Nursing Honeybee Behavior and Sensorial-Related Genes Are Altered by Deformed Wing Virus Variant A
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Inoculum Preparation
2.2. Honeybee Inoculation
2.3. Stimulus Preparation
2.4. Olfactometric Bioassays
2.5. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.6. Real-Time PCR Quantification for Viral Load and Gene Expression
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
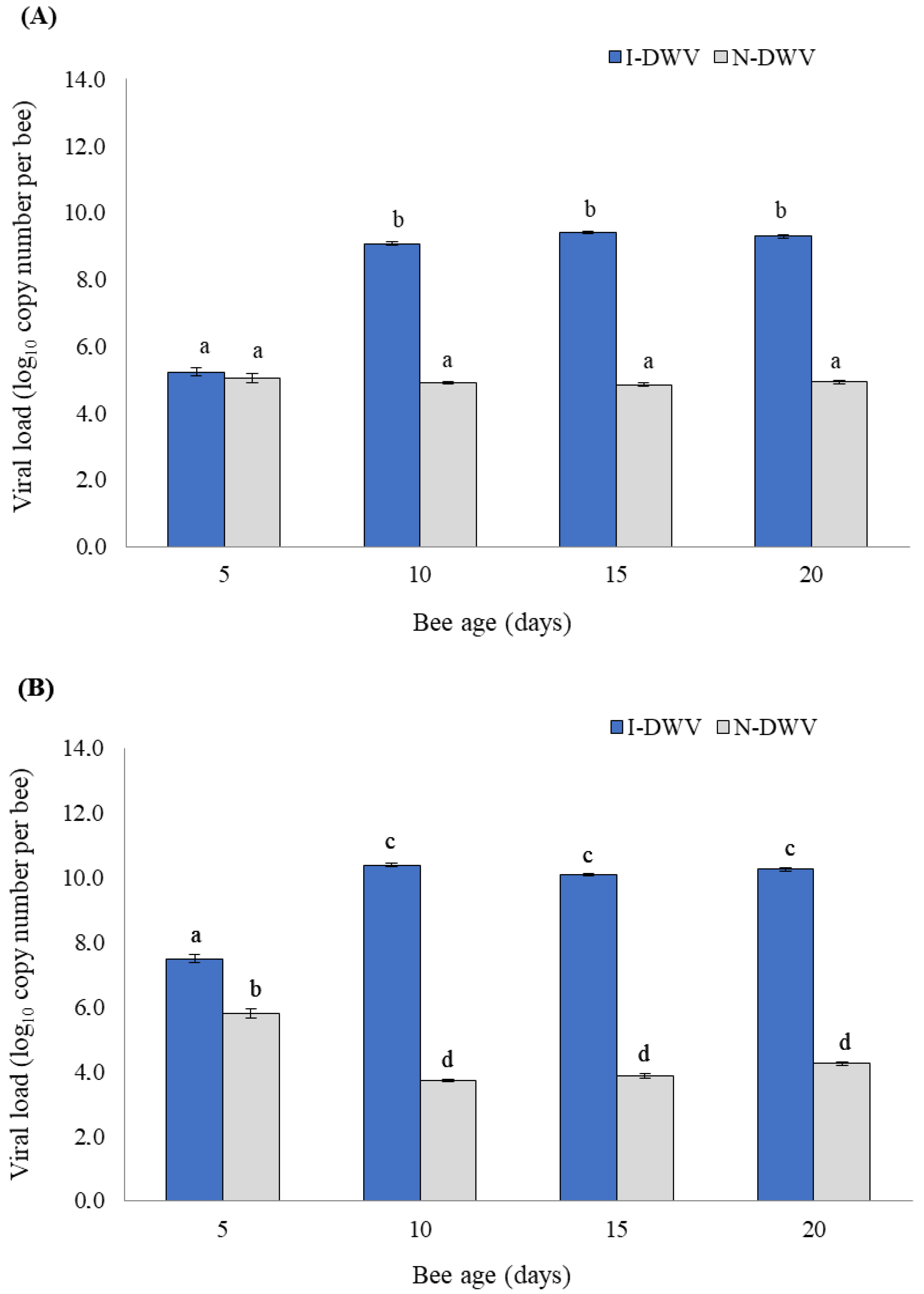
3.1. Viral Load in the Antenna and Head
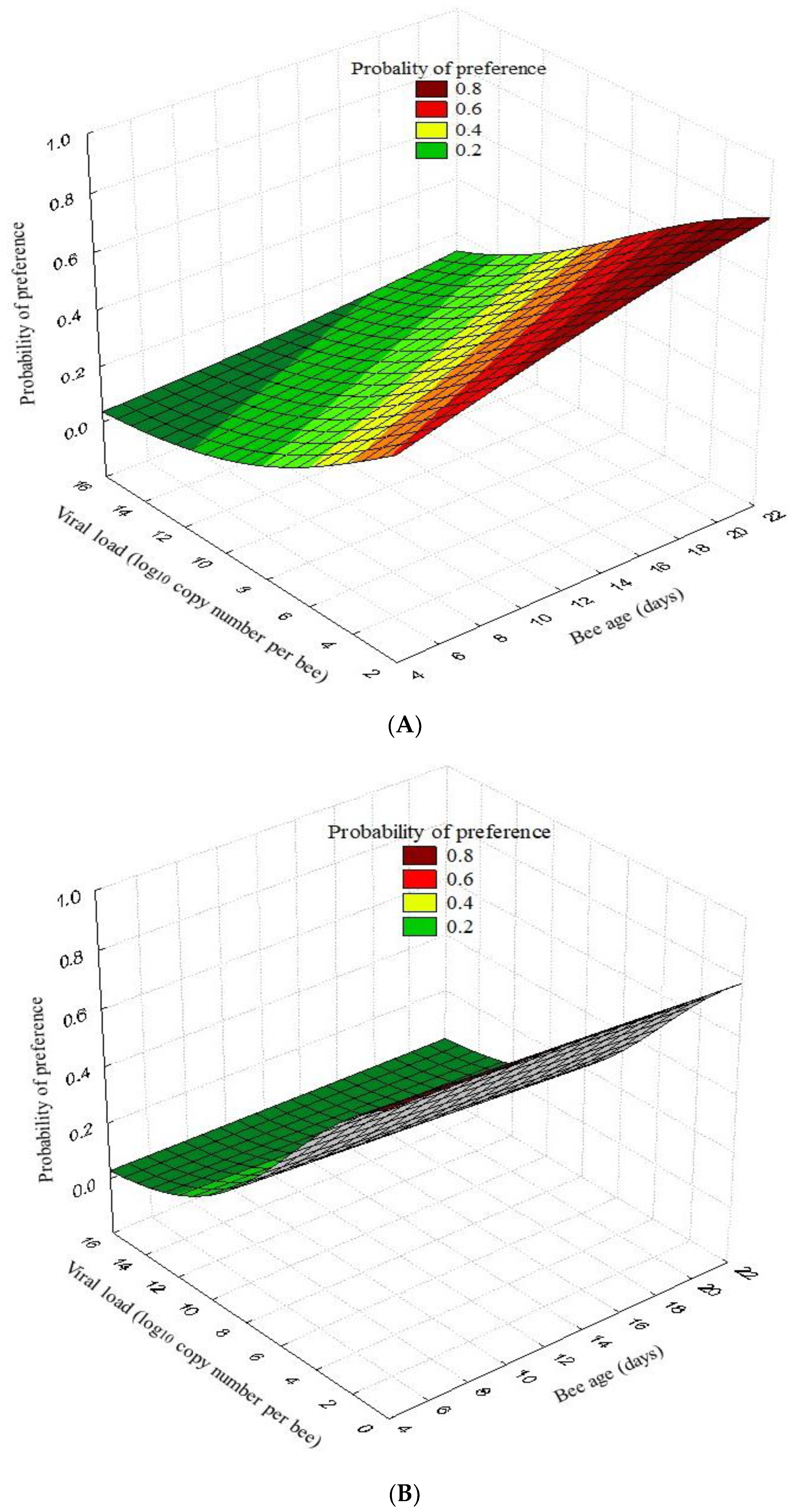
3.2. Olfactory Tests
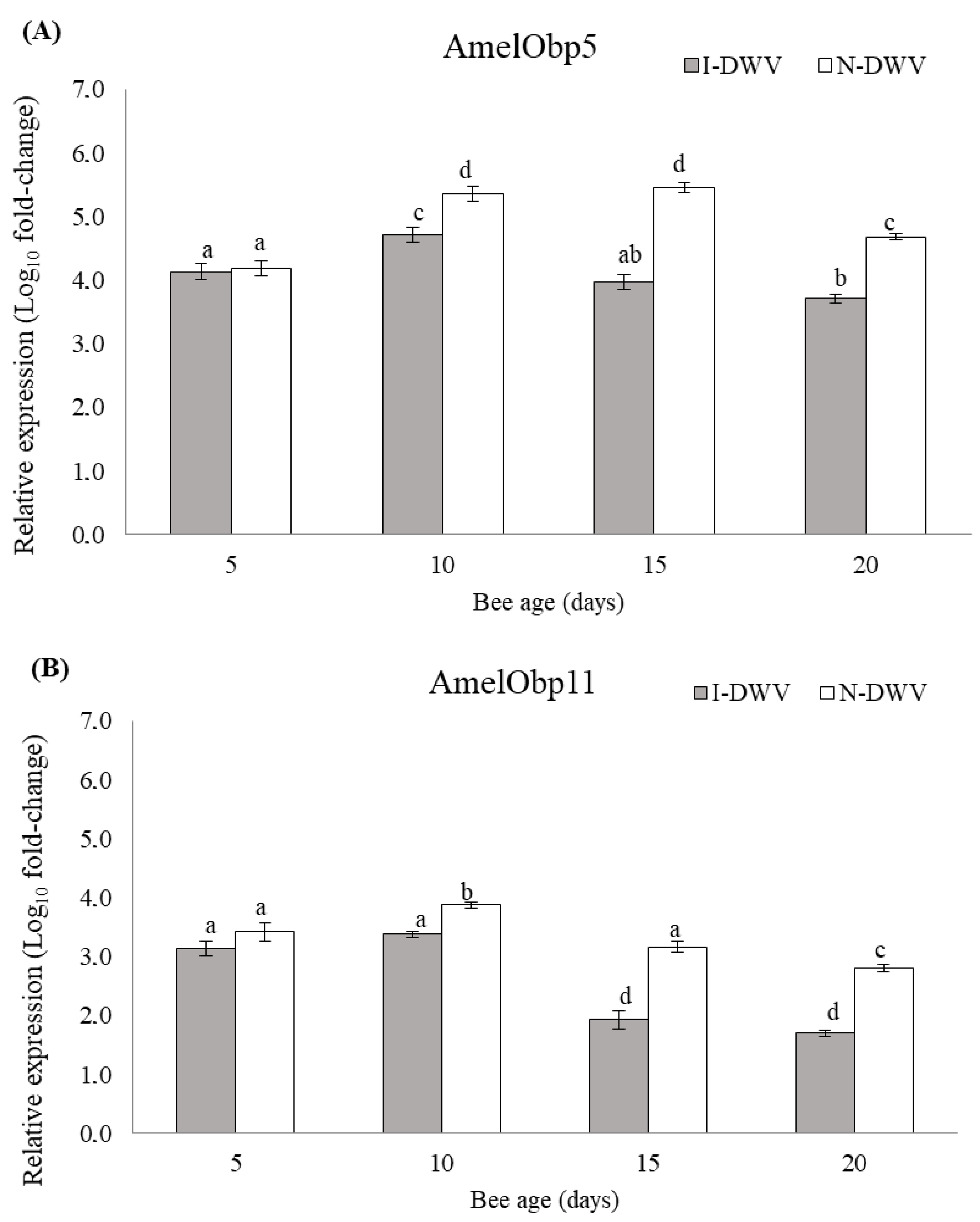
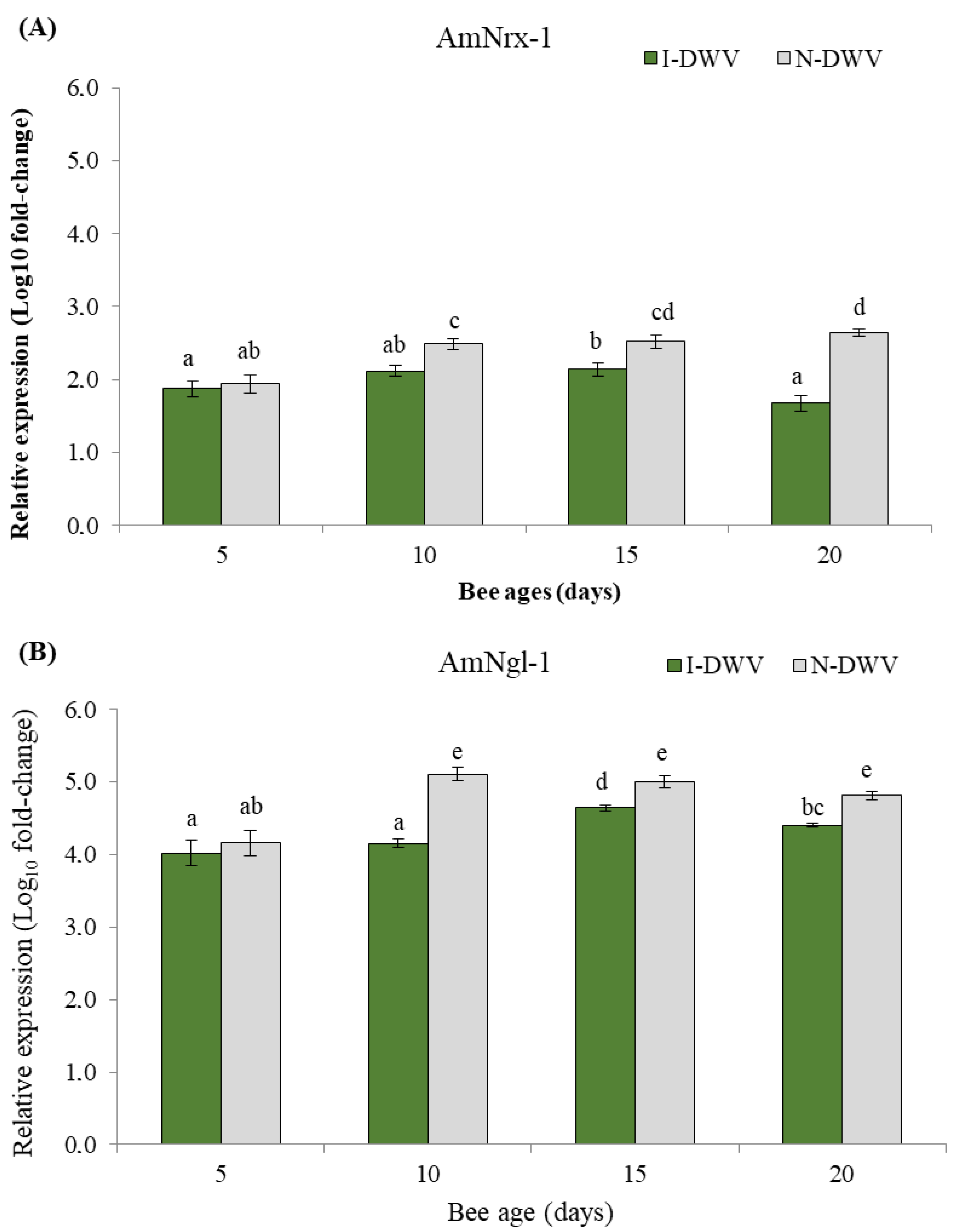
3.3. Gene Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Groot, A.T.; Dekker, T.; Heckel, D. The Genetic Basis of Pheromone Evolution in Moths. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 99–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liberles, S.D. Aversion and attraction through olfaction. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, W.S. Odorant reception in insects: Roles of receptors, binding proteins, and degrading enzymes. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-J.; Vieira, F.G.; He, X.-L.; Smadja, C.; Liu, R.; Rozas, J.; Field, L.M. Genome annotation and comparative analyses of the odorant-binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Zhu, J.; Wang, G.; Dani, F.R. Beyond chemoreception: Diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects. Biol. Rev. 2018, 93, 184–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forêt, S.; Maleszka, R. Function and evolution of a gene family encoding odorant binding-like proteins in a social insect, the honey bee (Apis mellifera). Genome Res. 2006, 16, 1404–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Luo, Y.; Lee, J.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Q.; Zeng, X. The Odorant-binding protein gene obp11 shows different spatiotemporal roles in the olfactory system of Apis mellifera ligustica and Apis cerana cerana. Sociobiology 2013, 60, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.X.; Zeng, X.N.