Phototaxis Characteristics of Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Erebidae)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Materials
2.3. Experimental Methods
2.3.1. Trapping Effects of Insecticidal Lamps with Different Wavelengths
2.3.2. Trapping Effects of L360 Insecticidal Lamps with Different Powers
2.3.3. Weight and Egg-Carrying Capacity Between Light-Trapped and Indoor-Emerged Adults
2.3.4. Observation of Phototaxis Behavior Indoor
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
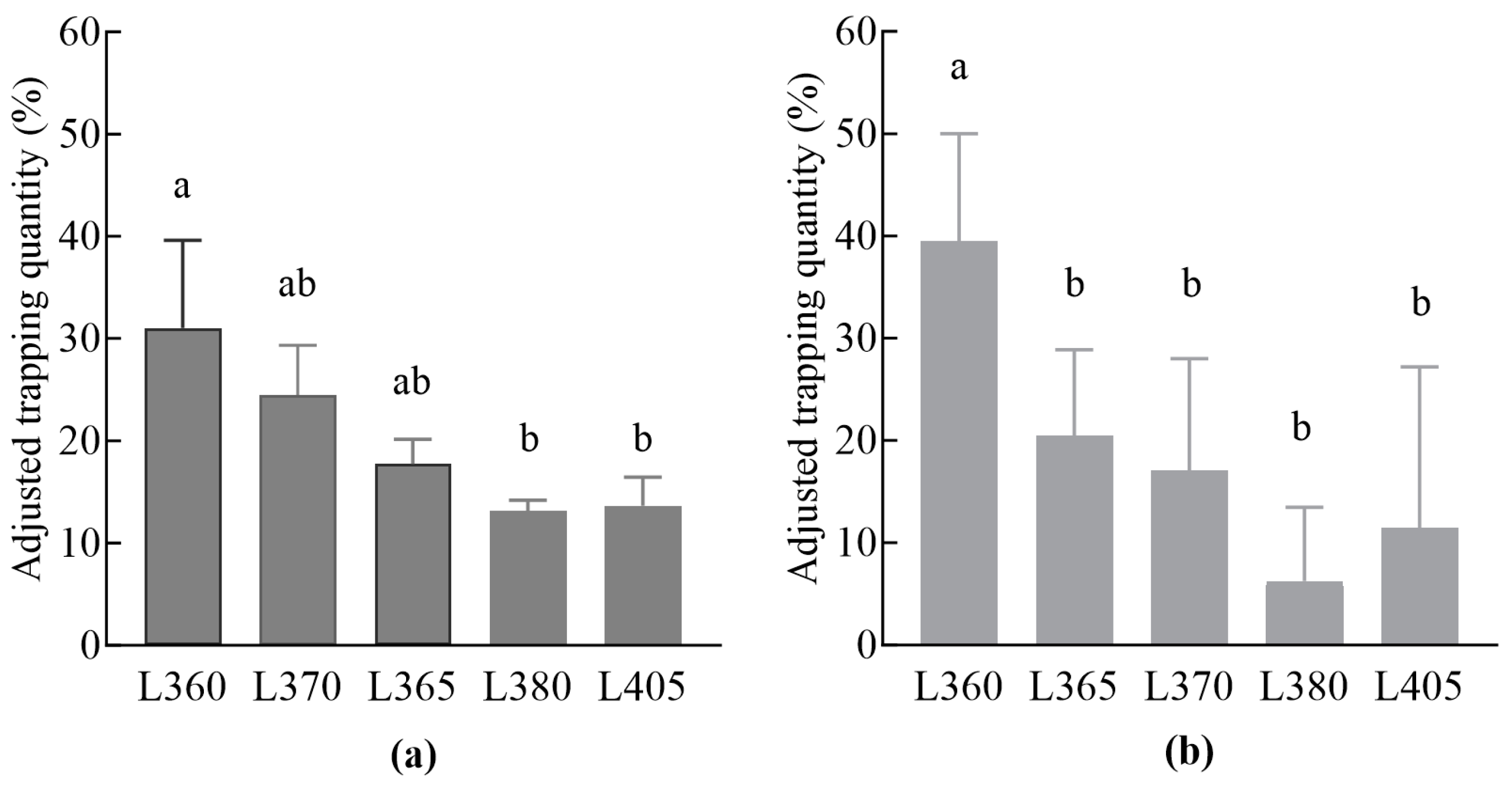
3.1. Trap Catches of Insecticidal Lamps with Different Wavelengths
3.1.1. Comparison of The Trapping Effects of Insecticidal Lamps with Different Wavelengths on Male and Female L. xylina
3.1.2. Light-Trapping Rhythm of Male and Female L. xylina
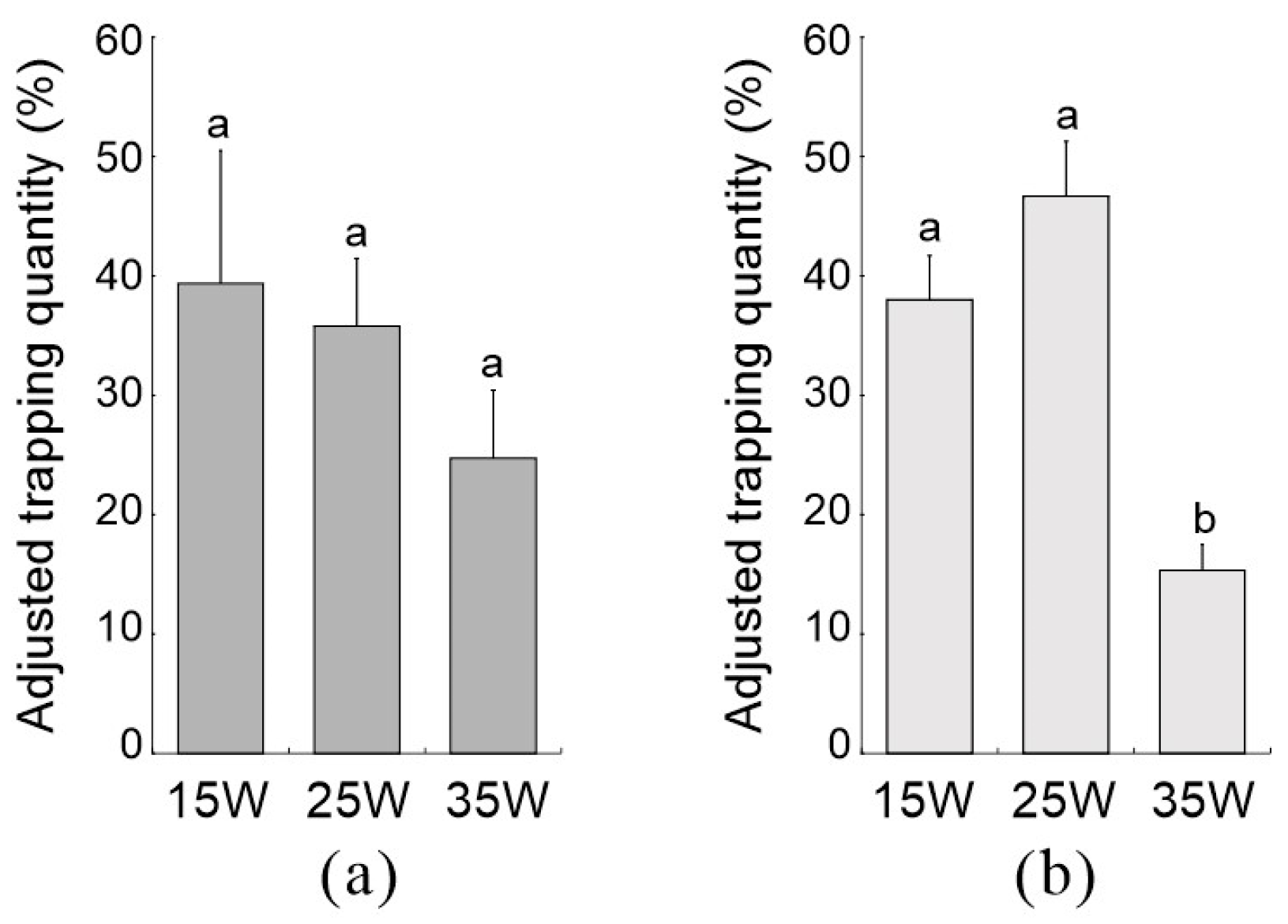
3.2. Comparison of Trapping Effects of L360 Insecticidal Lamps with Different Powers
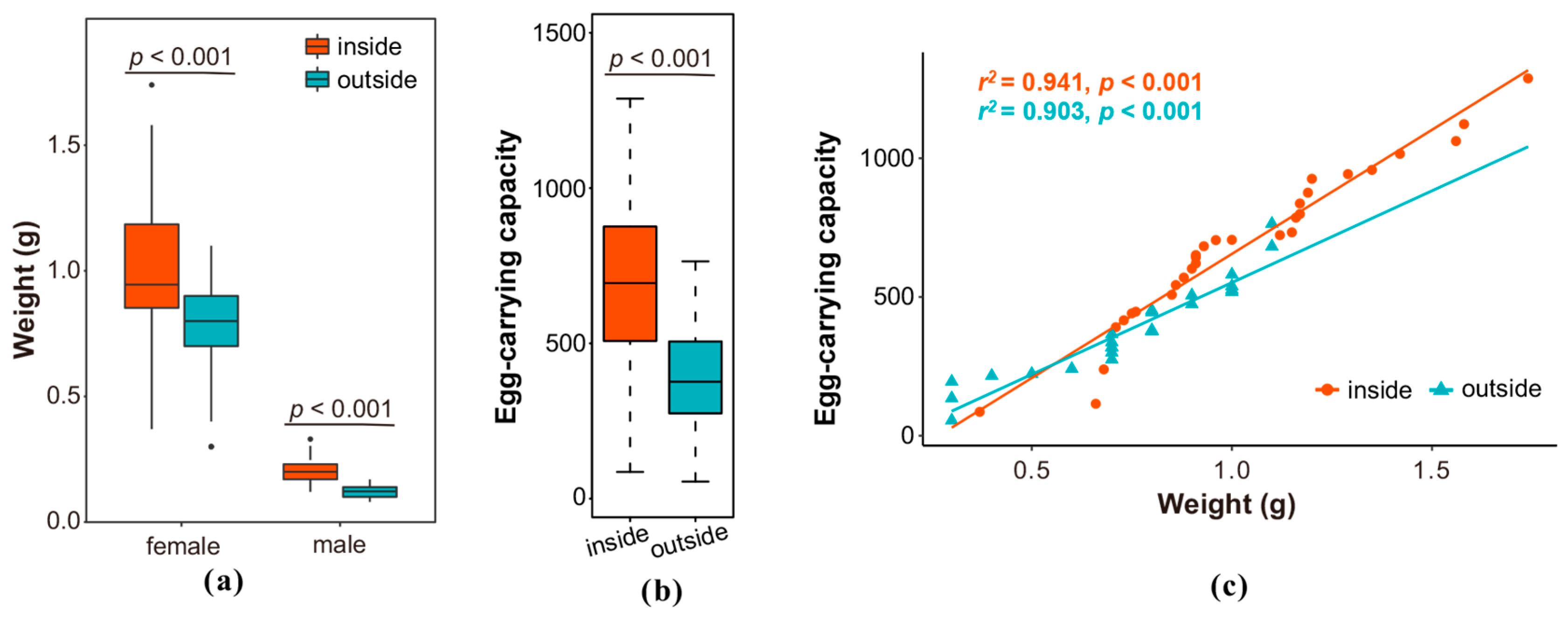
3.3. Comparison of Weight and Egg-Carrying Capacity Between Light-Trapped and Indoor-Emerged Adults
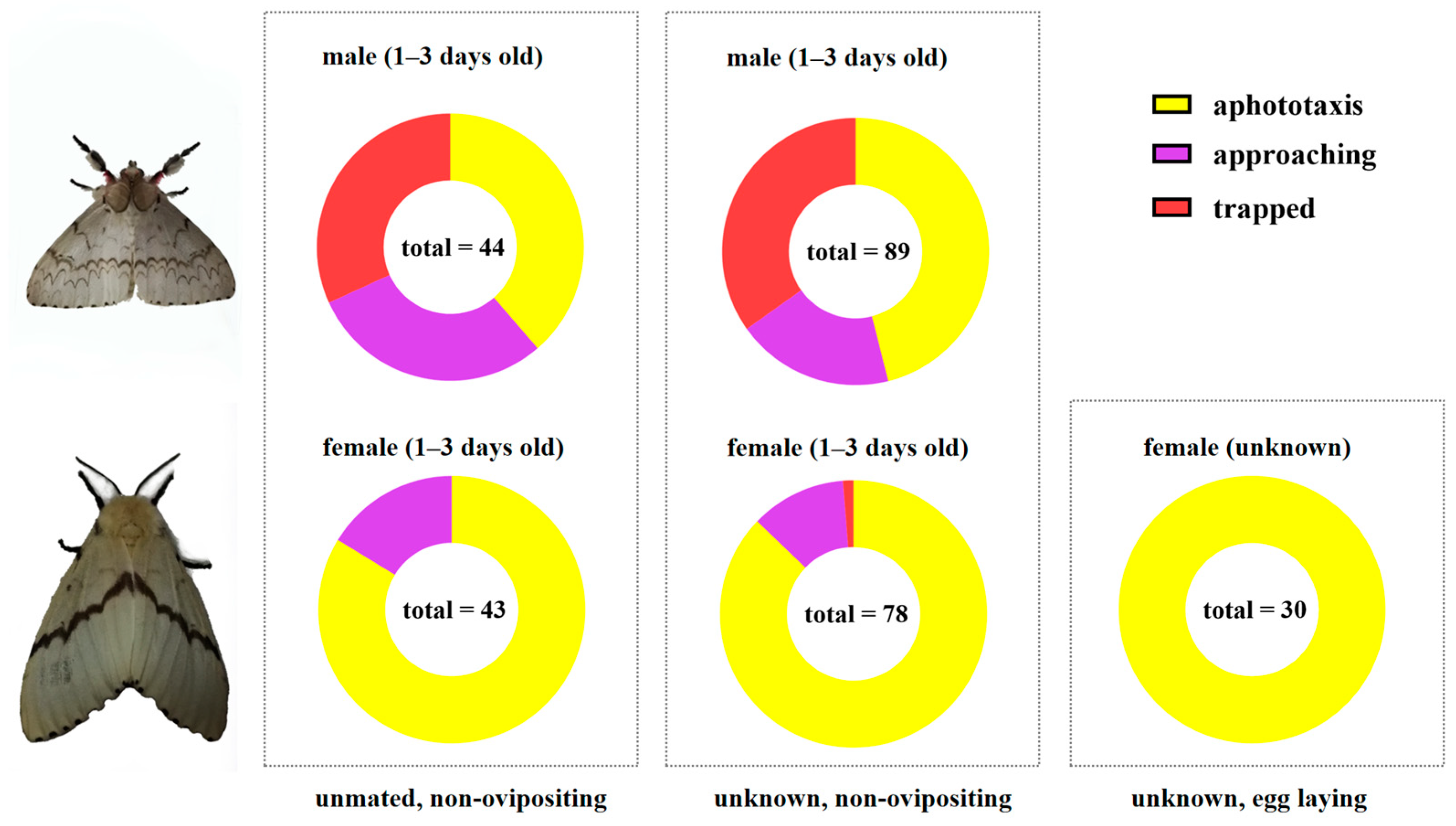
