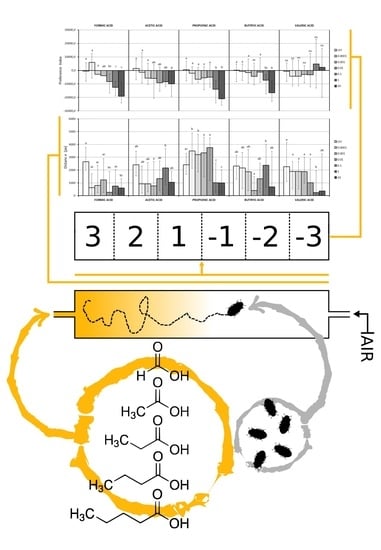
Repellent Effect of Volatile Fatty Acids on Lesser Mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. VFAs
2.2. Insects
2.3. Behavioral Tests
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wada-Katsumata, A.; Zurek, L.; Nalyanya, G.; Roelofs, W.L.; Zhang, A.; Schal, C. Gut bacteria mediate aggregation in the German cockroach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15678–15683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarlane, J.E.; Alli, I. Volatile fatty acids of frass of certain omnivorous insects. J. Chem. Ecol. 1985, 11, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarlane, J.E.; Alli, I. Aggregation of larvae of Blattella germanica (L.) by lactic acid present in excreta. J. Chem. Ecol. 1986, 12, 1369–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarlane, J.E.; Henneberry, G.O. Inhibition of the growth of an insect by fatty acids. J. Insect Physiol. 1965, 11, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlane, J.E. Repellent effect of volatile fatty acids of frass on larvae of german cockroach, Blattella germanica (L.) (Dictyoptera: Blattellidae). J. Chem. Ecol. 1984, 10, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, D.K.; McFarlane, J.E.; Alli, I. Repellency of volatile fatty acids present in frass of larval yellow mealworms, Tenebrio molitor L. (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae), to larval conspecifics. J. Chem. Ecol. 1990, 16, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, M.A.; Waltman, W.D. Transmission of Eimeria, Viruses, and Bacteria to Chicks: Darkling Beetles (Alphitobius diaperinus) as Vectors of Pathogens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 1996, 5, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, D.K.; McFarlane, J.E.; Alli, I. Aggregation in yellow mealworms, Tenebrio molitor L. (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) larvae. J. Chem. Ecol. 1989, 15, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochmatter, T.; Roduit, P.; Cianci, C.; Correll, N.; Jacot, J.; Martinoli, A. SwisTrack—A flexible open source tracking software for multi-agent systems. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Nice, France, 22–26 September 2008; pp. 4004–4010. [Google Scholar]
- Calenge, C. The package “adehabitat” for the R software: A tool for the analysis of space and habitat use by animals. Ecol. Model. 2006, 197, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vet, L.E.M.; Lenteren, J.C.V.; Heymans, M.; Meelis, E. An airflow olfactometer for measuring olfactory responses of hymenopterous parasitoids and other small insects. Physiol. Entomol. 1983, 8, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelinski, L.; Tiwari, S. Vertical T-maze choice assay for arthropod response to odorants. J. Vis. Exp. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFarlane, D.A.; Keeler, R.C.; Mizutani, H. Ammonia volatilization in a Mexican bat cave ecosystem. Biogeochemistry 1995, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belasco, I.J. Comparison of Urea and Protein Meals as Nitrogen Sources for Rumen Micro-Organisms: Urea Utilization and Cellulose Digestion I.J. Belasco The online version of this article, along with updated information and services, is located on the World Wide W. J. Anim. Sci. 1954, 13, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, R.L.; Martins, R.P. Trophic structure and natural history of bat guano invertebrate communities, with special reference to Brazilian caves. Trop. Zool. 1999, 12, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, O.J.; Geier, M.; Boeckh, J. Contribution of fatty acids to olfactory host finding of female Aedes aegypti. Chem. Senses 2000, 25, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baran, B.; Krzyżowski, M.; Cup, M.; Janiec, J.; Grabowski, M.; Francikowski, J. Repellent Effect of Volatile Fatty Acids on Lesser Mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus). Insects 2018, 9, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects9010035
Baran B, Krzyżowski M, Cup M, Janiec J, Grabowski M, Francikowski J. Repellent Effect of Volatile Fatty Acids on Lesser Mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus). Insects. 2018; 9(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects9010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaran, Bartosz, Michał Krzyżowski, Mikołaj Cup, Jakub Janiec, Mateusz Grabowski, and Jacek Francikowski. 2018. "Repellent Effect of Volatile Fatty Acids on Lesser Mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus)" Insects 9, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects9010035
APA StyleBaran, B., Krzyżowski, M., Cup, M., Janiec, J., Grabowski, M., & Francikowski, J. (2018). Repellent Effect of Volatile Fatty Acids on Lesser Mealworm (Alphitobius diaperinus). Insects, 9(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects9010035