rearing of Black Soldier Fly Larvae with Corn Straw and the Assistance of Gut Microorganisms in Digesting Corn Straw" Insects 15, no. 10: 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15100734
APA StyleWang, X., Tian, X., Liu, Z., Liu, Z., Shang, S., Li, H., Qu, J., & Chen, P. (2024). Rearing of Black Soldier Fly Larvae with Corn Straw and the Assistance of Gut Microorganisms in Digesting Corn Straw. Insects, 15(10), 734. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15100734







