Abstract
The purpose of this investigation was to compare concentric movement velocity (CMV) measured with the PUSH Band (v2.0) and a Vicon motion capture system (MC) during the back squat (SQ) and the bench press (BP) resistance exercises (RE). Twelve resistance-trained males (26.0 ± 5.5 years; 175.6 ± 4.9 cm; 96.3 ± 15.8 kg) completed ten repetitions at 50% of one-repetition maximum (1RM), and six repetitions at 75% 1RM for both BP and SQ. Four PUSH devices were utilized and attached to the subject’s right forearm, the center barbell, left and right sides of the barbell. MC markers were placed on top of each PUSH device. An overall analysis using a series of least-squares means contrasts suggested CMV did not differ (p > 0.05) between measurement technologies when position, RE, intensity and repetitions were combined. PUSH exhibited the highest Intraclass Correlation Coefficients (ICC = 0.835–0.961) and Pearson Product-Moment Correlation Coefficients (r = 0.742–0.949) at the arm and center barbell locations when compared with MC. The measurement of CMV between MC and PUSH compares favorably during moderate (i.e., 50%) and high (75%) intensity SQ and BP RE. These data indicate individuals can use the PUSH band v2.0 to accurately monitor CMV within a RE set for SQ and BP RE.
1. Introduction
Velocity-based RE training (VBT) has become a popular approach for strength and conditioning personnel to enhance sport performance. Strength and conditioning personnel can utilize VBT to improve motivation and performance throughout training [1]. The purpose of VBT is to monitor CMV in real time [2], as acute muscular fatigue has been reported to result in decreases in CMV [3]. By using monitoring technology, strength and conditioning personnel are able to detect these changes in CMV and adjust training loads in real time. It has been suggested VBT should utilize velocity thresholds of 10–20% to optimize performance adaptations [1]. Despite performing less work, recent research suggests VBT may provide a better means of improving muscular strength and athletic performance [4,5] than more traditional methods of RE training. Additionally, monitoring CMV at multiple training loads enables strength and conditioning personnel to not only predict an athlete’s 1RM [6], but also determine how many more repetitions an athlete can perform in a set until failure [7].
Currently, an issue with VBT is establishing valid and reliable assessment technologies for measuring CMV that is inexpensive and easy for strength and conditioning personnel to use in a group setting; linear transducers (LT) and MC are cumbersome and expensive but have been reported to provide accurate measures of CMV. Thus, LT and MC devices may be impractical for everyday use during training. Additionally, there is a paucity of investigations comparing cheap commercially available wearable technologies with gold standard devices to measure CMV during RE training.
PUSH Band v2.0 (PUSH) (PUSH Inc, Toronto, ON, Canada) is a six-axis inertial sensor that collects data at 1000 Hz via its 3D accelerometer and gyroscope. PUSH provides in real time CMV feedback on a rep-by-rep basis by connecting to an app on smartphones or tablets. Several published studies assessed PUSH during the SQ [8,9,10,11,12,13] and the BP [10,12,14,15,16]. However, there is a discrepancy in the literature regarding the ability of the PUSH Band to accurately measure CMV. Despite these discrepancies, a recent systematic review suggests PUSH is valid and reliable at measuring CMV regardless of the exercise movement performed [17].
In reference to this study, several published studies have compared PUSH to Vicon MC during the SQ [10,11,13], and the BP [10,14]. Additionally, no studies, to our knowledge, have compared measurements of CMV with PUSH versus Vicon MC across RE sets of six to ten repetitions during SQ and BP. The primary purpose of this investigation was to compare average CMV between PUSH and MC during SQ and BP completed at 50% 1RM and 75% 1RM. A secondary purpose was to determine which PUSH placement site provided the most accurate measures of CMV as compared to MC. The final purpose was to measure CMV across multiple repetitions completed during a single set of SQ and BP RE. We hypothesized that PUSH would provide accurate and reliable CMV measurements, and the arm and center barbell placements would provide the most accurate measurements of the four placement locations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Approach to the Problem
Participants reported to the laboratory once to complete ten repetitions at 50% 1RM, and six repetitions at 75% 1RM for both BP and SQ. The order of the RE mode was counterbalanced. Four PUSH devices were used and attached to the subject’s right arm, the left side of the barbell (LB), the right side of the barbell (RB) and the center of the barbell (CB), with MC markers placed directly on top of each PUSH. This design allowed us to compare measures of CMV between PUSH and MC during multiple resistance exercises, intensities, repetitions and to determine which measurement location provided the most accurate measurement of CMV when comparing PUSH with MC.
