Olfactory Response of Sitophilus zeamais Adults to Odours of Semolina Pasta and Semolina Pasta Enriched with Different Amounts of Acheta domesticus Powder
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insects
2.2. Pasta
2.2.1. Pasta Raw Materials
2.2.2. Pasta Making
2.3. Five-Choice Behavioural Bioassay
2.4. Two-Choice Behavioural Bioassay
2.5. HS-SPME-GC/MS Analysis of Volatile Components
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
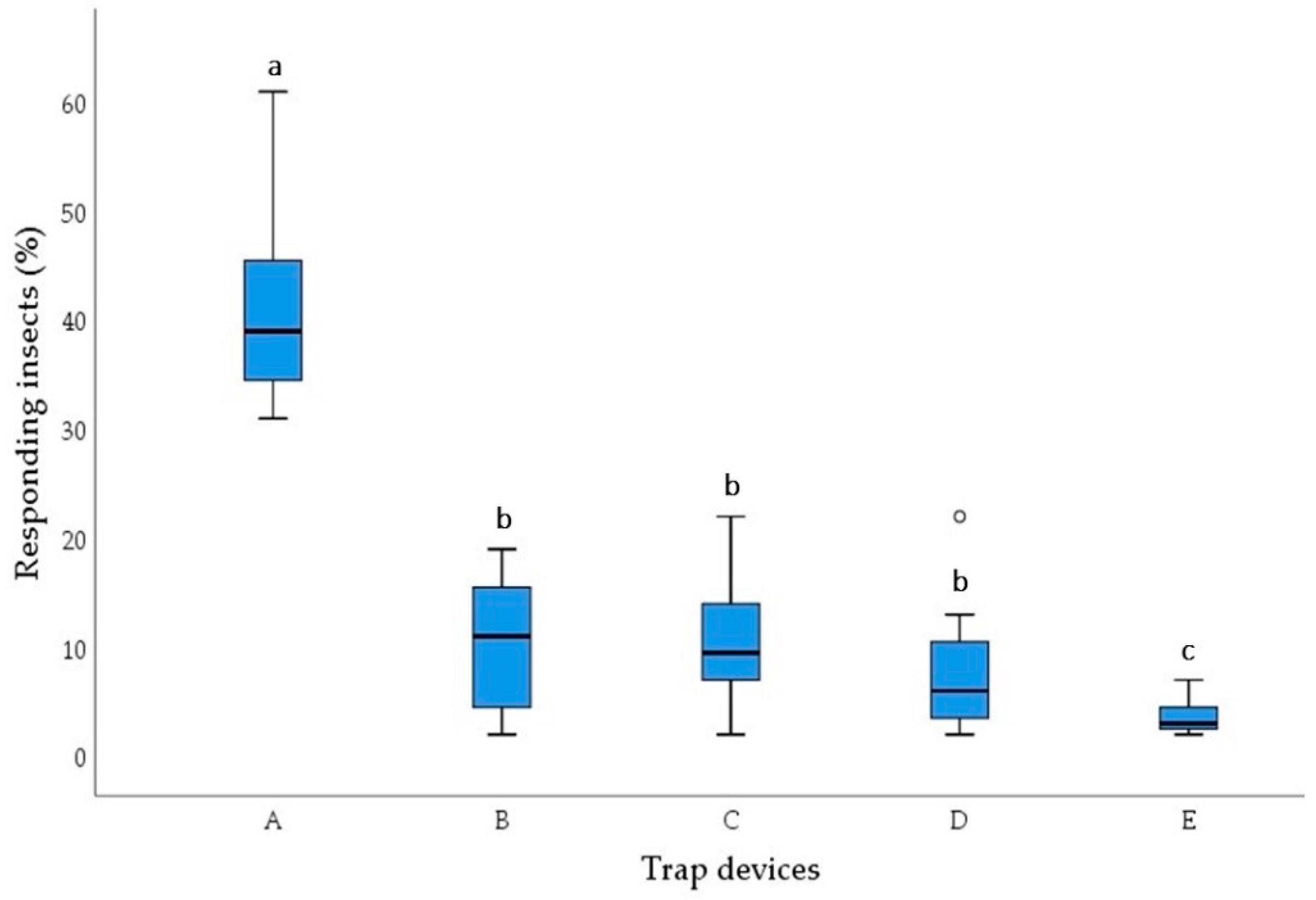
3.1. Five-Choice Behavioural Bioassay
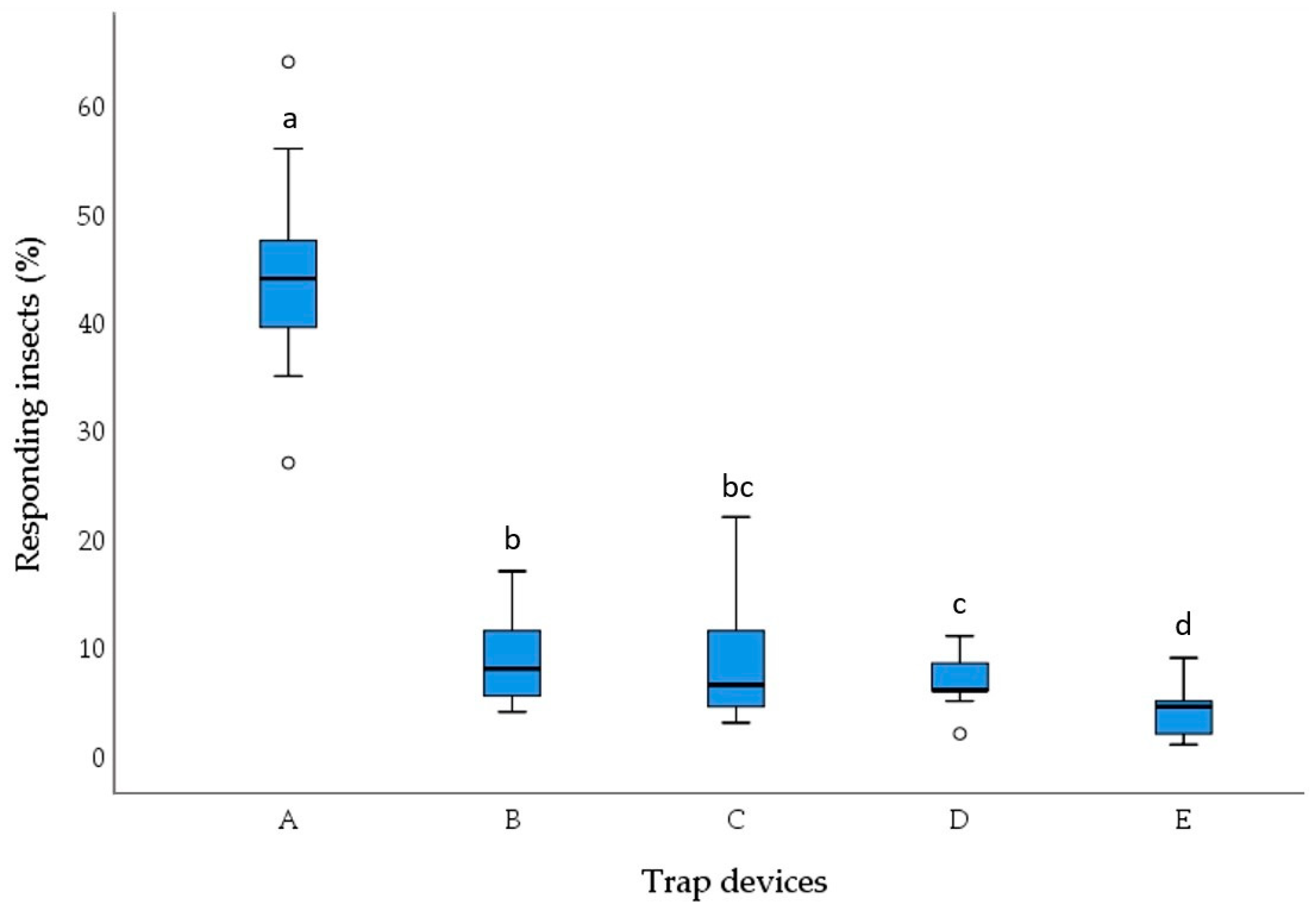
3.2. Two-Choice Behavioural Bioassay
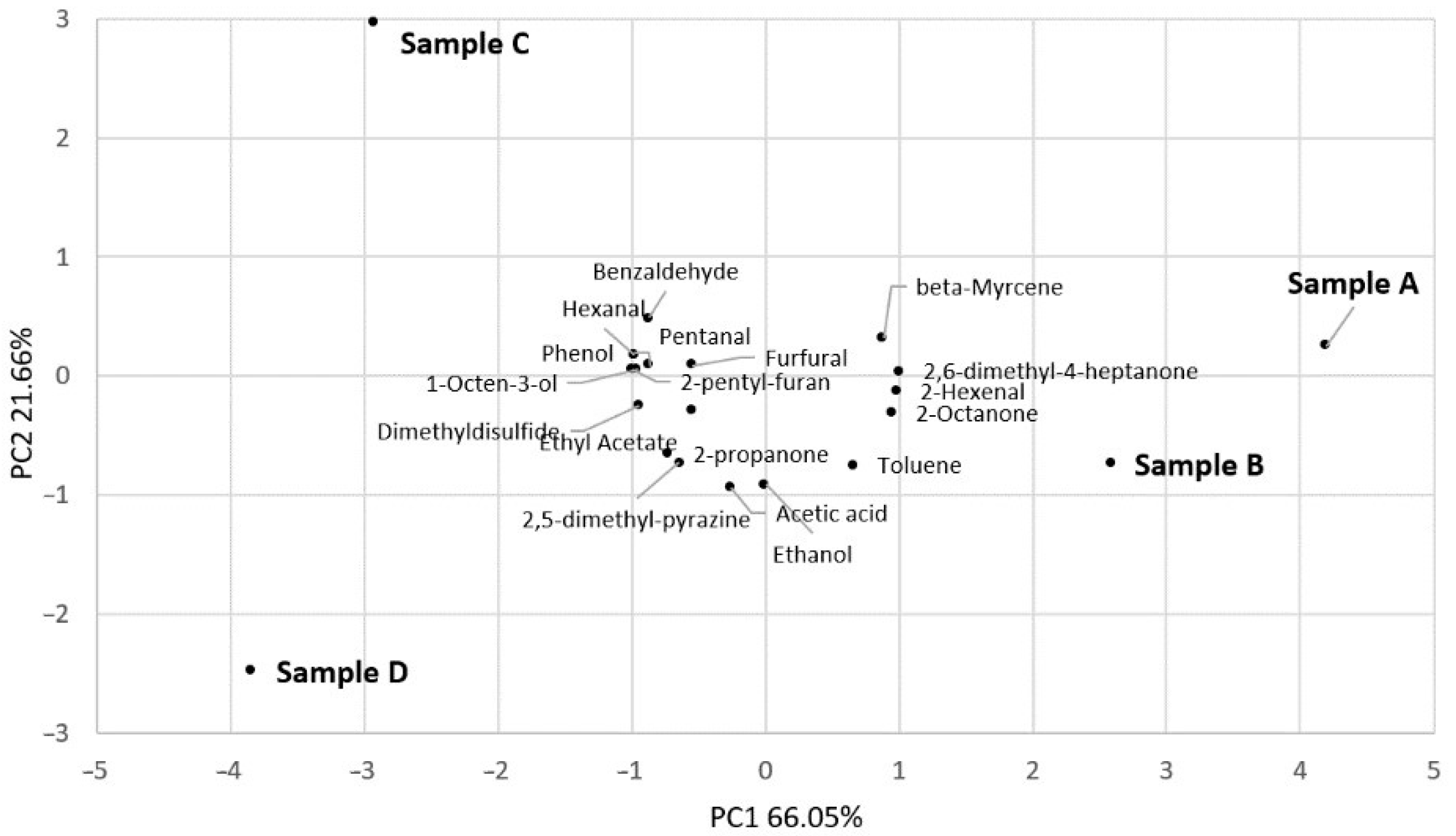
3.3. HS-SPME-GC/MS Analysis of Volatile Components
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Huis, A.; Van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects. Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; FAO Forestry Paper: Rome, Italy, 2013; pp. 1–190. [Google Scholar]
- De Castro, R.J.S.; Ohara, A.; Aguilar, J.G.D.S.; Domingues, M.A.F. Nutritional, Functional and Biological Properties of Insect Proteins: Processes for Obtaining, Consumption and Future Challenges. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 76, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.A.J.; De Oliveira, L.M.; Da Rocha, M.; Prentice, C. Edible insects: An alternative of nutritional, functional and bioactive compounds. Food Chem. 2020, 311, 126022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, I.; Peterson, A.; Madden, J.; Huang, E.; Amin, S.; Lammert, A. Will it cricket? Product development and evaluation of cricket (Acheta domesticus) powder replacement in sausage, pasta, and brownies. Foods 2022, 11, 3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, G.; Cullere, M.; Vegro, M.; Simonato, B.; Dalle Zotte, A. Potentiality of protein fractions from the house cricket (Acheta domesticus) and yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) for pasta formulation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 164, 113638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivadese, M.; Dindo, M.L. Edible insects: A historical and cultural perspective on entomophagy with a focus on western societies. Insects 2023, 14, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, A.; Cardone, G.; Jucker, C.; Savoldelli, S.; Marti, A. Technological performance of cricket powder (Acheta domes-ticus L.) in wheat-based formulations. Insects 