3.4. Phototactic Behavior of L. xylina Adults Indoors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer/Funders’ Note
References
- Van Grunsven, R.H.A.; Donners, M.; Boekee, K.; Tichelaar, I.; van Geffen, K.G.; Groenendijk, D.; Beredse, F.; Veenendaal, E.M. Spectral composition of light sources and insect phototaxis, with an evaluation of existing spectral response models. J. Insect Conserv. 2014, 18, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Song, H.S.; Li, C.S.; Huang, Q.Y.; Lei, C.L. Effect of several factors on the phototactic response of the oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.N.; Huang, Q.Y.; Lei, C.L. Advances in insect phototaxis and application to pest management: A review. Pest Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 3135–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Andres-Bragado, L.; Sprecher, S.G. Mechanisms of vision in the fruit fly. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 36, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimoda, M.; Honda, K.I. Insect reactions to light and its applications to pest management. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2013, 48, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontaine, J.D.; Fibiger, M. Revised higher classification of the Noctuoidea (Lepidoptera). Can. Entomol. 2006, 138, 610–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wahlberg, N.; Holloway, J.D.; Bergsten, J.; Fan, X.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W.; Wen, L.J.; Wang, M.; Nylin, S. Molecular phylogeny of Lymantriinae (Lepidoptera, Noctuoidea, Erebidae) inferred from eight gene regions. Cladistics 2015, 31, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Ren, Y.; Chen, P.; Tian, H.; Xu, A. The complete mitochondrial genome of Lymantria xylina with phylogenetic analysis. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019, 4, 3128–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, F. Molecular detection and genetic diversity of casuarina moth, Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). J. Insect Sci. 2018, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Ren, H.