2.2. Subjects
Twelve resistance trained males from DI collegiate football and collegiate club power-lifting teams volunteered to participate in this study. Any individuals who reported any past (six months) or current injury were excluded from this study. Anthropometric measurements were taken, and body composition was assessed with a bioelectrical impedance device (Inbody 770—Inbody USA, Cerritos, CA, USA) (Table 1). All subjects were informed of the study design as well as risks and benefits of participation, prior to the start of data collection. This study protocol was in accordance with ethical requirements and approved by the University’s Institutional Review Board.

Table 1.
Physical characteristics.
2.3. Procedures
Prior to the experimental protocol, subjects completed a standardized warm-up of cycling on a stationary ergometer for five minutes, followed by a personalized warm-up. Subjects were randomly assigned to perform BP or SQ, first. Each condition was performed in a 2D Smith Machine (Jones Commercial—BODYCRAFT, Lewis Center, OH, USA), which moves horizontally and vertically. PUSH devices were attached to the medial aspect of the LB and RB sleeves, and CB, in bar mode, and the right arm in body mode, as recommended by the manufacturer. Each PUSH was labeled (i.e., LB, RB, CB, and ARM) and used at the same location and connected to the same Apple Ipad via Bluetooth for each participant. Four separate Ipads were used, one for each PUSH band. MC markers were placed directly on top of each PUSH. Prior to data collect, a ten-camera digital MC (Vicon Motion Systems, Oxford, UK) system was calibrated to 3000 frames for each session. Each subject completed ten repetitions at 50% and six repetitions at 75% of self-reported 1RM, with five min rest between each set. The rational for using self-report 1RM is as follows; all subjects in our study were from DI collegiate football and collegiate club power-lifting teams. These individuals consistently trained at percentages of known 1RM values. Subjects were instructed to perform the concentric portion of each repetition at maximal effort and velocity, and perform the eccentric portion of each repetition in a slow and controlled manner. After the RE trails, subjects completed a form detailing the comfort of each exercise in the 2D Smith Machine. The 5-point scale range from; 1 (extremely uncomfortable—inhibited me greatly), 2 (very uncomfortable—inhibited me somewhat), 3 (a little uncomfortable—inhibited me a little), 4 (comfortable—did not inhibit me), 5 (completely comfortable—similar to free weights). Subjects ranked the SQ on average at 3.8 and the BP at 3.7.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
PUSH data was recorded in real-time and stored on separate Ipads for each device location. MC marker data for displacement and velocity was recorded and stored on Vicon Nexus software (Vicon Motion Systems, Oxford, UK) at 100 Hz, and exported to Microsoft Excel for analysis. Average CMV was calculated for each repetition during the concentric phase, which was used for analysis and was defined as the time difference between the 1st positive and 1st negative vertical velocity. Linear Mixed Model, with least-squares means post hoc analyses were performed to compare PUSH and MC CMV, with α = 0.05. Furthermore, ICC, Pearson’s product-moment correlation coefficients (r), MinMax Accuracy, Mean Absolute Error (MAE), and Mean Error (ME) were used to compare the viability of PUSH versus MC CMV. Additionally, Bland–Altman plots and then least products regression analyses were used to determine indices of bias. The lmodel2 package in R-statistical programming [18] was used for performing least products regression analysis to compare the CMV between MC and PUSH ([MC*PUSH]/2) to the difference in CMV between MC and PUSH (MC—PUSH) for each intensity, exercise, device placement, and repetition.