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, X.F.; Huang, W.Z.; Chen, H.S.; Luo, Y.X. Study of the obp5 gene in Apis mellifera ligustica and Apis cerana cerana. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 6482–6494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plettner, E.; Eliash, N.; Singh, N.K. The chemical ecology of host-parasite interaction as a target of Varroa destructor control agents. Apidologie 2017, 48, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, S.G.; Biesmeier, J.C.; Kremen, C.; Neumann, P.; Schweiger, O.; Kunin, W.E. Global pollinator declines: Trends, impacts and drivers. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2010, 25, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.M.; Steiner, R. Insect pollinator conservation policy innovations at subnational levels: Lessons for lawmakers. Environ. Sci. Policy 2019, 93, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- vanEngelsdorp, D.; Evans, J.D.; Saegerman, C.; Mullin, C.; Haubruge, E.; Nguyen, B.K.; Frazier, M.; Frazier, J.; Cox-Foster, D.; Chen, Y.; et al. Colony Collapse Disorder: A Descriptive Study. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.J.; Hardy, J.; Villalobos, E.; Martin-Hernández, R.; Nikaido, S.; Higes, M. Do the honeybee pathogens Nosema ceranae and deformed wing virus act synergistically? Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 506–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozinger, C.M.; Flenniken, M.L. Bee Viruses: Ecology, Pathogenicity, and Impacts. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 205–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brettell, L.E.; Mardoqueo, G.J.; Schroeder, D.C.; Jones, I.M.; da Silva, J.R.; Vicente-Rubiano, M.; Martin, S.J. A Comparison of Deformed Wing Virus in Deformed and Asymptomatic Honey Bees. Insects 2017, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benaets, K.; Van Geystelen, A.; Cardoen, D.; De Smet, L.; de Graaf, D.C.; Schoofs, L.; Larmuseau, M.H.; Brettell, L.E.; Martín, S.J.; Wenseleers, T. Covert deformed wing virus infections have long-term deleterious effects on honeybee foraging and survival. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20162149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevill, J.L.; de Souza, F.S.; Sharples, C.; Oliver, R.; Schroeder, D.C.; Martin, S.J. DWV-A Lethal to Honey Bees (Apis mellifera): A Colony Level Survey of DWV Variants (A, B, and C) in England, Wales, and 32 States across the US. Viruses 2019, 11, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, D.P.; Natsopoulou, M.E.; Doublet, V.; Furst, M.; Weging, S.; Brown, M.J.; Gogol-Doring, A.; Paxton, R.J.; Mallinger, R.E.; Gratton, C. Species richness of wild bees, but not the use of managed honeybees, increases fruit set of a pollinator-dependent crop. J. Appl. Ecol. 2016, 52, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Riveros, G.; Arismendi, N.; Zapata, N.; Evans, D.; Pérez, I.; Aldea, P.; Vargas, M. Occurrence, prevalence and viral load of deformed wing virus variants in Apis mellifera colonies in Chile. J. Apic. Res. 2019, 59, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, M.; Arismendi, N.; Riveros, G.; Zapata, N.; Bruna, A.; Vidal, M.; Rodríguez, M.; Gerding, M. Viral and intestinal diseases detected in Apis mellifera in Central and Southern Chile. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2017, 77, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Mercer, A.; Mitchell, A.; de Miranda, J.R.; Ward, V.; Mondet, F.; Bostina, M. Viral infections alter antennal epithelium ultrastructure in honey bees. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2019, 168, 107252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.; Ceballos, R.; Arismendi, N.; Dalmon, A.; Vargas, M. Variant A of the Deformed Wings Virus Alters the Olfactory Sensitivity and the Expression of Odorant Binding Proteins on Antennas of Apis mellifera. Insects 2021, 12, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.S.; Evans, E.C.; Pizzorno, M.C. Localization of deformed wing virus (DWV) in the brains of the honeybee, Apis mellifera Linnaeus. Virol. J. 2009, 6, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morfin, N.; Goodwin, P.H.; Guzman-Novoa, E. The Combined Effects of Varroa destructor Parasitism and Exposure to Neonicotinoids Affects Honey Bee (Apis mellifera L.) Memory and Gene Expression. Biology 2019, 9, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gusachenko, O.N.; Woodford, L.; Balbirnie-Cumming, K.; Ryabov, E.V.; Evans, D.J. Evidence for and against deformed wing virus spillover from honey bees to bumble bees: A reverse genetic analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arismendi, N.; Caro, S.; Castro, M.P.; Vargas, M.; Riveros, G.; Venegas, T. Impact of mixed infections of gut parasites Lotmaria passim and Nosema ceranae on the lifespan and immune-related biomarkers in Apis mellifera. Insects 2020, 11, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Ma, W.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, H.; Jiang, Y. Composition of Strawberry Flower Volatiles and Their Effects on Behavior of Strawberry Pollinators, Bombus terrestris and Apis mellifera. Agronomy 2023, 13, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondet, F.; Alaux, C.; Severac, D.; Rohmer, M.; Mercer, A.; Le Conte, Y. Antennae hold a key to Varroa-sensitive hygiene behaviour in honey bees. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 2003–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dong, X.; Kadowaki, T. Characterization of the copy number and variants of deformed wing virus (DWV) in the pairs of honey bee pupa and infesting Varroa destructor or Tropilaelaps mercedesae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Cox-Foster, D. Impact of an ectoparasite on the immunity and pathology of an invertebrate: Evidence for host immunosuppression and viral amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 7470–7475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renou, M.; Anton, S. Insect olfactory communication in a complex and changing world. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 42, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A.M.; Chahad-Ehlers, S.; Lima, A.L.A.; Taniguti, C.H.; Sobrinho, I., Jr.; Torres, F.R.; de Brito, R.A. Reference genes for accessing differential expression among developmental stages and analysis of differential expression of OBP genes in Anastrepha obliqua. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 17480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.