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, R.; Liu, M.; Zhang, F. Evaluation of the Potential Flight Ability of the Casuarina Moth, Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Insects 2024, 15, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Chen, S.L.; Xie, Q.M.; Cai, Q.J.; Wu, J. Study on the Lymantriid moth Lymantria xylina Swinhoe. Acta Entomol. Sin. 1981, 27, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, L.; Zuo, C.; Li, J.; Cui, Y.; Wen, X.; Cowan, D.; Wu, S.; Liu, M.; et al. Reproductive and Flight Characteristics of Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Erebidae) in Fuzhou, China. Insects 2024, 15, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.Y.; Hwang, F.C.; Shen, T.C. Shifts in developmental diet breadth of Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2007, 100, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; He, X.B. Diseases and Pests of Casuarina Trees in China, 1st ed.; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- De Waard, J.R.; Mitchell, A.; Keena, M.A.; Gopurenko, D.; Boykin, L.M.; Armstrong, K.F.; Pogue, M.G.; Lima, J.; Floyd, R.; Hanner, R.H.; et al. Towards a global barcode library for Lymantria (Lepidoptera: Lymantriinae) tussock moths of biosecurity concern. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdue University. Asian Defoliator Pathway-Based Survey Reference. Available online: http://download.ceris.purdue.edu/file/3288 (accessed on 1 March 2014).
- Purdue University. Lymantria xylina Datasheet_Asian Defoliator. Available online: http://download.ceris.purdue.edu/file/2288 (accessed on 5 February 2014).
- Pogue, M.; Schaefer, P.W. A Review of Selected Species of Lymantria Hübner (1819) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae: Lymantriinae) from Subtropical and Temperate Regions of Asia, Including the Descriptions of Three New Species, Some Potentially Invasive to North America; Forest Health Technology Enterprise Team: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- CABI. Lymantria xylina (Casuarina Tussock Moth). Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/pdf/10.1079/cabicompendium.31815 (accessed on 16 September 2022).