3. Results
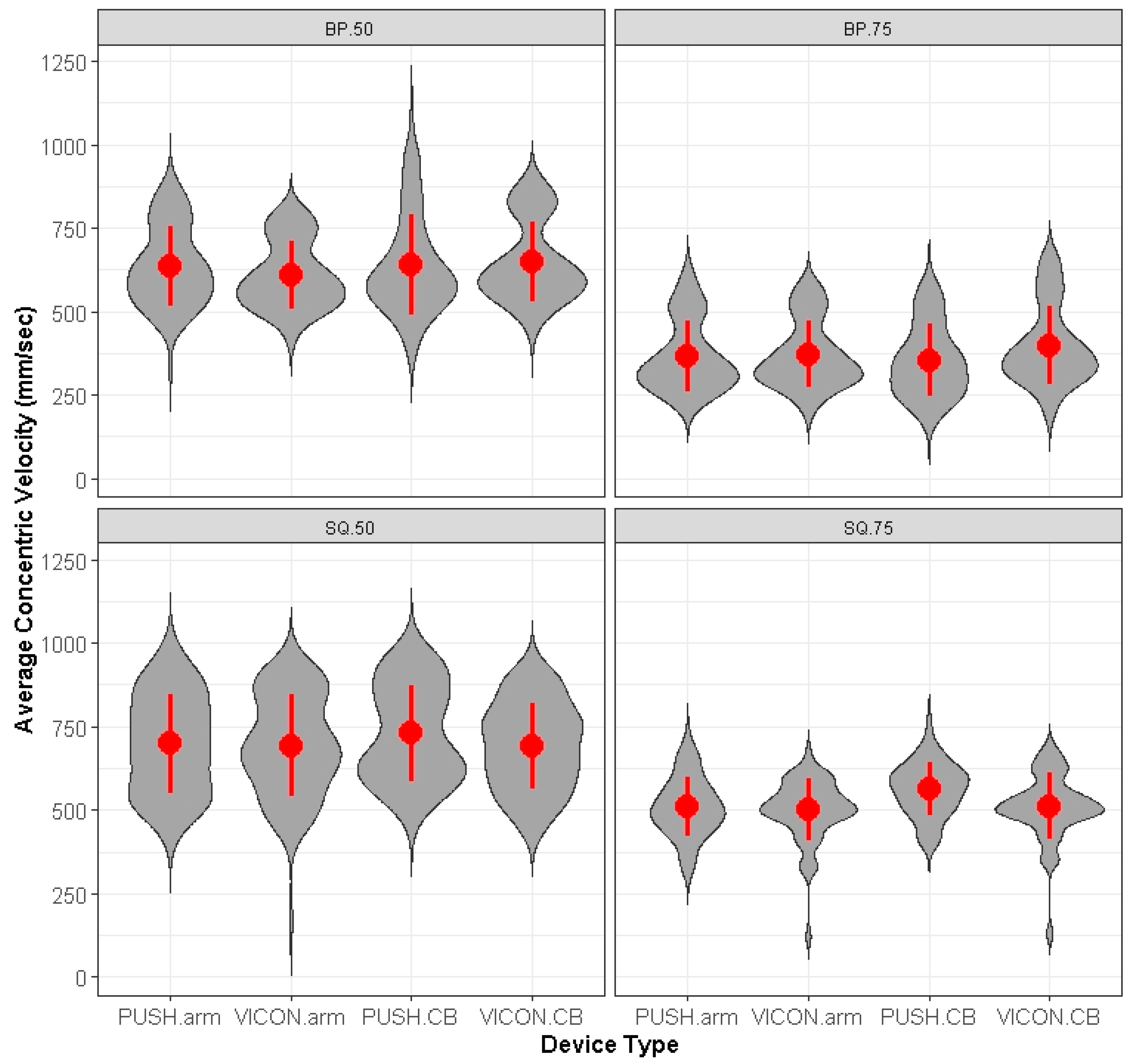
Out of 1544 data points for each device, there were 35 (2.3%) missed measurements with the VICON and 57 (3.7%) missed measurements for the PUSH. When one device missed a measurement at a location, the data was subsequently removed at that same location, exercise, intensity, and repetition for the other device. In all 92 measurements were removed from analysis. Thus, from 1544 measurements, we analyzed and compared 1452 measurements between each device. All missed measurements for PUSH occurred on the right and left barbell placement locations at 50% intensity. An overall analysis using a series of least-squares means, post hoc contrasts showed no significant differences (p > 0.05) between PUSH and MC CMV, when position, RE, intensity, and repetition were incorporated into the Linear Mixed Model. Figure 1 represents PUSH and VICON mean CMV and CMV dispersion for each RE intensity and exercise.