-J.; Zhang, G.-A.; Huang, W.; Birkett, M.A.; Field, L.M.; Pickett, J.A.; Pelosi, P. Revisiting the odorant-binding protein LUSH of Drosophila melanogaster: Evidence for odour recognition and discrimination. FEBS Lett. 2004, 558, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Zheng, M.-Y.; Sun, J.-B.; Khuhro, S.A.; Yan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Syed, Z.; Dong, S.-L. CRISPR/Cas9 mediated gene knockout reveals a more important role of PBP1 than PBP2 in the perception of female sex pheromone components in Spodoptera litura. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 115, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukas, R. Mortality rates of honey bees in the wild. Insect. Soc. 2008, 55, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Mueller, U. Virus infection causes specific learning deficits in honeybee foragers. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 274, 1517–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Lu, Y.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Wu, C.-P.; Tang, C.-K.; Wei, S.-C.; Wu, Y.-L. Deformed Wing Virus Infection Affects the Neurological Function of Apis mellifera by Altering Extracellular Adenosine Signaling. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 139, 103674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goblirsch, M.; Huang, Z.; Spivak, M. Physiological and behavioral changes in honey bees (Apis mellifera) induced by Nosema ceranae infection. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paris, L.; El Alaoui, H.; Delbac, F.; Diogon, M. Effects of the gut parasite Nosema ceranae on honey bee physiology and behavior. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 26, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.E. Genomics and integrative analyses of division of labor in honeybee colonies. Am. Nat. 2002, 160, S160–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seid, M.A.; Traniello, J.F.A. Age-related repertoire expansion and division of labor in Pheidole dentata (Hymenoptera: Formicidae): A new perspective on temporal polyethism and behavioral plasticity in ants. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2006, 60, 631–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, T.D. Division of labor among worker honey bees. Ethology 1986, 71, 249–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, B.R. Within-nest temporal polyethism in the honey bee. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2008, 62, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, E.; Corriale, M.; Arenas, A. Differences in olfactory sensitivity and odor detection correlate with foraging task specialization in honeybees Apis mellifera. J. Insect Physiol. 2022, 141, 104416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traniello, I.M.; Bukhari, S.A.; Kevill, J.; Ahmed, A.C.; Hamilton, A.R.; Naeger, N.L.; Schroeder, D.C.; Robinson, G.E. Meta-analysis of honey bee neurogenomic response links deformed wing virus type A to precocious behavioral maturation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, T.; Wolf, S.; Nicholls, E.; Groll, H.; Lim, K.S.; Clark, S.J.; Swain, J.; Osborne, J.L.; Haughton, A.J. Flight performance of actively foraging honey bees is reduced by a common pathogen. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2016, 8, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primers Names | Sequence | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| AmNrx-1 | F-CTGCTTCGAGCGACGACTAT | [24] |
| R-ACGACCGGATGGATGATTGG | ||
| AmNlg-1 | F-ATGTCGAGGATGCTGCGACTGGA | [24] |
| R-ACCTGTGCACTATCTCCTGTTGTA | ||
| DWV-A | F-TATCTTCATTAAAGCCACCTGGAA | [31] |
| R-TTCCTCATTAACTGTGTCGTTGAT | ||
| AmelOBP5 | F-ATGCGGAAATCGTGCTTGCA | [2] |
| R-TGCCATTACTCACGGGAAGA | ||
| AmelOBP1 | F-TGAGGATGTCGAAGCTACGGAA | [2] |
| R-CACGGAGCAATAAACGCTATGG | ||
| β -actin | F-ATGCCAACACTGTCCTTTCTGG | [31] |
| R-GACCCACCAATCCATACGGA |
| Bee Age (Days) | Pheromone (Benzyl Alcohol) vs. Air | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Status | Pheromone | χ2 | p-Value | Air | χ2 | p-Value | No Preference | χ2 | p-Value | |
| 5 | I-DWV | 0.33 | 1.36 | 0.243 | 0.30 | 3.75 | 0.053 | 0.37 | 6.70 | 0.010 |
| N-DWV | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.70 | |||||||
| 10 | I-DWV | 0.10 | 13.02 | <0.001 | 0.30 | 3.75 | 0.053 | 0.60 | 3.27 | 0.071 |