- Summerville, K.S.; Boulware, M.J.; Veech, J.A.; Crist, T.O. Spatial variation in species diversity and composition of forest Lepidoptera in eastern deciduous forests of North America. Conserv. Biol. 2003, 17, 1045–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keena, M.A.; Côté, M.J.; Grinberg, P.S.; Wallner, W.E. World distribution of female flight and genetic variation in Lymantria dispar (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae). Environ. Entomol. 2014, 37, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Wang, C.H. Characterization and polyhedrin gene cloning of Lymantria xylina multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2005, 88, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Kang, T.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Ryu, D.P.; Lee, H.S. Taxonomic review of the genus Lymantria (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Lymantriinae) in Korea. Entomol. Res. 2015, 45, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.H.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, H.S. DNA barcoding of the Korean Lymantria Hübner, 1819 (Lepidoptera: Erebidae: Lymantriinae) for quarantine inspection. J. Econ. Entomol. 2015, 108, 1596–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.H.; Choi, D.S.; Hong, K.J.; Park, S. Monitoring of hitchhiker insect pests collected on foreign vessels entering Korea using by DNA barcodes. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2023, 26, 102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.T.; Liao, C.T.; Ko, W.F.; Pai, K.F. Light attractive evaluation and insecticide trials of casuarina moth (Lymantria xylina Swinhoe) in Bagua Mountain area. Res. Rep. Agric. Improv. Field Taizhong Dist. 2010, 107, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Chen, K.; Zheng, X.; Chen, D.; Xu, D. Biological characteristics of Lymantria xylina and its prevention and control measures. Chin. Countrys. Well-Off Technol. 2009, 05, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Kooi, C.J.; Stavenga, D.G.; Arikawa, K.; Belušič, G.; Kelber, A. Evolution of insect color vision: From spectral sensitivity to visual ecology. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2021, 66, 435–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Q.; Du, Y.; Yun, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, J. Light trap experiments against Lymantria dispar adults. For. Pest Dis. 2014, 33, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zuo, C.; Wang, R.; Liang, G.; Wang, B.; Zhang, F. Studies on the Distribution of Lymantria xylina egg masses in Field. Highlights Sci. Online 2018, 11, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar]
- Garris, H.W.; Snyder, J.A. Sex-specific attraction of moth species to ultraviolet light traps. Southeast. Nat. 2010, 9, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.E.; Zwaan, B.J.; Brakefield, P.M. Evolution of sexual dimorphism in the Lepidoptera. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 56, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, D.J.; Hull-Sanders, H.M.; Hibbard, E.L.; Mastro, V.C. A comparison of electrophysiologically determined spectral responses in six subspecies of Lymantria. J. Econ. Entomol. 2014, 107, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafuku, M.; Shimizu, I.; Imai, H.; Shichida, Y. Sexual difference in color sense in a lycaenid butterfly, Narathura japonica. Zool. Sci. 2007, 24, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, H.S. Phototactic behavioral response of agricultural insects and stored-product insects to light-emitting diodes (LEDs). Appl. Biol. Chem. 2017, 60, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Shi, J.; Keena, M. Evaluation of the effects of light intensity and time interval after the start of scotophase on the female flight propensity of Asian gypsy moth (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Environ. Entomol. 2016, 45, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.; Mawji, N.; Meng, S.W.; Ng, D.T.; Smyrnis, N.E. The Effect of Exposure to Varying Light Wavelengths During Development on Locomotor Speed of Adult Drosophila Melanogaster. Available online: https://ojs.library.ubc.ca/index.php/expedition/article/download/184810/184489 (accessed on 20 February 2014).