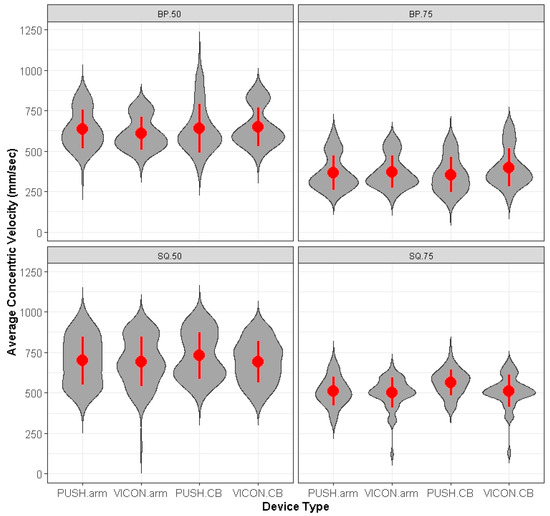
Figure 1.
Represents violin plots of PUSH versus MC mean and standard deviation CMV measurements at specific intensities, RE and placement sites. CB = center barbell; BP = bench press; SQ = squat; 50 = 50% intensity; 75 = 75% intensity.
In Table 2, the MAE, a measure of average error for each set between PUSH and MC ranged from 0.04 m/s to 0.11 m/s. Accuracy for PUSH ranged from 86.1% to 93.9%. Accuracy was determined by using function searches for the minimum value between PUSH and MC for each person and then divided by the maximum value between PUSH and MC. The mean was then used between devices for min/max ratios to calculate accuracy. A two-way random effects model was chosen for ICC and ranged from 0.671 to 0.961. Very strong correlations (r) were present and ranged from 0.722 to 0.949. ME, a measure of the direction of error, ranged from—0.03 to 0.06. Table 2 suggests high reliability between the SQ and BP at the arm and CB locations (ICC = 0.835–0.961); however, these values decreased at the RB and LB locations (ICC = 0.671–0.910).

Table 2.
Measures of accuracy and bias between PUSH and MC.
In Table 3, ICC, MAE and accuracy are shown when comparing the first half versus the second half of the repetitions in each set. The 50% intensity includes five repetitions in the first half and five repetitions in the second half, while the 75% intensity includes three repetitions in the first half and three repetitions in the second half. This data suggests PUSH accuracy remains constant over a set of six to ten repetitions when compared with MC.

Table 3.
Measures of accuracy for first half compared to last half of repetitions.