2022, 13, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncolini, A.; Milanović, V.; Aquilanti, L.; Cardinali, F.; Garofalo, C.; Sabbatini, R.; Clementi, F.; Belleggia, L.; Pasquini, M.; Mozzon, M.; et al. Lesser mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus) powder as a novel baking ingredient for manufacturing high-protein, mineral-dense snacks. Food Res. Int. 2020, 131, 109031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2023/5 of 3 January 2023 Authorising the Placing on the Market of Acheta Domesticus (House Cricket) Partially Defatted Powder as a Novel Food and Amending Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/2470 (Text with EEA Relevance), Document 32023R0005; EU: Brussels, Belgium, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, M.; Imamura, T.; Miyanoshita, A. Infestation and development of Sitophilus spp. in pouch-packaged spaghetti in Japan. J. Econ. Entomol. 2008, 101, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riudavets, J.; Lucas, E.; Pons, M.J. Insects and mites of stored products in the northeast of Spain. IOBC Bull. 2002, 25, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Stejskal, V.; Bostlova, M.; Nesvorna, M.; Volek, V.; Dolezal, V.; Hubert, J. Comparison of the resistance of mono and mul-tilayer packaging films to stored product insects in a laboratory test. Food Control 2017, 73, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trematerra, P.; Savoldelli, S. Pasta preference and ability to penetrate through packaging of Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Dryophthoridae). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2014, 59, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longstaff, B.C. Biology of the grain pest species of the genus Sitophilus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): A critical review. Prot. Ecol. 1981, 3, 83–130. [Google Scholar]
- Trematerra, P.; Pistillo, O.M.; Germinara, G.S.; Colacci, M. Bioactivity of cereal- and legume-based macaroni pasta volatiles to adult Sitophilus granarius (L.). Insects 2021, 12, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trematerra, P.; Germinara, G.S.; Colacci, M. Olfactory preferences of Sitophilus zeamais to Cereal- and Legume-based pasta. Insects 2024, 15, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinara, G.S.; De Cristofaro, A.; Rotundo, G. Behavioral responses of adult Sitophilus granarius to individual