Protein Intake in NCAA Division 1 Soccer Players: Assessment of Daily Amounts, Distribution Patterns, and Leucine Levels as a Quality Indicator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Dietary Data Collection and Analyses
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Dietary Energy and Protein Intake
3.3. Dietary Protein Distribution
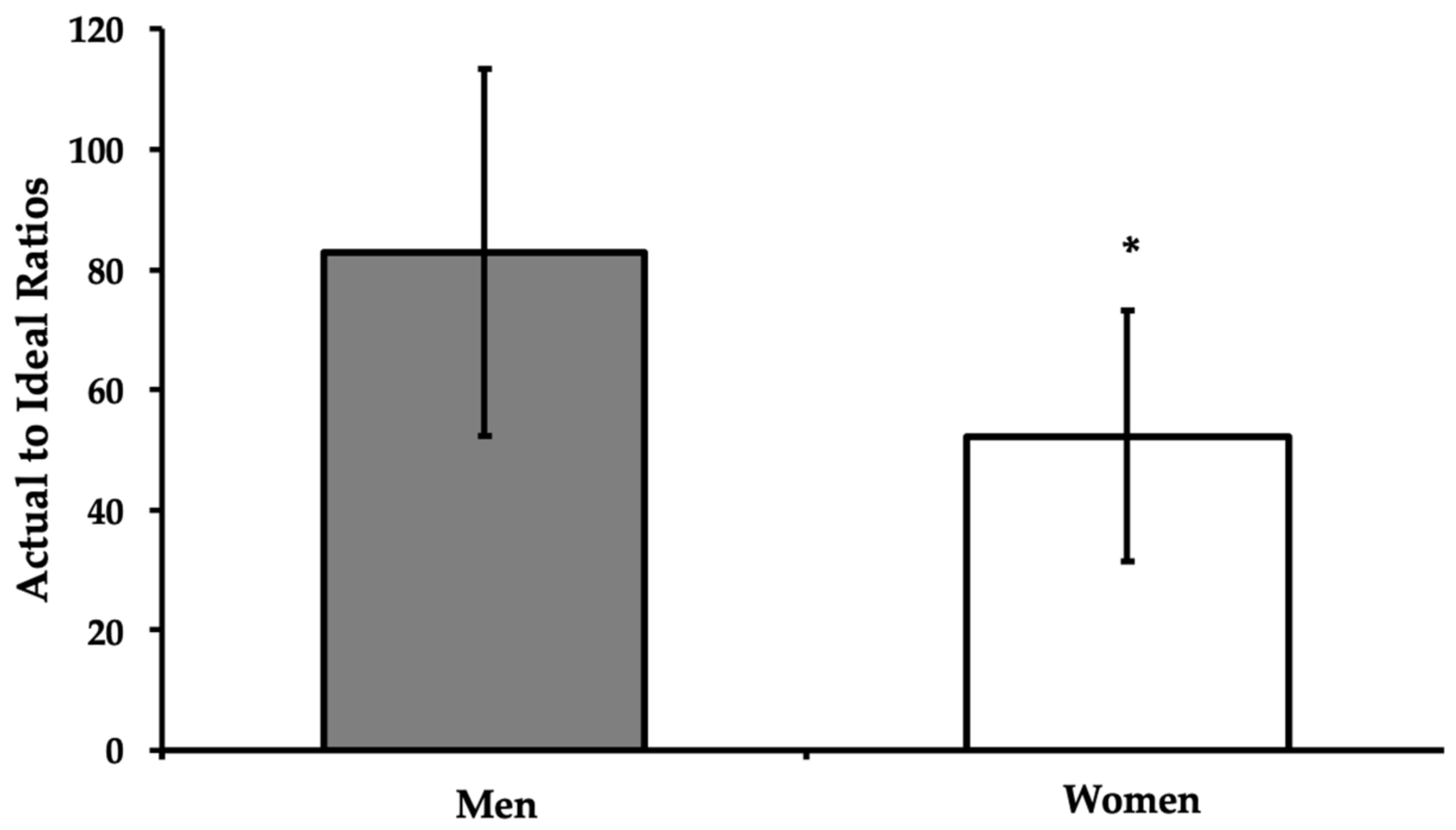
3.4. Dietary Protein Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Randell, R.K.; Clifford, T.; Drust, B.; Moss, S.L.; Unnithan, V.B.; De Ste Croix, M.B.A.; Datson, N.; Martin, D.; Mayho, H.; Carter, J.M.; et al. Physiological Characteristics of Female Soccer Players and Health and Performance Considerations: A Narrative Review. Sports Med. 2021, 51, 1377–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stølen, T.; Chamari, K.; Castagna, C.; Wisløff, U. Physiology of Soccer: An Update. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 501–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.; Maughan, R.J.; Gleeson, M.; Bilsborough, J.; Jeukendrup, A.; Morton, J.P.; Phillips, S.M.; Armstrong, L.; Burke, L.M.; Close, G.L.; et al. UEFA Expert Group Statement on Nutrition in Elite Football. Current Evidence to Inform Practical Recommendations and Guide Future Research. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, L.; Ruiz, F.; Lekue, J.A.; Irazusta, J.; Gil, S.M. Metabolic Impact of a Soccer Match on Female Players. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.M.; Van Loon, L.J.C. Dietary Protein for Athletes: From Requirements to Optimum Adaptation. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, S29–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tipton, K.D.; Wolfe, R.R. Protein and Amino Acids for Athletes. J. Sports Sci. 2004, 22, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esco, M.; Fedewa, M.; Cicone, Z.; Sinelnikov, O.; Sekulic, D.; Holmes, C. Field-Based Performance Tests Are Related to Body Fat Percentage and Fat-Free Mass, But Not Body Mass Index, in Youth Soccer Players. Sports 2018, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jäger, R.; Kerksick, C.M.; Campbell, B.I.; Cribb, P.J.; Wells, S.D.; Skwiat, T.M.; Purpura, M.; Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Ferrando, A.A.; Arent, S.M.; et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: Protein and Exercise. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, D.T.; Erdman, K.A.; Burke, L.M. Nutrition and Athletic Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2016, 48, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maughan, R.J.; Burke, L.M.; Kirkendall, D.T. F-MARC Nutrition for Football; Fédération Internationale de Football Association: Zürich, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, R.W.; Murphy, K.T.; McKellar, S.R.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Henselmans, M.; Helms, E.; Aragon, A.A.; Devries, M.C.; Banfield, L.; Krieger, J.W.; et al. A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Meta-Regression of the Effect of Protein Supplementation on Resistance Training-Induced Gains in Muscle Mass and Strength in Healthy Adults. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagawa, R.; Watanabe, D.; Ito, K.; Otsuyama, T.; Nakayama, K.; Sanbongi, C.; Miyachi, M. Synergistic Effect of Increased Total Protein Intake and Strength Training on Muscle Strength: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Sports Med.-Open 2022, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areta, J.L.; Burke, L.M.; Ross, M.L.; Camera, D.M.; West, D.W.D.; Broad, E.M.; Jeacocke, N.A.; Moore, D.R.; Stellingwerff, T.; Phillips, S.M.; et al. Timing and Distribution of Protein Ingestion during Prolonged Recovery from Resistance Exercise Alters Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis: Timing of Protein Ingestion after Exercise. J. Physiol. 