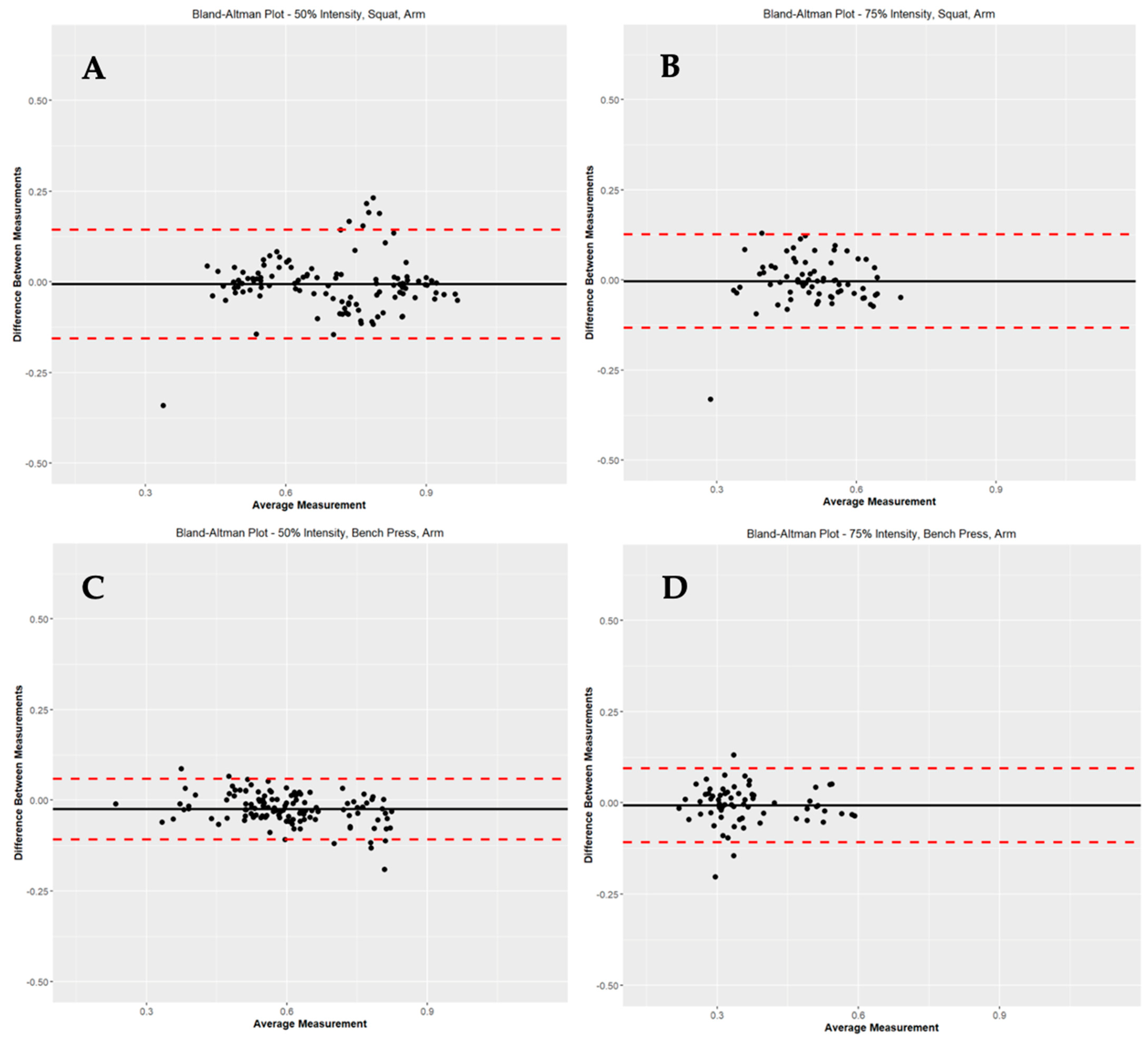
In Table 4, comparisons were made between CMV at the four locations. When comparing MC to MC, there were significant differences in CMV based on site locations (MC arm to MC CB, p < 0.05; MC arm to MC LB, p < 0.05; MC arm to MC RB, p < 0.05; MC CB to MC RB, p < 0.05). However, when PUSH was compared to MC at the same location (I.e., PUSH arm to MC arm, PUSH CB to MC CB, PUSH LB to MC LB, PUSH RB to MC LB), there were no significant differences in CMV. Figure 2 represents Bland-Altman Plots of PUSH versus MC at 50% and 75% SQ and BP for the Arm location.

Table 4.
Comparison of barbell concentric movement velocity at different site locations.
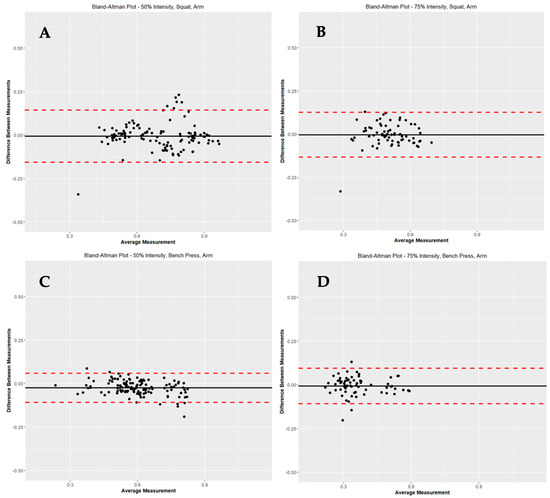
Figure 2.