cereal volatiles. J. Chem. Ecol. 2008, 34, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stejskal, V.; Kucerova, Z.; Lukas, J. Evidence and symptoms of pasta infestation by Sitophilus oryzae (Curculionidae; Coleoptera) in the Czech Republic. Plant Prot. Sci. 2004, 40, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Fields, P.; Taylor, W. The effect of repellents on penetration into packaging by stored-product insects. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2004, 40, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riudavets, J.; Salas, I.; Pons, M.J. Damage characteristics produced by insect pests in packaging film. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2007, 43, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinara, G.S.; Conte, A.; Lecce, L.; Di Palma, A.; Del Nobile, M.A. Propionic acid in bio-based packaging to prevent Sitophilus granarius (L.) (Coleoptera, Dryophthoridae) infestation in cereal products. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanassiou, C.G.; Riudavets, J.; Kavallieratos, G. Preventing stored-product insect infestations in packaged-food products. Stewart Postharvest Rev. 2011, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, M.A.; Vardeman, J.M.; Bagwell, J. Insect Resistant Packaging. In Stored Product Protection; Hagstrum, D.W., Phillips, T.W., Cuperus, G., Eds.; Kansas State University: Manhattan, KS, USA, 2012; pp. 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Scheff, D.S.; Sehgal, B.; Subramanyam, B. Evaluating penetration ability of Plodia interpunctella (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) larvae into multilayer polypropylene packages. Insects 2018, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöller, M.; Prozell, S.; Suma, P.; Russo, A. Biological control of stored product insects. In Recent Advances in Stored Product Protection; Athanassiou, C.G., Arthur, F.H., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 183–209. [Google Scholar]
- Vrabič Brodnjak, U.; Jordan, J.; Trematerra, P. Resistance of packaging against infestation by Sitophilus zeamais. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 2970–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, A.; Adamczak, J.; Chelminska, P.; Juszkiewicz, J.; Kowalczewski, P. Quality and nutritional/textural properties of durum wheat pasta enriched with cricket powder. Foods 2019, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICC. Standard Methods of the International Association for Cereal Science and Technology; ICC: Vienna, Austria, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- AACC. American Association of Cereal Chemists. Approved Methods of AACC, 11th ed.; American Association of Cereal Chemists: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zotta, T.; Di Renzo, T.; Sorrentino, A.; Reale, A.; Boscaino, F. Selection of non-Saccharomyces wine yeasts for the production of leavened doughs. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Dool, H.; Kratz, P.D. A Generalization of the Retention Index System Including Linear Temperature Programmed Gas-Liquid Partition Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1963, 11, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinara, G.S.; Rotundo, G.; De Cristofaro, A.; Giacometti, R. Risposte elettroantennografiche di Sitophilus granarius (L.) e S. zeamais Motschulsky a sostanze volatili dei cereali. Tec. Molit. 2002, 53, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- Cha, D.H.; Linn, C.E.; Teal, P.E.A.; Zhang, A.; Roelofs, W.L.; Loeb, G.M. Eavesdropping on plant volatiles by a specialist moth: Significance of ratio and concentration. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, T.J.; Wadhams, L.J.; Woodcock, C.M. Insect host location: A volatile situation. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, T.J.; Pickett, J.A. Perception of plant volatile blends by herbivorous insects-finding the right mix. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1605–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugravot, S.; Grolleau, F.; Macherel, D.; Rochetaing, A.; Hue, B.; Stankiewicz, M.; Heignard, J.; Lapied, B. Dimethyl disulfide exerts insecticidal neurotoxicity through mitochondrial dysfuntion and activation of insect K(ATP) channels. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 90, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.K.; Shin, S.C. Fumigant activity of plant essential oils and components from garlic (Allium sativum) and clove bud (Eugenia caryophyllata) oils against the Japanese termite (Reticulitermes speratus Kolbe). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4388–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lam, S.L.; Ho, S.H. Bioactivities of essential oil from Elletaria cardamomum (L.) Maton. to Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky and Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). J. Stored Prod. Res. 2000, 36, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Choi, W.S.; Lee, S.E.; Park, B.S. Fumigation toxicity of essential oils and their constituent compounds towards the rice weevil, Sitophilus oryzae L. Crop Prot. 2001, 20, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattudurai, G.; Paulraj, M.G.; Ignacimuthu, S. Fumigant toxicity of volatile synthetic compounds and natural oils against red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleopetera: Tenebrionidae). J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2012, 24, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germinara, G.S.; De Cristofaro, A.; Rotundo, G. Bioactivity of short-chain aliphatic ketones against adults of the granary weevil, Sitophilus granarius (L.). Pest Manag. Sci. 2012, 68, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordlund, D.A.; Lewis, W.J. Terminology of chemical releasing stimuli in intraspecific and interspecific interactions. J. Chem. Ecol. 1976, 2, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgar, M.A.; Crespi, B.J. Cannibalism: Ecology and Evolution among Diverse Taxa; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1992; pp. 1–376. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, M.L.; Mitchell, R.F.; Reagel, P.F.; Hanks, L.M. Causes and consequences of cannibalism in non-carnivorous insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolivar-Silva, D.; Guedes, N.M.P.; Guedes, R.N. Larval cannibalism and fitness in the stored grain weevils Sitophilus granarius and Sitophilus zeamais. J. Pest Sci. 2018, 91, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Values | Durum Wheat Semolina | Cricket Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Energy value | 1446 kJ/346 kcal | 1738 kJ/415.4 kcal |
| Fat | 2.0 g | 9.0 g |
| Carbohydrates | 67.0 g | 5.0 g |
| Fibre | 2.8 g | 9.2 g |
| Protein | 13.5 g | 74.0 g |
| Salt | 0.005 g | 1.1 g |
| Samples | Moisture | Fat | Carbohydrates * | Dietary Fibre | Protein (N*6.25) | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 10.6 | 2.1 | 69.5 | 2.9 | 14.2 | 0.73 |
| B | 10.6 | 2.4 | 69.9 | 3.2 | 17.0 | 0.89 |
| C | 10.6 | 2.8 | 62.2 | 3.5 | 19.9 | 1.04 |
| D | 10.6 | 3.1 | 58.6 | 3.8 | 22.7 | 1.19 |
| Samples | Bait Trap Devices (±SE) | Unbaited Control (±SE) | Student’s t-Test | Response Index (±SE) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-Value | p-Value | ||||