| N-DWV | 0.53 | 0.10 | 0.37 | |||||||
| 15 | I-DWV | 0.13 | 10.80 | 0.001 | 0.13 | 0.00 | 0.992 | 0.73 | 9.64 | 0.002 |
| N-DWV | 0.53 | 0.13 | 0.33 | |||||||
| 20 | I-DWV | 0.23 | 8.30 | 0.004 | 0.23 | 1.92 | 0.166 | 0.53 | 3.36 | 0.067 |
| N-DWV | 0.60 | 0.10 | 0.30 | |||||||
| Bee Age (Days) | Pheromone (Benzyl Alcohol) vs. Essential Oil | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Status | Pheromone | χ2 | p-Value | Essential Oil | χ2 | p-Value | No Preference | χ2 | p-Value | |
| 5 | I-DWV | 0.23 | 0.09 | 0.766 | 0.07 | 1.46 | 0.228 | 0.70 | 1.15 | 0.284 |
| N-DWV | 0.27 | 0.17 | 0.57 | |||||||
| 10 | I-DWV | 0.20 | 7.18 | 0.007 | 0.07 | 1.46 | 0.228 | 0.73 | 11.28 | 0.001 |
| N-DWV | 0.53 | 0.17 | 0.30 | |||||||
| 15 | I-DWV | 0.10 | 11.43 | 0.001 | 0.27 | 0.32 | 0.573 | 0.63 | 13.61 | <0.001 |
| N-DWV | 0.50 | 0.33 | 0.17 | |||||||
| 20 | I-DWV | 0.07 | 1.46 | 0.228 | 0.27 | 11.28 | 0.001 | 0.67 | 17.78 | <0.001 |
| N-DWV | 0.17 | 0.70 | 0.13 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diego, S.; Nolberto, A.; Pablo, A.J.; Ricardo, C.; Nelson, Z.; Marisol, V. Nursing Honeybee Behavior and Sensorial-Related Genes Are Altered by Deformed Wing Virus Variant A. Insects 2024, 15, 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020080
Diego S, Nolberto A, Pablo AJ, Ricardo C, Nelson Z, Marisol V. Nursing Honeybee Behavior and Sensorial-Related Genes Are Altered by Deformed Wing Virus Variant A. Insects. 2024; 15(2):80. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020080
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiego, Silva, Arismendi Nolberto, Alveal Juan Pablo, Ceballos Ricardo, Zapata Nelson, and Vargas Marisol. 2024. "Nursing Honeybee Behavior and Sensorial-Related Genes Are Altered by Deformed Wing Virus Variant A" Insects 15, no. 2: 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020080
APA StyleDiego, S., Nolberto, A., Pablo, A. J., Ricardo, C., Nelson, Z., & Marisol, V. (2024). Nursing Honeybee Behavior and Sensorial-Related Genes Are Altered by Deformed Wing Virus Variant A. Insects, 15(2), 80. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15020080