Represents Bland–Altman Plots of PUSH versus MC for the arm position at 50% squat (A), 75% squat (B), 50% bench press (C) and 75% bench press (D).
Descriptive statistics from MC and PUSH CMV, mean differences and 95% Confidence Intervals (CI) around the mean differences are presented in Table 5. These data suggest PUSH CMV is not significantly higher or lower than MC across intensity, condition or device position. The data were then analyzed using least products regression analysis to evaluate fixed and/or proportional bias when comparing PUSH with MC CMV. Results of the least products regression analyses are presented in Table 6, which suggests PUSH has significant fixed and proportional bias for CMV regardless of intensity and device position. Fixed bias indicates PUSH CMV differs from MC CMV by a constant amount and proportional bias indicates PUSH CMV differs from MC CMV by an amount proportional to MC CMV.

Table 5.
Mean (SD) for MC and PUSH CMV with mean difference and 95% Confidence Intervals; by intensity, exercise and device position. If the 95% Confidence Interval does not cross 0, the mean difference is considered significantly different.

Table 6.
Results of least product regression analyses by intensity, exercise and device position. If the 95% CI for the slope does not include 1.0, proportional bias is present (*). If the 95% CI for the intercept does not include 0, fixed bias is present (**).
4. Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first investigation to compare PUSH to MC during the SQ and BP RE at training intensities and volumes that most mimic actual training loads. PUSH provided accurate measures of CMV during the SQ and BP RE, when compared to MC (See Table 2 and Table 3). Table 2 indicates PUSH and MC CMV are similar for each condition. Overall, PUSH arm resulted in the best measures of CMV, closely followed by the CB; these positions exhibited highest measures of ICCs, least MAE and indicators of bias (see Table 2 and Table 3). However, there are some discrepancies in the literature regarding the comparability of PUSH CMV with criterion measurement systems [8,9,11,12,13,14,15,16,19,20].
Discrepancies between our data and other published studies regarding PUSH accuracy are likely due to differences in measurement methodologies used to monitor CMV. We used a ten-camera MC system with optical markers placed directly on top each PUSH. CMV was compared between PUSH and MC at various intensities and rep ranges for each placement site. Previous studies using LT as the gold-standard measurement technology to compare PUSH with could not make the same comparisons [9,12,16,19]. As a result, these data lead researchers to conclude PUSH results in poor validity and/or reliability during RE across various intensities. The differences between these previous investigations and our data are likely the result of different measurement methodologies. Several studies placed the LT on the outside of the barbell and PUSH on the subject’s forearm [9,12,16,19], while others placed PUSH on the subject’s forearm, with a single MC marker on the outside of the barbell [11,13,15]. When comparing MC to MC, our data suggests there are significant differences in CMV at different barbell locations (MC arm to MC CB, p < 0.05; MC arm to MC LB, p < 0.05; MC arm to MC RB, p < 0.05; MC CB to MC RB, p < 0.05). However, when PUSH was compared to MC at the same location (I.e., PUSH arm to MC arm, PUSH CB to MC CB, PUSH LB to MC LB, PUSH RB to MC LB), there were no significant differences in CMV (Table 4). Our data suggests when PUSH was placed on the subject’s arm and the criterion measurement system (MC) was placed at a different location on the barbell, differences in CMV were recorded between measurement techniques. The results from our study can potentially explain why studies that compared PUSH CMV at the arm location to a criterion measurement system placed on one end of the barbell reported poor CMV validity and/or reliability; CMV was significantly different at different barbell locations when measured either by PUSH or MC. This is likely a function of differences in individual bar paths. During RE the bar may move away from a perfect parallel position, resulting in differences in peak and average CMV near the ends of the barbell, regardless of measurement methodologies. A recent investigation reported similar results to ours in which differences were observed in CMV based on different device placement locations [11]. Therefore, device placement must be taken into consideration when performing CMV validity and/or reliability measures.