| A vs. E | 62.4 ± 3.0 | 5.6 ± 1.6 | 16.591 | <0.001 | 56.8 ± 3.4 a |
| B vs. E | 54.6 ± 4.5 | 4.8 ± 0.9 | 10.919 | <0.001 | 49.8 ± 4.0 a |
| C vs. E | 56.0 ± 6.0 | 5.2 ± 1.7 | 8.172 | <0.001 | 50.8 ± 5.9 a |
| D vs. E | 53.2 ± 4.8 | 4.8 ± 2.2 | 12.033 | <0.001 | 48.4 ± 1.9 a |
| F vs. E | 10.0 ± 1.8 | 8.0 ± 1.5 | 0.853 | 0.419 | 2.0 ± 2.3 b |
| Samples | Bait Trap Devices (±SE) | Unbaited Control (±SE) | Student’s t-Test | Response Index (±SE) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t-Value | p-Value | ||||
| A vs. E | 63.0 ± 4.1 | 3.0 ± 0.7 | 14.384 | <0.001 | 60.0 ± 4.5 a |
| B vs. E | 55.2 ± 4.8 | 5.4 ± 1.4 | 9.920 | <0.001 | 49.8 ± 4.9 a |
| C vs. E | 53.8 ± 7.2 | 3.6 ± 0.8 | 6.922 | <0.001 | 50.2 ± 7.3 a |
| D vs. E | 47.8 ± 4.9 | 5.0 ± 1.2 | 8.420 | <0.001 | 42.8 ± 5.2 a |
| F vs. E | 9.2 ± 2.1 | 7.6 ± 1.4 | 0.637 | 0.542 | 1.6 ± 3.4 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trematerra, P.; Colacci, M.; Messia, M.C.; Trivisonno, M.C.; Reale, A.; Boscaino, F.; Germinara, G.S. Olfactory Response of Sitophilus zeamais Adults to Odours of Semolina Pasta and Semolina Pasta Enriched with Different Amounts of Acheta domesticus Powder. Insects 2024, 15, 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15090634
Trematerra P, Colacci M, Messia MC, Trivisonno MC, Reale A, Boscaino F, Germinara GS. Olfactory Response of Sitophilus zeamais Adults to Odours of Semolina Pasta and Semolina Pasta Enriched with Different Amounts of Acheta domesticus Powder. Insects. 2024; 15(9):634. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15090634
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrematerra, Pasquale, Marco Colacci, Maria Cristina Messia, Maria Carmela Trivisonno, Anna Reale, Floriana Boscaino, and Giacinto Salvatore Germinara. 2024. "Olfactory Response of Sitophilus zeamais Adults to Odours of Semolina Pasta and Semolina Pasta Enriched with Different Amounts of Acheta domesticus Powder" Insects 15, no. 9: 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15090634
APA StyleTrematerra, P., Colacci, M., Messia, M. C., Trivisonno, M. C., Reale, A., Boscaino, F., & Germinara, G. S. (2024). Olfactory Response of Sitophilus zeamais Adults to Odours of Semolina Pasta and Semolina Pasta Enriched with Different Amounts of Acheta domesticus Powder. Insects, 15(9), 634. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects15090634








