Ascarosides and Symbiotic Bacteria of Entomopathogenic Nematodes Regulate Host Immune Response in Galleria mellonella Larvae
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects and Symbiotic Bacteria Culture
2.2. Ascarosides
2.3. Injection of G. mellonella Larvae
2.4. Larval Mortality and Color Intensity Change
2.5. RNA Extraction and cDNA Preparation
2.6. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.7. Amplicon Sequencing
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ascarosides Delayed the G. mellonella Larvae Mortality
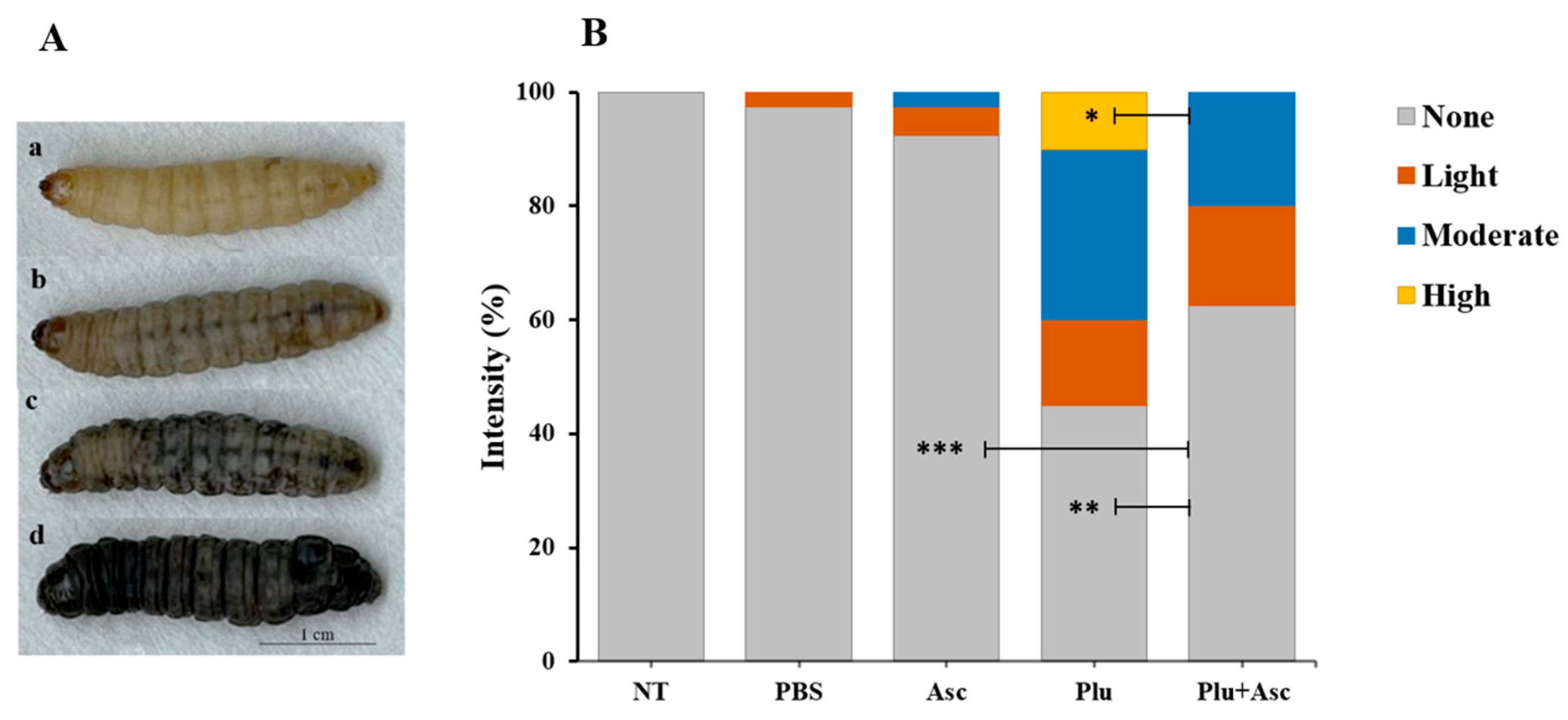
3.2. Ascarosides Reduce the Degree of Color Change in G. mellonella Larvae
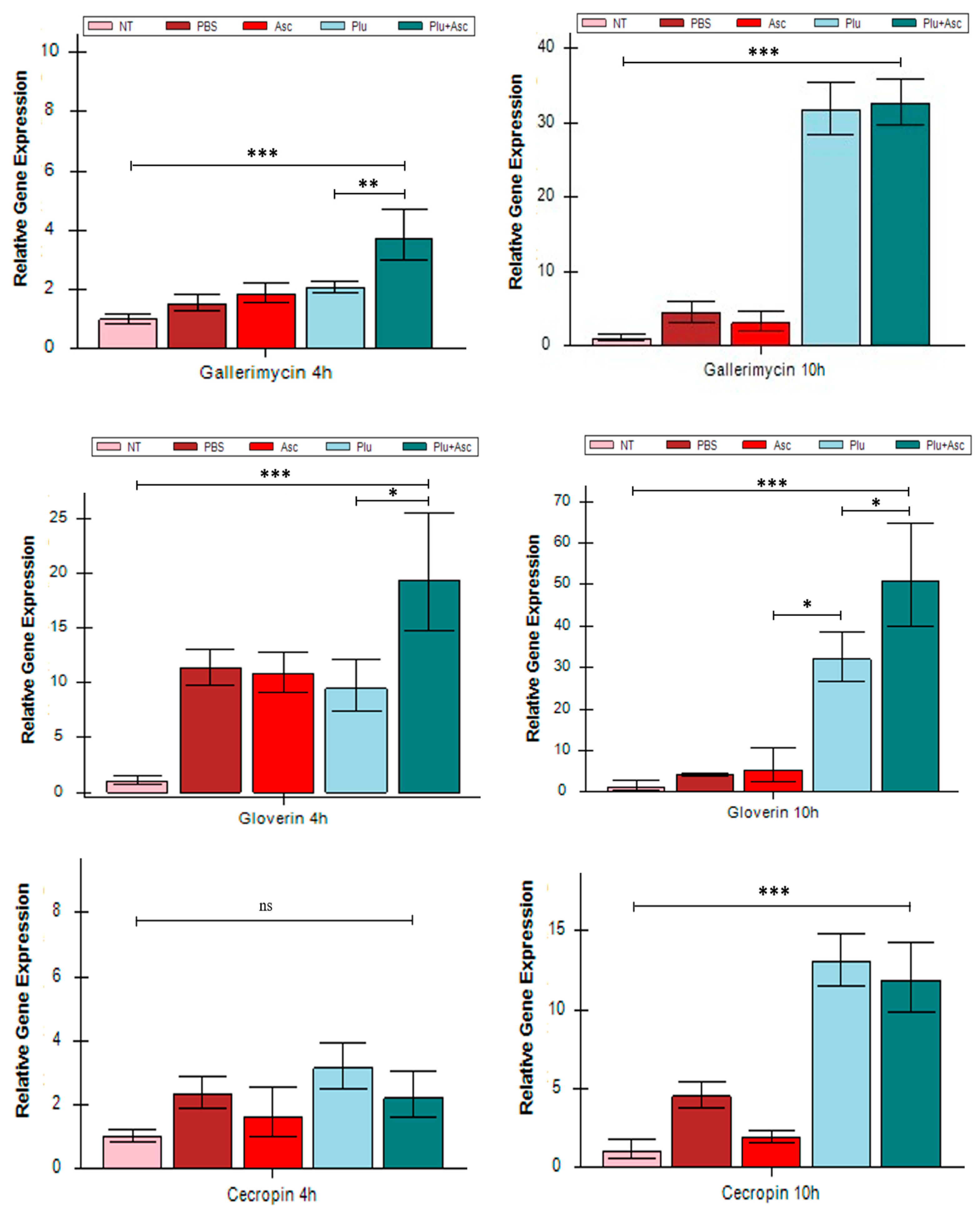
3.3. Ascarosides and Symbiotic Bacteria Activated Antimicrobial Peptide Expression
3.4. Hemolin Was Up-Regulated in Response to Ascarosides and Symbiotic Bacteria
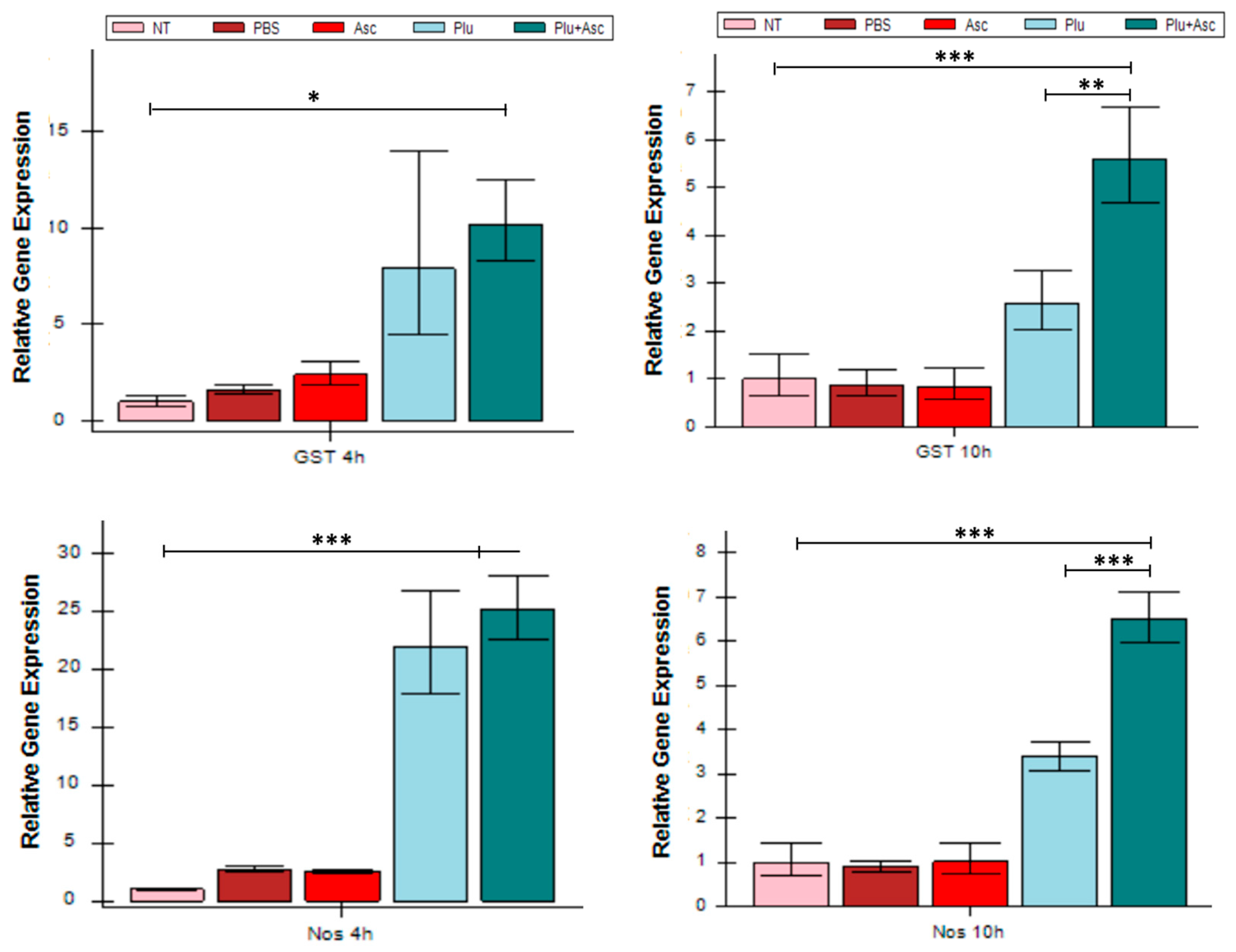
3.5. ROS/RNS-Related Gene Expression Increased in Response to Symbiotic Bacteria and Ascarosides
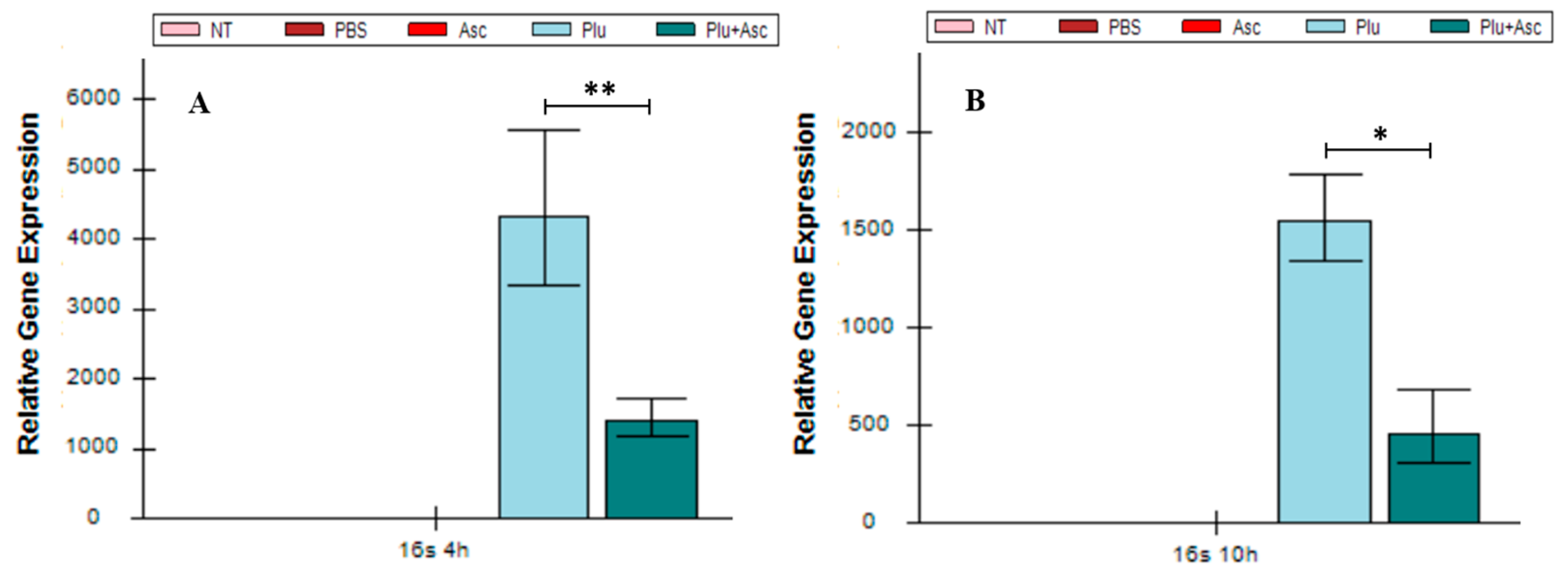
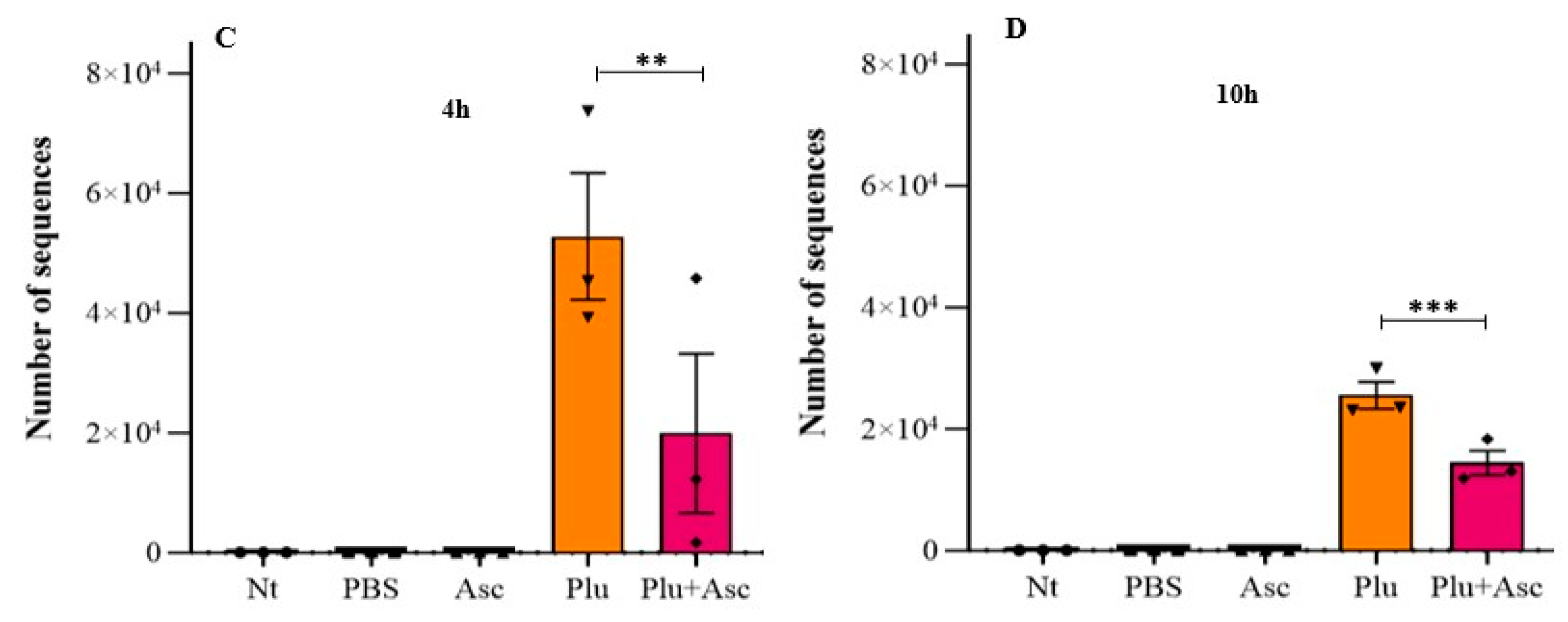
3.6. Ascarosides and Symbiotic Bacteria Decrease Symbiotic Bacterial Load
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wojda, I.; Staniec, B.; Sułek, M.; Kordaczuk, J. The greater wax moth Galleria mellonella: Biology and use in immune studies. Pathog. Dis. 2020, 78, ftaa057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayres, J.S. Inflammasome-microbiota interplay in host physiologies. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kamada, N.; Seo, S.U.; Chen, G.Y.; Nunez, G. Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanda, N.B.; Hou, Y. The symbiotic bacteria-Xenorhabdus nematophila All and Photorhabdus luminescens H06 strongly affected the phenoloxidase activation of nipa palm hispid, Octodonta nipae (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae) larvae. Pathogens 2023, 12, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeven, R.; Mc-Callum, K.C.; Garsin, D.A. Speculations on the activation of ROS generation in C. elegans innate immune signaling. Worm 2012, 1, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, P.; Chmiel, D.; Gacek, G.J. Antibacterial peptides of the moth Galleria mellonella. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2001, 48, 1191–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojda, I. Immunity of the greater wax moth Galleria mellonella. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vertyporokh, L.; Wojda, I. Immune response of Galleria mellonella after injection with non-lethal and lethal dosages of Candida albicans. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2020, 170, 107327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostaff, M.J.; Stange, E.F.; Wehkamp, J. Antimicrobial peptides and gut microbiota in homeostasis and pathology. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 1465–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolouri-Moghaddam, M.R.; Tonk, M.; Schreiber, C.; Salzig, D.; Czermak, P.; Vilcinskas, A.; Rahnamaeian, M. The potential of the Galleria mellonella innate immune system is maximized by the co-presentation of diverse antimicrobial peptides. Biol. Chem. 2016, 397, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belien, T. Entomopathogenic nematodes as biocontrol agents of insect pests in orchards. CABI Rev. 2018, 13, 92499691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askar, A.G.; Yüksel, E.; Bozbuğa, R.; Öcal, A.; Kütük, H.; Dinçer, D.; Canhilal, R.; Dababat, A.A.; Imren, M. Evaluation of entomopathogenic nematodes against common wireworm species in potato cultivation. Pathogens 2023, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, C.; Campbell, H.; Pope, T. Potential of Entomopathogenic Nematodes to control the cabbage stem flea beetle Psylliodes chrysocephala. Insects 2023, 14, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, J.; Salame, L.; Nasser, A.; Glazer, I.; Ment, D. Survival and efficacy of entomopathogenic nematodes on exposed surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftherianos, I.; Shokal, U.; Yadav, S.; Kenney, E.; Maldonado, T. Insect immunity to entomopathogenic nematodes and their mutualistic bacteria. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 402, 123–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rougon-Cardoso, A.; Flores-Ponce, M.; Ramos-Aboites, H.; Martínez-Guerrero, C.E.; Hao, Y.J.; Cunha, L.; Rodríguez-Martínez, J.A.; Ovando-Vázquez, C.; Bermúdez-Barrientos, J.R.; Abreu-Goodger, C.; et al. The genome, transcriptome, and proteome of the nematode Steinernema carpocapsae: Evolutionary signatures of a pathogenic lifestyle. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brivio, M.F.; Mastore, M. Nematobacterial complexes and insect hosts: Different weapons for the same war. Insects 2018, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, A.; Schäfer, A.; Bender, A.; Steimle, A.; Beier, S.; Parusel, R.; Frick, J.S. Galleria mellonella: A novel invertebrate model to distinguish intestinal symbionts from pathobionts. Front. Immunol. 2018, 19, 2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.Z.; Serra, L.; Lu, D.; Mortazavi, A.; Dillman, A.R. A core set of venom proteins is released by entomopathogenic nematodes in the genus Steinernema. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, S.C.; Nguyen, S.; Boulanger, M.J.; Dillman, A.R. The FAR protein family of parasitic nematodes. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillo, J.C.; Creasy, T.; Kumari, P.; Shetty, A.; Shokal, U.; Tallon, L.J.; Eleftherianos, I. Drosophila anti-nematode and antibacterial immune regulators revealed by RNA-Seq. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Daugherty, S.; Shetty, A.C.; Eleftherianos, I. RNAseq analysis of the Drosophila response to the entomopathogenic nematode Steinernema. G3 Genes|Genomes|Genet. 2017, 7, 1955–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artyukhin, A.B.; Zhang, Y.K.; Akagi, A.E.; Panda, O.; Sternberg, P.W.; Schroeder, F.C. Metabolomic “Dark Matter” dependent on peroxisomal β-oxidation in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2841–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, P.Y.; Jung, M.; Yim, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Park, M.; Hong, E.; Lee, W.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, K.; Paik, Y.K. Chemical structure and biological activity of the Caenorhabditis elegans dauer-inducing pheromone. Nature 2005, 433, 541–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butcher, R.A.; Fujita, M.; Schroeder, F.C.; Clardy, J. Small molecule pheromones that control dauer development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, J.; Kaplan, F.; Ajredini, R.; Zachariah, C.; Alborn, H.T.; Teal, P.E.A.; Malik, R.U.; Edison, S.A.; Sternberg, P.W.; Schroeder, F.C. A blend of small molecules regulates both mating and development in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 2008, 454, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, F.; Alborn, H.; von Reuss, S.H.; Ajredini, R.; Ali, J.G.; Akyazi, F.; Stelinski, L.L.; Edison, S.A.; Schroeder, F.C.; Teal, P.E. Interspecific nematode signals regulate dispersal behavior. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguez, J.H.; Conner, E.S.; Zhou, Y.; Ciche, T.A.; Ragains, J.R.; Butcher, R.A. A novel ascaroside controls the parasitic life cycle of the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 961–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Qin, P.; Chinta, S.; Kong, X.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; et al. Ascarosides coordinate the dispersal of a plant-parasitic nematode with the metamorphosis of its vector beetle. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Cao, L.; Huang, Z.; Gu, X.; Cui, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; Han, R. Influence of the ascarosides on the recovery, yield and dispersal of entomopathogenic nematodes. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2022, 188, 107717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X. Nematode pheromones: Structures and functions. Molecules 2023, 28, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klessig, D.F.; Manohar, M.; Baby, S.; Koch, A.; Danquah, W.B.; Luna, E.; Park, H.J.; Kolkman, J.M.; Turgeon, B.G.; Nelson, R.; et al. Nematode ascaroside enhances resistance in a broad spectrum of plant–pathogen systems. J. Phytopathol. 2019, 167, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, M.; Tenjo-Castano, F.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.K.; Kumari, A.; Williamson, V.M.; Wang, X.; Klessig, D.F.; Schroeder, F.C. Plant metabolism of nematode pheromones mediates plant-nematode interactions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.K.; Manohar, M.; Artyukhin, A.B.; Kumari, A.; Tenjo-Castano, F.J.; Nguyen, H.; Routray, P.; Choe, A.; Klessig, D.F.; et al. Nematode signaling molecules are extensively metabolized by animals, plants, and microorganisms. ACS Chem. Biol. 2021, 16, 1050–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Qiu, Y.; Ribeiro dos Santos, A.M.; Yin, Y.; Li, Y.E.; Vinckier, N.; Nariai, N.; Benaglio, P.; Raman, A.; Li, A.; et al. Systematic analysis of binding of transcription factors to noncoding variants. Nature 2021, 591, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhurst, R.J. Morphological and functional dimorphism in Xenorhabdus spp.; bacteria symbiotically associated with the insect pathogenic nematodes Neoplectana and Heterorhabditis. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1980, 121, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.; Tafesh-Edwards, G.; Kenney, E.; Toubarro, D.; Simões, N.; Eleftherianos, I. Excreted secreted products from the parasitic nematode Steinernema carpocapsae manipulate the Drosophila melanogaster immune response. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Rao, Z.C.; Cao, L.; De-Clercq, P.; Han, R.C. Infection of Ophiocordyceps sinensis Fungus Causes Dramatic Changes in the Microbiota of Its Thitarodes Host. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 577268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, J.R.; Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N. UpSetR: An R package for the visualization of intersecting sets and their properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2938–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Yoshiga, T. Bacterial feeding nematodes ingest haemocytes in the haemocoel of the insect Galleria mellonella. Parasitology 2020, 147, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallem, E.A.; Rengarajan, M.; Ciche, T.A.; Sternberg, P.W. Nematodes, bacteria, and flies: A tripartite model for nematode parasitism. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roder, A.C.; Wang, Y.; Butcher, R.A.; Stock, S.P. Influence of symbiotic and non-symbiotic bacteria on pheromone production in Steinernema nematodes (Nematoda, Steinernematidae). J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb212068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogensen, T.H. Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2009, 22, 240–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aderem, A.; Ulevitch, R.J. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 2000, 7, 406–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, P.; Zdybicka-Barabas, A.; Cytrynska, M. A Different repertoire of Galleria mellonella antimicrobial peptides in larvae challenged with bacteria and fungi. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftherianos, I.; Gökçen, F.; Felföldi, G.; Millichap, P.J.; Trenczek, T.E.; Ffrench-Constant, R.H.; Reynolds, S.E. The immunoglobulin family protein Hemolin mediates cellular immune responses to bacteria in the insect Manduca sexta. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.Q.; Kanost, M.R. Binding of hemolin to bacterial lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid. An immunoglobulin superfamily member from insects as a pattern-recognition receptor. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 1827–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brivio, M.F.; Mastore, M. When appearance misleads: The role of the entomopathogen surface in the relationship with its host. Insects 2020, 11, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, W.J. Role of DUOX in gut inflammation: Lessons from Drosophila model of gut-microbiota interactions. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2014, 3, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, S.; Mandrekar, P. Cellular stress response and innate immune signaling: Integrating pathways in host defense and inflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Yang, L.; Pang, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, P.; Gao, G.; Cheng, G. A Mesh-Duox pathway regulates homeostasis in the insect gut. Nat. Microbiol. 2017, 2, 17020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, P.P.; Rossoni, R.D.; Ribeiro, F.C.; Silva, M.P.; Souza, C.M.; Jorge, A.O.C.; Junqueira, J.C. Two sporulated Bacillus enhance immunity in Galleria mellonella protecting against Candida albicans. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krams, I.A.; Kecko, S.; Jõers, P.; Trakimas, G.; Elferts, D.; Krams, R.; Luoto, S.; Rantala, M.J.; Inashkina, I.; Gudrā, D.; et al. Microbiome symbionts and diet diversity incur costs on the immune system of insect larvae. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 4204–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.E.; Howard, A.; Kasprzak, A.B.; Gordon, K.H.; East, P.D. A peptidomics study reveals the impressive antimicrobial peptide arsenal of the wax moth Galleria mellonella. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Sato, K.; Shibuya, M.; Zeiger, D.M.; Butcher, R.A.; Ragains, J.R.; Clardy, J.; Touhara, K.; Sengupta, P. Two chemoreceptors mediate developmental effects of dauer pheromone in C. elegans. Science 2009, 326, 994–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Reilly, D.K.; Yu, J.; Srinivasan, J.; Schroeder, F.C. Photoaffinity probes for nematode pheromone receptor identification. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 18, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Sato, E.; Sugita, T. Acute melanization of silkworm hemolymph by peptidoglycans of the human commensal bacterium Cutibacterium acnes. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garriga, A.; Mastore, M.; Morton, A.; Pino, F.G.D.; Brivio, M.F. Immune response of Drosophila suzukii larvae to infection with the nematobacterial complex Steinernema carpocapsae-Xenorhabdus nematophila. Insects 2020, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.J.; Seo, S.; Shrestha, S.; Kim, Y. Bacterial metabolites of an entomopathogenic bacterium, Xenorhabdus nematophila, inhibit a catalytic activity of phenoloxidase of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 21, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.; Lee, S.; Hong, Y.; Kim, Y. Phospholipase A2 inhibitors synthesized by two entomopathogenic bacteria, Xenorhabdus nematophila and Photorhabdus temperata subsp. temperata. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 3816–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pena, J.M.; Carrillo, M.A.; Hallem, E.A. Variation in the susceptibility of Drosophila to different entomopathogenic nematodes. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 1130–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, F.C. Modular assembly of primary metabolic building blocks: A chemical language in C. elegans. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, Y.P.; Mahanti, P.; Schroeder, F.C.; Sternberg, P.W. Nematode-trapping fungi eavesdrop on nematode pheromones. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manosalva, P.; Manohar, M.; Von-Reuss, S.H.; Chen, S.; Koch, A.; Kaplan, F.; Choe, A.; Micikas, R.J.; Wang, X.; Kogel, K.H.; et al. Conserved nematode signalling molecules elicit plant defenses and pathogen resistance. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinoda, S.; Itakura, A.; Sasano, H.; Miyake, R.; Kawabata, H.; Asano, Y. Rational design of the soluble variant of l-pipecolic acid hydroxylase using the α-helix rule and the hydropathy contradiction rule. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 29508–29516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, L.; Ning, J.; Wickham, J.D.; Tian, H.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Sun, J. miR-31-5p regulates cold acclimation of the wood-boring beetle Monochamus alternatus via ascaroside signaling. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perier, J.D.; Kaplan, F.; Lewis, E.E.; Alborn, H.; Schliekelman, P.; Toews, M.D.; Schiller, K.C.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.I. Enhancing entomopathogenic nematode efficacy with Pheromones: A field study targeting the pecan weevil. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2024, 203, 108070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro-Ilan, D.I.; Kaplan, F.; Oliveira-Hofman, C.; Schliekelman, P.; Hans, T.A.; Lewis, E.E. Conspecific pheromone extracts enhance entomopathogenic infectivity. J. Nematol. 2019, 51, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chantab, K.; Rao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Han, R.; Cao, L. Ascarosides and Symbiotic Bacteria of Entomopathogenic Nematodes Regulate Host Immune Response in Galleria mellonella Larvae. Insects 2024, 15, 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070514
Chantab K, Rao Z, Zheng X, Han R, Cao L. Ascarosides and Symbiotic Bacteria of Entomopathogenic Nematodes Regulate Host Immune Response in Galleria mellonella Larvae. Insects. 2024; 15(7):514. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070514
Chicago/Turabian StyleChantab, Kanjana, Zhongchen Rao, Xuehong Zheng, Richou Han, and Li Cao. 2024. "Ascarosides and Symbiotic Bacteria of Entomopathogenic Nematodes Regulate Host Immune Response in Galleria mellonella Larvae" Insects 15, no. 7: 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070514
APA StyleChantab, K., Rao, Z., Zheng, X., Han, R., & Cao, L. (2024). Ascarosides and Symbiotic Bacteria of Entomopathogenic Nematodes Regulate Host Immune Response in Galleria mellonella Larvae. Insects, 15(7), 514. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15070514