When previous studies utilized a similar measurement methodology, placing a MC marker directly on top of PUSH [14,20] or placing PUSH on the arm and MC markers on the elbow and hand [21], the data suggested PUSH provides reliable measures of CMV during a barbell bench press [14], a counter movement jump [20], a biceps curl and shoulder press RE [21]. The results reported in these studies are in general agreement with the results of our study. This suggests PUSH accurately monitors CMV when compared to MC (ICC = 0.835–0.961; r = 0.742–0.949) at the arm and CB locations during moderate to intense SQ and BP RE. Similarities in our results and these previous studies [14,20,21] may be explained by the similarities in the measurement methodologies that were employed; we compared PUSH CMV with MC CMV by placing MC markers on PUSH devices rather than measuring PUSH at the arm position and then comparing this value with the criterion CMV values measured at different barbell locations (i.e., end of right or left barbell) [9,12,13,15,16,19].
One unique purpose of our study was to determine if and/or to what degree PUSH measures of CMV were in agreement with MC in the ability to track changes in CMV (i.e., loss in CMV) across repetitions completed within a set of RE. To our knowledge, no other published studies have compared PUSH CMV with MC CMV across multiple repetitions, while using intensities that that mimic actual training loads (i.e., 75% 1RM), and while employing RE that are typically used for training purposes. Past studies [8,9,12,14,15,16,19], all used a similar methodology of performing one to three repetitions at given intensities, while our study measured CMV for six consecutive repetitions at 75% 1RM and ten consecutive repetitions at 50% 1RM for both SQ and BP RE to determine if PUSH could track velocity loss across a RE set. The purpose of VBT is to monitor fluctuations in CMV in real time [2], as acute muscular fatigue has been reported to influence CMV [3] and a drop in CMV below a predetermined threshold can be used to terminate a set [4]. The information in Table 3, suggests PUSH can accurately monitor velocity loss in real time as changes in CMV compared favorably between PUSH and MC across the first and second halves of a set, for SQ and BP at 50% and 75% 1RM. These data suggest PUSH can be used to accurately monitor CMV loss over the course of a set of both SQ and BP RE using a Jones machine. Since subjects reported an average comfort score of 3.7–3.8 (on a Likert scale of 0–5) for the Jones machine compared to the use of free-weights during the BP and SQ RE, respectively, the use of the Jones machine may have inhibited the subjects’ movement comfort when performing these exercises. Therefore, future investigations should determine whether differences arise in CMV and with the accuracy of PUSH between the use of the Jones machine and the use of free-weights during SQ and BP RE. This will provide better insight into whether strength and conditioning personnel can effectively use the PUSH in everyday strength and conditioning settings for the assessment of CMV and the use of VBT.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, there were no statistically significant differences between PUSH and MC CMV as a function of RE, device placement, intensity and repetition number. On a rep-by-rep basis, PUSH arm location provided the most accurate measurement of CMV for SQ and BP RE when compared with MC, closely followed by the CB location. Overall, these data suggest PUSH provides accurate and reliable real-time measurements of CMV when compared to MC and PUSH can effectively be used to detect changes in CMV on a rep-by-rep basis to facilitate the use of VBT.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.Z.P., D.M. and R.P.C.; methodology, E.Z.P., C.G., D.M. and R.P.C.; formal analysis, E.S., R.P.C.; investigation, E.Z.P., C.G., E.S., R.P.C.; resources, E.S., R.P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, E.Z.P., R.P.C.; writing—review and editing, E.Z.P., C.G., D.M., E.S., R.P.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Miami University (protocol code #01902r and date of approval 06/03/2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Włodarczyk, M.; Adamus, P.; Zieliński, J.; Kantanista, A. Effects of velocity-based training on strength and power in elite athletes-A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Moreno, M.; Rodríguez-Rosell, D.; Pareja-Blanco, F.; Mora-Custodio, R.; González-Badillo, J.J. Movement velocity as indicator of relative intensity and level of effort attained during the set in pull-up exercise. Int. J. Sport. Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 1378–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareja-Blanco, F.; Rodríguez-Rosell, D.; Sánchez-Medina, L.; Gorostiaga, E.M.; González-Badillo, J.J. Effect of movement velocity during resistance training on neuromuscular performance. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2014, 35, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareja-Blanco, F.; Rodríguez-Rosell, D.; Sánchez-Medina, L.; Sanchis-Moysi, J.; Dorado, C.; Mora-Custodio, R.; Yañez-García, J.M.; Morales-Alamo, D.; Pérez-Suárez, I.; Calbet, J.A.L.; et al. Effects of velocity loss during resistance training on athletic performance, strength gains and muscle adaptations. Scan. J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2017, 27, 724–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pareja-Blanco, F.; Sánchez-Medina, L.; Suárez-Arrones, L.; González-Badillo, J.J. Effects of velocity loss during resistance training on performance in professional soccer players. Int. J. Sport. Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loturco, I.; Kobal, R.; Moraes, J.E.; Kitamura, K.; Cal Abad, C.C.; Pereira, L.A.; Nakamura, F.Y. Predicting the maximum dynamic strength in bench press: The high precision of the bar velocity approach. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 1127–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Badillo, J.J.; Yañez-García, J.M.; Mora-Custodio, R.; Rodríguez-Rosell, D. Velocity loss as a variable for monitoring resistance exercise. Int. J. Sport. Med. 2017, 38, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balsalobre-Fernández, C.; Kuzdub, M.; Poveda-Ortiz, P.; Campo-Vecino, J.D. Validity and reliability of the push wearable device to measure movement velocity during the back squat exercise. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 1968–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banyard, H.G.; Nosaka, K.; Sato, K.; Haff, G.G. Validity of various methods for determining velocity, force and power in the backsquat. Int. J. Sport. Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, D.E.; Guy, J.H.; Elsworthy, N.; Kean, C. Validity of the push band 2.0 and speed4lifts to measure velocity during upper and lower body free-weight resistance exercises. J. Sport. Sci. 2022, 40, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritschi, R.; Seiler, J.; Gross, M. Validity and effects of placement of velocity-based training devices. Sports 2021, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orange, S.T.; Metcalfe, J.W.; Liefeith, A.; Marshall, P.; Madden, L.A.; Fewster, C.R.; Vince, R.V. Validity and reliability of a wearable inertial sensor to measure velocity and power in the back squat and bench press. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2398–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.W.; Rogerson, D.; Dorrell, H.F.; Ruddock, A.; Barnes, A. The reliability and validity of current technologies for measuring barbell velocity in the free-weight back squat and power clean. Sports 2020, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, J.; Augustus, S.; Austin, K.; Comfort, P.; McMahon, J.; Mundy, P.; Haff, G.G. The reliability and validity of the bar-mounted push bandtm 2.0 during bench press with moderate and heavy loads. J. Sport. Sci. 2019, 37, 2685–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Castilla, A.; Piepoli, A.; Delgado-García, G.; Garrido-Blanca, G.; García-Ramos, A. Reliability and concurrent validity of seven commercially available devices for the assessment of movement velocity at different intensities during the bench press. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Tillaar, R.; Ball, N. Validity and reliability of kinematics measured with push band vs. linear encoder in bench press and push-ups. Sports 2019, 7, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, F.M.; Akyildiz, Z.; Pino-Ortega, J.; Rico-González, M. Validity and reliability of the inertial measurement unit for barbell velocity assessments: A systematic review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Chéry, C.; Ruf, L. Reliability of the load-velocity relationship and validity of the push to measure velocity in the deadlift. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2370–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lake, J.P.; Augustus, S.; Austin, K.; Mundy, P.; McMahon, J.J.; Comfort, P.; Haff, G.G. The validity of the push band 2.0 during vertical jump performance. Sports 2018, 6, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Beckham, G.; Carroll, K.; Bazyler, C.; Sha, Z.; Haff, G.G. Validity of wireless devices measuring velocity of resistance exercises. J. Trainology 2015, 4, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).