2013, 591, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, D.R.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Witard, O.; Breen, L.; Burd, N.A.; Tipton, K.D.; Phillips, S.M. Protein Ingestion to Stimulate Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis Requires Greater Relative Protein Intakes in Healthy Older Versus Younger Men. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2015, 70, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, R.W.; McGlory, C.; Phillips, S.M. Nutritional Interventions to Augment Resistance Training-Induced Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy. Front. Physiol. 2015, 6, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Breen, L.; Burd, N.A.; Hector, A.J.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Josse, A.R.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Resistance Exercise Enhances Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis with Graded Intakes of Whey Protein in Older Men. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 1780–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devries, M.C.; McGlory, C.; Bolster, D.R.; Kamil, A.; Rahn, M.; Harkness, L.; Baker, S.K.; Phillips, S.M. Protein Leucine Content Is a Determinant of Shorter- and Longer-Term Muscle Protein Synthetic Responses at Rest and Following Resistance Exercise in Healthy Older Women: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devries, M.C.; McGlory, C.; Bolster, D.R.; Kamil, A.; Rahn, M.; Harkness, L.; Baker, S.K.; Phillips, S.M. Leucine, Not Total Protein, Content of a Supplement Is the Primary Determinant of Muscle Protein Anabolic Responses in Healthy Older Women. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieu, I.; Balage, M.; Sornet, C.; Giraudet, C.; Pujos, E.; Grizard, J.; Mosoni, L.; Dardevet, D. Leucine Supplementation Improves Muscle Protein Synthesis in Elderly Men Independently of Hyperaminoacidaemia: Leucine and Protein Metabolism in the Elderly. J. Physiol. 2006, 575, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millward, D.J.; Layman, D.K.; Tomé, D.; Schaafsma, G. Protein Quality Assessment: Impact of Expanding Understanding of Protein and Amino Acid Needs for Optimal Health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1576S–1581S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, L.E.; Wilson, G.J.; Moulton, C.J.; Layman, D.K. Meal Distribution of Dietary Protein and Leucine Influences Long-Term Muscle Mass and Body Composition in Adult Rats. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.M.; Chevalier, S.; Leidy, H.J. Protein “Requirements” beyond the RDA: Implications for Optimizing Health. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikosky, M.A.; Cifelli, C.J.; Agarwal, S.; Fulgoni, V.L. Association of Dietary Protein Intake and Grip Strength Among Adults Aged 19+ Years: NHANES 2011–2014 Analysis. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 873512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.R.; Robinson, M.J.; Fry, J.L.; Tang, J.E.; Glover, E.I.; Wilkinson, S.B.; Prior, T.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Ingested Protein Dose Response of Muscle and Albumin Protein Synthesis after Resistance Exercise in Young Men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamerow, M.M.; Mettler, J.A.; English, K.L.; Casperson, S.L.; Arentson-Lantz, E.; Sheffield-Moore, M.; Layman, D.K.; Paddon-Jones, D. Dietary Protein Distribution Positively Influences 24-h Muscle Protein Synthesis in Healthy Adults. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, J.; Tomita, T.; Arimitsu, T.; Fujita, S. Evenly Distributed Protein Intake over 3 Meals Augments Resistance Exercise–Induced Muscle Hypertrophy in Healthy Young Men. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtzman, B.; Ackerman, K.E. Recommendations and Nutritional Considerations for Female Athletes: Health and Performance. Sports Med. 2021, 51, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, D.; Convit, L.; Condo, D.; Carr, A.J.; Hamilton, D.L.; Slater, G.; Snipe, R.M.J. Protein Requirements of Pre-Menopausal Female Athletes: Systematic Literature Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielik, K.; Książek, A.; Zagrodna, A.; Słowińska-Lisowska, M. How Do Male Football Players Meet Dietary Recommendations? A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, M.V.; Lundsgaard, A.; Christensen, P.M.; Christensen, L.; Randers, M.B.; Mohr, M.; Nybo, L.; Kiens, B.; Fritzen, A.M. Nutritional Optimization for Female Elite Football Players—Topical Review. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2022, 32, 81–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, L.; Naughton, R.J.; Close, G.L.; Di Michele, R.; Morgans, R.; Drust, B.; Morton, J.P. Daily Distribution of Macronutrient Intakes of Professional Soccer Players From the English Premier League. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2017, 27, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdman, K.A.; Tunnicliffe, J.; Lun, V.M.; Reimer, R.A. Eating Patterns and Composition of Meals and Snacks in Elite Canadian Athletes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2013, 23, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillen, J.B.; Trommelen, J.; Wardenaar, F.C.; Brinkmans, N.Y.J.; Versteegen, J.J.; Jonvik, K.L.; Kapp, C.; de Vries, J.; van den Borne, J.J.G.C.; Gibala, M.J.; et al. Dietary Protein Intake and Distribution Patterns of Well-Trained Dutch Athletes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2017, 27, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, K.; Slater, G.; King, N.; Byrne, N. The Measurement and Interpretation of Dietary Protein Distribution During a Rugby Preseason. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2015, 25, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, C.; Gill, N.; Darry, K.; Posthumus, L.; Sims, S. Daily Protein Distribution Patterns in Professional and Semi-Professional Male Rugby Union Players. J. Sport Exerc. Sci. 2022, 6, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishisaka, M.M.; Zorn, S.P.; Kristo, A.S.; Sikalidis, A.K.; Reaves, S.K. Assessing Dietary Nutrient Adequacy and the Effect of Season—Long Training on Body Composition and Metabolic Rate in Collegiate Male Basketball Players. Sports 2022, 10, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine. Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; p. 10490. ISBN 978-0-309-08525-0. [Google Scholar]
- Longland, T.M.; Oikawa, S.Y.; Mitchell, C.J.; Devries, M.C.; Phillips, S.M. Higher Compared with Lower Dietary Protein during an Energy Deficit Combined with Intense Exercise Promotes Greater Lean Mass Gain and Fat Mass Loss: A Randomized Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, E.A.; Colenso-Semple, L.; McKellar, S.R.; Yau, T.; Ali, M.U.; Fitzpatrick-Lewis, D.; Sherifali, D.; Gaudichon, C.; Tomé, D.; Atherton, P.J.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Protein Intake to Support Muscle Mass and Function in Healthy Adults. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burd, N.A.; West, D.W.; Moore, D.R.; Atherton, P.J.; Staples, A.W.; Prior, T.; Tang, J.E.; Rennie, M.J.; Baker, S.K.; Phillips, S.M. Enhanced Amino Acid Sensitivity of Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis Persists for up to 24 h after Resistance Exercise in Young Men. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenfeld, B.J.; Aragon, A.A. How Much Protein Can the Body Use in a Single Meal for Muscle-Building? Implications for Daily Protein Distribution. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witard, O.C.; Garthe, I.; Phillips, S.M. Dietary Protein for Training Adaptation and Body Composition Manipulation in Track and Field Athletes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardon-Thomas, D.; Riviere, T.; Tieges, Z.; Greig, C. Dietary Protein in Older Adults: Adequate Daily Intake but Potential for Improved Distribution. Nutrients 2017, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hone, M.; Nugent, A.P.; Walton, J.; McNulty, B.A.; Egan, B. Habitual Protein Intake, Protein Distribution Patterns and Dietary Sources in Irish Adults with Stratification by Sex and Age. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 33, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeuninx, B.; Greig, C.A.; Breen, L. Amount, Source and Pattern of Dietary Protein Intake Across the Adult Lifespan: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.L.; Bergia, R.E., III; Campbell, W.W. Protein Distribution and Muscle-Related Outcomes: Does the Evidence Support the Concept? Nutrients 2020, 12, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jespersen, S.E.; Agergaard, J. Evenness of Dietary Protein Distribution Is Associated with Higher Muscle Mass but Not Muscle Strength or Protein Turnover in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 3185–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Templeman, I.; Smith, H.A.; Walhin, J.-P.; Middleton, B.; Gonzalez, J.T.; Karagounis, L.G.; Johnston, J.D.; Betts, J.A. Unacylated Ghrelin, Leptin, and Appetite Display Diurnal Rhythmicity in Lean Adults. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 130, 1534–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, P.S.; Guilkey, D.K.; Popkin, B.M. Trends in Breakfast Consumption of US Adults between 1965 and 1991. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1996, 96, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micha, R.; Wallace, S.K.; Mozaffarian, D. Red and Processed Meat Consumption and Risk of Incident Coronary Heart Disease, Stroke, and Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Circulation 2010, 121, 2271–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Jal, M.; Suñé-Negre, J.M.; Pérez-Lozano, P.; García-Montoya, E. Trends in the Food and Sports Nutrition Industry: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2405–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maykish, A.; Nishisaka, M.M.; Talbott, C.K.; Reaves, S.K.; Kristo, A.S.; Sikalidis, A.K. Comparison of Whey Versus Almond Protein Powder on Nitrogen Balance in Female College Students; The California Almond Protein Powder Project (CAlmond-P3). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froiland, K.; Koszewski, W.; Hingst, J.; Kopecky, L. Nutritional Supplement Use among College Athletes and Their Sources of Information. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2004, 14, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.A.; McDaniel, J.L.; Breitbach, A.P.; Weiss, E.P. Perceived Protein Needs and Measured Protein Intake in Collegiate Male Athletes: An Observational Study. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2011, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebine, N.; Rafamantanantsoa, H.H.; Nayuki, Y.; Yamanaka, K.; Tashima, K.; Ono, T.; Saitoh, S.; Jones, P.J.H. Measurement of Total Energy Expenditure by the Doubly Labelled Water Method in Professional Soccer Players. J. Sports Sci. 2002, 20, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morehen, J.C.; Rosimus, C.; Cavanagh, B.P.; Hambly, C.; Speakman, J.R.; Elliott-Sale, K.J.; Hannon, M.P.; Morton, J.P. Energy Expenditure of Female International Standard Soccer Players: A Doubly Labeled Water Investigation. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmans, N.Y.; Iedema, N.; Plasqui, G.; Wouters, L.; Saris, W.H.; van Loon, L.J.; van Dijk, J.-W. Energy Expenditure and Dietary Intake in Professional Football Players in the Dutch Premier League: Implications for Nutritional Counselling. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, L.; Orme, P.; Naughton, R.J.; Close, G.L.; Milsom, J.; Rydings, D.; O’Boyle, A.; Di Michele, R.; Louis, J.; Hambly, C.; et al. Energy Intake and Expenditure of Professional Soccer Players of the English Premier League: Evidence of Carbohydrate Periodization. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2017, 27, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, E.R.; Zinn, C.; Rowlands, D.S.; Brown, S.R. A Systematic Review of Dietary Protein During Caloric Restriction in Resistance Trained Lean Athletes: A Case for Higher Intakes. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2014, 24, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettler, S.; Mitchell, N.; Tipton, K.D. Increased Protein Intake Reduces Lean Body Mass Loss during Weight Loss in Athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atherton, P.J.; Etheridge, T.; Watt, P.W.; Wilkinson, D.; Selby, A.; Rankin, D.; Smith, K.; Rennie, M.J. Muscle Full Effect after Oral Protein: Time-Dependent Concordance and Discordance between Human Muscle Protein Synthesis and MTORC1 Signaling. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1080–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capling, L.; Beck, K.; Gifford, J.; Slater, G.; Flood, V.; O’Connor, H. Validity of Dietary Assessment in Athletes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Men | Women | |
|---|---|---|
| Sample size (n) | 13 | 23 |
| Age (years) | 19.7 ± 1.3 | 19.4 ± 1.5 |
| Height (cm) | 180.3 ± 7.8 | 167.0 ± 5.4 |
| Body weight (kg) | 72.9 ± 7.4 | 63.5 ± 5.5 |
| BMI | 22.4 ± 1.4 | 22.7 ± 1.3 |
| Men | Women | |
|---|---|---|
| Total energy (kcal) | 2714 ± 529 | 1907 ± 447 * |
| Protein (g) | 151.8 ± 39.4 | 87.7 ± 23.9 * |
| Protein (g/kg BW) | 2.08 ± 0.51 | 1.38 ± 0.35 * |
| Protein (% total kcal) | 22.77 ± 5.99 | 18.53 ± 3.57 * |
| % Consuming ≥1.6 g/kg BW/Day | % Consuming ≥0.4 g/kg BW at Breakfast | % Consuming ≥0.4 g/kg BW at Lunch | % Consuming ≥0.4 g/kg BW at Dinner | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 77.0% | 15.4% | 53.8% | 84.6% |
| Women | 35.0% | 8.7% | 43.5% | 73.9% |
| Total | 50.0% | 11.1% | 47.2% | 77.8% |
| Men | Women | |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast protein (g) | 23.25 ± 15.19 | 16.20 ± 6.25 |
| Breakfast protein (g/kg BW) | 0.33 ± 0.23 | 0.26 ± 0.11 |
| Lunch protein (g) | 42.54 ± 24.79 | 24.42 ± 10.28 |
| Lunch protein (g/kg BW) | 0.60 ± 0.39 | 0.38 ± 0.16 |
| Dinner protein (g) | 51.77 ± 20.51 | 31.11 ± 11.60 |
| Dinner protein (g/kg BW) | 0.71 ± 0.26 | 0.49 ± 0.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwon, J.; Nishisaka, M.M.; McGrath, A.F.; Kristo, A.S.; Sikalidis, A.K.; Reaves, S.K. Protein Intake in NCAA Division 1 Soccer Players: Assessment of Daily Amounts, Distribution Patterns, and Leucine Levels as a Quality Indicator. Sports 2023, 11, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11020045
Kwon J, Nishisaka MM, McGrath AF, Kristo AS, Sikalidis AK, Reaves SK. Protein Intake in NCAA Division 1 Soccer Players: Assessment of Daily Amounts, Distribution Patterns, and Leucine Levels as a Quality Indicator. Sports. 2023; 11(2):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11020045
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwon, Jun, Morgan M. Nishisaka, Alexandra F. McGrath, Aleksandra S. Kristo, Angelos K. Sikalidis, and Scott K. Reaves. 2023. "Protein Intake in NCAA Division 1 Soccer Players: Assessment of Daily Amounts, Distribution Patterns, and Leucine Levels as a Quality Indicator" Sports 11, no. 2: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11020045
APA StyleKwon, J., Nishisaka, M. M., McGrath, A. F., Kristo, A. S., Sikalidis, A. K., & Reaves, S. K. (2023). Protein Intake in NCAA Division 1 Soccer Players: Assessment of Daily Amounts, Distribution Patterns, and Leucine Levels as a Quality Indicator. Sports, 11(2), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/sports11020045