- Iwaizumi, R.; Arakawa, K.; Koshio, C. Nocturnal flight activities of the female Asian gypsy moth, Lymantria dispar (Linnaeus) (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2010, 45, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefer, P.W. Mass flights of Lymantria dispar japonica and Lymantria mathura (Erebidae: Lymantriinae) to commercial lighting, with notes on female viability and fecundity. J. Lepid. Soc. 2014, 2, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Luo, Y.; Shi, J. The influence of geographic population, age, and mating status on the flight activity of the Asian gypsy moth Lymantria dispar (Lepidoptera: Erebidae) in China. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2017, 52, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.; Liao, C.; Chen, C.; Ko, W. Biological characteristics of Casuarina Moth Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae) in Bagua Mountain Area. Res. Rep. Agric. Improv. Field Taizhong Dist. 2006, 93, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.C.; Shae, Y.S.; Liu, C.S.; Tan, C.W.; Hwang, S.Y. Relationships between egg mass size and egg number per egg mass in the casuarina moth, Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae). Environ. Entomol. 2003, 32, 752–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zera, A.J.; Denno, R.F. Physiology and ecology of dispersal polymorphism in insects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1997, 42, 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, P.A. Evaluating the life-history trade-off between dispersal capability and reproduction in wing dimorphic insects: A meta-analysis. Biol. Rev. 2011, 86, 813–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tigreros, N.; Davidowitz, G. Flight-fecundity tradeoffs in wing-monomorphic insects. Adv. Insect Physiol. 2019, 56, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cheng, L.; Chapman, J.W.; Sappington, T.W.; Liu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, X. Juvenile hormone regulates the shift from migrants to residents in adult oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, W.; Zeng, L.; Zhang, Z.; He, H.; Wang, F.; Xie, X. Effects of juvenile hormone analog and days after emergence on the reproduction of oriental armyworm, Mythimna separata (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) populations. Insects 2022, 13, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Zhu, D.H. Flight and flight energy accumulation related to the daily rhythm of juvenile hormone titer in the wing-dimorphic cricket Velarifictorus aspersus. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2023, 171, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No. | Central Wavelength (nm) | Voltage (V) | Power (W) | Manufacturer | Electric Insecticidal Part |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L360 | 363 | 12 | 15 | Guanhongya | GP-LH18B |
| 363 | 12 | 15 | LOIHOI | GP-LH18B | |
| 363 | 220 | 25 | LOIHOI | GP-LH2203 | |
| 363 | 220 | 35 | LOIHOI | GP-LH2203 | |
| L365 | 365 | 12 | 15 | LOIHOI | GP-LH18B |
| L370 | 368 | 12 | 15 | Guanhongya | GP-LH18B |
| L380 | 378 | 12 | 15 | Guanhongya | GP-LH18B |
| L405 | 439 | 12 | 15 | Guanhongya | GP-LH18B |
| Year | Emergence Period | Lamp | Total Trapping | Maximum Daily Trapping | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | Sex Ratio | Female | Male | Sex Ratio | |||
| 2018 | Late peak period | L360 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 |
| (6 days) | L365 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | |
| L370 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | ||
| L380 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | ||
| L405 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | ||
| 2019 | Peak period | L360 | 2 | 1046 | 1:523 | 1 | 773 | 1:186 |
| (3 days) | L365 | 1 | 502 | 1:502 | 1 | 234 | 1:212 | |
| L370 | 3 | 655 | 1:218 | 2 | 312 | 1:130 | ||
| L380 | 1 | 364 | 1:364 | 1 | 200 | 1:112 | ||
| L405 | 2 | 335 | 1:168 | 2 | 147 | 1:62 | ||
| Period | Mean ± S.E. | Cumulative Percent | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female | Male | Female | Male | |
| 19:00–20:00 | 1.3 ± 1.3 a | 14.3 ± 5.5 c | 44.4 | 1.5 |
| 20:00–21:00 | 1.0 ± 0.6 a | 35.0 ± 9.0 bc | 77.8 | 5.1 |
| 21:00–22:00 | 0.3 ± 0.3 a | 117.0 ± 37.0 abc | 88.9 | 17.2 |
| 22:00–23:00 | 0.3 ± 0.3 a | 212.3 ± 80.9 ab | 100 | 39.1 |
| 23:00–0:00 | 0 a | 285.0 ± 89.3 a | 100 | 68.6 |
| 0:00–1:00 | 0 a | 179.7 ± 94.6 abc | 100 | 87.2 |
| 1:00–2:00 | 0 a | 90.0 ± 54.3 bc | 100 | 96.5 |
| 2:00–3:00 | 0 a | 24.3 ± 9.8 c | 100 | 99.0 |
| 3:00–4:00 | 0 a | 9.7 ± 4.2 c | 100 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, R.; Peng, X.; Li, J.; Xu, C.; Cui, Y.; Liu, M.; Zhang, F. Phototaxis Characteristics of Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Insects 2025, 16, 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040338
Zhang J, Wang B, Wang R, Peng X, Li J, Xu C, Cui Y, Liu M, Zhang F. Phototaxis Characteristics of Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Insects. 2025; 16(4):338. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040338
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jifeng, Baode Wang, Rong Wang, Xiancheng Peng, Junnan Li, Changchun Xu, Yonghong Cui, Mengxia Liu, and Feiping Zhang. 2025. "Phototaxis Characteristics of Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Erebidae)" Insects 16, no. 4: 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040338
APA StyleZhang, J., Wang, B., Wang, R., Peng, X., Li, J., Xu, C., Cui, Y., Liu, M., & Zhang, F. (2025). Phototaxis Characteristics of Lymantria xylina (Lepidoptera: Erebidae). Insects, 16(4), 338. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects16040338






